Abstract
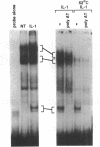
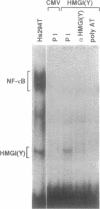
Expression of the chemokine MGSA/GRO is upregulated as melanocytes progress to melanoma cells. We demonstrate that constitutive and cytokine induced MGSA/GRO alpha expression requires multiple DNA regulatory regions between positions -143 to -62. We have previously shown that the NF-kappa B element at -83 to -65 is essential for basal and cytokine induced MGSA/GRO alpha promoter activity in the Hs294T melanoma and normal retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, respectively. Here, we have determined that the Sp1 binding element located approximately 42 base pairs upstream from the NF-kappa B element binds Sp1 and Sp3 constitutively and this element is necessary for basal MGSA/GRO alpha promoter activity. We demonstrate that the high mobility group proteins HMGI(Y) recognize the AT-rich motif nested within the NF-kappa B element in the MGSA/GRO alpha promoter. Loss of either NF-kappa B or HMGI(Y) complex binding by selected point mutations in the NF-kappa B element results in decreased basal and cytokine induced MGSA/GRO alpha promoter activity. Thus, these results indicate that transcriptional regulation of the chemokine MGSA/GRO alpha requires at least three transcription factors: Sp1, NF-kappa B and HMGI(Y).
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anisowicz A., Messineo M., Lee S. W., Sager R. An NF-kappa B-like transcription factor mediates IL-1/TNF-alpha induction of gro in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B., Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines--CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balentien E., Han J. H., Thomas H. G., Wen D. Z., Samantha A. K., Zachariae C. O., Griffin P. R., Brachmann R., Wong W. L., Matsushima K. Recombinant expression, biochemical characterization, and biological activities of the human MGSA/gro protein. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10225–10233. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordoni R., Fine R., Murray D., Richmond A. Characterization of the role of melanoma growth stimulatory activity (MGSA) in the growth of normal melanocytes, nevocytes, and malignant melanocytes. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Dec;44(4):207–219. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240440403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. I., Nishinaka T., Kwan K., Kitabayashi I., Yokoyama K., Fu Y. H., Grünwald S., Chiu R. The retinoblastoma gene product RB stimulates Sp1-mediated transcription by liberating Sp1 from a negative regulator. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4380–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney J. E., Johnson K. R., Magnuson N. S., Sylvester S. R., Reeves R. High-mobility group protein HMG-I localizes to G/Q- and C-bands of human and mouse chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1975–1982. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R., Birnstiel M. L. Cloning of cDNAs coding for human HMG I and HMG Y proteins: both are capable of binding to the octamer sequence motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):5947–5959. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.5947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton T. S., Nissen M. S., Reeves R. Specific A . T DNA sequence binding of RP-HPLC purified HMG-I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 27;143(1):260–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90659-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emili A., Greenblatt J., Ingles C. J. Species-specific interaction of the glutamine-rich activation domains of Sp1 with the TATA box-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1582–1593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert C. A., Baker J. B. Interleukin-8: a review. Cancer Invest. 1993;11(6):743–750. doi: 10.3109/07357909309046949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Nagano K., Kawakami K. Possible implications of Sp1-induced bending of DNA on synergistic activation of transcription. Gene. 1993 Dec 22;136(1-2):341–343. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90492-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe G. J., Peters W. P., Roberts W., Kurtzberg J., Stuart A., Wang A. M., Stoudemire J. B. Modulation of macrophage colony stimulating factor in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1992 Apr;54(4):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90138-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Disney J. E., Wyatt C. R., Reeves R. Expression of mRNAs encoding mammalian chromosomal proteins HMG-I and HMG-Y during cellular proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Mar;187(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90118-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lehn D. A., Elton T. S., Barr P. J., Reeves R. Complete murine cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and tissue expression of the high mobility group protein HMG-I(Y). J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18338–18342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lehn D. A., Reeves R. Alternative processing of mRNAs encoding mammalian chromosomal high-mobility-group proteins HMG-I and HMG-Y. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2114–2123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi-Barve S. S., Rangnekar V. V., Sells S. F., Rangnekar V. M. Interleukin-1-inducible expression of gro-beta via NF-kappa B activation is dependent upon tyrosine kinase signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18018–18029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Production of interleukin-8 by human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes in response to interleukin-1 or tumour necrosis factor. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Yoshimura T., Rot A., Noer K., Walz A., Baggiolini M., Walz D. A., Goetzl E. J., Castor C. W. Chemotactic activity and receptor binding of neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1 (NAP-1) and structurally related host defense cytokines: interaction of NAP-2 with the NAP-1 receptor. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Mar;49(3):258–265. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis H., Kaszubska W., DeLamarter J. F., Whelan J. Cooperativity between two NF-kappa B complexes, mediated by high-mobility-group protein I(Y), is essential for cytokine-induced expression of the E-selectin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):5701–5709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Mak G., Franza B. R., Jr In vitro study of functional involvement of Sp1, NF-kappa B/Rel, and AP1 in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-mediated HIV-1 long terminal repeat activation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30616–30619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Courey A. J., Wall J. S., Jackson S. P., Hough P. V. DNA looping and Sp1 multimer links: a mechanism for transcriptional synergism and enhancement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5670–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei S., Colombo M. P., Melani C., Silvani A., Parmiani G., Herlyn M. Expression of cytokine/growth factors and their receptors in human melanoma and melanocytes. Int J Cancer. 1994 Mar 15;56(6):853–857. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser B., Clark-Lewis I., Zwahlen R., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil-activating properties of the melanoma growth-stimulatory activity. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1797–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Mahe Y., Matsushima K. Cooperative interaction of nuclear factor-kappa B- and cis-regulatory enhancer binding protein-like factor binding elements in activating the interleukin-8 gene by pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21128–21133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Mukaida N., Yasumoto K., Rice N., Ishikawa Y., Horiguchi H., Murakami S., Matsushima K. The interleukin-8 AP-1 and kappa B-like sites are genetic end targets of FK506-sensitive pathway accompanied by calcium mobilization. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8582–8589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Edwards N. L., Duckett C. S., Agranoff A. B., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. A cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is required for HIV-1 enhancer activation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3551–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram T. G., Reeves R., Hosick H. L. Elevated high mobility group-I(Y) gene expression is associated with progressive transformation of mouse mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2655–2660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A., Lawson D. H., Nixon D. W., Chawla R. K. Characterization of autostimulatory and transforming growth factors from human melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;45(12 Pt 1):6390–6394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A., Thomas H. G. Melanoma growth stimulatory activity: isolation from human melanoma tumors and characterization of tissue distribution. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Feb;36(2):185–198. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240360209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sater R. A. Basal expression of the human macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) gene in K562 cells. Leuk Res. 1994 Feb;18(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadendorf D., Möller A., Algermissen B., Worm M., Sticherling M., Czarnetzki B. M. IL-8 produced by human malignant melanoma cells in vitro is an essential autocrine growth factor. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2667–2675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Persoon N. L., Christophers E. Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes secrete, apart from neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8, a second neutrophil-activating protein. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence identity with melanoma growth stimulatory activity. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1091–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck R. L., Wood L. D., Jaffe G. J., Richmond A. MGSA/GRO transcription is differentially regulated in normal retinal pigment epithelial and melanoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):791–802. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. K., Gutman M., Radinsky R., Bucana C. D., Fidler I. J. Expression of interleukin 8 correlates with the metastatic potential of human melanoma cells in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 15;54(12):3242–3247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Tsuboi A., Miyatake S., Arai K., Arai N. Inducible and non-inducible factors co-operatively activate the GM-CSF promoter by interacting with two adjacent DNA motifs. Int Immunol. 1990;2(8):787–794. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.8.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvadia A. J., Rogers K. T., Higgins P. D., Murata Y., Martin K. H., Humphrey P. A., Horowitz J. M. Sp-1 binds promoter elements regulated by the RB protein and Sp-1-mediated transcription is stimulated by RB coexpression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley M. Z., Thanos D., Read M. A., Maniatis T., Collins T. A striking similarity in the organization of the E-selectin and beta interferon gene promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6464–6475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer U., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Sherry B. Genomic cloning and promoter analysis of macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta, members of the chemokine superfamily of proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):4996–5012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto K., Okamoto S., Mukaida N., Murakami S., Mai M., Matsushima K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma synergistically induce interleukin 8 production in a human gastric cancer cell line through acting concurrently on AP-1 and NF-kB-like binding sites of the interleukin 8 gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22506–22511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet P. C., Verrijzer C. P. Bending of DNA by transcription factors. Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]