Abstract
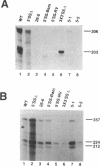
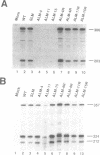
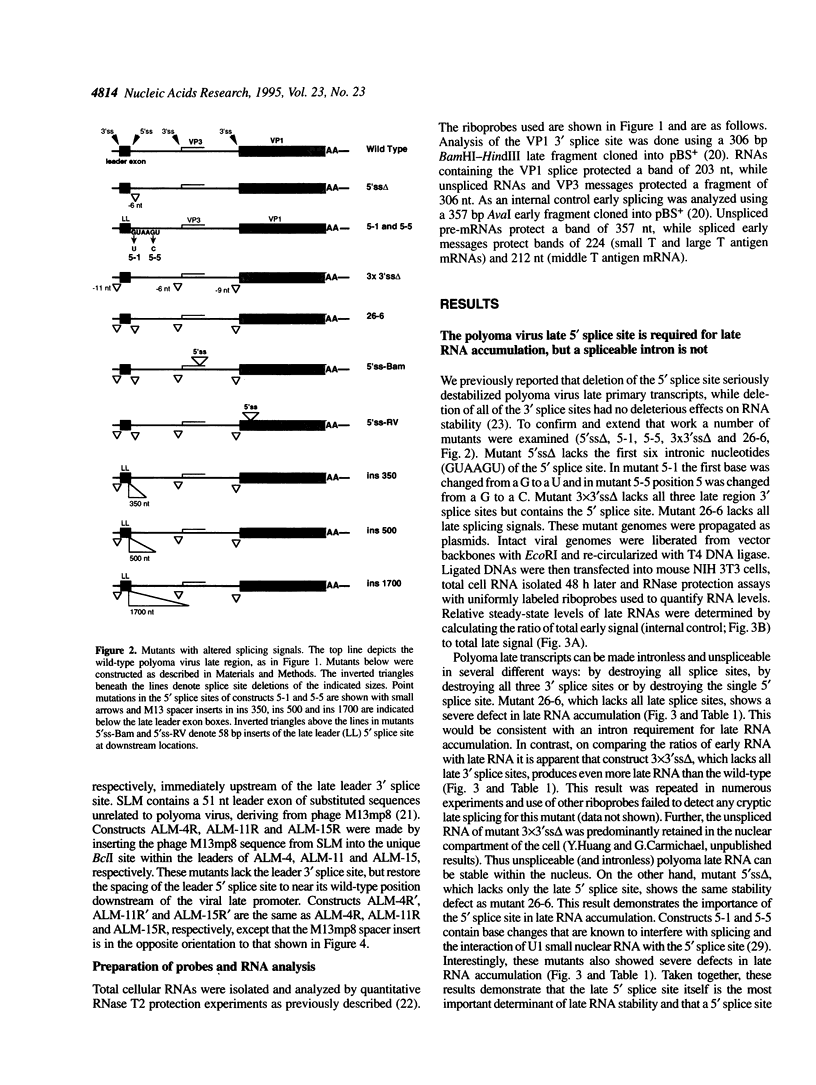
We have examined the influence of splicing signals on the stability of polyoma virus late RNAs in the nucleus. Late primary transcripts contain a single 5' splice site and three alternative 3' splice sites. In earlier work we showed that the presence of introns was not required for late RNA accumulation, however, the 5' splice site was essential, as removal of only the 5' splice site was sufficient to destabilize late RNAs up to 100-fold when compared with early RNAs. A complementary clone which retained the 5' splice site but which carried small deletions of all late region 3' splice sites produced wild-type levels of unspliced late RNA. In order to extend this work we have constructed additional types of mutants. Point mutations in the 5' splice site confirmed its importance for RNA stability. Other mutants included constructs in which the spacing between the 5' splice site and the late promoter was altered and 5' splice site insertion mutants where a 58 bp fragment containing the 5' splice site sequence was inserted separately at various restriction sites in the late region. Both types of mutants lacked all of the late 3' splice sites and had only a single 5' splice site. RNase protection analyses of late and early RNAs from these constructs revealed that moving the 5' splice site away from the late promoter (or from its normal context) destabilized late RNAs > 10-fold relative to the wild-type. We conclude that both 5' splice site integrity and its proximity to the late promoter play important roles in the nuclear stability of polyoma virus late RNAs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Efficiency of processing of viral RNA during the early and late phases of productive infection by polyoma virus. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):628–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.628-635.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Polyoma virus giant RNAs contain tandem repeats of the nucleotide sequence of the entire viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late leader region serves an essential spacer function necessary for viability and late gene expression. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):417–425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.417-425.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Carmichael G. G. The length but not the sequence of the polyoma virus late leader exon is important for both late RNA splicing and stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2593–2610. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Marlor C. W., Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G. Leader-to-leader splicing is required for efficient production and accumulation of polyomavirus late mRNAs. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):85–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.85-93.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G., Luo Y. Splice site requirement for the efficient accumulation of polyoma virus late mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3011–3017. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Berg P. Comparison of intron-dependent and intron-independent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4395–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Carmichael G. G. Deletion analysis of the polyomavirus late promoter: evidence for both positive and negative elements in the absence of early proteins. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3634–3642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3634-3642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Roome A. J., Carmichael G. G. Replication-dependent transactivation of the polyomavirus late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):992–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.992-1001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis J., Fromm M., Walbot V. Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1183–1200. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Viral gene expression in polyoma virus-transformed rat cells and their cured revertants. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):150–163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.150-163.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Arrand J. R., Kamen R. Localization of three major cappe 5' ends of polyoma virus late mRNA's within a single tetranucleotide sequence in the viral genome. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.902-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Legon S., Kamen R. Multiple 5' terminal cap structures in late polyoma virus RNA. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser C. S., Simonsen C. C., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Expression of abbreviated mouse dihydrofolate reductase genes in cultured hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. K., Kainz M. S., Merrill G. F. Introns are inconsequential to efficient formation of cellular thymidine kinase mRNA in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4576–4581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Khoury G. Rescue of a splicing defective mutant by insertion of an heterologous intron. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):634–637. doi: 10.1038/286634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Splicing as a requirement for biogenesis of functional 16S mRNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Splicing and the formation of stable RNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Leder P. SV40 recombinants carrying rabbit beta-globin gene coding sequences. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori K., Angel P., Le Beau M. M., Karin M. Structure and chromosomal localization of the functional intronless human JUN protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9148–9152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. D. A survey on intron and exon lengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9893–9908. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R. P., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late pre-mRNA processing: DNA replication-associated changes in leader exon multiplicity suggest a role for leader-to-leader splicing in the early-late switch. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5823–5832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5823-5832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus early-late switch is not regulated at the level of transcription initiation and is associated with changes in RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8993–8997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Mertz J. E. HnRNP L binds a cis-acting RNA sequence element that enables intron-dependent gene expression. Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 15;9(14):1766–1780. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.14.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X. B., Heimer J., Rekosh D., Hammarskjöld M. L. U1 small nuclear RNA plays a direct role in the formation of a rev-regulated human immunodeficiency virus env mRNA that remains unspliced. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7598–7602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. The structure of one of the eight or more distinct chromosomal genes for human interferon-alpha. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):401–408. doi: 10.1038/287401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Williams G. T. The intron requirement for immunoglobulin gene expression is dependent upon the promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6713–6724. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu W. S., Mertz J. E. Simian virus 40 late transcripts lacking excisable intervening sequences are defective in both stability in the nucleus and transport to the cytoplasm. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4386–4394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4386-4394.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staknis D., Reed R. SR proteins promote the first specific recognition of Pre-mRNA and are present together with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle in a general splicing enhancer complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7670–7682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarn W. Y., Steitz J. A. SR proteins can compensate for the loss of U1 snRNP functions in vitro. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2704–2717. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Characterisation of polyoma late mRNA leader sequences by molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4867–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Leung H., Weiner A. M. The natural 5' splice site of simian virus 40 large T antigen can be improved by increasing the base complementarity to U1 RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):3018–3020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.3018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]