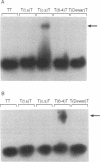
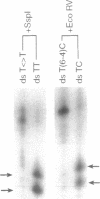
Abstract
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleaver J. E. Restriction enzyme cleavage of ultraviolet-damaged simian virus 40 and pBR322 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamola A. A., Yamane T. Sensitized photodimerization of thymine in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):443–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc J. E., Borden A., Lawrence C. W. The thymine-thymine pyrimidine-pyrimidone(6-4) ultraviolet light photoproduct is highly mutagenic and specifically induces 3' thymine-to-cytosine transitions in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9685–9689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Adair G. M., Nairn R. S. Inhibition of transient gene expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells by triplet-sensitized UV-B irradiation of transfected DNA. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 Nov;50(5):639–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb04320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Allison J. P., Nairn R. S. Immunoprecipitation of pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts and cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in uv-irradiated DNA. Radiat Res. 1990 Sep;123(3):299–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Clarkson J. M. Induction of photoproducts in synthetic polynucleotides by far and near ultraviolet radiation. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Dec;40(6):735–741. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb04645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Cleaver J. E., Epstein J. H. Repair of pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts in mouse skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jul;95(1):55–59. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12873312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Nairn R. S., Alvillar J. A., Clarkson J. M. Loss of thymine dimers from mammalian cell DNA. The kinetics for antibody-binding sites are not the same as that for T4 endonuclease V sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 30;697(3):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Nairn R. S. The biology of the (6-4) photoproduct. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 Jun;49(6):805–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb05578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Nichols A. F., Keeney S., Smith C. A., Taylor J. S., Linn S., Sancar A. Comparative analysis of binding of human damaged DNA-binding protein (XPE) and Escherichia coli damage recognition protein (UvrA) to the major ultraviolet photoproducts: T[c,s]T, T[t,s]T, T[6-4]T, and T[Dewar]T. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21301–21308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Taylor J. S. Preparation and characterization of a set of deoxyoligonucleotide 49-mers containing site-specific cis-syn, trans-syn-I, (6-4), and Dewar photoproducts of thymidylyl(3'-->5')-thymidine. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11143–11151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda D. L., Smith C. A., Taylor J. S., Sancar A. Effect of sequence, adduct type, and opposing lesions on the binding and repair of ultraviolet photodamage by DNA photolyase and (A)BC excinuclease. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10694–10700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. S., O'Day C. L. cis-syn thymine dimers are not absolute blocks to replication by DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli in vitro. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1624–1632. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]