Abstract
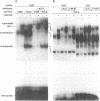
The hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) was first described as a DNA binding activity that specifically recognizes an 8 bp motif known to be essential for hypoxia-inducible erythropoietin gene transcription. Subsequently HIF-1 activity has also been found in cell lines which do not express erythropoietin, suggesting that HIF-1 is part of a widespread oxygen sensing mechanism. In electrophoretic mobility shift assays HIF-1 DNA binding activity is only detectable in nuclear extracts of cells cultivated in a low oxygen atmosphere. In addition to HIF-1, a constitutive DNA binding activity also specifically binds the HIF1 probe. Here we report that CRE and AP1 oligonucleotides efficiently competed for binding of the HIF1 probe to this constitutive factor, whereas HIF-1 activity itself remained unaffected. Monoclonal antibodies raised against the CRE binding factors ATF-1 and CREB-1 supershifted the constitutive factors ATF-1 and CREB-1 supershifted the constitutive factor, while Jun and Fos family members, which constitute the AP-1 factor, were immunologically undetectable. Recombinant ATF-1 and CREB-1 proteins bound HIF1 probes either as homodimers or as heterodimers, indicating a new binding specificity for ATF-1/CREB-1. Finally, reporter gene assays in HeLa cells treated with either a cAMP analogue or a phorbol ester suggest that the PKA, but not the PKC signalling pathway is involved in oxygen sensing.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck I., Ramirez S., Weinmann R., Caro J. Enhancer element at the 3'-flanking region controls transcriptional response to hypoxia in the human erythropoietin gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15563–15566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck I., Weinmann R., Caro J. Characterization of hypoxia-responsive enhancer in the human erythropoietin gene shows presence of hypoxia-inducible 120-Kd nuclear DNA-binding protein in erythropoietin-producing and nonproducing cells. Blood. 1993 Aug 1;82(3):704–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard K. L., Acquaviva A. M., Galson D. L., Bunn H. F. Hypoxic induction of the human erythropoietin gene: cooperation between the promoter and enhancer, each of which contains steroid receptor response elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5373–5385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firth J. D., Ebert B. L., Pugh C. W., Ratcliffe P. J. Oxygen-regulated control elements in the phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and lactate dehydrogenase A genes: similarities with the erythropoietin 3' enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6496–6500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. A., Glass G. A., Cunningham J. M., Bunn H. F. The regulated expression of erythropoietin by two human hepatoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Masson N., Jones N. C., Lee K. A. The cellular transcription factor CREB corresponds to activating transcription factor 47 (ATF-47) and forms complexes with a group of polypeptides related to ATF-43. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6192–6203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Totty N. F., Jones N. C. Identification and functional characterisation of the cellular activating transcription factor 43 (ATF-43) protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4601–4609. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin: structure, control of production, and function. Physiol Rev. 1992 Apr;72(2):449–489. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.2.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. The molecular mechanism of erythropoietin action. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):649–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalli E., Sassone-Corsi P. Signal transduction and gene regulation: the nuclear response to cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17359–17362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Masson N. Transcriptional regulation by CREB and its relatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 23;1174(3):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90191-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A. P., Levy N. S., Wegner S., Goldberg M. A. Transcriptional regulation of the rat vascular endothelial growth factor gene by hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 2;270(22):13333–13340. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.22.13333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. K., Suggs S., Lin C. H., Browne J. K., Smalling R., Egrie J. C., Chen K. K., Fox G. M., Martin F., Stabinsky Z. Cloning and expression of the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7580–7584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Cox S. R., Morita T., Kourembanas S. Hypoxia regulates vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in endothelial cells. Identification of a 5' enhancer. Circ Res. 1995 Sep;77(3):638–643. doi: 10.1161/01.res.77.3.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan A., Curtin P. T. A 24-base-pair sequence 3' to the human erythropoietin gene contains a hypoxia-responsive transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3928–3932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti H. H., Jung H. H., Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Hypoxia and cobalt stimulate lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Dec;429(2):216–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00374315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson N., John J., Lee K. A. In vitro phosphorylation studies of a conserved region of the transcription factor ATF1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4166–4173. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell P. H., Pugh C. W., Ratcliffe P. J. Inducible operation of the erythropoietin 3' enhancer in multiple cell lines: evidence for a widespread oxygen-sensing mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Habener J. F. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate response element binding protein (CREB) and related transcription-activating deoxyribonucleic acid-binding proteins. Endocr Rev. 1993 Jun;14(3):269–290. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-3-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh C. W., Tan C. C., Jones R. W., Ratcliffe P. J. Functional analysis of an oxygen-regulated transcriptional enhancer lying 3' to the mouse erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10553–10557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L., Koury S. T., Nejfelt M. K., Gearhart J. D., Antonarakis S. E. Cell-type-specific and hypoxia-inducible expression of the human erythropoietin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8725–8729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L., Nejfelt M. K., Chi S. M., Antonarakis S. E. Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3' to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L., Roth P. H., Fang H. M., Wang G. L. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23757–23763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L., Wang G. L. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5447–5454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Jiang B. H., Rue E. A., Semenza G. L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5510–5514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. Characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and regulation of DNA binding activity by hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21513–21518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. Desferrioxamine induces erythropoietin gene expression and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 DNA-binding activity: implications for models of hypoxia signal transduction. Blood. 1993 Dec 15;82(12):3610–3615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. General involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in transcriptional response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):1230–1237. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A. Regulation of glycolytic enzyme RNA transcriptional rates by oxygen availability in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;77(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00230147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]