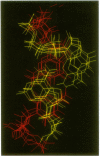
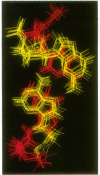
Abstract
The occurrence and NMR solution structure of a class of biloop hairpins containing the sequence 5'-CGXYAG are presented. These hairpins, which are variations on a sequence found in the reverse transcript of the human T-cell leukemia virus 2 (HLV2), show elevated melting points and high chemical stability toward denaturation by urea. Hairpins with the 5'-CGXYAG configuration have melting points 18-20 degrees higher than hairpins with 5'-CAXYGG or 5'-GGXYAC configurations. The identities of the looping bases, X and Y above, play a negligible role in determining the stability of this DNA hairpin stability. This is very different from G-A based loops in RNA, where the third base must be a purine for high stability [the GNRA loops; V.P. Antao, S.Y. Lai and I. Tinoco, Jr (1991) Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 5901-5905]. We show that these properties are associated with a four base helix unit that contains both a sheared GA base pair and a Watson-Crick CG base pair upon which it is stacked. As an understanding of the significance of AG base pairs has become increasingly important in the structural biology of nucleic acids, we compute an 0.7-0.9 A precision ensemble of NMR solution structures using iterative relaxation matrix methods. Calculations performed on NMR-derived structures indicate that neither base-base electrostatic interactions, nor base-solvent dispersive interactions, are significant factors in determining the observed differences in hairpin stability. Thus the stability of the 5'-CGXYAG configuration would appear to derive from favorable base-base London/van der Waals interactions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antao V. P., Tinoco I., Jr Thermodynamic parameters for loop formation in RNA and DNA hairpin tetraloops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):819–824. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Yaremchuk A., Tukalo M., Cusack S. The 2.9 A crystal structure of T. thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Ser). Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1404–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8128220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Hunter W. N., Kneale G., Kennard O. Molecular structure of the G.A base pair in DNA and its implications for the mechanism of transversion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2402–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Leonard G. A., Booth E. D., Chambers J. Crystal structure and stability of a DNA duplex containing A(anti).G(syn) base-pairs. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):455–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonnaux C., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Guschlbauer W., Fazakerley G. V. Solution structure of an oncogenic DNA duplex containing a G.A mismatch. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5449–5458. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. W., Chou S. H., Reid B. R. Base pairing geometry in GA mismatches depends entirely on the neighboring sequence. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1037–1041. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A., Leach D. R. Two-base DNA hairpin-loop structures in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 25;22(21):4361–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.21.4361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. A., Honig B. The electrostatic contribution to DNA base-stacking interactions. Biopolymers. 1992 Feb;32(2):145–159. doi: 10.1002/bip.360320205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene K. L., Jones R. L., Li Y., Robinson H., Wang A. H., Zon G., Wilson W. D. Solution structure of a GA mismatch DNA sequence, d(CCATGAATGG)2, determined by 2D NMR and structural refinement methods. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 8;33(5):1053–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00171a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Pardi A. Structural features that give rise to the unusual stability of RNA hairpins containing GNRA loops. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):191–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1712983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirao I., Kawai G., Yoshizawa S., Nishimura Y., Ishido Y., Watanabe K., Miura K. Most compact hairpin-turn structure exerted by a short DNA fragment, d(GCGAAGC) in solution: an extraordinarily stable structure resistant to nucleases and heat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):576–582. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jucker F. M., Pardi A. GNRA tetraloops make a U-turn. RNA. 1995 Apr;1(2):219–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira M., Kanagawa M., Sato H., Uesugi S., Fujii S., Kohno T., Maeda T. Formation of sheared G:A base pairs in an RNA duplex modelled after ribozymes, as revealed by NMR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 25;22(14):2752–2759. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.14.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira M., Sato H., Mishima K., Uesugi S., Fujii S. NMR studies of G:A mismatches in oligodeoxyribonucleotide duplexes modelled after ribozymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5418–5424. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J. Calculating thermodynamic data for transitions of any molecularity from equilibrium melting curves. Biopolymers. 1987 Sep;26(9):1601–1620. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pley H. W., Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of a hammerhead ribozyme. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):68–74. doi: 10.1038/372068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privé G. G., Heinemann U., Chandrasegaran S., Kan L. S., Kopka M. L., Dickerson R. E. Helix geometry, hydration, and G.A mismatch in a B-DNA decamer. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):498–504. doi: 10.1126/science.3310237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidor B., Irikura K. K., Brooks B. R., Karplus M. Dynamics of DNA oligomers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):231–252. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesnaver G., Breslauer K. J. The contribution of DNA single-stranded order to the thermodynamics of duplex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimberly B. A common RNA loop motif as a docking module and its function in the hammerhead ribozyme. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Nov;1(11):820–827. doi: 10.1038/nsb1194-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimberly B., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr The conformation of loop E of eukaryotic 5S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1078–1087. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Winker S., Gutell R. R. Architecture of ribosomal RNA: constraints on the sequence of "tetra-loops". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa S., Ueda T., Ishido Y., Miura K., Watanabe K., Hirao I. Nuclease resistance of an extraordinarily thermostable mini-hairpin DNA fragment, d(GCGAAGC) and its application to in vitro protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jun 25;22(12):2217–2221. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.12.2217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]