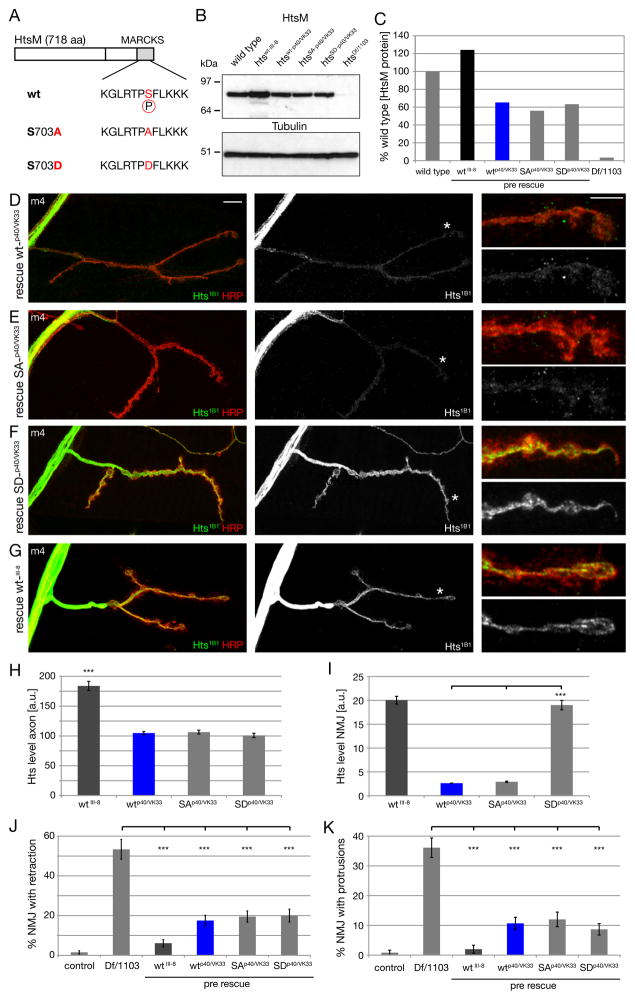
Figure 8. Control of synaptic Hts-M localization via phosphorylation of S703.
A) Schematic of the wild type, non-phosphorylatable (S703A) and phospho-mimic (S703D) Hts-M sequences.
B) Western Blot of third instar larval brains comparing Hts-M levels in wild type, mutant and the different presynaptic rescue animals.
C) Quantification of the Western Blots. We observe identical expression levels between the site-integrated constructs wt-p40/VK33, SA-p40/VK33 and SD-p40/VK33 in the mutant background. The P-element mediated insertion wt_III-8 expresses approximately 2-fold higher levels of Hts-M compared to the site-integrated constructs and approximately 120% of wild type. The site-integrated insertions express only approximately 60% of wild type Hts-M levels.
D-G) Visualization of axonal and presynaptic HtsM levels in rescued animals expressing different HtsM constructs presynaptically (genotypes as in B, C) on muscle 4. The site-integrated constructs (D-F) express identical levels of wt, SA and SD mutant forms of HtsM. Animals are stained with Hts-1B1 and Hrp to mark the presynaptic membrane.
D) Expression of wild type HtsM results in very low levels of HtsM within the presynaptic nerve terminal.
E) Expression of non-phosphorylatable HtsM (SA) results in similarly low levels of HtsM within the presynaptic nerve terminal.
F) Expression of a phospho-mimic form of HtsM (SD) results in highly abundant HtsM protein within the presynaptic nerve terminal.
G) The P-element insertion wt_III-8 used for all phenotypic rescues (Fig. 4) expresses high levels of HtsM in the presynaptic nerve terminal.
H) Quantification of HtsM levels in the axon. Identical levels can be observed for the three site-integrated constructs while the p-element insertion shows an approximate 2-fold increase, corresponding to the 2-fold higher expression levels observed in B-C.
I) Quantification of HtsM levels within the presynaptic nerve terminal. The presynaptic levels of the Hts-SD variant are approximately 5-fold increased compared to wt and SA variants.
J) Quantification of synapse retractions at m4 for the different phenotypes.
K) Quantification of protrusions on m4. All constructs significantly rescue the protrusion phenotype. The original wild type construct that expresses higher levels of Hts rescues better than the site-integrated versions (n > 150 for all genotypes for J, K; *** indicates p < 0.001, ANOVA; Error bars represent SEM).