Abstract
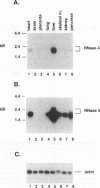
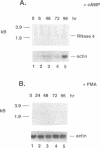
We have isolated a unique genomic fragment encoding human ribonuclease 4 (RNase 4) of the mammalian ribonuclease gene family, whose members include pancreatic ribonuclease, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, eosinophil cationic protein and angiogenin. We have determined that the coding sequence of RNase 4 resides on a single exon found on human chromosome 14. The mRNA encoding RNase 4 was detected by Northern analysis in a number of human somatic tissues, including pancreas, lung, skeletal muscle, heart, kidney and placenta, but not brain; liver represents the most abundant source. Interestingly, the mRNA encoding RNase 4 is approximately 2 kb in length, which is approximately twice as large as the mRNAs encoding other members of this gene family. A larger (approximately 2.4 kb), second transcript was detected in hepatic, pancreatic and renal tissues. The approximately 2 kb RNase 4 mRNA was detected in cells of the human promyelocytic leukemia line, HL-60, that had been treated with dibutyryl-cAMP to promote neutrophilic differentiation. In contrast, no mRNA encoding RNase 4 could be detected in cells treated with phorbol myristic acid (PMA), an agent promoting differentiation toward monocyte/macrophages, suggesting the existence of elements regulating tissue specific expression of this gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja S. K., Shetty A., Tiffany H. L., Murphy P. M. Comparison of the genomic organization and promoter function for human interleukin-8 receptors A and B. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26381–26389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardelt W., Mikulski S. M., Shogen K. Amino acid sequence of an anti-tumor protein from Rana pipiens oocytes and early embryos. Homology to pancreatic ribonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S. C., Wu H. P., Banks T. C., Eissa N. T., Moss J. Structural diversity in the 5'-untranslated region of cytokine-stimulated human inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10625–10630. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. The HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line: proliferation, differentiation, and cellular oncogene expression. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Di Donato A., Parente A., Piccoli R. Seminal RNase: a unique member of the ribonuclease superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90042-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R., Collins S., Trujillo J., McCredie K., Ahearn M., Tsai S., Metzgar R., Aulakh G., Ting R., Ruscetti F. Characterization of the continuous, differentiating myeloid cell line (HL-60) from a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1979 Sep;54(3):713–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Bell M. P., Checkel J. L., Ackerman S. J., McKean D. J. Biochemical and functional similarities between human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein: homology with ribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3146–3150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann K. J., Ten R. M., Loegering D. A., Jenkins R. B., Heise M. T., Schad C. R., Pease L. R., Gleich G. J., Barker R. L. Structure and chromosome localization of the human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein genes: evidence for intronless coding sequences in the ribonuclease gene superfamily. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):535–546. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugg M., Schein C. H. The DNA sequences of the human and hamster secretory ribonucleases determined with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):612–612. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haviland D. L., Borel A. C., Fleischer D. T., Haviland J. C., Wetsel R. A. Structure, 5'-flanking sequence, and chromosome location of the human N-formyl peptide receptor gene. A single-copy gene comprised of two exons on chromosome 19q.13.3 that yields two distinct transcripts by alternative polyadenylation. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4168–4174. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gough A., Xu W., Lane D. P., Spurr N. K. Chromosome mapping of the human gene encoding the 68-kDa nuclear antigen (p68) by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6211–6214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie M., Nitta R., Ohgi K., Niwata Y., Watanabe H., Iwama M., Beintema J. J., Sanda A., Takizawa Y. Primary structure of a non-secretory ribonuclease from bovine kidney. J Biochem. 1988 Aug;104(2):289–296. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama M., Sanda A., Ohgi K., Hofsteenge J., Irie M. Purification and primary structure of a porcine kidney non-secretory ribonuclease. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1993 Dec;57(12):2133–2138. doi: 10.1271/bbb.57.2133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. S., Soucek J., Matousek J., Raines R. T. Structural basis for the biological activities of bovine seminal ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10525–10530. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5494–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. S., Sun L., Satoh T., Fisher L. M., Spry C. J. Human eosinophil major basic protein, a mediator of allergic inflammation, is expressed by alternative splicing from two promoters. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 1;305(Pt 3):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj3050921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastronicola M. R., Piccoli R., D'Alessio G. Key extracellular and intracellular steps in the antitumor action of seminal ribonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1995 May 15;230(1):242–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misawa H., Ishii K., Deguchi T. Gene expression of mouse choline acetyltransferase. Alternative splicing and identification of a highly active promoter region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20392–20399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima-Iijima S., Hamada H., Reddy P., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure of the human cytoplasmic beta-actin gene: interspecies homology of sequences in the introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6133–6137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta K., Ozaki K., Ishikawa M., Furusawa S., Hosono M., Kawauchi H., Sasaki K., Takayanagi Y., Tsuiki S., Hakomori S. Inhibition of cell proliferation by Rana catesbeiana and Rana japonica lectins belonging to the ribonuclease superfamily. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):920–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri M., Carsana A., Furia A., Libonati M. Sequence analysis of a cloned cDNA coding for bovine seminal ribonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):275–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. F., Ackerman S. J., Tenen D. G. Human eosinophil cationic protein. Molecular cloning of a cytotoxin and helminthotoxin with ribonuclease activity. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):163–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. F., Dyer K. D., Tiffany H. L., Gonzalez M. Rapid evolution of a unique family of primate ribonuclease genes. Nat Genet. 1995 Jun;10(2):219–223. doi: 10.1038/ng0695-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H. F., Tenen D. G., Ackerman S. J. Molecular cloning of the human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: a member of the ribonuclease gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4460–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak S. M., Fett J. W., Yao Q. Z., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin mRNA in human tumor and normal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1240–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90781-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasso M. P., Carsana A., Confalone E., Cosi C., Sorrentino S., Viola M., Palmieri M., Russo E., Furia A. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the bovine brain ribonuclease and its expression in different regions of the brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6469–6474. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno M., Futami J., Tsushima Y., Akutagawa K., Kosaka M., Tada H., Yamada H. Molecular cloning and expression of human ribonuclease 4 cDNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Apr 26;1261(3):424–426. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(95)00040-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of a human colon carcinoma-secreted enzyme with pancreatic ribonuclease-like activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7255–7264. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Parente A., Farina B., Greco L., La Montagna R., Leone E. Complete amino-acid sequence of bovine seminal ribonuclease, a dimeric protein from seminal plasma. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Oct;368(10):1305–1312. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini A. M., Hemmings B. A., Hofsteenge J. Residues 36-42 of liver RNase PL3 contribute to its uridine-preferring substrate specificity. Cloning of the cDNA and site-directed mutagenesis studies. Protein Sci. 1994 Mar;3(3):459–466. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Weiner L. H., Swain J. L. Tissue distribution and developmental expression of the messenger RNA encoding angiogenin. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):280–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2440105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weremowicz S., Fox E. A., Morton C. C., Vallee B. L. Localization of the human angiogenin gene to chromosome band 14q11, proximal to the T cell receptor alpha/delta locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):973–981. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H. M., Strydom D. J. The amino acid sequence of human ribonuclease 4, a highly conserved ribonuclease that cleaves specifically on the 3' side of uridine. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 1;217(1):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]