Abstract
A first glimpse into the proteome of Rhodobacter capsulatus revealed more than 450 [with over 210 cytoplasmic and 185 extracytoplasmic known as well as 55 unknown] proteins that are identified with high degree of confidence using nLC-MS/MS analyses. The accumulated data provide a solid platform for ongoing efforts to establish the proteome of this species and the cellular locations of its constituents. They also indicate that, at least 40 of the identified proteins, which were annotated in genome databases as unknown hypothetical proteins, correspond to predicted translation products that are indeed present in cells under the growth conditions used in this work. In addition, matching the identification labels of the proteins reported between the two available R. capsulatus genome databases (ERGO-light with RRCxxxxx and NT05 with NT05RCxxxx numbers) indicated that eleven such proteins are listed only in the latter database.
Introduction
The Gram negative, purple non-sulfur facultative phototrophic bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus is a model organism that is intensely studied for various aspects of major metabolic pathways such as photosynthesis and respiration (Zannoni 1995; Hunter, Daldal et al. 2009). Using this species, which exhibits highly versatile growth modes including anoxygenic light (i. e., photosynthesis), anoxygenic dark (i. e. anaerobic respiration) and oxygenic (i. e., light independent aerobic respiration) metabolisms, physiologically relevant cellular responses to the availability of light or oxygen can be examined at the molecular level (Hunter, Daldal et al. 2009). Indeed, a complete definition of the presence, regulation and biogenesis of various cellular components in response to the changing environmental conditions greatly benefits from global analyses approaches, including transcriptomic and proteomic studies (Park et al. 2005; Wasinger 2006). Thus, along with the transcriptional studies, availability of qualitative and quantitative description of R. capsulatus proteomes under defined growth conditions is extremely invaluable. Towards this end, we have initiated an effort to define the complete proteome of this species (Onder et al. 2008), and we present here a first glimpse to this developing protein identification dataset.
Materials and Methods
Wild type R. capsulatus strain MT1131 was grown under respiratory growth condition in enriched MPYE (mineral-peptone-yeast extracts) medium (Daldal, Chen et al. 1986), under standard culture conditions (1 L medium in 2 L flask, shaken at approximately 150 rpm at 35°C in dark for approximately 36 hrs) (Myllykallio, Jenney et al. 1997). Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4°C (5000 × g, 20 min), washed with ice cold 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, and gently resuspended in cold extraction buffer consisting of 1 mg/ml of polymyxin B sulfate, 20 mM Tris-HCl, 250 mM NaCl, [pH 8.0] (5 ml/g of wet cells) (Ren and Thony-Meyer 2001; Onder, Turkarslan et al. 2008). The suspension was gently stirred for 1 hour at 4 °C and centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was carefully transferred into a clean tube, re-centrifuged at 150,000 × g for 2 hours at 4 °C and saved as the periplasmic fractions at −20 °C. Polymyxin treated cells pellets were then resuspended in 50 mM MOPS, 100 mM KCl (pH 8.0) buffer and processed using a French pressure cell, as described earlier (Onder, Turkarslan et al. 2008). After centrifugation for 2 hrs at 45,000 rpm, supernatants (i. e., cytoplasmic fractions) and pellets (i. e., membrane fractions) were processed separately for analyses of their protein contents.
Soluble or periplasmic proteins were precipitated with trichloroacetic (TCA)/acetone (20% w/v), washed twice with ice-cold acetone to remove residual TCA, and dried under vacuum. Pellets were resuspended in two dimensional-gel electrophoresis (2D-GE) sample solubilization buffer (SSB: 8 M urea, 4% CHAPS, 40 mM Tris, 0.2% Bio-Lyte-pH 3–10, 65 mM DTT) at room temperature until complete solubilization. For 2D-GE, samples containing 300 μg of solubilized proteins were applied to an 18 cm, pH 4–7 immobilized pH gradient (IPG) strips (Bio-Rad), and following a 12 hours passive rehydration, isoelectrofocusing (IEF) was carried out by using PROTEAN IEF Cell (Bio-Rad) at 20 °C at a maximum of 7000 V for 15–18 hours, and the strips thus prepared were kept frozen at −20 °C until use. For the second dimension sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), IPG strips were reduced with 1% w/v dithiothreitol (DTT) and alkylated with 2.5% w/v iodoacetamide at room temperature, both prepared in equilibration buffer consisting of 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.8, 6 M urea, 30% v/v glycerol, 2% SDS and 0.02% bromophenol blue. After equilibration, the IPG strips were layered on top of the second dimension resolving gel slabs and overlaid with a solution of molten 0.5% agarose in SDS electrophoresis buffer. The second dimension Laemmli-type SDS-PAGE was carried out using 11% gels without any stacking at 40 mA per gel in a Protean II XL cell (Bio-Rad), and gels were stained with colloidal coomassie brillant blue (Neuhoff, Stamm et al. 1990). Spots or bands were manually excised from gels and subjected to in-gel trypsin digestions (Onder, Yoon et al. 2006). Tryptic peptide extracts were analyzed using a nanoLC-MS/MS set up (LCQ Deca XP Plus mass spectrometer from Thermo Scientific, coupled to an Ultimate Nano liquid chromatography system from DIONEX). Tryptic peptide mixtures were first loaded onto a μ-precolumn (C18, 5 μm, 100 Å, 300 μm i.d. × 5 mm) (DIONEX), and washed for 4 min at a flow rate of 0.25 μl/min with the LC buffer A, then transferred onto an analytical C18-nanocapillary HPLC column (DIONEX, Acclaim PepMap100, C18 column (75 μm i.d. by 150 mm) with a 3 μm particle size and a 100 Å pore diameter for fractionation. A fused silica tip with 8-μm aperture (New Objective, Woburn, MA) was used for nanospray ionization of peptides eluting from the column. Mass spectra were analyzed using the DTA generation and SEQUEST search algorithms within Bioworks 3.3 software (Thermo Scientific) and R. capsulatus protein databases (ERGO Light from http://www.ergo-light.com or in-house available NT05 data bases). The following parameters were used for SEQUEST analyses: as appropriate trypsin or GluC were selected as the proteolytic enzymes, with trypsin cleavage only after arginine and lysine was allowed, and the number of maximal internal (missed) cleavage sites was set to 2–4. Mass tolerance for precursor and fragment ions was 2.0–2.5 and 1.0, respectively. Methionine oxidation and cysteine carbamidomethylation were set as variable modification with maximum modification set to 2, and default setting was used for all other variables. Matching peptides were filtered according to correlation scores (XCorr at least 1.5, 2.0 and 2.5 for +1, +2 and +3 charged peptides, respectively, and ΔCN > 0.1) to give high confidence of protein identification, and proteins were considered as significant only when at least two peptides were identified with the SEQUEST filter settings mentioned above. The R. capsulatus proteins thus identified were examined with bioinformatic tools. Prediction softwares SignalP (version 3.0) (Bendtsen, Nielsen et al. 2004) (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) and PSORTb (version 2.0) (Gardy, Laird et al. 2005) (http://www.psort.org/psortb/) were used to predict the likely sub-cellular localization of identified proteins.
Results and Discussion
A long-term objective of this study is the establishment of a comprehensive proteomic reference database for R. capsulatus under different growth conditions. This physiological proteomics will then establish an important step to enable detailed analyses of major metabolic pathways of this organism extending from photosynthesis to respiration. To this end, we use modern proteomic approaches involving 1D- and 2D-GE combined with liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry techniques. In addition, as comprehensive proteome analyses are often limited by physiological constraints and technical issues, to maximize the number of proteins identified, to reduce the sample complexity and also to detect low abundance proteins, we prepare overlapping subproteomes of periplasmic, cytoplasmic and membrane fractions of R. capsulatus cells grown under different conditions, and analyze these samples as described in Materials and Methods. These analyzes identified so far more than over 450 R. capsulatus proteins that are grouped into different cellular function categories listed in Table 1. Tentative sub-cellular localizations of these proteins are also indicated using the PSORTb v 2.0 prediction software trained on bacterial protein sub-cellular localization prediction (Gardy, Laird et al. 2005). Of these proteins, 218 are predicted to be cytoplasmic and 187 are assigned to be exported proteins. Among the latter extracytoplasmic proteins, 52 and 94 of them are considered to be periplasmic and integral membrane proteins, respectively. Clearly, the predictive analysis is highly successful as for only 53 out of the 450 identified proteins a cellular localization could not be attributed reliably using PSORTb program. Moreover, global distributions of the identified proteins into different cellular function categories are also analyzed, and the results are presented as a pie chart. Even though the available data set is not yet exhaustive, it appears that “Energy Metabolism” and “Transport and Binding Proteins” categories are among the most populated groups of proteins with 82 and 79 members, respectively. Remarkably, while a large fraction of the identified proteins correspond to proteins of known functions, yet 49 of them have undefined roles, and among the latter group 41 of them were initially annotated as hypothetical proteins in either or both (ERGO-light with RRCxxxxx and NT05 with NT05RCxxxx numbers) of R. capsulatus genome databases (Table 1). Our data establish that these translation products are indeed real, and searches for defining their functions can now be initiated on firm grounds. We believe that data set that is under construction is of great value for rapid progress of current and future studies focused on Rhodobacter species (Du et al. 2008). This ever-growing data set is providing a platform onto which we can build future qualitative and quantitative comparisons for various cellular components under defined physiological conditions. A current example to the point is illustrated by one of our recent studies where a portion of our accumulated proteomics data of R. capsulatus, once combined with standard in-depth biochemical and molecular genetic approaches, yielded exquisite understanding in detailed molecular terms of an unusual physiological situation simply detected by a growth phenotype (Onder, Turkarslan et al. 2008). We believe that establishment of a comprehensive proteomic data for R. capsulatus species, like in many other cases, will be invaluable to provide much needed impetus for understanding the global biology of this organism with a “systems” level organization.
Table I.
Complete list of R. capsulatus proteins identified by nLC-MS/MS analyses. Identified proteins are categorized according to their predominant function as reported in the current literature (ref). Protein names, enzyme commission (EC) numbers, gene acronyms, ERGO-light (RRCxxxxx) and NT05 (NT05RCxxxx) identification numbers are indicated. Sub-cellular localization of each protein was predicted by PSORTb and SignalP analyses, and C, EC, P, IM, OM and M were used to designate cytoplasmic, extracytoplasmic, periplasmic, inner membrane, outer membrane and membrane proteins, respectively.
| Protein Name | EC Number | Gene Name | ERGO* | NT05* | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
AMINO ACID BIOSYNTHESIS | |||||
|
Aromatic amino acid family | |||||
| Ornithine cyclodeaminase, Ocd | 4.3.1.12 | arcB | RRC00632 | NT05RC2206 | C |
| Tryptophan synthase beta subunit, TrpB | 4.2.1.20 | trpB | RRC01000 | NT05RC2658 | C |
| Tryptophan synthase alpha subunit, TrpA | 4.2.1.20 | trpA | RRC00192 | NT05RC3179 | C |
| Aromatic-aminoacid aminotransferase, Arat (aroat) | 2.6.1.57 | tyrB | RRC01763 | NT05RC3527 | C |
|
Aspartate family | |||||
| Dihydrodipicolinate synthase | 4.2.1.52 | dapA | RRC02939 | NT05RC0396 | C |
| Aspartokinase (Aspartate kinase) | 2.7.2.4 | lysC | RRC02984 | NT05RC0439 | C |
| 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase | 1.5.1.20 | metF | RRC03981 | NT05RC0510 | C |
| 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate homocysteine methyltransferase/Methionine synthase I | 2.1.1.13 | metH | RRC01233 | NT05RC2273 | C |
| Threonine synthase, ThrC | 4.2.99.2 | thrC | RRC00242 | NT05RC3231 | C |
|
Glutamate family | |||||
| Glutamate synthase NADPH large chain, NADPH-Gogat | 1.4.1.13 | gltA | RRC04596 | NT05RC0170 | C |
| Glutamate synthase NADPH small chain, NADPH-Gogat | 1.4.1.13 | gltD | RRC03219 | NT05RC0172 | C |
| Argininosuccinate synthase | 6.3.4.5 | argG | RRC03172 | NT05RC0219 | C |
| Glutamate N-acetyl transferase/Arginine biosynthesis bifunctional protein, ArgJ | 2.3.1.35/2.3.1.1 | argJ | RRC04654 | NT05RC0229 | C |
| N-acetyl-gamma-glutamyl-phosphate reductase, ArgC | 1.2.1.38 | argC | RRC03917 | NT05RC0575 | C |
| Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase | 1.5.1.2 | proC | RRC04153 | NT05RC1196 | C |
| Glutamine synthetase, GlnA | 6.3.1.2 | glnA | RRC03526 | NT05RC1748 | C |
| Acetyltransferase/gnat family | 2.3.1.- | RRC01355 | NT05RC2400 | ||
|
Histidine family | |||||
| Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase, cyclase subunit, HisF | 4.1.3.- | hisF | RRC04158 | NT05RC1201 | C |
| Phosphoribosylformimino-5-aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide isomerase | 5.3.1.16 | hisA | RRC04159 | NT05RC1202 | C |
| Imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase, glutamine amidotransferase subunit, HisH | 2.4.2.- | hisH | RRC04493 | NT05RC1232 | C |
| Histidinol dehydrogenase, HisD | 1.1.1.23 | hisD | RRC01022 | NT05RC2681 | C |
|
Pyruvate family | |||||
| 3-Isopropylmalate dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.85 | leuB | RRC03293 | NT05RC0087 | C |
| Ketol-acid reductoisomerase/2-Dehydropantoate 2-reductase | 1.1.1.86 | ilvC | RRC02733 | NT05RC1266 | C |
|
Serine family | |||||
| Cysteine synthase A, CysK | 2.5.1.47 | cysK | RRC00998 | NT05RC2657 | |
| O-acetylhomoserine thiol-lyase (O-acetylhomoserinesulfhydrylase)/Homocysteine synthase | 2.5.1.49/4.2.99.8 | metY | RRC00762 | NT05RC2915 | C |
| Cysteine synthase (O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase)/O-acetylserine thiol-lyase, CSase | 2.5.1.47/4.2.99.8 | RRC00087 | NT05RC3089 | ||
| Phosphoserine aminotransferase | 2.6.1.52 | serC | RRC05753 | NT05RC3593 | CM |
|
BIOSYNTHESIS OF COFACTORS, PROSTHETIC GROUPS, AND CARRIERS | |||||
|
Chlorophyll and bacteriochlorphyll | |||||
| Light-independent protochlorophyllide reductase, iron-sulfur ATP-binding protein | 1.18.-.- | bchL | RRC02850 | NT05RC0691 | C |
| Bacteriochlorophyll synthase 33 kDa chain/Geranylgeranylbacteriochlorophyllide synthase | 2.5.1.- | bchG | RRC02841 | NT05RC0700 | CM |
| Bacteriochlorophyll-geranylgeranyl reductase | 1.3.1.- | bchP | RRC02839 | NT05RC0702 | CM |
| Magnesium chelatase ATPase subunit I | 6.6.1.1 | bchI | RRC02835 | NT05RC0706 | C |
| 2-Desacetyl-2-hydroxyethyl bacteriochlorophyllide A dehydrogenase, BchC | 1.-.-.- | bchC | RRC02826 | NT05RC0715 | CM |
| Chlorophyllide reductase 35 kDa protein, BchA(XYZ) | 1.18.-.- | bchA | RRC02825 | NT05RC0716 | C |
|
Folic acid | |||||
| MoxR-like ATPase/AAA_3 ATPase | RRC04552 | NT05RC0619 | C | ||
| 5-methyltetrahydrofolate corrinoid iron sulfur protein methyltransferase/Dihydropteroate synthase, Dhps | 1.2.99.2 | acsE | RRC03586 | NT05RC1686 | C |
| Para-aminobenzoate synthetase component I, PabB | 4.1.3.-/6.3.5.8 | pabB | RRC01115 | NT05RC2770 | C |
| Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+)/Methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase/Bifunctional protein, FolD | 1.5.1.5/3.5.4.9 | folD | RRC00338 | NT05RC3327 | C |
|
Glutathione and analogs | |||||
| Glutathione synthetase | 6.3.2.3 | gshB | RRC04009 | NT05RC0483 | C |
|
Heme, porphyrin, and cobalamin | |||||
| Ferrochelatase | 4.99.1.1 | hemH | RRC04666 | NT05RC0206 | C |
| Cobaltochelatase subunit, CobS | 6.6.1.2 | cobS | RRC01954 | NT05RC0874 | C |
| Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase | 4.1.1.37 | hemE | RRC04134 | NT05RC1222 | CM |
| Porphobilinogen deaminase | 2.5.1.61 | hemC | RRC04136 | NT05RC1223 | C |
| 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase | 2.3.1.37 | hemA | RRC04400 | NT05RC1506 | CM |
| Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase | 4.2.1.24 | hemB | RRC06033 | NT05RC1890 | |
| Precorrin-8X methylmutase/Precorrin isomerase, HBAsynthase | 5.4.1.2 | cobH | RRC00650 | NT05RC2138 | C |
| Cobalamin biosynthesis protein, CobD | cobD | RRC00706 | NT05RC2147 | CM | |
| Nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase, CobT | 2.4.2.21 | cobT | RRC00590 | NT05RC2151 | C |
|
Menaquinone and ubiquinone | |||||
| 3-Demethylubiquinone 3-methyltransferase | 2.1.1.64 | ubiG | RRC03170 | NT05RC0221 | C |
| Ubiquinone biosynthesis protein AARF/2-Polyprenylphenol 6-hydroxylase | ubiB | RRC03386 | NT05RC3680 | CM | |
|
Pantothenate and coenzyme A | |||||
| Pantoate-beta-alanine Ligase | 6.3.2.1 | panC | RRC02990 | NT05RC0445 | C |
|
Pyridine nucleotides | |||||
| UDP-sugar diphosphatase/5′-Nucleotidase | 3.6.1.45/3.1.3.5 | ushA | RRC01089 | NT05RC2743 | P |
|
Riboflavin, FMN, and FAD | |||||
| Riboflavin biosynthesis protein, RibF | 2.7.1.26/2.7.7.2 | ribF | RRC00565 | NT05RC2178 | C |
| Riboflavin biosynthesis protein, RibAB/GTP cyclohydrolase II/3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase | 3.5.4.25/4.1.2.- | ribAB | RRC00220 | NT05RC3210 | C |
|
Thiamine | |||||
| Thiamin-phosphate pyrophosphorylase | 2.5.1.3 | thiE | RRC06023 | NT05RC1674 | C |
|
Other | |||||
| Iron-sulfur cluster assembly ATP-dependent transporter, SufC | sufC | RRC01541 | NT05RC1963 | C, CM | |
|
CELL ENVELOPE | |||||
|
Biosynthesis and degradation of murein sacculus and peptidoglycan | |||||
| Glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase | 2.7.7.24 | rfbA | RRC03209 | NT05RC0184 | C |
| dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose reductase | 1.1.1.133 | rfbD | RRC03208 | NT05RC0185 | EC |
| dTDP-glucose-4,6-dehydratase | 4.2.1.46 | rfbB | RRC03206 | NT05RC0187 | EC |
| dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose 3,5-epimerase (reductase) | 5.1.3.13 | rfbC | RRC03205 | NT05RC0188 | EC |
| Glucans biosynthesis protein, MdoG | mdoG | RRC04027 | NT05RC0391 | P | |
| Soluble lytic murein transglycosylase | 3.2.1.- | slt | RRC02941 | NT05RC0397 | P |
| Cell elongation specific D,D-transpeptidase/Peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase | 2.4.1.129 | ftsl | RRC04232 | NT05RC0836 | C, CM |
| UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide-pyrophosphoryl-undecaprenol N-acetylglucosamine transferase | 2.4.1.227 | murG | RRC04656 | NT05RC0856 | CM |
| Peptidoglycan-binding domain 1 protein | RRC02722 | NT05RC1256 | EC | ||
| D-alanyl-D-alanine serine-type carboxypeptidase | 3.4.16.4 | RRC02699 | NT05RC1306 | CM | |
| UDP-N-acetylglucosamine diphosphorylase/glucosamine-1-phosphate N-acetyltransferase, GlmU | 2.7.7.23/2.3.1.157 | glmU | RRC04347 | NT05RC1565 | C |
| Alanine racemase, Alr | 5.1.1.1 | alr | RRC03627 | NT05RC1640 | C |
| Succinoglycan biosynthesis transport protein, ExoP | 2.7.1.112 | exoP | RRC01472 | NT05RC2037 | CM |
| D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase (D-alanyl-D-alanine-endopeptidase)/Penicillin-binding protein 4, PBP-4 | dacB | RRC01098 | NT05RC2752 | C | |
| Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein/OmpA-MotB family protein | RRC04613 | NT05RC3334 | OM | ||
| Membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase B | 3.2.1.- | mltB | RRC05698 | NT05RC3538 | CM, P |
|
Other | |||||
| Competence lipoprotein/Tetratricopeptide TPR_2 repeat protein | comL | RRC01947 | NT05RC0865 | M | |
|
CELLULAR PROCESSES | |||||
|
Adaptations to atypical conditions | |||||
| Transcriptional regulator/Methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase | 1.8.4.- | msrB | RRC00410 | NT05RC3399 | EC |
|
Cell division | |||||
| Cell division ATP-binding protein, FtsE | 3.6.3.- | ftsE | RRC00317 | NT05RC3307 | CM |
|
Chemotaxis and motility | |||||
| Flagellar hook protein, FlgE | flgE | RRC00713 | NT05RC0007 | OM | |
| Flagellar hook-associated protein 1, FlgK | flgK | RRC00714 | NT05RC0008 | OM | |
| Flagellar hook-associated protein 3, FlgL | flgL | RRC00715 | NT05RC0009 | OM | |
| Flagellar biosynthetic protein, FlhA | flhA | RRC03323 | NT05RC0057 | CM | |
| Methyl-accepting chemotaxis sensory transducer | RRC04109 | NT05RC1237 | CM | ||
| Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein, McpA | mcpA | RRC01082 | NT05RC2737 | CM | |
| Flagellin protein | fliC | RRC03417 | NT05RC3674 | P | |
|
Detoxification | |||||
| Dihaem cytochrome c551 peroxidase | 1.11.1.5 | ccpA | RRC00728 | NT05RC0020 | P |
| Glutathione peroxidase | 1.11.1.9 | gpx | RRC02811 | NT05RC0730 | P |
| Phosphinothricin N-acetyltransferase/gnat family | 2.3.1.- | pat | RRC04226 | NT05RC0842 | |
| NAD-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.1 | adh | RRC04460 | NT05RC1433 | C |
| Catalase/peroxidase, HPI | 1.11.1.6/1.11.1.7 | katG | RRC03460 | NT05RC1815 | |
| Beta-lactamase/hypothetical protein | 3.5.2.6 | RRC00641 | NT05RC2200 | CM | |
| Beta-lactamase family protein/putative beta-lactamase | 3.5.2.6 | bla | RRC00550 | NT05RC2365 | P |
| Superoxide dismutase (Fe) | 1.15.1.1 | sodB | RRC01365 | NT05RC2413 | |
| Toluene tolerance protein, Ttg2D | ttg2D | RRC01770 | NT05RC3534 | ||
| Peroxiredoxin, AhpC/Glutaredoxin domain protein | 1.11.1.15 | ahpC | RRC05718 | NT05RC3559 | |
|
Pathogenesis | |||||
| Virulence-associated protein E | RRC00816 | NT05RC2862 | |||
| Iron-regulated protein frpC/Rhizobiocin, RzcA | frpC/rzcA | RRC00341 | NT05RC3330 | EC | |
|
Toxin production and resistance | |||||
| Bicyclomycin resistance protein/Drug resistance transporter, Bcr | RRC02414 | NT05RC1893 | M | ||
| Iron-regulated protein, FrpC/Bifunctional hemolysin-adenylate cyclase (cyclolysin), AC-HLY | frpC | RRC01135 | NT05RC2792 | EC | |
|
CENTRAL INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM | |||||
|
Amino sugars | |||||
| N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase | 3.5.1.25 | nagA | RRC05751 | NT05RC3592 | |
|
Nitrogen fixation | |||||
| Nitrogenase Iron Protein | 1.18.6.1 | nifH | RRC03785 | NT05RC0610 | C |
| Iron-sulfur cluster assembly NifU domain protein | 1.18.6.1 | nifU | RRC00380 | NT05RC3369 | C |
| Nitrogenase cofactor biosynthesis protein, NifB | 1.18.6.1 | nifB | RRC03905 | NT05RC3406 | C |
| Nitrogenase MoFe cofactor biosynthesis protein, NifE | 1.18.6.1 | nifE | RRC00431 | NT05RC3420 | C |
|
Nitrogen metabolism | |||||
| Nitrogen regulatory protein P-II | glnB | RRC03527 | NT05RC1747 | C | |
|
Polyamine biosynthesis | |||||
| Agmatinase | 3.5.3.11 | speB | RRC03474 | NT05RC1799 | C |
| Arginase, RocF | 3.5.3.1 | rocF | RRC00631 | NT05RC2207 | C |
|
One-carbon metabolism | |||||
| Trimethylamine methyltransferase family protein, MttB | mttB | RRC02448 | NT05RC1856 | CM | |
| 2-Hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate hydrolase or acyltransferase | 3.7.1.- | bphD | RRC01136 | NT05RC2793 | C |
|
Phosphorus compounds | |||||
| Bacterial phosphonate metabolism protein, PhnI | phnI | RRC04121 | NT05RC1247 | C | |
|
Sulfur metabolism | |||||
| Nitrilotriacetate monooxygenase component B | 1.14.13.- | ntaB | RRC00711 | NT05RC0005 | C |
| 3′(2′),5′-bisphosphate nucleotidase | 3.1.3.7 | cysQ | RRC05208 | NT05RC0131 | C, CM |
|
Other | |||||
| Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [NADP+], Ssdh | 1.2.1.16 | gabD | RRC02976 | NT05RC0431 | C |
| Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase alpha subunit | 5.4.99.2 | mutB | RRC02025 | NT05RC0954 | |
| S-adenosylmethionine synthetase | 2.5.1.6 | metK | RRC01795 | NT05RC1167 | C |
| Gamma-aminobutyrate aminotransferase/Aminotransferase class-III | 2.6.1.19/2.6.1.18 | RRC01241 | NT05RC2282 | C | |
| Exopolyphosphatase/Pyrophosphate phosphohydrolase family II | 3.6.1.11 | ppx | RRC00932 | NT05RC2590 | C |
| Acetate-CoA ligase, AcsA | 6.2.1.1 | acsA | RRC01093 | NT05RC2746 | CM |
|
DNA METABOLISM | |||||
|
DNA replication, recombination, and repair | |||||
| DNA Polymerase III beta chain | 2.7.7.7 | dnaN | RRC00708 | NT05RC0002 | C |
| ATP-dependent DNA helicase II, PcrA | 3.6.1.- | pcrA | RRC04357 | NT05RC1555 | |
| Replicative DNA helicase | 3.6.1.- | dnaB | RRC03626 | NT05RC1641 | C |
| NAD-dependent DNA ligase, LigA | 6.5.1.2 | ligA | RRC03535 | NT05RC1737 | C |
| Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, Ssb/Helix-destabilizing protein | ssb | RRC02420 | NT05RC1887 | C | |
| DNA polymerase I, Pol I | 2.7.7.7 | pol1 | RRC00937 | NT05RC2594 | C |
| DNA primase | 2.7.7.- | dnaG | RRC00201 | NT05RC3187 | C |
| Primosomal protein N′ | priA | RRC00361 | NT05RC3351 | C | |
| Exodeoxyribonuclease III | 3.1.11.2 | exoDNase_III | RRC00493 | NT05RC3477 | |
| DNA mismatch repair protein, MutS | mutS | RRC05797 | NT05RC3643 | CM | |
|
ENERGY METABOLISM | |||||
|
Amino acids and amines | |||||
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | 3.3.1.1 | ahcY | RRC03330 | NT05RC0050 | C |
| Serine hydroxymethyl transferase | 2.1.2.1 | glyA | RRC03001 | NT05RC0457 | C |
| Alanine dehydrogenase | 1.4.1.1 | ald | RRC03987 | NT05RC0504 | C |
| Tyrosine phenol-lyase/Beta-tyrosinase | 4.1.99.2 | tlp | RRC03952 | NT05RC0536 | CM |
| Sarcosine oxidase beta subunit/FAD dependent oxidoreductase | 1.5.3.1 | soxB | RRC03939 | NT05RC0550 | CM |
| Aminomethyltransferase/Glycine cleavage system T protein | 2.1.2.10 | gcvT | RRC03644 | NT05RC1190 | C |
| Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (acylating) | 1.2.1.27 | mmsA | RRC03635 | NT05RC1631 | C |
| Propanediol utilization protein, PduB | pduB | RRC01267 | NT05RC2309 | ||
| Tyrosine phenol-lyase/Beta-tyrosinase | 4.1.99.2 | tpl | RRC01364 | NT05RC2411 | C |
| Sarcosine oxidase gamma subunit | 1.5.3.1 | soxG | RRC01367 | NT05RC2415 | |
| Sarcosine oxidase alpha subunit | 1.5.3.1 | soxA | RRC01368 | NT05RC2416 | C |
| Sarcosine oxidase beta subunit | 1.5.3.1 | soxB | RRC01370 | NT05RC2418 | C |
| Aminotransferase, DegT/DnrJ/EryC1/StrS family | RRC00767 | NT05RC2910 | |||
| LMW-protein-tyrosine-phosphatase, PTPase/Small, acidic phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase (PYprotein phosphatase) | 3.1.3.48 | ptpA | RRC00274 | NT05RC3261 | |
| D-alanine aminotransferase (D-aspartateaminotransferase)/D-amino acid aminotransferase/D-amino acidtransaminase, Daat | 2.6.1.21 | daat | RRC01700 | NT05RC3299 | C |
| Ornithine cyclodeaminase | 4.3.1.12 | arcB | RRC05768 | NT05RC3610 | C |
|
Anaerobic | |||||
| Trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase 1, TMAO reductase 1 | 1.7.2.3 | RRC05612 | NT05RC2976 | P | |
|
ATP-proton motive force interconversion | |||||
| ATP synthase subunit I b chain | 3.6.3.14 | ATP_synt_b | RRC04287 | NT05RC0776 | EC |
| ATP synthase F1 beta subunit, AtpD | 3.6.1.34 | atpD | RRC00103 | NT05RC3105 | C |
| ATP synthase F1 alpha subunit, AtpA | 3.6.1.34 | atpA | RRC00106 | NT05RC3107 | C |
| ATP synthase F1 delta subunit, AtpH | 3.6.1.34 | atpH | RRC00107 | NT05RC3108 | C |
|
Biosynthesis and degradation of polysaccharides | |||||
| Anhydromuramoyl-peptide exo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase | 3.2.1.- | nagZ | RRC01974 | NT05RC0895 | C |
| Periplasmic beta-glucosidase (Gentiobiase) (Cellobiase)/Beta-D-glucoside glucohydrolase | 3.2.1.21 | bglX | RRC01186 | NT05RC2528 | P |
|
Electron transport | |||||
| Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase, Gcd | 1.3.99.7 | gcd | RRC04664 | NT05RC0023 | C |
| Electron transfer flavoprotein alpha or large subunit (alpha-Etf or Etfls) | alpha-etf | RRC03239 | NT05RC0149 | ||
| Electron transfer flavoprotein beta or small subunit (beta-Etf or Etfss) | beta-etf | RRC03238 | NT05RC0150 | ||
| Oxidoreductase, FAD-binding/Homologous to D-amino acid dehydrogenase/Glycine oxidase family | RRC02945 | NT05RC0400 | |||
| Electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase. EFT-Qo (Electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase) | 1.5.5.1 | EFT-Qo | RRC03955 | NT05RC0533 | |
| Sulfide-quinone reductase, Sqr | 1.8.5.- | sqr | RRC04245 | NT05RC0820 | CM, P |
| Cytochrome c oxidase, cbb3-type, subunit I | 1.9.3.1 | ccoN | RRC04162 | NT05RC1206 | CM |
| Cytochrome c oxidase, cbb3-type, subunit II monoheme subunit | 1.9.3.1 | ccoO | RRC04163 | NT05RC1207 | CM |
| Cytochrome c oxidase, cbb3-type, subunit III, diheme subunit | 1.9.3.1 | ccoP | RRC04165 | NT05RC1209 | CM |
| Cytochrome c2 | cycA | RRC02712 | NT05RC1293 | P | |
| NADH-quinone oxidoreductase chain D | 1.6.5.3 | nuoD | RRC02454 | NT05RC1585 | C |
| NADH-quinone oxidoreductase chain E | 1.6.5.3 | nuoE | RRC02455 | NT05RC1586 | CM |
| Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 8, Acad-8/Isobutyryl-coa dehydrogenase/activator-recruited cofactor 42 kDa component, Arc42 | 1.3.99.2 | RRC02499 | NT05RC1630 | C | |
| Ferredoxin-NADP reductase | 1.18.1.2 | fpr | RRC03609 | NT05RC1659 | C |
| N-ethylmaleimide reductase/Xenobiotic reductase, XenB | 1.7.1.- | xenB | RRC03600 | NT05RC1668 | |
| Cytochrome c551 peroxidase/cytochrome c peroxidase, Ccp | 1.11.1.5 | ccpA | RRC03475 | NT05RC1798 | P |
| Thiol-disulfide Isomerase/Thioredoxin, redoxin domain protein | RRC02397 | NT05RC1909 | |||
| Cytochrome P450 like protein | RRC01166 | NT05RC2544 | C | ||
| Cytochrome c-type cyt cy | cycY | RRC00961 | NT05RC2616 | CM, P | |
| Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase iron-sulfur subunit, PetA | 1.10.2.2 | petA | RRC00780 | NT05RC2896 | CM |
| Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase cytochrome b subunit, PetB | 1.10.2.2 | petB | RRC00781 | NT05RC2897 | CM |
| Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase Cytochrome c1 subunit, PetC | 1.10.2.2 | petC | RRC00779 | NT05RC2898 | CM |
| Ferredoxin I, FdI | fd1 | RRC00758 | NT05RC2920 | C | |
| Cytochrome c-type biogenesis protein CcmH (Ccl2) | ccl2/ccmH | RRC00287 | NT05RC3273 | CM, P | |
| Cytochrome P450 family protein | 1.14.15.3 | RRC00405 | NT05RC3394 | C | |
| Sulfide dehydrogenase (flavocytochrome c)/FAD-dependent pyridine nucleotide-disulphide oxidoreductase | 1.8.2.- | fccB | RRC00443 | NT05RC3435 | EC |
|
Fermentation | |||||
| Phosphate acetyltransferase/Phosphate butyryltransferase | 2.3.1.8/2.3.1.19 | pta | RC01951 | NT05RC0870 | C |
|
Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | |||||
| Phosphoenolpyruvate-protein phosphotransferase, PtsP | 2.7.3.9 | ptsP | RRC02985 | NT05RC0440 | C |
| Triosephosphate isomerase | 5.3.1.1 | tpiA | RRC03602 | NT05RC1666 | C |
| Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase type I | 4.1.2.13 | fba | RRC03492 | NT05RC1781 | C |
| Phosphoglycerate kinase | 2.7.2.3 | pgk | RRC03491 | NT05RC1782 | C |
| Enolase/Phosphopyruvate hydratase | 4.2.1.11 | eno | RRC03484 | NT05RC1789 | C |
| Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, class II, Calvin cycle subtype | 4.1.2.13 | fba | RRC02394 | NT05RC1912 | C |
| Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase B | 1.2.1.12 | gap | RRC02393 | NT05RC1913 | C |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, type I Gap | 1.2.1.12 | gap | RRC04329 | NT05RC2258 | C |
| Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, putative aldolase, YneB | 4.1.2.13 | yneB | RRC00008 | NT05RC3011 | CM |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase (FMN-linked) [cytochrome]/(S)-2-hydroxy-acid oxidase | 1.1.2.3/1.1.3.15 | lldD | RRC00194 | NT05RC3180 | |
|
Pentose phosphate pathway | |||||
| Ribose 5-phosphate isomerase A | 5.3.1.6 | rpiA | RRC01215 | NT05RC2502 | C |
| Ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase/Pentose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase | 5.1.3.1 | rpe | RRC00013 | NT05RC3016 | CM |
| Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, class II GlpX | 3.1.3.11 | glpX | RRC00208 | NT05RC3195 | CM |
| Transaldolase, putative | 2.2.1.2 | RRC00360 | NT05RC3349 | C | |
|
Photosynthesis | |||||
| Light-harvesting protein B-870, alpha chain | pufA | RRC02820 | NT05RC0721 | P | |
| Light-harvesting protein B-800/850, alpha chain | pucA | RRC02342 | NT05RC2651 | P | |
| Light-harvesting protein B-800/850, gamma chain | pucE | RRC00994 | NT05RC2653 | CM | |
| Photosynthetic reaction center H subunit | puhA | RRC02853 | NT05RC0688 | CM | |
| Photosynthetic reaction center L subunit | pufL | RRC02819 | NT05RC0722 | CM | |
| Photosynthetic reaction center M subunit | pufM | RRC02818 | NT05RC0723 | CM | |
|
Sugars | |||||
| Xylose Isomerase | 5.3.1.5 | xylA | RRC00720 | NT05RC0014 | C |
| Xylulose kinase | 2.7.1.17 | xylB | RRC00721 | NT05RC0015 | C |
| Nucleoside-diphosphate-sugar epimerase | RRC03125 | NT05RC0264 | CM | ||
| Phosphoglycolate phosphatase, Gph | 3.1.3.18 | gph | RRC02398 | NT05RC1908 | |
| Phosphoribulokinase 1 | 2.7.1.19 | cbbP | RRC02391 | NT05RC1915 | C |
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain 2 | 4.1.1.39 | rbcL | RRC02395 | NT05RC1911 | C |
| Phosphoglucomutase/Glucose phosphomutase, Pgm | 5.4.2.2 | pgm | RRC02387 | NT05RC1919 | C |
|
TCA cycle | |||||
| Malate dehydrogenase, NAD-dependent | 1.1.1.37 | mdh | RRC02795 | NT05RC0747 | C |
| Succinyl-CoA synthetase beta chain | 6.2.1.5 | sucC | RRC02793 | NT05RC0750 | C |
| Succinyl-CoA synthetase alpha chain | 6.2.1.5 | sucD | RRC02792 | NT05RC0751 | C |
| Isocitrate dehydrogenase, NADP-dependent | 1.1.1.42 | idh2 | RRC01533 | NT05RC1971 | C |
| Aconitate hydratase | 4.2.1.3 | acnA | RRC04337 | NT05RC2248 | C |
|
FATTY ACID AND PHOSPHOLIPID METABOLISM | |||||
|
Biosynthesis | |||||
| CDP-diacylglycerol--glycerol-3-phosphate 3-phosphatidyltransferase | 2.7.8.5 | pgsA | RRC02959 | NT05RC0413 | CM |
| MaoC domain protein dehydratase | maoC | RRC02782 | NT05RC0761 | C | |
| Dehydrogenase with MaoC-like domain | RRC02783 | NT05RC0761 | C | ||
| Putative phosphatidylserine decarboxylase homolog | 4.1.1.65 | psd | RRC04174 | NT05RC0957 | CM |
| Acyl-CoA thioesterase I precurser/Lipolytic enzyme, G-D-S-L family | 3.1.2- | acot1 | RRC04139 | NT05RC1226 | P |
| Malonyl-CoA-[acyl-carrier-protein] transacylase, FabD | 2.3.1.39 | fabD | RRC03525 | NT05RC1749 | |
| 3-Oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier protein] synthase, FabF | 2.3.1.179 | fabF | RRC03521 | NT05RC1754 | C |
| Enoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] reductase (NADH) | 1.3.1.9 | fab1 | RRC01406 | NT05RC2453 | C |
| 3-Oxoacyl-(acyl-carrier protein) reductase/Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase, SDR | 1.1.1.100 | fabG | RRC01189 | NT05RC2525 | C |
| Enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase [NADH] (NADH-dependent enoyl-ACP reductase) | 1.3.1.9 | RRC05546 | NT05RC2794 | C | |
| 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase II, FabF | fabF | RRC01138 | NT05RC2795 | C | |
| Beta-hydroxyacyl-(acyl-carrier-protein) dehydratase, FabA | 4.2.1.60 | fabA | RRC01139 | NT05RC2796 | C |
| 3-Hydroxyacyl-Coa dehydrogenase type-2, type II HADH/3-Hydroxy-2-methylbutyryl-Coa Dehydrogenase | 1.1.1.35 | hadh | RRC00129 | NT05RC3126 | C |
|
Degradation | |||||
| Succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase subunit b, Oxct b | 2.8.3.5 | scoB | RRC00248 | NT05RC3237 | C |
|
Other | |||||
| Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase/Acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase | 2.3.1.9 | Acat | RRC00329 | NT05RC3317 | C |
|
PROTEIN FATE | |||||
|
Degradation of proteins, peptides, and glycopeptides | |||||
| Secreted protease C precursor | 3.4.24.- | RRC03223 | NT05RC0167 | EC | |
| Peptidase T, PepT | 3.4.11.- | pepT | -- | NT05RC0370 | C |
| Peptidase, M20/M25/M40 family | 3.5.1.14 | RRC04401 | NT05RC1505 | C | |
| N-acyl-L-amino acid amidohydrolase/Hippuricase | 3.5.1.14 | RRC02444 | NT05RC1861 | C | |
| ATP-dependent protease La/ATP-dependent endopeptidase, Lon | 3.4.21.53 | RRC01049 | NT05RC2706 | C | |
| Leucyl/phenylalanyl-tRNA-protein transferase | 2.3.2.- | aat | RRC01073 | NT05RC2731 | CM |
| ATP-dependent endopeptidase clp proteolytic subunit, ClpP | 3.4.21.92 | clpP | RRC01078 | NT05RC2735 | CM |
| Oligoendopeptidase F, putative | 3.4.24.- | pepF | RRC00748 | NT05RC2930 | C |
|
Protein and peptide secretion and trafficking | |||||
| Protein-export chaperone, SecB | secB | RRC00736 | NT05RC0029 | C | |
| Protein secretion ABC efflux permease and ATP-binding protein/Type I secretion processing peptidase | RRC03199 | NT05RC0194 | CM | ||
| Preprotein translocase, SecA subunit | secA | RRC03160 | NT05RC0231 | C | |
| Peptidase M16 domain protein/Zinc protease | 3.4.99.- | RRC03108 | NT05RC0280 | CM | |
| Peptidase M16 domain protein/Insulinase family Zinc protease | 3.4.99.- | RRC03107 | NT05RC0281 | EC | |
| 60 kDa inner membrane insertion protein, YidC | yidC | RRC03045 | NT05RC0360 | CM | |
| General secretion pathway protein D/Type II and III secretion system protein | gspD | RRC03968 | NT05RC0522 | OM | |
| SecY stabilizing Integral membrane protein | secY | RRC01986 | NT05RC0911 | CM | |
| Hemin import ATP-binding protein, HmuV/Transporter | hmuV | RRC04502 | NT05RC1071 | C, CM | |
| Preprotein translocase, YajC subunit | yajC | RRC02443 | NT05RC1862 | CM | |
| Survival protein, SurA/PpiC-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | 5.2.1.8 | surA | -- | NT05RC2819 | EC |
| Microcin-processing peptidase 2 protein, TldD | tldD | RRC00243 | NT05RC3232 | M | |
| Tol system periplasmic component, YbgF/tetratricopeptide TPR_2 | ybgF | RRC05669 | NT05RC3333 | EC | |
| Outer membrane lipoprotein carrier protein, LolA | lolA | RRC00485 | NT05RC3469 | EC | |
| Type I secretion adaptor protein (HlyD family)/RTX secretion protein D | type_I_hlyD | RRC05697 | NT05RC3537 | C, CM | |
|
Protein folding and stabilization | |||||
| PpiC-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | 5.2.1.8 | -- | NT05RC0230 | OM | |
| Chaperone protein, DnaK | dnaK | RRC03154 | NT05RC0235 | C | |
| Thiol:disulfide interchange protein DsbA (DsbA oxidoreductase) | dsbA | RRC03149 | NT05RC0240 | EC | |
| Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, cyclophilin type | RRC03490 | NT05RC1783 | P | ||
| Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, PPIase/Rotamase/Cyclophilin/Cyclosporin A-bindingprotein, CYP B | 5.2.1.8 | cypB | RRC03489 | NT05RC1784 | CM |
| Outer membrane protein thiol:disulfide interchange protein DsbA-like | dsbA | RRC03455 | NT05RC1820 | EC | |
| Trigger Factor, PPIase, Tig | 5.2.1.8 | tig | RRC00692 | NT05RC2098 | C |
| Putative peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | 5.2.1.8 | RRC01410 | NT05RC2457 | ||
| Endopeptidase, DegP/Periplasmic serine protease | 3.4.21.- | degP | RRC01208 | NT05RC2508 | P |
| 10 kDa chaperonin, GroES | groS | RRC00934 | NT05RC2591 | C | |
| 60 kDa chaperonin, GroEL | groL | RRC00935 | NT05RC2592 | C | |
| ATP-dependent chaperone, ClpB | clpB | RRC05711 | NT05RC3551 | C | |
| Co-chaperone, GrpE | grpE | RRC05796 | NT05RC3642 | C | |
|
Protein modification and repair | |||||
| Carboxyl-processing protease (Tail specific protease) | 3.4.21.102 | RRC03302 | NT05RC0077 | CM | |
| Universal stress family protein | uspA | RRC02802 | NT05RC0740 | C | |
| Universal stress protein UspA and related nucleotide-binding domain protein | uspA | RRC04161 | NT05RC1205 | C | |
| Nitrilase/cyanide hydratase and apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase | RRC01014 | NT05RC2673 | |||
| Leucyl aminopeptidase | 3.4.11.1 | pepA | RRC04532 | NT05RC2823 | C |
| Protein-L-isoaspartate o-methyltransferase | 2.1.1.77 | Pcmt1 | RRC00264 | NT05RC3250 | C |
|
Other | |||||
| Von Willebrand factor type A domain protein/CBBO | RRC03776 | NT05RC0600 | C | ||
|
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS | |||||
|
Ribosomal proteins: synthesis and modification | |||||
| LSU ribosomal protein, L12 (L7/L12) | rplL | RRC03083 | NT05RC0305 | C | |
| SSU ribosomal protein, S3 | rpsC | RRC03069 | NT05RC0320 | C | |
| LSU ribosomal protein, L14 | rplN | RRC03064 | NT05RC0325 | C | |
| LSU ribosomal protein, L6 | rpl6P | RRC03059 | NT05RC0330 | C | |
| SSU ribosomal protein, S5 | rpsE | RRC03057 | NT05RC0332 | C | |
| SSU ribosomal protein, S13 | rpsM | RRC03051 | NT05RC0339 | C | |
| SSU ribosomal protein, S11 | rpsK | RRC03050 | NT05RC0340 | C | |
| LSU ribosomal protein, L19 (or L31) | rpmE | RRC03026 | NT05RC0377 | C | |
| SSU ribosomal protein, S1 | rpsA | RRC01790 | NT05RC1173 | C | |
| SSU ribosomal protein, S2 | rpsB | RRC02403 | NT05RC1903 | C | |
| LSU ribosomal protein, L9 | rplI | RRC00691 | NT05RC2101 | C | |
|
Translation factors | |||||
| Translation elongation factor Tu | tuf | RRC03808 | NT05RC0153 | C | |
| Protein translation elongation factor G (EF-G) | fusA | RRC02509 | NT05RC0311 | C | |
| Protein translation elongation factor Tu (EF-TU) | tuf | RRC03235 | NT05RC0312 | C | |
| Protein translation elongation factor Tu (EF-TU) | tuf | RRC03808 | NT05RC0312 | C | |
| Translation Elongation and release factor G (GTPase) | GTPase | RRC04353 | NT05RC1559 | C | |
| Peptide chain release factor 2, RF-2 | prfB | RRC02481 | NT05RC1613 | C | |
| Protein translation elongation factor Ts (EF-Ts) | tsf | RRC02402 | NT05RC1904 | C | |
| Bacterial peptide chain release factor 3 (RF-3), PrfC | prfC | RRC06068 | NT05RC2425 | C | |
|
tRNA and rRNA base modification | |||||
| Aspartyl/glutamyl-tRNA amidotransferase subunit A | 6.3.5.- | gatA | RRC00798 | NT05RC2879 | CM |
| Aspartyl/glutamyl-tRNA amidotransferase subunit B (Asp/Glu-ADT subunit B) | 6.3.5.- | gatB | RRC01959 | NT05RC0880 | C |
| D-Tyrosyl-tRNA deacylase, Dtd | 3.1.-.- | dtd | RRC00975 | NT05RC2630 | C |
|
tRNA aminoacylation | |||||
| Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase | 6.1.1.2 | trpS | RRC04002 | NT05RC0490 | C |
| Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase | 6.1.1.12 | aspS | RRC03937 | NT05RC0553 | C |
| Seryl-tRNA synthetase | 6.1.1.11 | serS | RRC04397 | NT05RC1510 | C, CM |
| Prolyl-tRNA synthetase | proRS | -- | NT05RC2575 | C | |
| Phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase, beta subunit | 6.1.1.20 | pheT | RRC06104 | NT05RC3289 | C |
|
PURINES, PYRIMIDINES, NUCLEOSIDES, AND NUCLEOTIDES | |||||
|
Nucleotide and nucleoside interconversions | |||||
| Adenylate kinase (ATP-AMP transphosphorylase)/Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase | 2.7.4.3/2.7.4.6 | adk | RRC03052 | NT05RC0338 | C |
| Nucleoside diphosphate kinase, Ndk/NDP kinase/Nucleoside-2-P kinase | 2.7.4.6 | ndk | RRC03479 | NT05RC1794 | C |
|
Purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis | |||||
| GMP synthase [glutamine-hydrolyzing] | 6.3.5.2 | guaA | RRC00895 | NT05RC1941 | C |
| Formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase | 3.5.1.10 | purU | RRC01205 | NT05RC2511 | |
|
Pyrimidine ribonucleotide biosynthesis | |||||
| Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase, large subunit | 6.3.5.5 | carB | RRC03938 | NT05RC0552 | CM, P |
| Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase | 2.4.2.10 | pyrE | RRC03625 | NT05RC1642 | C |
| Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP+] beta subunit/dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family protein | 1.3.1.2 | DPYD | RRC00991 | NT05RC2646 | C |
|
Salvage of nucleosides and nucleotides | |||||
| Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase, Apt | 2.4.2.7 | apt | RRC01698 | NT05RC3227 | C |
| Purine nucleotide phosphorylase | 2.4.2.1 | RRC00387 | NT05RC3376 | C | |
|
2′-Deoxyribonucleotide metabolism | |||||
| Pyrimidine-specific ribonucleoside hydrolase, RihA/Cytidine/uridine-specific hydrolase | 3.2.-.- | rihA | RRC03481 | NT05RC1792 | C |
|
Other | |||||
| Nucleoside-binding protein/Bmp family protein | RRC04244 | NT05RC0821 | EC | ||
| Xanthine dehydrogenase, small subunit | 1.17.1.4 | xdhA | RRC04239 | NT05RC0827 | C |
|
REGULATORY FUNCTIONS | |||||
|
DNA interactions | |||||
| Transcriptional regulator, LuxR family | luxR | RRC03806 | NT05RC0343 | C | |
| Cell cycle transcriptional regulator, CtrA/Response regulator SokA | ctrA | RRC03536 | NT05RC1736 | C | |
| Transcriptional regulatory protein BaeR, Alkaline phosphatase synthesis | baeR | RRC00026 | NT05RC3031 | C | |
|
Protein interactions | |||||
| Regulatory protein, SenC(PrrC) | senC/prrC/sco1 | RRC03336 | NT05RC0044 | CM | |
| Phosphohistidine phosphatase, SixA/Phosphoglycerate mutase family protein | 3.1.3.- | sixA | RRC04024 | NT05RC0354 | |
| Protease activity modulator | hflK | RRC01212 | NT05RC2505 | ||
|
Small molecule interactions | |||||
| Diguanylate cyclase/phosphodiesterase with PAS/PAC and GAF sensor | 2.7.7.65 | RRC00149 | NT05RC3141 | C | |
|
Two-component systems | |||||
| Two component response regulator (winged helix family) | -- | NT05RC0276 | C | ||
|
Other | |||||
| Response regulator/ggdef domain protein | RRC06082 | NT05RC2762 | |||
| Phosphate transport system regulatory protein, PhoU | phoU | RRC05801 | NT05RC3647 | C | |
|
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION | |||||
|
Two-component systems | |||||
| Methyl-accepting chemotaxis sensory transducer, McpA | mcpA | RRC04620 | NT05RC1409 | CM | |
| Sensory transduction histidine protein kinase | 2.7.3.- | RRC05028 | NT05RC1570 | CM | |
| Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein, McpC | mcpC | RRC03579 | NT05RC1694 | CM | |
| Sensory transduction protein kinase | 2.7.3.- | RRC01105 | NT05RC2760 | ||
| Two-component response sensory transduction histidine kinase, potential phosphate regulatory protein | RRC06094 | NT05RC2997 | C | ||
| Two component system integral membrane signal transduction histidine kinase | 2.7.3.- | RRC00027 | NT05RC3032 | CM | |
|
TRANSCRIPTION | |||||
|
Degradation of RNA | |||||
| Polyribonucleotide nucleotidyltransferase/Polynucleotidephosphorylase, PNPase | 2.7.7.8 | RRC03090 | NT05RC0297 | C | |
| Ribonuclease E, RNase E | 3.1.4.- | RNaseEG | RRC05484 | NT05RC2263 | C |
| Translation initiation inhibitor/Endoribonuclease L-PSP | RRC05722 | NT05RC3562 | CM | ||
|
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | |||||
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase beta subunit | 2.7.7.6 | rpoB | RRC03082 | NT05RC0306 | C |
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase beta’ subunit | 2.7.7.6 | rpoC | RRC03080 | NT05RC0307 | C |
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase, alpha subunit | 2.7.7.6 | rpoA | RRC03049 | NT05RC0341 | C |
|
Transcription factors | |||||
| Sigma 54 modulation protein/ribosomal protein S30EA or factor Y | rpoX | RRC03265 | NT05RC0121 | C | |
| Transcription elongation factor, GreA | greA | RRC03954 | NT05RC0534 | C | |
| Transcriptional regulator, LysR family | lysR | RRC03919 | NT05RC0572 | C | |
| Transcription elongation factor, NusA/N utilization substance protein A | nusA | RRC03167 | NT05RC224 | C | |
|
Other | |||||
| Putative AraC family transcriptional regulator | RRC04375 | NT05RC1537 | CM | ||
|
TRANSPORT AND BINDING PROTEINS | |||||
|
Amino acids, peptides and amines | |||||
| Transporter/import inner membrane translocase, subunit Tim44 homolog | Sec? | RRC00738 | NT05RC0031 | CM | |
| Oligopeptide-binding protein, OppA/Extracellular solute-binding protein, family 5 | oppA | RRC03230 | NT05RC0161 | P | |
| Glutamate/glutamine/aspartate/asparagine-binding protein, BztA | bztA | RRC03799 | NT05RC0350 | P | |
| Glutamine-binding protein/Extracellular solute-binding protein, family 3 | RRC04018 | NT05RC0474 | P | ||
| Type II secretion system protein E | RRC03965 | NT05RC0525 | CM, P | ||
| Putative lysine-arginine-ornithine or histidine binding periplasmic protein | RRC02872 | NT05RC0650 | P | ||
| Oligopeptide-binding Protein OppA/Extracellular solute-binding protein family | oppA | RRC02807 | NT05RC0735 | CM, P | |
| Dipeptide-binding protein/Extracellular solute-binding protein, family | RRC01964 | NT05RC0885 | P | ||
| Dipeptide transport ATP-binding protein, DppD/Oligopeptide transport ATP-binding protein, OppD | oppD | RRC01967 | NT05RC0888 | C, CM | |
| Glycine betaine/L-proline transport system binding protein, ProX | proX | RRC02010 | NT05RC0936 | ||
| Spermidine/putrescine ABC transporter ATP-binding subunit | RRC02709 | NT05RC1297 | C, CM | ||
| Putative polyamine ABC transporter, periplasmic polyamine-binding protein | RRC02708 | NT05RC1298 | EC | ||
| Polyamine ABC transporter, permease protein | RRC02707 | NT05RC1299 | CM | ||
| Probable phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate-5-kinase | RRC04081 | NT05RC1419 | EC | ||
| ABC Polyamine/Opine/Phosphonate transporter, periplasmic ligand binding protein | RRC04469 | NT05RC1423 | EC | ||
| ABC transporter ATP-binding protein/Methionine import ATP-binding protein, MetN | metN | RRC03629 | NT05RC1638 | CM | |
| Leucine-, Isoleucine-, Valine-, Threonine and Alanine-binding Protein/Extracellular ligand-binding receptor | braC | RRC00901 | NT05RC1935 | P | |
| Putrescine transport ATP-binding protein, PotG | potG | RRC01528 | NT05RC1977 | C | |
| Putrescine transport system permease protein, PotI | potI | RRC01527 | NT05RC1978 | CM | |
| Spermidine/putrescine transport system permease protein, PotB/Binding-protein-dependent inner membrane transport component | potB | RRC01526 | NT05RC1979 | CM | |
| Spermidine/putrescine-binding protein/Extracellular solute-binding protein, family 1 | RRC01245 | NT05RC2286 | P | ||
| Taurine ABC transporter, periplasmic taurine-binding protein | RRC01299 | NT05RC2343 | EC | ||
| Spermidine/Putrescine-binding periplasmic protein | RRC01326 | NT05RC2370 | P | ||
| Oligopeptide-binding protein, OppA | oppA | RRC01333 | NT05RC2377 | P | |
| Branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein, LivF | livF | RRC01157 | NT05RC2553 | C, CM | |
| His/Glu/Gln/Arg/opine family ABC transporter/Periplasmic His/Glu/Gln/Arg/opine family-binding protein | RRC00775 | NT05RC2902 | P | ||
| Spermidine/putrescine-binding protein, ABC polyamine transporter, periplasmic substrate-binding protein | RRC00091 | NT05RC3093 | P | ||
| Branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase | 2.6.1.42 | RRC00377 | NT05RC3367 | C | |
| ABC transporter, Cyd cysteine exporter family permease/ATP-binding protein, CydC | cydC | RRC00404 | NT05RC3393 | CM | |
| ABC branched amino acid transporter family, periplasmic substrate-binding subunit | RRC05738 | NT05RC3577 | EC | ||
| ABC branched amino acid transporter family, ATPase subunit | RRC05739 | NT05RC3578 | C, CM | ||
|
Anions | |||||
| Molybdate ABC transporter, periplasmic molybdate-binding protein | modA | RRC03762 | NT05RC0585 | P | |
| Molybdate ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein, ModC | modC | RRC03907 | NT05RC0587 | C, CM | |
| Thiosulfate-binding protein | -- | NT05RC2870 | P | ||
| Membrane protein MosC, major facilitator superfamily MFS_1 | mosC | RRC00195 | NT05RC3181 | CM | |
| Phosphate transport ATP-binding protein, PstB | pstB | RRC05802 | NT05RC3648 | C, CM | |
| Phosphate ABC transporter, permease protein, PstA | pstA | RRC05803 | NT05RC3649 | CM | |
| ABC phosphate transporter, inner membrane subunit, PstC | pstC | RRC03394 | NT05RC3650 | CM | |
| Phosphate-Binding Periplasmic Protein | RRC03395 | NT05RC3651 | P | ||
|
Carbohydrates, organic alcohols, and acids | |||||
| D-xylose ABC transporter, D-xylose-binding protein | xylF | RRC00724 | NT05RC0018 | P | |
| Mannitol-binding protein/Trap dicarboxylate transporter, Dctp subunit | RRC04462 | NT05RC1431 | EC | ||
| Alpha-glucoside-binding protein/ABC alpha-glucoside transporter, periplasmic substrate-binding protein | algE | RRC03427 | NT05RC1851 | EC | |
| Alpha-glucoside transport ATP-binding protein, AglK | algK | RRC03422 | NT05RC1855 | C, CM | |
| Fructose binding periplasmic protein, FrcB | frcB | -- | NT05RC2111 | P | |
| Sorbitol-binding protein/Potential maltose-binding protein | RRC00677 | NT05RC2114 | EC | ||
| ABC sugar transporter, periplasmic binding protein/D-Galactose-binding/Ribitol-binding protein | RRC02337 | NT05RC2476 | P | ||
| Mannitol-binding protein | RRC01191 | NT05RC2524 | EC | ||
| Ribose ABC transporter, D-ribose-binding protein | RRC01127 | NT05RC2784 | P | ||
| Ribose transport ATP-binding protein RbsA/ABC transporter, carbohydrate uptake transporter-2 (CUT2) family | rbsA | RRC01129 | NT05RC2786 | C, CM | |
| C4-dicarboxylate-binding periplasmic protein | RRC00169 | NT05RC3156 | P | ||
|
Cations and iron carrying compounds | |||||
| Manganese transport protein, MntH | mntH | RRC03871 | NT05RC0626 | CM | |
| Iron (III) Dicitrate-binding periplasmic protein | fecB | RRC04484 | NT05RC1088 | EC | |
| Outer membrane siderophore receptor/TonB-dependent siderophore receptorR | fiu | RRC04402 | NT05RC1504 | OM | |
| Sensor protein, KdpD | 2.7.3.- | kdpD | RRC01313 | NT05RC2357 | CM |
| Transporter/TrkA-C domain protein | -- | NT05RC2388 | CM | ||
| TonB-system energizer ExbB/TolQ protein | exbB | RRC01434 | NT05RC2479 | CM | |
| 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase/short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase, SDR | 1.3.1.28 | entA | RRC01183 | NT05RC2531 | C |
| 25 kD Outer-membrane immunogenic protein/Rhizobiocin, RzcA | rzcA | RRC01603 | NT05RC2572 | OM | |
| Iron-regulated protein, FrpC | frpC | RRC01604 | NT05RC2573 | EC | |
| Iron-regulated protein FrpC/poly(beta-D-mannuronate) C5 epimerase 3 (Mannuronanepimerase 3) | frpC | RRC00309 | NT05RC3297 | EC | |
|
Porins | |||||
| Porin | RRC03116 | NT05RC0272 | OM | ||
|
Other | |||||
| Putative membrane protein | RRC03140 | NT05RC0250 | CM | ||
| Acetyltransferase/MobC protein | 2.3.1.- | mobC | RRC02973 | NT05RC0428 | |
| Acriflavin resistance plasma membrane protein B | acrB | RRC02995 | NT05RC0450 | CM | |
| Acriflavin resistance periplasmic protein | RRC02881 | NT05RC0641 | P | ||
| Periplasmic component of efflux system/HlyD family protein | RRC02879 | NT05RC0643 | CM, P | ||
| ABC transporter, substrate-binding protein, aliphatic sulphonates/Taurine-Binding Periplasmic Protein | RRC06012 | NT05RC1459 | EC | ||
| ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | RRC04420 | NT05RC1484 | CM | ||
| Transporter | RRC04392 | NT05RC1517 | |||
| ABC transporter, fused ATPase and inner membrane subunit | RRC01360 | NT05RC2407 | CM | ||
| Putative transport protein, YidE/Integral membrane protein with TrkA domains | yidE | RRC01177 | NT05RC2535 | CM | |
| Oligopeptide-binding protein/extracellular solute-binding protein, family 5 | RRC00960 | NT05RC2615 | EC | ||
| ABC-type nitrate/sulfonate/bicarbonate transport systems, periplasmic component, TauA | tauA | RRC00984 | NT05RC2639 | EC | |
| Iron(III)-binding periplasmic protein | RRC01044 | NT05RC2700 | P | ||
| Thiamin/thiamin pyrophosphate ABC transporter, thiamin/thiamin pyrophospate-binding protein, ThiB | thiB | RRC01667 | NT05RC2825 | P | |
| Acriflavin resistance protein E/Efflux transporter, RND family, MFP subunit | RRC00805 | NT05RC2872 | CM, P | ||
| Acriflavin resistance plasma membrane protein | RRC00803 | NT05RC2873 | CM | ||
| TolB protein | tolB | RRC00346 | NT05RC3335 | P | |
| ABC transporter, periplasmic substrate-binding protein | RRC00383 | NT05RC3372 | P | ||
|
UNCLASSIFIED | |||||
|
Role category not yet assigned | |||||
| Myo-inositol-1(or 4)-monophosphatase (I-1-Pase) | 3.1.3.25 | RRC03984 | NT05RC0507 | C | |
| Myo-inositol-1(or 4)-monophosphatase family protein | 3.1.3.25 | RRC01989 | NT05RC0915 | ||
| Lipoprotein, putative | RRC01112 | NT05RC2767 | EC | ||
| Inositol monophosphatase/ADP-ribosylglycohydrolase, CysQ Protein | 3.1.3.25 | RRC00266 | NT05RC3253 | ||
|
UNKNOWN FUNCTION | |||||
|
General | |||||
| Filament-A precursor (Peptidase M23B) | filA | RRC03301 | NT05RC0078 | C, CM | |
| Putative iojap protein family homolog | RRC03298 | NT05RC0081 | C | ||
| Pentapeptide repeat family protein | RRC04445 | NT05RC1451 | EC | ||
| Outer membrane protein E/Membrane protein involved in aromatic hydrocarbon degradation | RRC01502 | NT05RC2007 | OM | ||
|
HYPOTHETICAL PROTEINS | |||||
|
Conserved Domain proteins | |||||
| ErfK/YbiS/YcfS/YnhG family protein | RRC02993 | NT05RC0448 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC03927 | NT05RC0563 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC03926 | NT05RC0564 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical membrane spanning protein | RRC02854 | NT05RC0687 | CM | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC02456 | NT05RC1587 | |||
| Hypothetical cytosolic protein of unknown function | RRC02483 | NT05RC1615 | C | ||
| Hypothetical protein/GfdT protein | RRC03541 | NT05RC1732 | C | ||
| Conserved hypothetical membrane associated protein | RRC03520 | NT05RC1755 | C, CM | ||
| Hypothetical Membrane Associated Protein/Invasion associated family protein | RRC00884 | NT05RC1952 | EC | ||
| Hypothetical protein | RRC01494 | NT05RC2016 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical cytosolic protein | RRC00597 | NT05RC2240 | C | ||
| Hypothetical Exported Protein | RRC01358 | NT05RC2405 | EC | ||
| Hypothetical membrane associated protein/pyrrolo-quinoline quinone | RRC01359 | NT05RC2406 | CM | ||
| Hypothetical protein | -- | NT05RC2634 | |||
| Hypothetical protein/lipoprotein, putative | RRC01128 | NT05RC2785 | |||
| Hypothetical membrane spanning protein of unknown function | RRC06091 | NT05RC2994 | CM | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC06095 | NT05RC3026 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical protein, Phage Minor Tail Protein | RRC02354 | NT05RC3046 | CM | ||
| Hypothetical protein | RRC05643 | NT05RC3064 | C | ||
| Hypothetical cytosolic protein, prophage Lp2 protein | RRC00072 | NT05RC3071 | CM | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | -- | NT05RC3075 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical Protein | RRC00313 | NT05RC3301 | C | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein/Permease | RRC00389 | NT05RC3378 | EC | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC00393 | NT05RC3382 | EC | ||
| Conserved hypothetical cytosolic protein | RRC00413 | NT05RC3402 | C | ||
| Conserved hypothetical Exported Protein | RRC01759 | NT05RC3524 | CM, P | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC03402 | NT05RC3658 | P | ||
|
Conserved Hypothetical proteins | |||||
| Conserved hypothetical (transglutaminase-like) protein | RRC03327 | NT05RC0053 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical cytosolic protein | RRC03249 | NT05RC0139 | C | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein/Glucose-1-phosphate adenyltransferase | 2.7.7.27 | -- | NT05RC0925 | ||
| OmpA family hypothetical protein | RRC03674 | NT05RC0952 | EC | ||
| Conserved hypothetical protein/Aminomethyltransferase | 2.1.2.10 | RRC03662 | NT05RC0993 | C | |
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC01788 | NT05RC1175 | |||
| Hypothetical Cytosolic Protein | RRC03645 | NT05RC1186 | |||
| Hypothetical protein | RRC02694 | NT05RC1315 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC02685 | NT05RC1327 | |||
| Conserved hypothetical protein | RRC06004 | NT05RC1351 | EC | ||
| Outer membrane protein/Inner membrane lipoprotein YiaD | yiaD | RRC00951 | NT05RC2605 | OM | |
| Hypothetical Membrane Spanning Protein | RRC01102 | NT05RC2757 | CM | ||
| Conserved hypothetical Exported Protein (Mucoidy inhibitor A) | RRC01654 | NT05RC2839 | EC | ||
| Conserved hypothetical Exported Protein | RRC03610 | NT05RC2917 | CM, P | ||
| GTP-binding protein/conserved hypothetical protein | RRC00370 | NT05RC3360 | C | ||
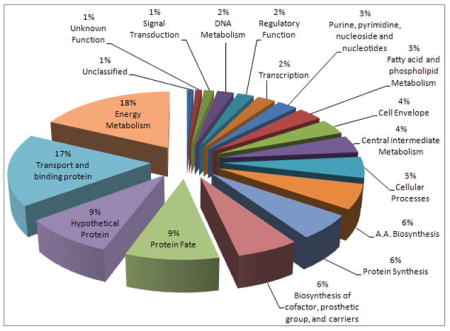
Figure 1.
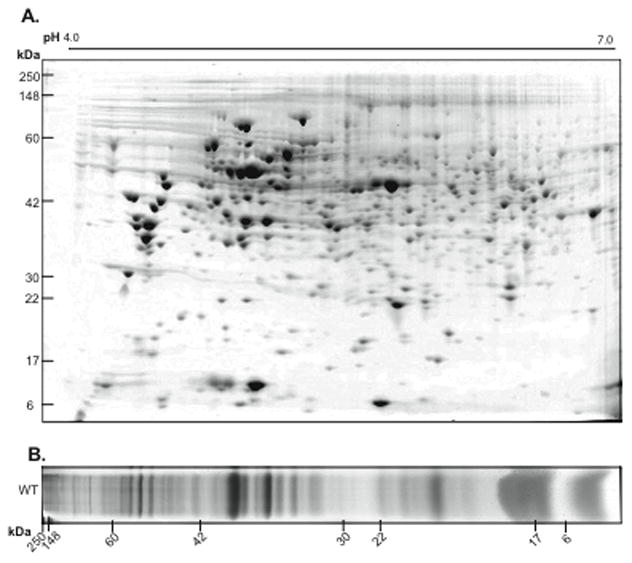
Representative 1D- and 2D-gel analyses of R. capsulatus protein samples. A. Periplasmic fraction proteins of R. capsulatus were separated by 2D-GE, with pH 4–7 IPG and SDS–PAGE, as first and second dimensions. B. Chromatophore membranes of R. capsulatus were separated on 1D-GE using SDS PAGE. In both cases, protein samples were prepared as described in Materials and Methods, gels were stained with colloidal coomassie blue and protein spots or bands were excised and trypsin digested for identification by nano-LC-MS/MS.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from DOE ER9120053 and NIH GM38237 to F.D.
References
- Myllykallio H, Jenney FE Jr, Jr, Moomaw CR, et al. Cytochrome c(y) of Rhodobacter capsulatus is attached to the cytoplasmic membrane by an uncleaved signal sequence-like anchor. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:2623–2631. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.8.2623-2631.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Q, Thony-Meyer L. Physical interaction of CcmC with heme and the heme chaperone CcmE during cytochrome c maturation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:32591–32596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103058200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onder O, Yoon H, Naumann B, et al. Modifications of the lipoamide-containing mitochondrial subproteome in a yeast mutant defective in cysteine desulfurase. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1426–1436. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600099-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onder O, Turkarslan S, Sun D, et al. Overproduction or absence of the periplasmic protease DegP severly compromises bacterial growth in the absence of the dithiol:disulfide oxidoreductase DsbA. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008;7:875–890. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700433-MCP200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff V, Stamm R, Pardowitz I, et al. Essential problems in quantification of proteins following colloidal staining with coomassie brilliant blue dyes in polyacrylamide gels, and their solution. Electrophoresis. 1990;11:101–117. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, et al. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardy JL, Laird MR, Chen F, et al. PSORTb v.2.0: expanded prediction of bacterial protein subcellular localization and insights gained from comparative proteome analysis. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:617–623. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannoni D. Aerobic and anaerobic electron transport chains in anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria. In: Blankenship RE, Madigan MT, Bauer CE, editors. Anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 1995. pp. 949–971. [Google Scholar]
- Park SJ, Lee SY, Cho J, et al. Global physiological understanding and metabolic engineering of microorganisms based on omics studies. Appl Microb Biotechnol. 2005;68:567–79. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-0081-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasinger V. Holistic biology of microorganisms: genomics, transcriptomics, andproteomics. Methods Biochem Anal. 2006;49:3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daldal F, Cheng S, Applebaum J, et al. Cytochrome c(2) is not essential for photosynthetic growth of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:2012–2016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter NC, Daldal F, Thurnauer MC, Beatty JT, editors. The Purple Phototrophic Bacteria. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Du X, Callister SJ, Manes NP, et al. A computational strategy to analyze label-free temporal bottom-up proteomics data. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:2595–604. doi: 10.1021/pr0704837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


