Abstract
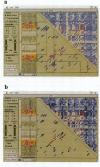
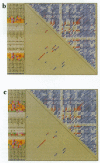
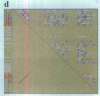
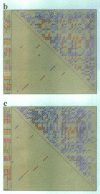
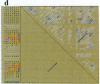
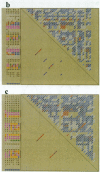
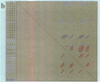
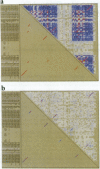
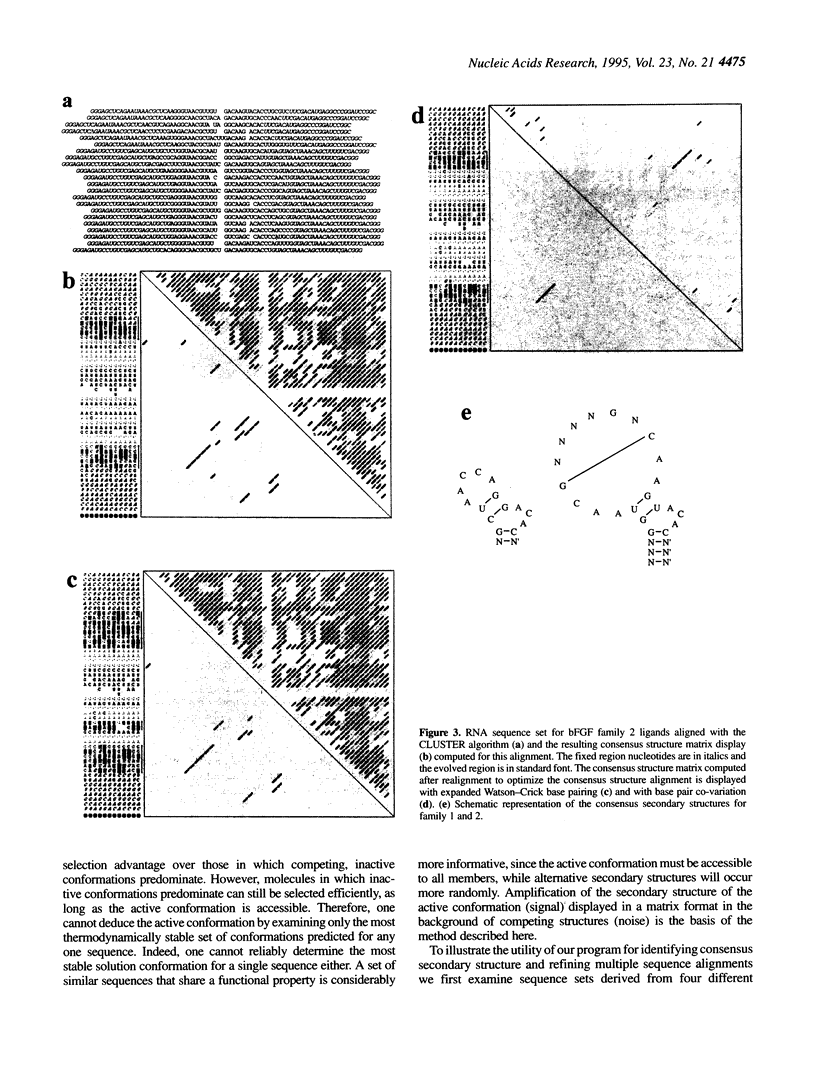
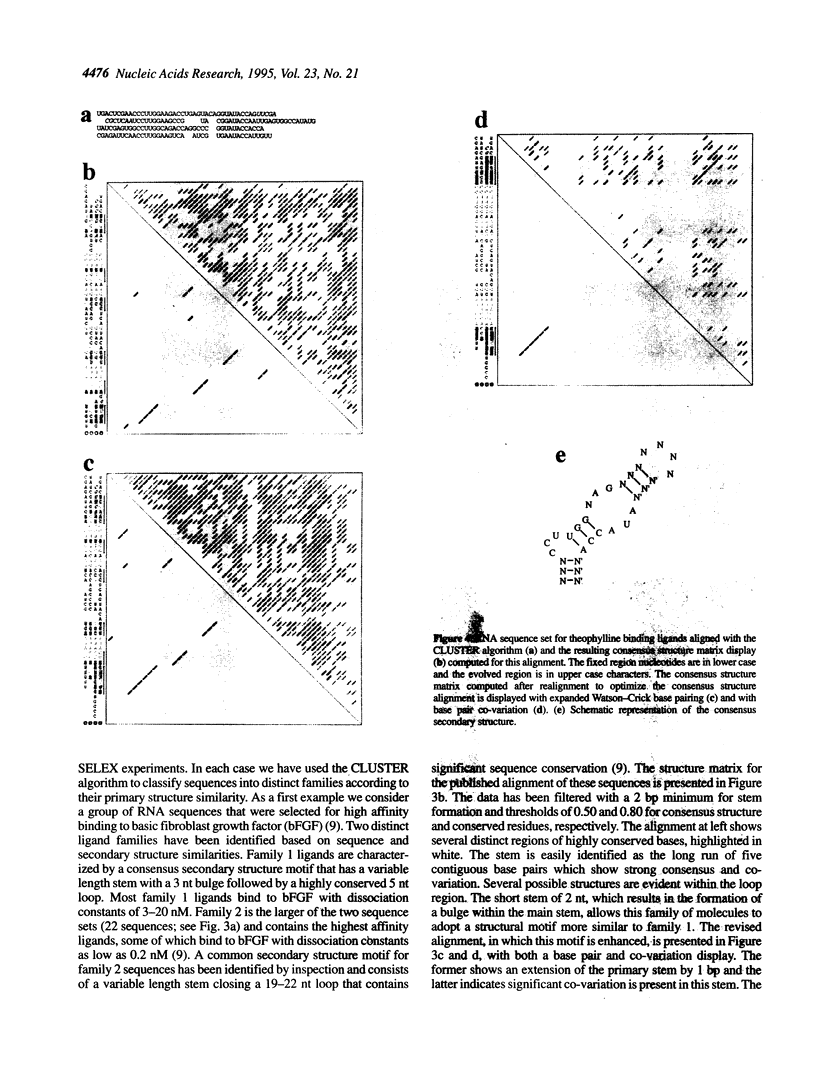
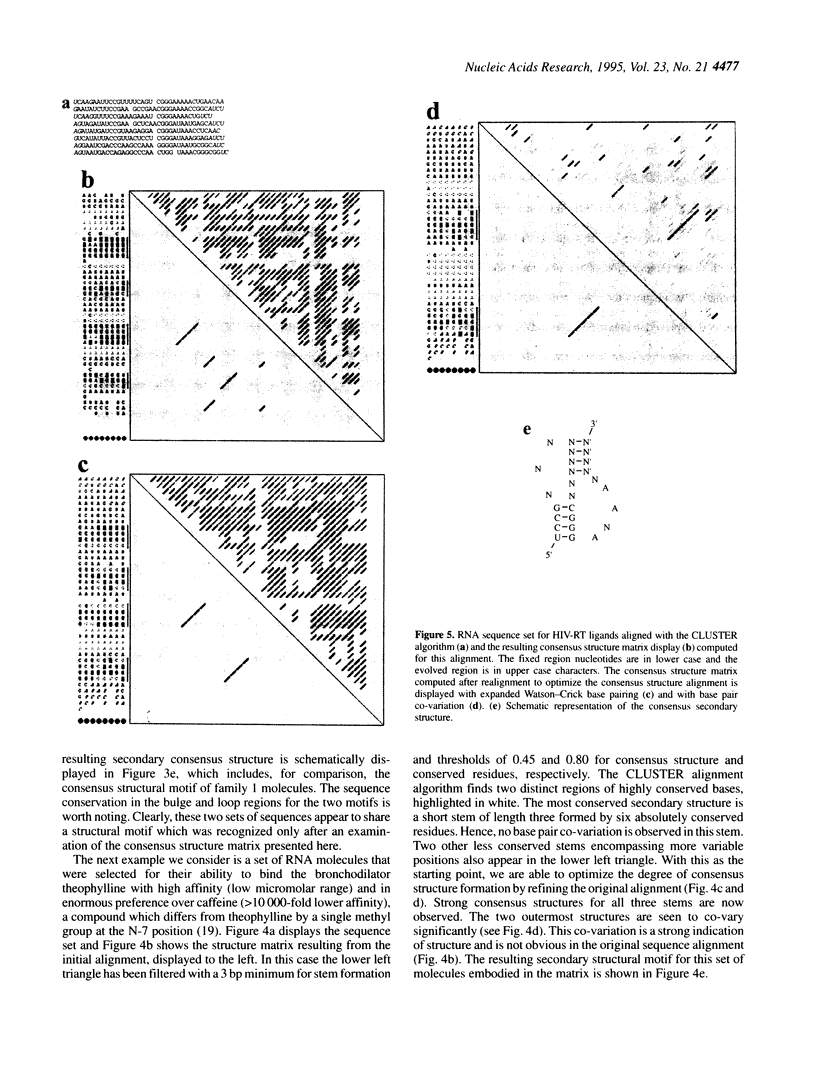
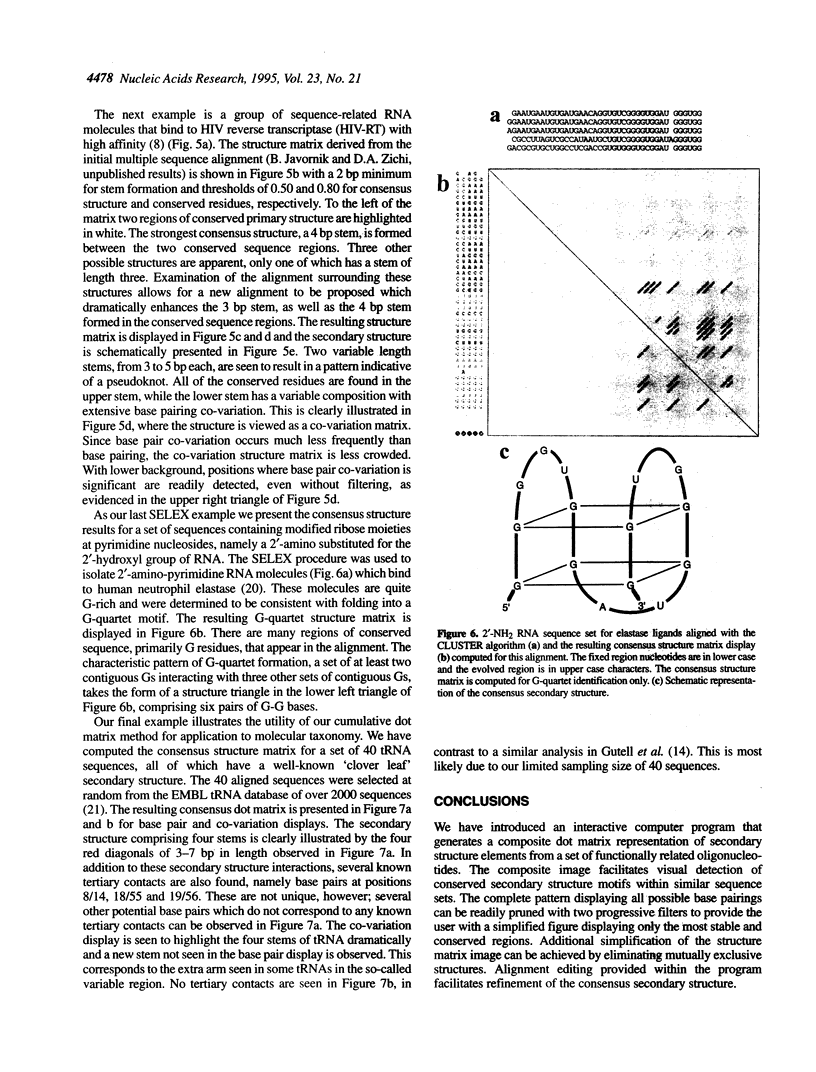
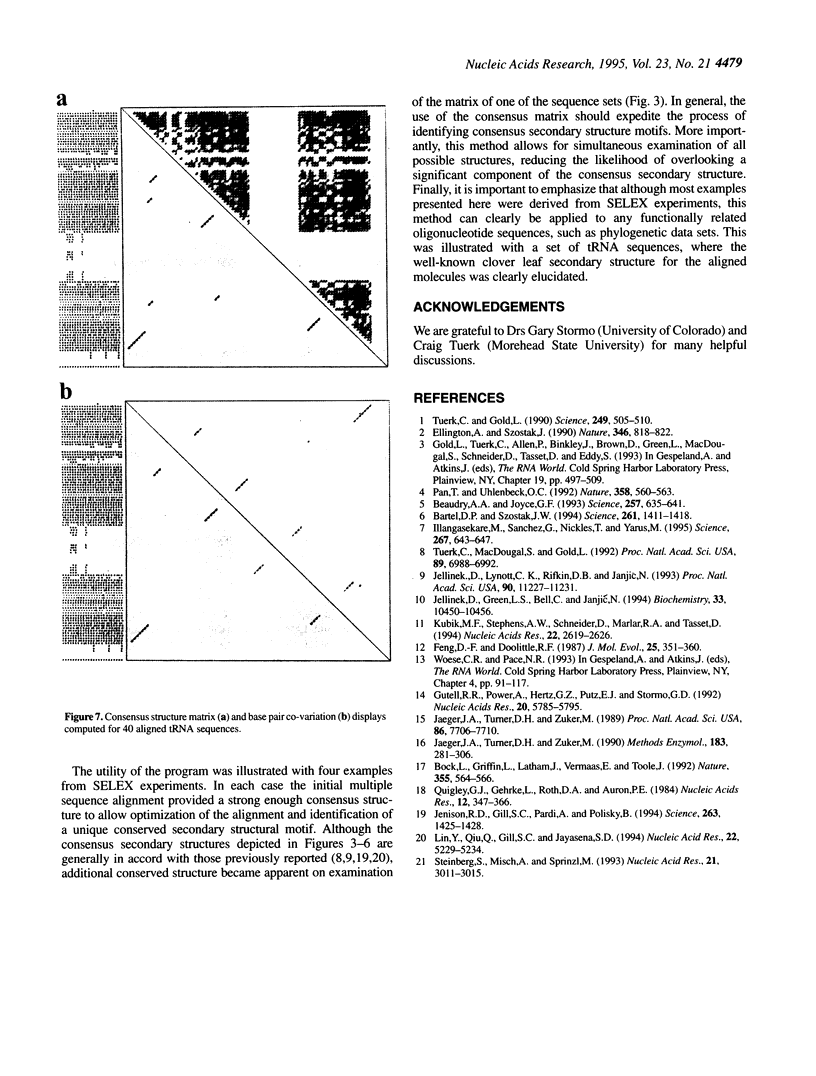
We present a computer-aided approach for identifying and aligning consensus secondary structure within a set of functionally related oligonucleotide sequences aligned by sequence. The method relies on visualization of secondary structure using a generalization of the dot matrix representation appropriate for consensus sequence data sets. An interactive computer program implementing such a visualization of consensus structure has been developed. The program allows for alignment editing, data and display filtering and various modes of base pair representation, including co-variation. The utility of this approach is demonstrated with four sample data sets derived from in vitro selection experiments and one data set comprising tRNA sequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel D. P., Szostak J. W. Isolation of new ribozymes from a large pool of random sequences [see comment]. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1411–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.7690155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudry A. A., Joyce G. F. Directed evolution of an RNA enzyme. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):635–641. doi: 10.1126/science.1496376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock L. C., Griffin L. C., Latham J. A., Vermaas E. H., Toole J. J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):564–566. doi: 10.1038/355564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Power A., Hertz G. Z., Putz E. J., Stormo G. D. Identifying constraints on the higher-order structure of RNA: continued development and application of comparative sequence analysis methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5785–5795. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illangasekare M., Sanchez G., Nickles T., Yarus M. Aminoacyl-RNA synthesis catalyzed by an RNA. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):643–647. doi: 10.1126/science.7530860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Predicting optimal and suboptimal secondary structure for RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:281–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek D., Green L. S., Bell C., Janjić N. Inhibition of receptor binding by high-affinity RNA ligands to vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10450–10456. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek D., Lynott C. K., Rifkin D. B., Janjić N. High-affinity RNA ligands to basic fibroblast growth factor inhibit receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11227–11231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison R. D., Gill S. C., Pardi A., Polisky B. High-resolution molecular discrimination by RNA. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1425–1429. doi: 10.1126/science.7510417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubik M. F., Stephens A. W., Schneider D., Marlar R. A., Tasset D. High-affinity RNA ligands to human alpha-thrombin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2619–2626. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y., Qiu Q., Gill S. C., Jayasena S. D. Modified RNA sequence pools for in vitro selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 11;22(24):5229–5234. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.24.5229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. A small metalloribozyme with a two-step mechanism. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):560–563. doi: 10.1038/358560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Gehrke L., Roth D. A., Auron P. E. Computer-aided nucleic acid secondary structure modeling incorporating enzymatic digestion data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):347–366. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S., Misch A., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3011–3015. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., MacDougal S., Gold L. RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]