Abstract
Abasic (AP) sites in DNA are potentially lethal and mutagenic. 'Class II' AP endonucleases initiate the repair of these and other DNA lesions. In yeast, the predominant enzyme of this type is Apn1, and its elimination sensitizes the cells to killing by simple alkylating agents or oxidants, and raises the rate of spontaneous mutation. We investigated the ability of the major human class II AP endonuclease, Ape, which is structurally unrelated to Apn1, to replace the yeast enzyme in vivo. Confocal immunomicroscopy studies indicate that approximately 25% of the Ape expressed in yeast is present in the nucleus. High-level Ape expression corresponding to approximately 7000 molecules per nucleus, equal to the normal Apn1 copy number, restored resistance to methyl methanesulfonate to near wild-type levels in Apn1-deficient (apn1-) yeast. Ape expression in apn1- yeast provided little protection against H2O2 challenges, consistent with the weak 3'-repair diesterase activity of the human enzyme. Ape expression at approximately 2000 molecules per nucleus reduced the spontaneous mutation rate of apn1- yeast to that seen for wild-type cells. Because Ape has a powerful AP endonuclease but weak 3'-diesterase activity, these findings indicate that endogenously generated AP sites can drive spontaneous mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF


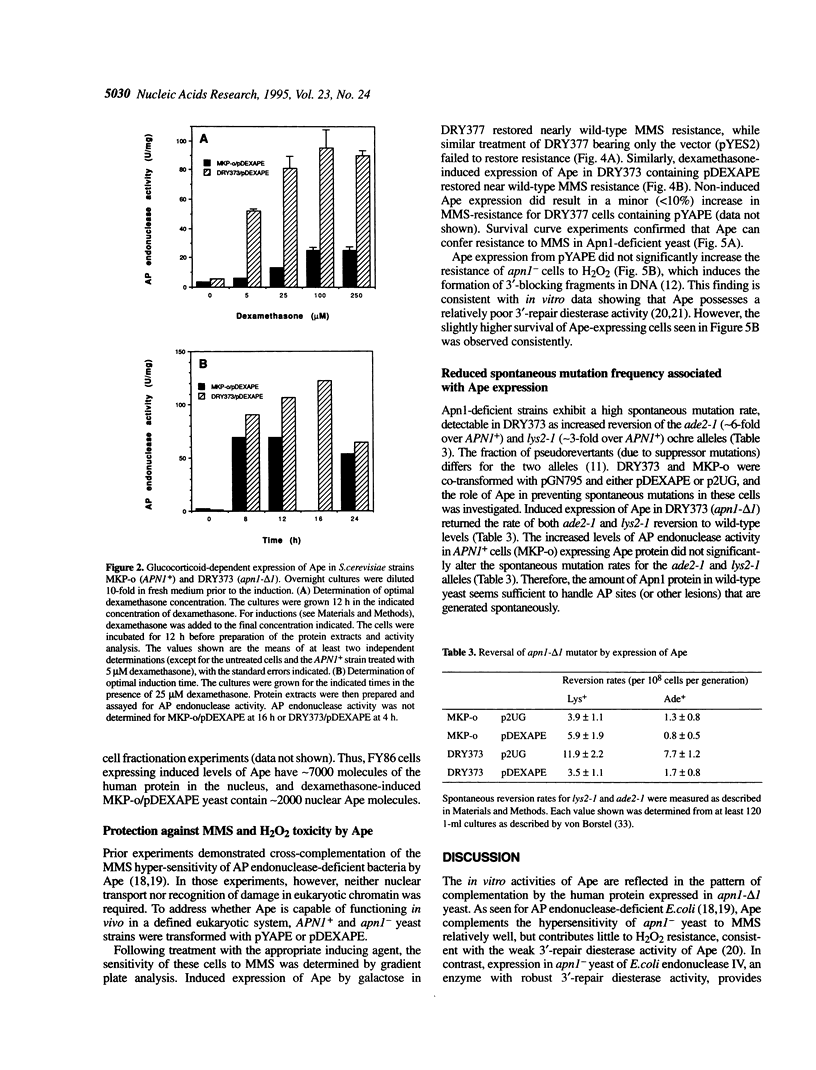
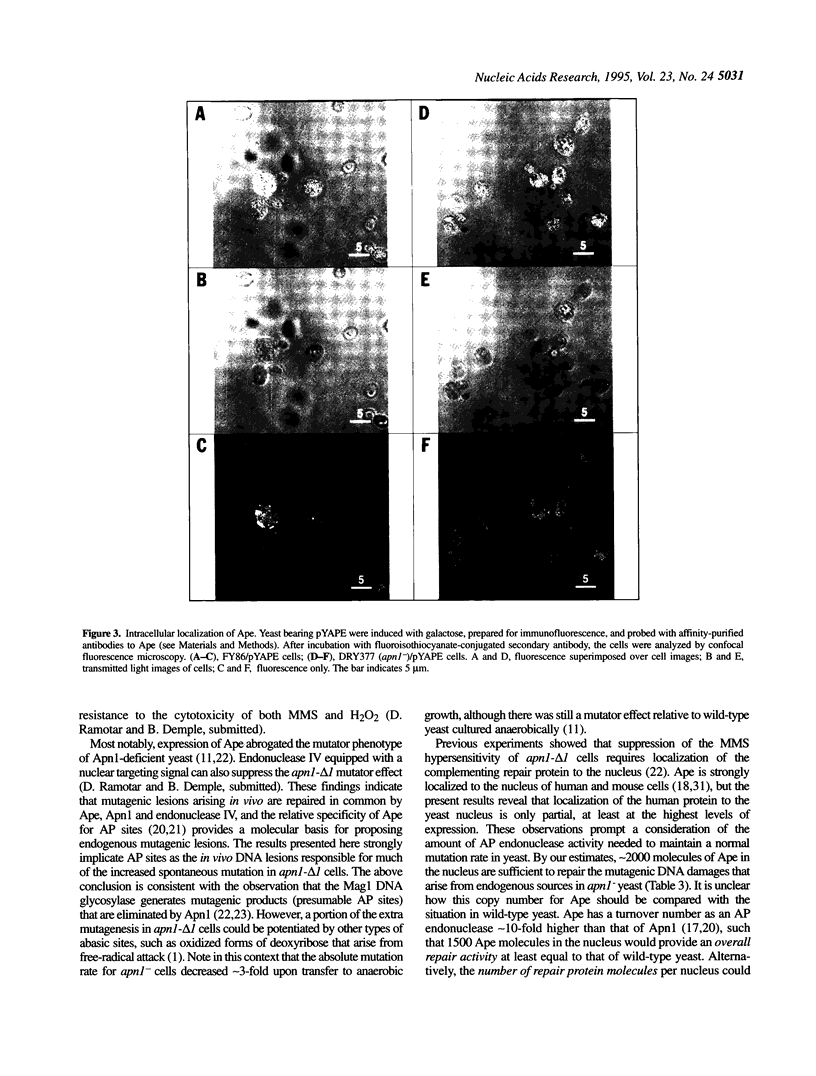


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Shigenaga M. K., Hagen T. M. Oxidants, antioxidants, and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7915–7922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. S., Herman T., Demple B. Two distinct human DNA diesterases that hydrolyze 3'-blocking deoxyribose fragments from oxidized DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5907–5914. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Saporito S. M., Spitzer S. G., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV (nfo) mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1120-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Harrison L. Repair of oxidative damage to DNA: enzymology and biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:915–948. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Herman T., Chen D. S. Cloning and expression of APE, the cDNA encoding the major human apurinic endonuclease: definition of a family of DNA repair enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11450–11454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Johnson A., Fung D. Exonuclease III and endonuclease IV remove 3' blocks from DNA synthesis primers in H2O2-damaged Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7731–7735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. W., Demple B. Yeast DNA 3'-repair diesterase is the major cellular apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease: substrate specificity and kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18017–18022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. W., Demple B. Yeast DNA diesterase for 3'-fragments of deoxyribose: purification and physical properties of a repair enzyme for oxidative DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18009–18016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz B. A., Henson E. S., Roche H., Ramotar D., Nunoshiba T., Demple B. Specificity of the mutator caused by deletion of the yeast structural gene (APN1) for the major apurinic endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8165–8169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Demple B. Analysis of class II (hydrolytic) and class I (beta-lyase) apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases with a synthetic DNA substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5069–5075. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Shapiro R., Demple B. Metalloenzymes in DNA repair. Escherichia coli endonuclease IV and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Apn1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22893–22898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):709–715. doi: 10.1038/362709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Heat-induced deamination of cytosine residues in deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3405–3410. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Preston B. D. Mutagenesis by apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:201–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbaugh D. W., Linn S. Further characterization of human fibroblast apurinic/apyrimidinic DNA endonucleases. The definition of two mechanistic classes of enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11743–11752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schena M., Yamamoto K. R. An inducible expression vector for both fission and budding yeast. Gene. 1990 Feb 14;86(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff S. C., Spira A. I., Johnson A. W., Demple B. Yeast structural gene (APN1) for the major apurinic endonuclease: homology to Escherichia coli endonuclease IV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4193–4197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramotar D., Kim C., Lillis R., Demple B. Intracellular localization of the Apn1 DNA repair enzyme of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nuclear transport signals and biological role. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20533–20539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramotar D., Popoff S. C., Gralla E. B., Demple B. Cellular role of yeast Apn1 apurinic endonuclease/3'-diesterase: repair of oxidative and alkylation DNA damage and control of spontaneous mutation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4537–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson C. N., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding a human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease that corrects DNA repair and mutagenesis defects in E. coli xth (exonuclease III) mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5519–5523. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saporito S. M., Smith-White B. J., Cunningham R. P. Nucleotide sequence of the xth gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4542–4547. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4542-4547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Borstel R. C. Measuring spontaneous mutation rates in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;20:1–24. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)62005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Grossman L. Phosphodiesterases involved in DNA repair. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1987;60:1–34. doi: 10.1002/9780470123065.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. M., 3rd, Takeshita M., Grollman A. P., Demple B. Incision activity of human apurinic endonuclease (Ape) at abasic site analogs in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16002–16007. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters T. A., Henner W. D., Russell P. S., McCullough A., Jorgensen T. J. Removal of 3'-phosphoglycolate from DNA strand-break damage in an oligonucleotide substrate by recombinant human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 May 25;22(10):1866–1873. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.10.1866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao W., Samson L. In vivo evidence for endogenous DNA alkylation damage as a source of spontaneous mutation in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



