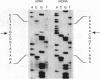
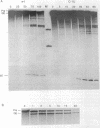
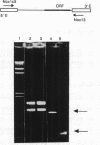
Abstract
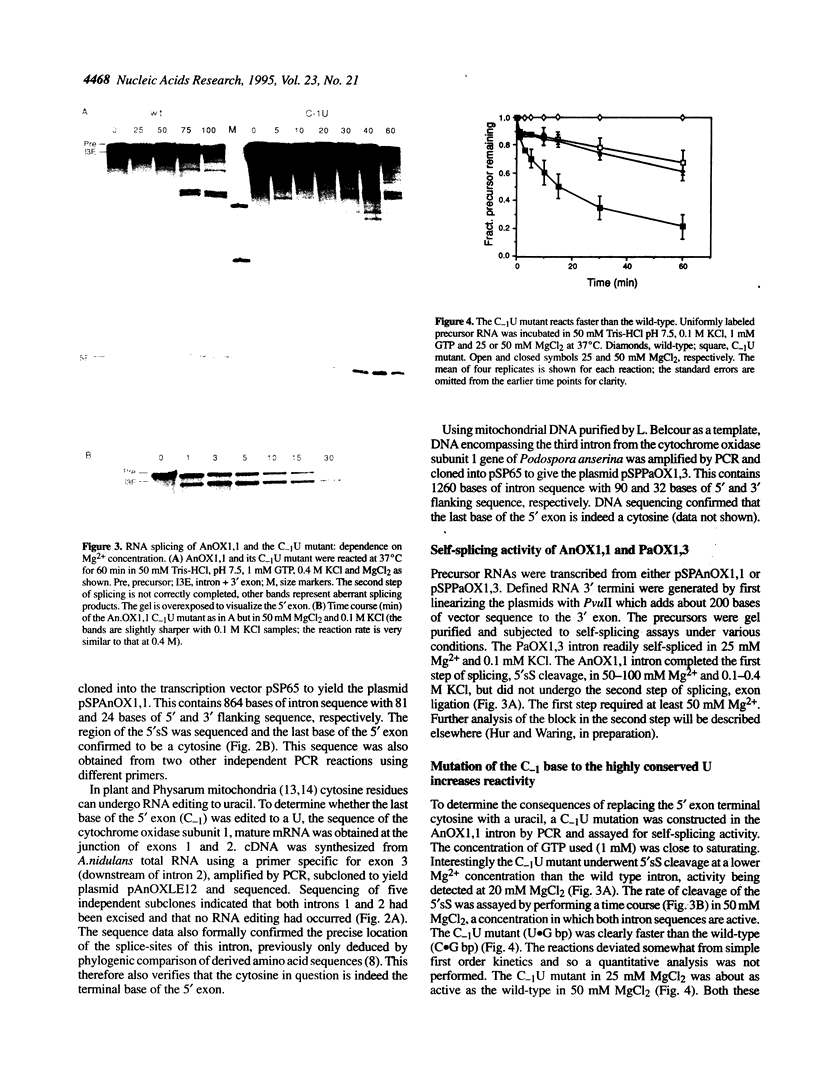
In virtually all of the 200 group I introns sequenced thus far, the specificity of 5' splice-site cleavage is determined by a basepair between a uracil base at the end of the 5' exon and a guanine in an intron guide sequence which pairs with the nucleotides flanking the splice-site. It has been reported that two introns in the cytochrome oxidase subunit I gene of Aspergillus nidulans and Podospora anserina are exceptions to this rule and have a C.G basepair in this position. We have confirmed the initial reports and shown for one of them that RNA editing does not convert the C to a U. Both introns autocatalytically cleave the 5' splice-site. Mutation of the C to U in one intron reduces the requirement for Mg2+ and leads to an increase in the rate of cleavage. As the C base encodes a highly conserved amino acid, we propose that it is selected post-translationally at the level of protein function, despite its inferior splicing activity.
Full text
PDF
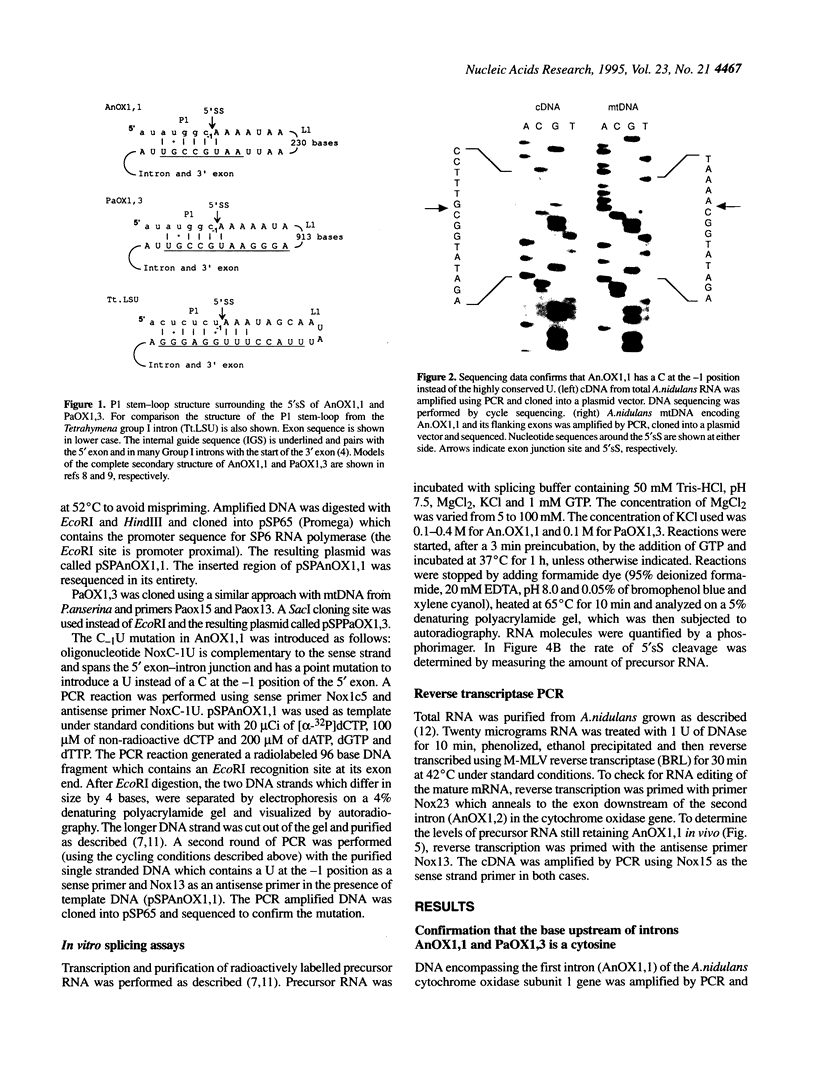


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain F. H., Varani G. Divalent metal ion binding to a conserved wobble pair defining the upstream site of cleavage of group I self-splicing introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):341–350. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barfod E. T., Cech T. R. The conserved U.G pair in the 5' splice site duplex of a group I intron is required in the first but not the second step of self-splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3657–3666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. Phage T4 introns: self-splicing and mobility. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:363–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua P. C., Kierzek R., Johnson K. A., Turner D. H. Dynamics of ribozyme binding of substrate revealed by fluorescence-detected stopped-flow methods. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1355–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.1455230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Michel F., McNally K. L. DNA sequence analysis of the 24.5 kilobase pair cytochrome oxidase subunit I mitochondrial gene from Podospora anserina: a gene with sixteen introns. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):381–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00340719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudna J. A., Cormack B. P., Szostak J. W. RNA structure, not sequence, determines the 5' splice-site specificity of a group I intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7402–7406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs W. D., Cech T. R. A tertiary interaction in the Tetrahymena intron contributes to selection of the 5' splice site. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1198–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Covello P. S. RNA editing in plant mitochondria and chloroplasts. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):64–71. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D. Evidence for processivity and two-step binding of the RNA substrate from studies of J1/2 mutants of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 11;31(5):1386–1399. doi: 10.1021/bi00120a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. F. The mitochondrial genome of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: highly homologous introns are inserted at the same position of the otherwise less conserved cox1 genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Aspergillus nidulans. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2129–2136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partono S., Lewin A. S. Autocatalytic activities of intron 5 of the cob gene of yeast mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2562–2571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldanha R., Mohr G., Belfort M., Lambowitz A. M. Group I and group II introns. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):15–24. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scazzocchio C. Group I introns: do they only go home? Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Cech T. R. Minor groove recognition of the conserved G.U pair at the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction site. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):675–679. doi: 10.1126/science.7839142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Cech T. R. Tertiary interactions with the internal guide sequence mediate docking of the P1 helix into the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13593–13604. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh E. R., Waring R. B. Base pairing between the 3' exon and an internal guide sequence increases 3' splice site specificity in the Tetrahymena self-splicing rRNA intron. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2960–2965. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Brown T. A., Ray J. A., Scazzocchio C., Davies R. W. Three variant introns of the same general class in the mitochondrial gene for cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 in Aspergillus nidulans. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2121–2128. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., May G. S., Morris N. R. Characterization of an inducible expression system in Aspergillus nidulans using alcA and tubulin-coding genes. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B., Herschlag D., Cech T. R. Mutations in a nonconserved sequence of the Tetrahymena ribozyme increase activity and specificity. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]