Abstract
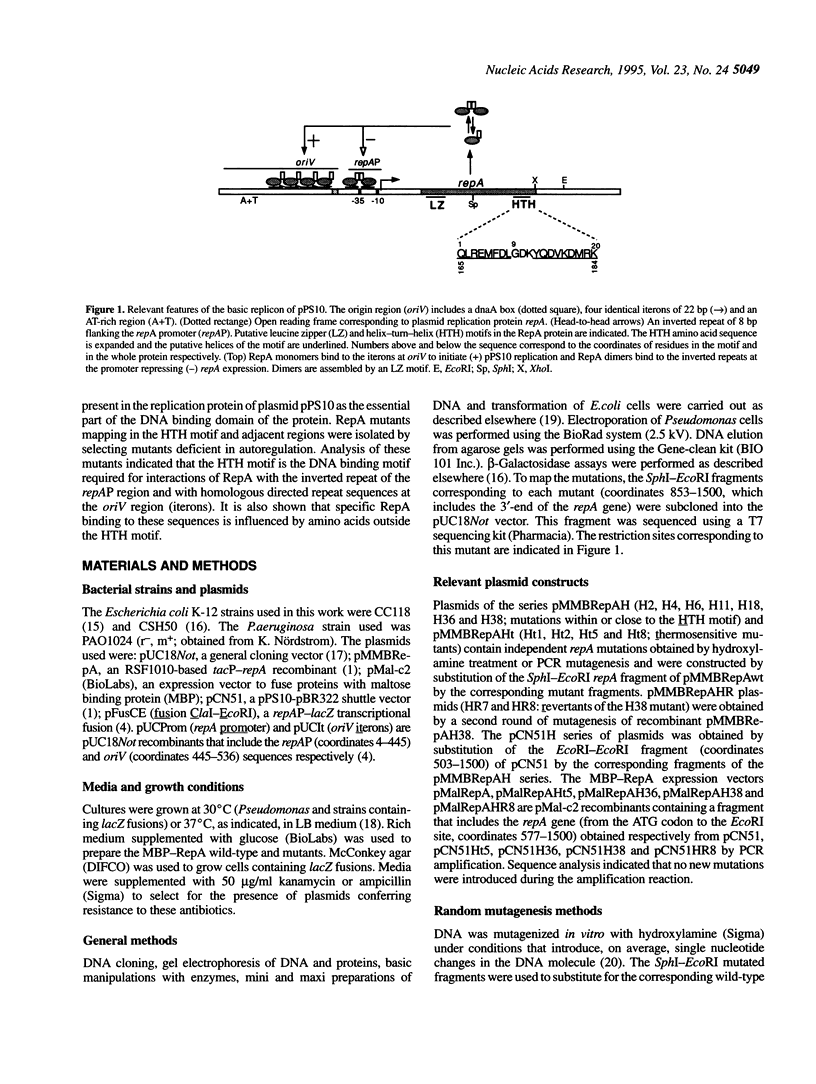
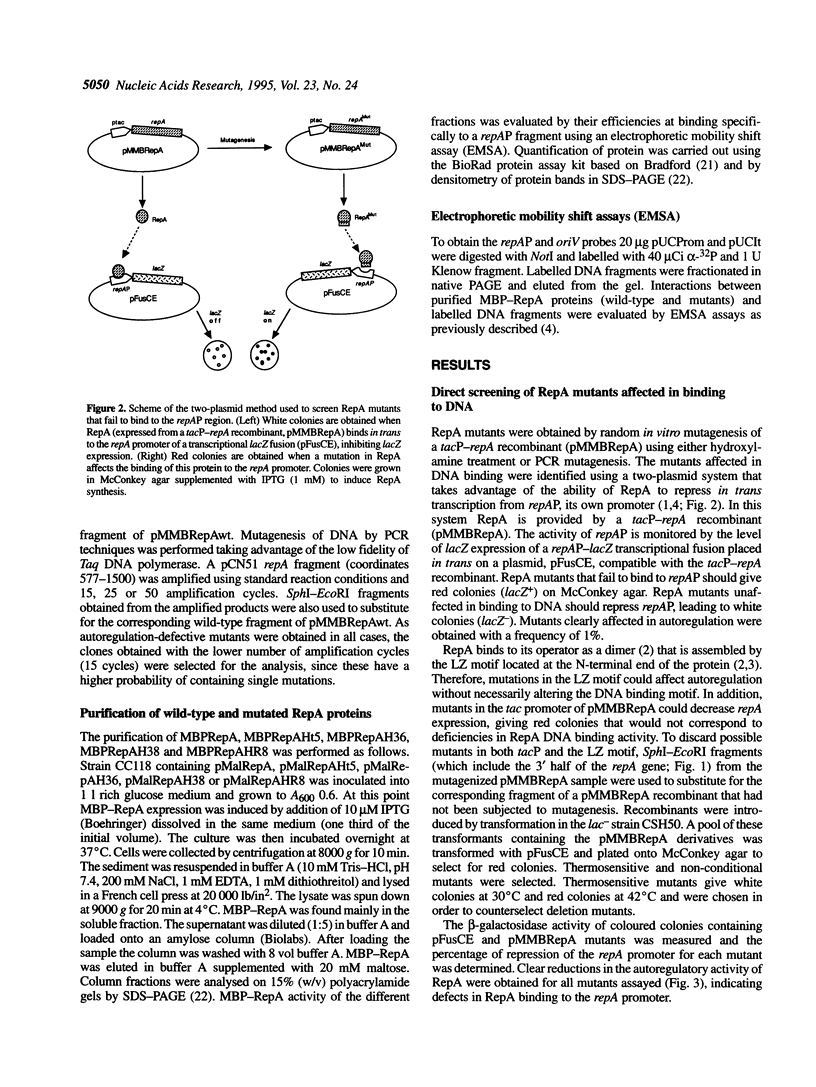
The initiator protein of the plasmid pPS10, RepA, has a putative helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif at its C-terminal end. RepA dimers bind to an inverted repeat at the repA promoter (repAP) to autoregulate RepA synthesis. [D. García de Viedma, et al. (1996) EMBO J. in press]. RepA monomers bind to four direct repeats at the origin of replication (oriV) to initiate pPS10 replication This report shows that randomly generated mutations in RepA, associated with defficiencies in autoregulation, map either at the putative HTH motif or in its vicinity. These mutant proteins do not promote pPS10 replication and are severely affected in binding to both the repAP and oriV regions in vitro. Revertants of a mutant that map in the vicinity of the HTH motif have been obtained and correspond to a second amino acid substitution far upstream of the motif. However, reversion of mutants that map in the helices of the motif occurs less frequently, at least by an order of magnitude. All these data indicate that the helices of the HTH motif play an essential role in specific RepA-DNA interactions, although additional regions also seem to be involved in DNA binding activity. Some mutations have slightly different effects in replication and autoregulation, suggesting that the role of the HTH motif in the interaction of RepA dimers or monomers with their respective DNA targets (IR or DR) is not the same.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A. K., Rodgers D. W., Drottar M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):899–907. doi: 10.1126/science.3187531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Matthews B. W. The helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1903–1906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G. The winged-helix DNA-binding motif: another helix-turn-helix takeoff. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):773–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. Gel retardation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:103–117. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08010-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghino J. L., Helinski D. R. Essentiality of the three carboxyl-terminal amino acids of the plasmid RK2 replication initiation protein TrfA for DNA binding and replication activity in gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24926–24932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghino J. L., Helinski D. R., Toukdarian A. E. Isolation and characterization of DNA-binding mutants of a plasmid replication initiation protein utilizing an in vivo binding assay. Plasmid. 1994 Jan;31(1):89–99. doi: 10.1006/plas.1994.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Lane A. N., Sanderson M. R. Structural aspects of protein-DNA recognition. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):1–23. doi: 10.1042/bj2780001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García de Viedma D., Giraldo R., Ruiz-Echevarría M. J., Lurz R., Díaz-Orejas R. Transcription of repA, the gene of the initiation protein of the Pseudomonas plasmid pPS10, is autoregulated by interactions of the RepA protein at a symmetrical operator. J Mol Biol. 1995 Mar 24;247(2):211–223. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Rapid purification of a cloned gene product by genetic fusion and site-specific proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4692–4696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo R., Nieto C., Fernandez-Tresguerres M. E., Diaz R. Bacterial zipper. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):866–866. doi: 10.1038/342866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greener A., Filutowicz M. S., McEachern M. J., Helinski D. R. N-terminal truncated forms of the bifunctional pi initiation protein express negative activity on plasmid R6K replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):24–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00259447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Sekiguchi M. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of R plasmid by in vitro mutagenesis with hydroxylamine. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1561–1563. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1561-1563.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero M., de Lorenzo V., Timmis K. N. Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6557–6567. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6557-6567.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J., Drummond M. Construction of chimeric proteins from the sigma N-associated transcriptional activators VnfA and AnfA of Azotobacter vinelandii shows that the determinants of promoter specificity lie outside the 'recognition' helix of the HTH motif in the C-terminal domain. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(4):813–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen D., Upegui-Gonzalez L. C., Caro L. Monomers and dimers of the RepA protein in plasmid pSC101 replication: domains in RepA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8923–8927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson L., Ray D. S. Mechanism of autonomous control of the Escherichia coli F plasmid: purification and characterization of the repE gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):413–424. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga F., Kawasaki Y., Ishiai M., Nishikawa K., Yura T., Wada C. DNA-binding domain of the RepE initiator protein of mini-F plasmid: involvement of the carboxyl-terminal region. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(8):1994–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.8.1994-2001.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto C., Giraldo R., Fernández-Tresguerres E., Díaz R. Genetic and functional analysis of the basic replicon of pPS10, a plasmid specific for Pseudomonas isolated from Pseudomonas syringae patovar savastanoi. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 20;223(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90661-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdier D. G., Porcella A., Costa R. H. The DNA-binding specificity of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead domain is influenced by amino-acid residues adjacent to the recognition helix. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2755–2766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]