Abstract
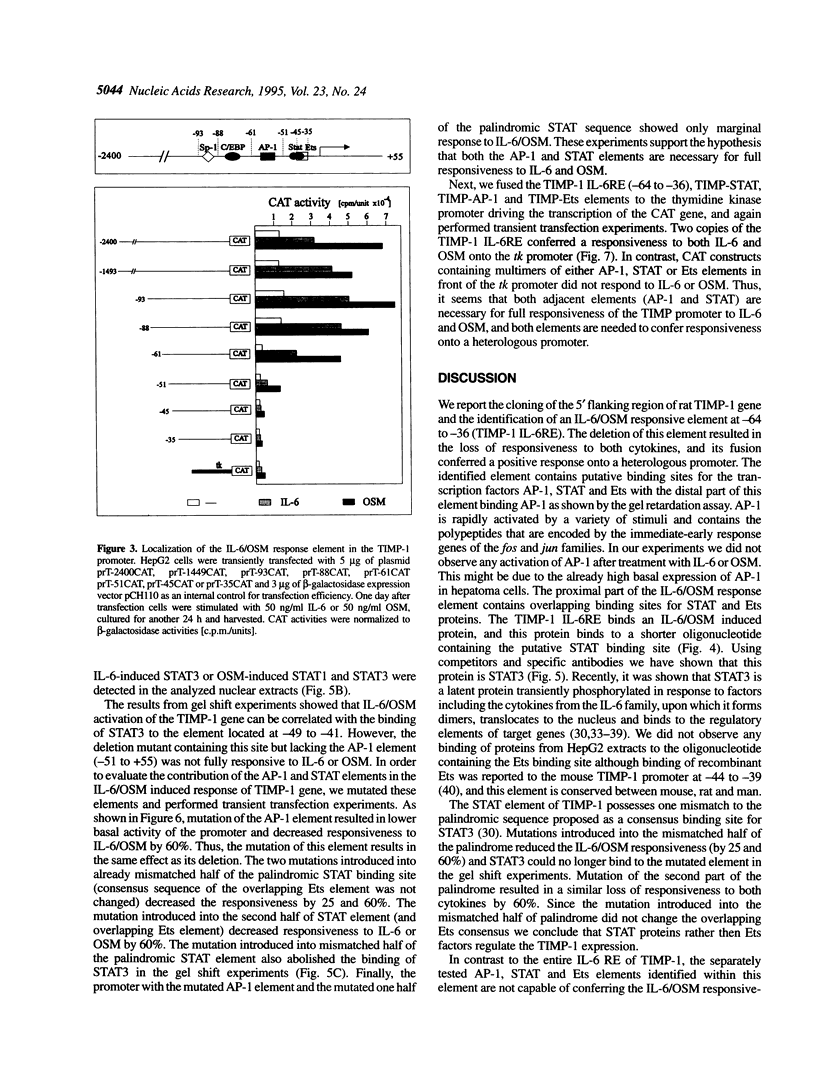
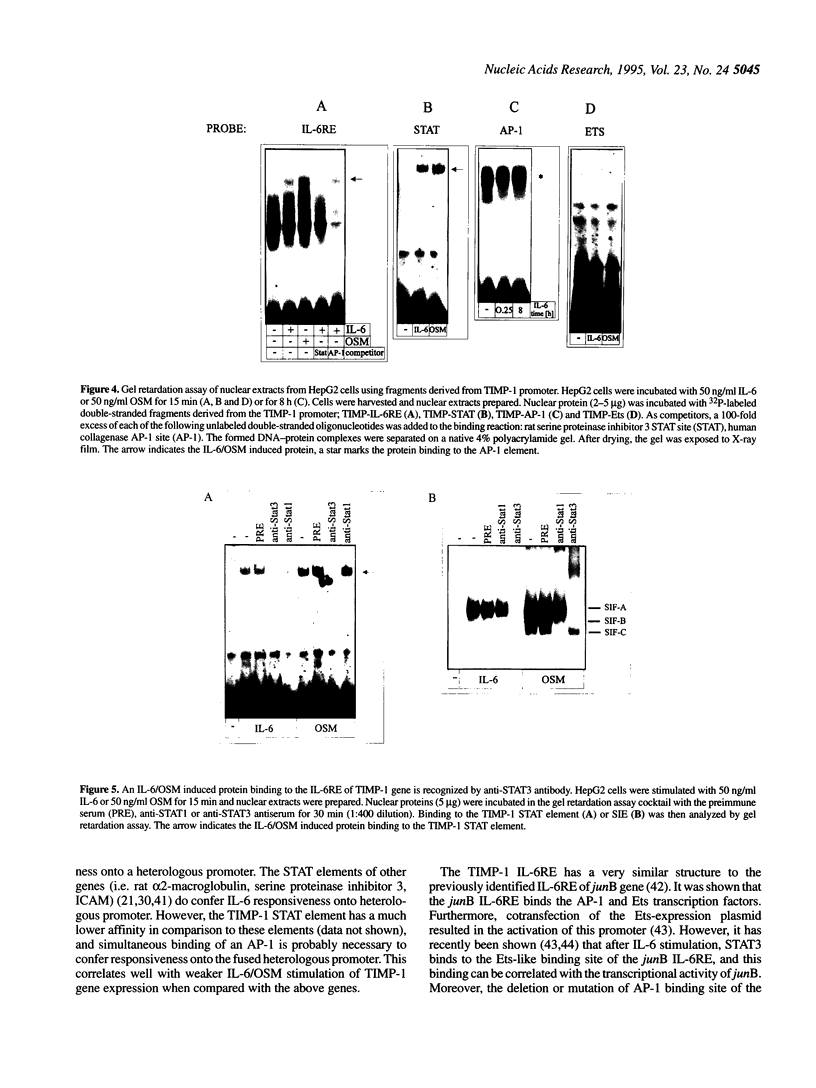
The rat tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1) gene is expressed in rat hepatocytes, and this expression is up-regulated by interleukin 6 (IL-6). We report here the cloning of the 5' flanking region of the rat TIMP-1 gene and identification of an IL-6/oncostatin M (OSM) response element at -64 to -36 which functions in hepatic cells. Within this element we have identified two functional binding sites for transcription factors AP-1 (activatory protein-1) and STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription). IL-6/OSM stimulation induces binding of a protein, identified as STAT3, to the IL-6/OSM response element, while binding of the AP-1 protein was constitutive. Binding sites for both AP-1 and STAT3 are necessary for full responsiveness of the TIMP-1 promoter to IL-6/OSM, as shown by deletion and mutation analysis. Furthermore, the entire IL-6/OSM response element conferred responsiveness onto a heterologous promoter, whereas this has not been observed when AP-1 and STAT elements were separately tested.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Nishio Y., Inoue M., Wang X. J., Wei S., Matsusaka T., Yoshida K., Sudo T., Naruto M., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. The acute phase response. Immunol Today. 1994 Feb;15(2):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Sommer A., Thompson R. C., Anderson D. C., Smith C. G., Welgus H. G., Stricklin G. P. Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffer P., Lutticken C., van Puijenbroek A., Klop-de Jonge M., Horn F., Kruijer W. Transcriptional regulation of the junB promoter: analysis of STAT-mediated signal transduction. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 2;10(5):985–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Whitham S. E., Docherty A. J., Angel P., Heath J. K. Transforming growth factor beta modulates the expression of collagenase and metalloproteinase inhibitor. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1899–1904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Rocheleau H., Sharma R. R., Wills A. J., Cowie A., Hassell J. A., Heath J. K. Involvement of AP1 and PEA3 binding sites in the regulation of murine tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) transcription. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Nov 15;1171(1):41–55. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90138-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Waterhouse P., Holman M. L., Denhardt D. T. A growth-responsive gene (16C8) in normal mouse fibroblasts homologous to a human collagenase inhibitor with erythroid-potentiating activity: evidence for inducible and constitutive transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8863–8878. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujitani Y., Nakajima K., Kojima H., Nakae K., Takeda T., Hirano T. Transcriptional activation of the IL-6 response element in the junB promoter is mediated by multiple Stat family proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 29;202(2):1181–1187. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordula T., Güttgemann I., Rose-John S., Roeb E., Osthues A., Tschesche H., Koj A., Heinrich P. C., Graeve L. Synthesis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in human hepatoma cells (HepG2). Up-regulation by interleukin-6 and transforming growth factor beta 1. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 23;313(2):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81431-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordula T., Travis J. Activation of the rat serine proteinase inhibitor 3 gene by interferon gamma via the interleukin 6-responsive element. Biochem J. 1995 Jul 1;309(Pt 1):63–67. doi: 10.1042/bj3090063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Coffer P., Yuan J., Schwartz C., Caldenhoven E., Schindler C., Kruijer W., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Interleukin-6-induced serine phosphorylation of transcription factor APRF: evidence for a role in interleukin-6 target gene induction. FEBS Lett. 1995 Feb 27;360(2):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00076-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Wegenka U. M., Yuan J., Buschmann J., Schindler C., Ziemiecki A., Harpur A. G., Wilks A. F., Yasukawa K., Taga T. Association of transcription factor APRF and protein kinase Jak1 with the interleukin-6 signal transducer gp130. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8272872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNaul K. L., Chartrain N., Lark M., Tocci M. J., Hutchinson N. I. Discoordinate expression of stromelysin, collagenase, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in rheumatoid human synovial fibroblasts. Synergistic effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on stromelysin expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17238–17245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Werb Z. Biosynthesis of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases by human fibroblasts in culture. Stimulation by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate and interleukin 1 in parallel with collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3079–3083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Kusafuka T., Takeda T., Fujitani Y., Nakae K., Hirano T. Identification of a novel interleukin-6 response element containing an Ets-binding site and a CRE-like site in the junB promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3027–3041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeb E., Graeve L., Hoffmann R., Decker K., Edwards D. R., Heinrich P. C. Regulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 gene expression by cytokines and dexamethasone in rat hepatocyte primary cultures. Hepatology. 1993 Dec;18(6):1437–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose-John S., Dietrich A., Marks F. Molecular cloning of mouse protein kinase C (PKC) cDNA from Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., DARNELL J. E. Sedimentation characteristics of rapidly labelled RNA from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Gilman M. Z. A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1739–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.8397445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Ito A., Mori Y. Interleukin 6 enhances the production of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) but not that of matrix metalloproteinases by human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):824–829. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer T. S., Sanders L. K., Nathans D. Cooperative transcriptional activity of Jun and Stat3 beta, a short form of Stat3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9097–9101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Boulton T. G., Farruggella T., Ip N. Y., Davis S., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Barbieri G., Pellegrini S. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8272873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Onisto M., Levy A. T., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) mRNA expression in tumor cell lines and human tumor tissues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13933–13938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. T., Hawkes S. P. Role of the 21-kDa protein TIMP-3 in oncogenic transformation of cultured chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10676–10680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Decker T., Schindler C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The signalling pathways of interleukin-6 and gamma interferon converge by the activation of different transcription factors which bind to common responsive DNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1657–1668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Blenis J., Li H. C., Schindler C., Chen-Kiang S. Requirement of serine phosphorylation for formation of STAT-promoter complexes. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):1990–1994. doi: 10.1126/science.7701321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3 and Stat4: members of the family of signal transducers and activators of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4806–4810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]