Abstract
We report the preparation of two linear constructs which, when transformed into the procyclic form of Trypanosoma brucei, become stably inherited artificial mini-chromosomes. Both of the two constructs, one of 10 kb and the other of 13 kb, contain a T.brucei PARP promoter driving a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene. In the 10 kb construct the CAT gene is followed by one hygromycin phosphotransferase (Hph) gene, and in the 13 kb construct the CAT gene is followed by three tandemly linked Hph genes. At each end of these linear molecules are telomere repeats and subtelomeric sequences. Electroporation of these linear DNA constructs into the procyclic form of T.brucei generated hygromycin-B resistant cell lines. In these cell lines, the input DNA remained linear and bounded by the telomere ends, but it increased in size. In the cell lines generated by the 10 kb construct, the input DNA increased in size to 20-50 kb. In the cell lines generated by the 13 kb constructs, two sizes of linear DNAs containing the input plasmid were detected: one of 40-50 kb and the other of 150 kb. The increase in size was not the result of in vivo tandem repetitions of the input plasmid, but represented the addition of new sequences. These Hph containing linear DNA molecules were maintained stably in cell lines for at least 20 generations in the absence of drug selection and were subsequently referred to as trypanosome artificial mini-chromosomes, or TACs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Torres-Muñoz J. E., Cross G. A. Stable transformation of Leptomonas seymouri by circular extrachromosomal elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. Discontinuous transcription and antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:701–732. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Greaves D. R. Programmed gene rearrangements altering gene expression. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):658–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3544215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun R., Schönenberger Cultivation and in vitro cloning or procyclic culture forms of Trypanosoma brucei in a semi-defined medium. Short communication. Acta Trop. 1979 Sep;36(3):289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Cellular and genetic aspects of antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:83–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid J., Sollner-Webb B. Stable integrative transformation of Trypanosoma brucei that occurs exclusively by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2118–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesdiener K., Garciá-Anoveros J., Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. Chromosome organization of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6079–6083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapler G. M., Coburn C. M., Beverley S. M. Stable transfection of the human parasite Leishmania major delineates a 30-kilobase region sufficient for extrachromosomal replication and expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1084–1094. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Ward H. M., Miles M. A., Kendall G. A shuttle vector which facilitates the expression of transfected genes in Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3963–3969. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laban A., Tobin J. F., Curotto de Lafaille M. A., Wirth D. F. Stable expression of the bacterial neor gene in Leishmania enriettii. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):572–574. doi: 10.1038/343572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
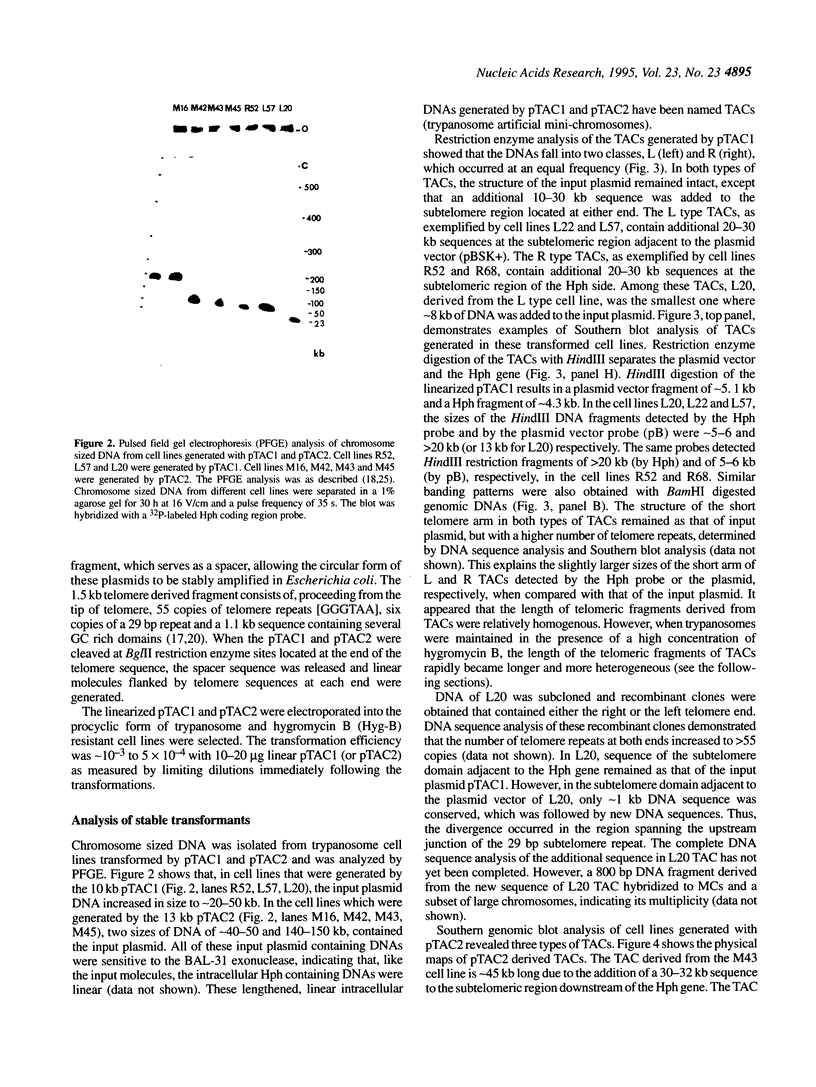
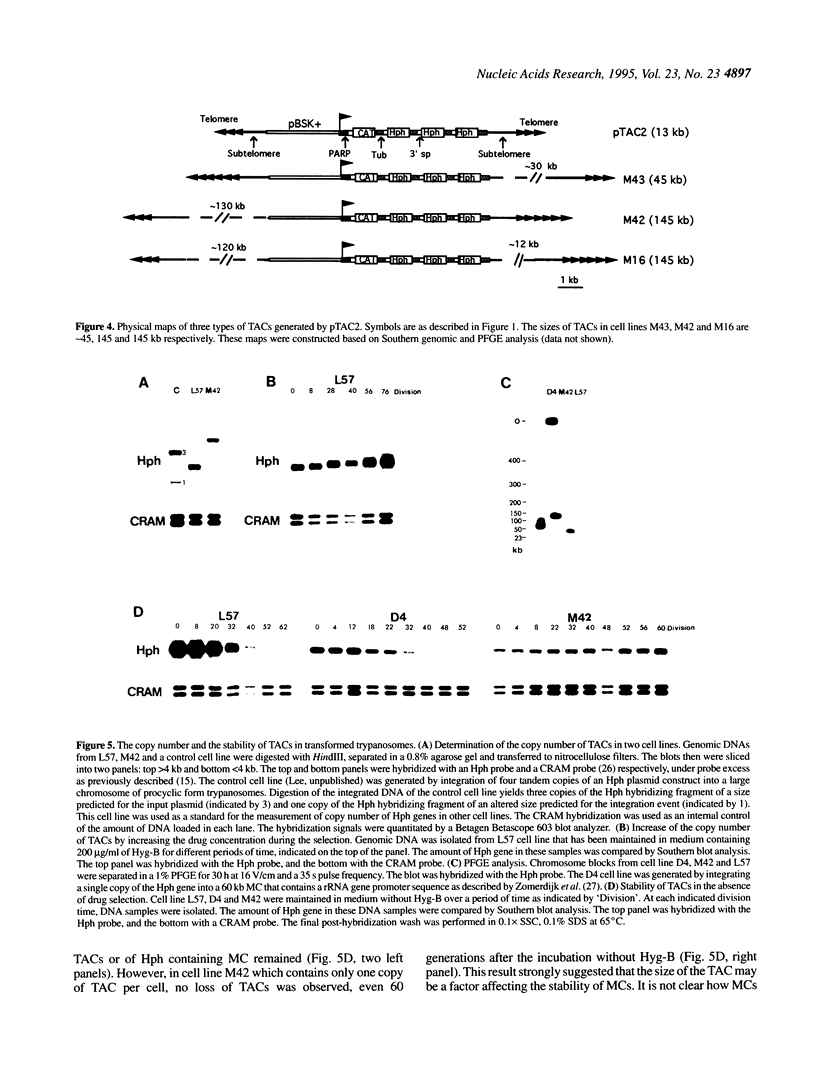
- Lee M. G. A foreign transcription unit in the inactivated VSG gene expression site of the procyclic form of Trypanosoma brucei and formation of large episomes in stably transformed trypanosomes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1995 Feb;69(2):223–238. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)00186-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Bihain B. E., Russell D. G., Deckelbaum R. J., Van der Ploeg L. H. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a cysteine-rich cell surface protein located in the flagellar pocket of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4506–4517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Van der Ploeg L. H. Homologous recombination and stable transfection in the parasitic protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1583–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2177225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., van der Ploeg L. H. The hygromycin B-resistance-encoding gene as a selectable marker for stable transformation of Trypanosoma brucei. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):255–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg S., Agabian N. Mitochondrial minicircle DNA supports plasmid replication and maintenance in nuclei of Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paindavoine P., Zampetti-Bosseler F., Pays E., Schweizer J., Guyaux M., Jenni L., Steinert M. Trypanosome hybrids generated in tsetse flies by nuclear fusion. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3631–3636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik P. K., Fang X., Cross G. A. The region encompassing the procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) gene promoter plays a role in plasmid DNA replication in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4111–4118. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik P. K., Kulkarni S. K., Cross G. A. Autonomously replicating single-copy episomes in Trypanosoma brucei show unusual stability. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2529–2538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea C., Glass D. J., Parangi S., Van der Ploeg L. H. Variant surface glycoprotein gene expression site switches in Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):6056–6063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloof P., Menke H. H., Caspers M. P., Borst P. Size fractionation of Trypanosoma brucei DNA: localization of the 177-bp repeat satellite DNA and a variant surface glycoprotein gene in a mini-chromosomal DNA fraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3889–3901. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Bernards A., Rijsewijk F. A., Borst P. Characterization of the DNA duplication-transposition that controls the expression of two genes for variant surface glycoproteins in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):593–609. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Liu A. Y., Borst P. Structure of the growing telomeres of Trypanosomes. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smith C. L., Polvere R. I., Gottesdiener K. M. Improved separation of chromosome-sized DNA from Trypanosoma brucei, stock 427-60. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3217–3227. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiden M., Osheim Y. N., Beyer A. L., Van der Ploeg L. H. Chromosome structure: DNA nucleotide sequence elements of a subset of the minichromosomes of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3823–3834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Kieft R., Borst P. A ribosomal RNA gene promoter at the telomere of a mini-chromosome in Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2725–2734. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek A. L., Mol C. A., Kieft R., Borst P. Stable transformation of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 May;59(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90014-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek A. L., Ouellette M., Borst P. Targeted insertion of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene into the tubulin gene cluster of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):174–175. doi: 10.1038/348174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]