Abstract
In this report, we demonstrate that quartz nanopipettes modified with an imidazole-terminated silane respond to metal ions (Co2+) in solution. The response of nanopipettes is evaluated through examination of the ion current rectification response. By cycling nanopipettes between solutions of different pH, adsorbed Co2+ can be released from the nanopipette surface, to regenerate binding sites of the nanopipette. These results demonstrate that rectification-based sensing strategies for nanopore sensors can benefit from selection of recognition elements with intermediate binding affinities, such that reversible responses to be attained.
INTRODUCTION
Transmission of ions through nanometer-scale pores and channels is an essential process in living systems1. Recently, a number of ex vivo systems based on transmitting ion currents have been studied, with a focus on both increasing the understanding of biological systems and developing new tools and devices that use ionic currents2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7. For instance, α-hemolysin protein nanopores8, 9, 10 and abiotic silicon nitride/oxide nanopores11, 12, have been utilized to study fundamentals of ion transport and to develop sensing schemes based on ion-currents. Advantages that protein pores possess include uniform, well-characterized dimensions and the ability to perform site-directed mutations to incorporate additional functionality, while advantages abiotic pores possess can include mechanical and chemical stability as well as high pore densities per unit area.
A number of abiotic nanopore platforms have evolved, each with unique attributes suitable to different applications. These platforms include solid-state silicon nanopores11, 12, glass nanopores13, 14, 15, 16, 17, polymer membranes18, 19, 20, 21, alumina membranes22, 23, lithographically fabricated nanochannels24, 25 and pulled-nanopipettes26. In the work described here, we make use of quartz nanopipettes, fabricated by simple heating and separation of a quartz capillary, to study the transport of ions by nanopores. Previous nanopipette studies of ion transport26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31 have established the ease of preparation and versatility in application of this nanopore platform. Chemical functionalization of nanopores21, 32, 33 has been explored recently to develop chemically or biochemically responsive nanopores. For example, nanopipettes that respond to proteins28, polymers29 and DNA27, 31 have been described.
In particular, the current-voltage response of a nanopore, especially an asymmetric nanopore, can be employed to evaluate changes in surface charge3, 34, 35 and thus serve to transduce analyte binding. Asymmetric nanopores can possess asymmetry in shape (e.g. conical or pyramidal)36, 37, 38 or in charge distribution39, 40. Sensing processes rely on qualitative evaluation of the current-voltage response expressed as changes in the ion current rectification (ICR) response. Ionic rectification is useful for to report changes in surface charge when dimensions of the nanopore are comparable to the Debye length, as the concentration of the counter-ions in the nanopore can be enhanced or depleted due to electrostatic interactions. In general, strong-binding recognition elements have been exploited to effect signal transduction through irreversible changes in the current-voltage response.
Herein, we describe chemically modified nanopipettes that use a responsive coating of dihydroimidazole (DHI) (bound through silane chemistry to the nanopipette surface) as probes for cobalt ions in solution. Additionally, changes in the current-voltage response induced by cobalt ions can be reversed through control of the solution pH to create a reversible nanopore sensor. These findings are significant as they develop a better understanding of signal transduction with nanopores and develop reusable nanopores with reversible responses.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Fabrication, functionalization and characterization of nanopipettes
Quartz capillaries (0.7 mm (I.D.) and 1.0 mm (O.D.), Sutter Instrument, Novato, CA) were treated with piranha solution (30% H2O2:H2SO4 =1:3) prior to use to remove organic contaminants. Cleaned capillaries were then fashioned into nanopipettes with a CO2-laser-based pipette puller (P-2000, Sutter Instrument, Novato, CA). Solutions were backfilled into nanopipettes using a microfill needle (World Precision Instrument, Inc.) and subsequently centrifuged to ensure solutions reached the tip of nanopipette.
Previous studies have investigated nanopore modification with silane chemistry31, 41, 42. Here, a three-step procedure was adopted to graft N-[3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl]-4,5-dihydroimidazole (DHI) onto the tip of nanopipette. First, 0.2 mL of DHI (0.74 mmol) was mixed with 1.0 mL pure ethanol and stirred for 5 min. Nanopipettes, washed with water and ethanol, were backfilled with this DHI solution and centrifuged to fill the tip. Nanopipettes were then placed in pure ethanol overnight, followed by a thorough wash with ethanol and distilled water prior to current-voltage characterization. The procedure employed here leads to thin DHI coatings that do not block the opening of the nanopipette. The procedure does not preclude possible multilayer formation. It is also possible that some DHI-silane diffuses out of the nanopipette and modifies the exterior of the nanopipette with this procedure. Such modification is outside the “sensing zone”19, 21 for conical nanopore structures, and effects on resistance measurements are expected to be minimal.
Current-voltage characteristics were measured with a picoammeter/voltage source (Keithley Instruments, Inc). A Ag/AgCl electrode was inserted inside of nanopipette and a Ag/AgCl reference electrode was placed in an external electrolyte bath. To characterize DHI-modified nanopipettes, current-voltage curves of nanopipettes were recorded both before and after DHI modification. Response to cobalt ions was measured after addition of cobalt acetate to the external bath electrolyte. Recordings of non-modified quartz nanopipettes under the same experimental conditions were treated as control measurements. Current-voltage curves reported represent averages of at least two replicant measurements on the same nanopipette. Multiple pipettes (≥3) responded with a similar trend, but due to fluctuations in pore size (see supporting information) the results cannot be directly averaged. The ICR responses reported were averaged from multiple pipettes (n=3). In all current-voltage measurements, the potential was swept from −1.0 V to +1.0 V at a rate of 0.1 V/s, with 0.1 M KCl, 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH adjusted as indicated in results and discussion).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
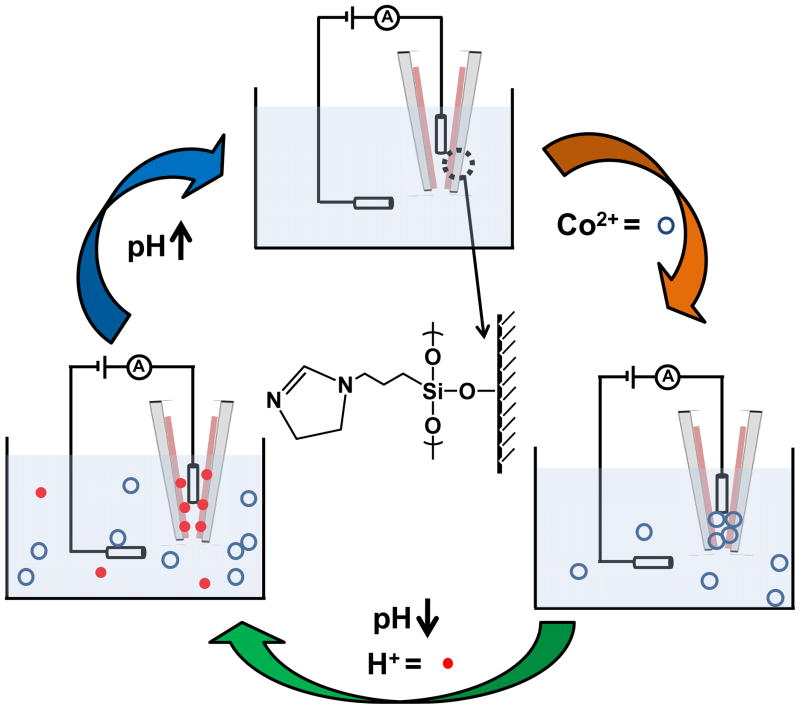
The general scheme for reversible metal-ion sensing with DHI-modified nanopipettes is shown in Figure 1. Recognition of metal ions is accomplished via chemical functionalization of a nanopipette with a thin film of DHI through the formation of siloxane bonds on the surface of the nanopipette. The recognition element, DHI, possesses free tertiary amines; when these amines are deprotonated, they serve as binding sites for metal cations in solution, as illustrated here with cobalt (II) ions. Binding of metal ions to DHI in the thin film can be reversed through changes in pH to regenerate the sensing properties of the nanopipette. Protonation of the tertiary amines of DHI in acidic media displaces the bound metal ions. Adjusting the pH to more basic conditions results in deprotonation of the tertiary amines of DHI and subsequent regeneration of binding sites of the nanopipette.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of N-[3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl]-4,5-dihydroimidazole (DHI) grafted nanopipette with response of Co(II) ( ) and its regeneration process with proton addition (
) and its regeneration process with proton addition ( ).
).
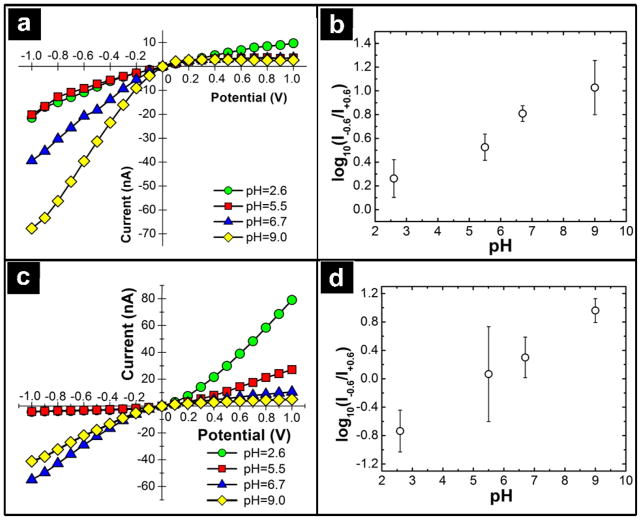
The net surface charge of the nanopipette can be monitored through the current-voltage response of the nanopipette under different conditions. In Figure 2a, the current-voltage response of a bare (unmodified) nanopipette is shown as a function of pH.
Figure 2.
(a) Current-voltage response of a bare quartz nanopipette at pH 2.6 ( ), 5.5 (
), 5.5 ( ), 6.7(
), 6.7( ), and 9.0(
), and 9.0( ); (b) Dependence of ion-current rectification (ICR) response on electrolyte pH for a bare quartz nanopipette; (c) Current-voltage response of DHI-modified nanopipette at pH 2.6 (
); (b) Dependence of ion-current rectification (ICR) response on electrolyte pH for a bare quartz nanopipette; (c) Current-voltage response of DHI-modified nanopipette at pH 2.6 ( ), 5.5 (
), 5.5 ( ), 6.7 (
), 6.7 ( ), and 9.0 (
), and 9.0 ( ); (d) Dependence of ion-current rectification response on electrolyte pH for a DHI-modified nanopipette.
); (d) Dependence of ion-current rectification response on electrolyte pH for a DHI-modified nanopipette.
| (Equation 1) |
The trend observed is similar to previous reports for conical nanopore structures with negative surface charge. Under basic conditions (e.g. pH = 9.0) silanol groups (pI ~1–4)43 on the surface of the nanopipette are deprotonated, which results in a rectified current response in which higher currents are measured at negative potentials, as opposed to the corresponding positive potentials. The origins of rectification are based on surface charge44 and the conical geometry45 of the nanopipette, and have been discussed in detail in other reports. As the solution is acidified, dissociated silanol groups on the surface of the nanopipette become protonated, which results in removal of the surface charge of the nanopipette and a corresponding decrease in the observed current rectification. The protonation state of silanol groups on the nanopipette can be quantified through the ion current rectification (ICR) response. The ICR response is expressed as the logarithm of the ratio at −/+ 600 mV, as shown in Equation 1. In Figure 2, the ICR response is plotted as a function of pH for the bare and DHI-modified nanopipette. Plotted in this fashion, the observed responses approach linearity. For the bare nanopipette, the ICR response is in good agreement with previously published reports for glass/quartz nanopipettes26. At high pH, the silanol groups are deprotonated, relative to low pH, resulting in greater observed current rectification. For the DHI-modified nanopipette, the current-voltage response is indicative of a surface with two charge states present. Variable charge states are introduced by DHI groups, which can carry a cationic charge when protonated, and silanol groups, which can carry an anionic charge when deprotonated.
The variable surface charge of the nanopipette results in pH-dependent rectification of either cations or anions. At high pH, silanol groups and DHI groups on the surface of the nanopipette are deprotonated, leading to an overall anionic surface charge. This produces a current-voltage response that mimics the bare nanopipette in Figure 2a. As the pH of the solution is lowered (pH = 6.7 and 5.5), the ICR ratio decreases as the nanopipette approaches a neutral net surface charge. Finally at low pH, protonated DHI and silanol groups result in a reversal of the rectification observed at high pH. From Equation 1, the differences in ICR response can be calculated, and the effect of pH and resultant surface charge ascertained. It should be noted that the ICR response can be considered by a simple ratio of current values, but a logarithmic relationship affords closer inspection for systems which exhibit reversals in rectification.
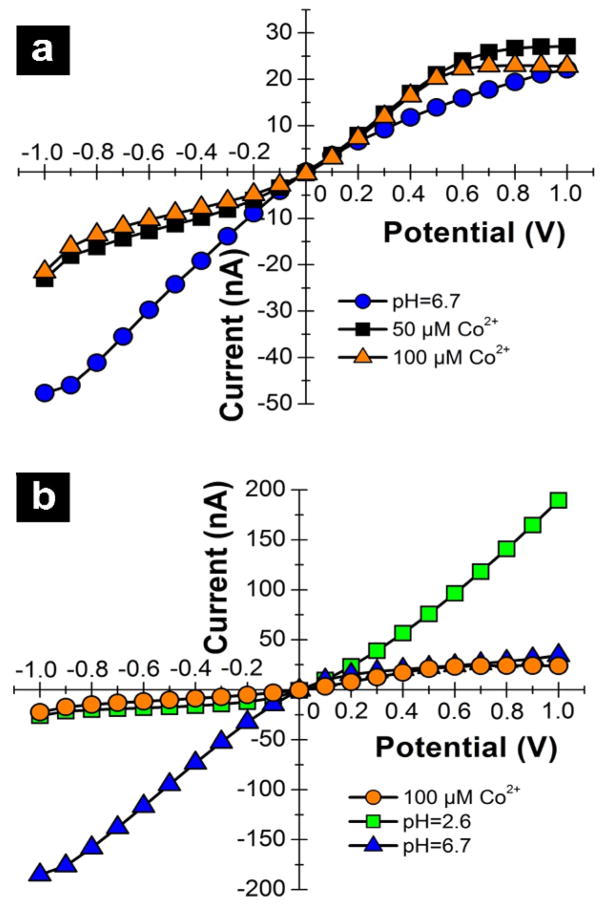
Previous reports have described the use of DHI for sequestration of divalent metal ions at surfaces46, 47, 48, 49. Here, we are interested in examining the binding and subsequent release of a metal ion, to develop a nanopore which can be regenerated. To test this approach, cobalt acetate was added to an external solution bathing DHI-modified nanopipettes. The current-voltage responses to 0.1 M KCl at pH 6.7 prior to and after the addition of two aliquots of cobalt acetate are plotted in Figure 3a. The initial current voltage response at pH 6.7 is similar to the response shown in Figure 2c. Addition of cobalt ions has the net effect of decreasing the ICR ratio, from 1.87 (pH 6.7) to 0.53 (50 μM Co2+). An increase the solution concentration to 100 μM results in little change in ICR response, suggesting that DHI sites capable of complexing cobalt are saturated at these concentrations. Interestingly, the current-voltage response in the presence of Co2+ appears more complex than for a surface of pure cationic or anionic charge. Presently, this complexity is not understood, but possibly arises from the Co2+-ligand interactions or Co2+ solubility50, 51, as the effects are not observed in the case of simple protonation of the imidazole.
Figure 3.
(a) Current-voltage response of a DHI-modified nanopipette without Co2+ ( ); Current-voltage response with 50 μM Co(II) added to bulk electrolyte (
); Current-voltage response with 50 μM Co(II) added to bulk electrolyte ( ); Current-voltage response with 100 μM Co2+ in bulk electrolyte (
); Current-voltage response with 100 μM Co2+ in bulk electrolyte ( ); All measurements were performed in 0.1 M KCl, 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH=6.7), present both in the nanopipette and the bulk electrolyte; (b) Current-voltage response with 100 μM Co2+ (
); All measurements were performed in 0.1 M KCl, 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH=6.7), present both in the nanopipette and the bulk electrolyte; (b) Current-voltage response with 100 μM Co2+ ( );Current-voltage response after altering pH of bulk electrolyte to 2.6 (
);Current-voltage response after altering pH of bulk electrolyte to 2.6 ( );Current-voltage response after altering bulk electrolyte pH back to 6.7 (
);Current-voltage response after altering bulk electrolyte pH back to 6.7 ( )
)
To regenerate the nanopipette sensor, the DHI-modified nanopipette with adsorbed Co2+ ions was soaked in a low pH solution, in which protons displace the bound cobalt ions. Immersing the nanopipette in a solution of intermediate pH results in regeneration of suitable binding sites for metal ions. The cycle used is shown in Figure 3b, where the ICR response first indicates protonation of surface sites and subsequent return to the initial state observed for DHI-modified nanopipettes. Additional exposure to cobalt ions resulted in current-voltage responses similar to those observed in Figure 3a (see supporting information).
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have examined DHI-modified nanopipettes and the current-voltage response of these nanopipettes to changes in pH and divalent metal ions. Through examination of the ICR response, a qualitative picture of the surface charge for the nanopipette was attained. Binding of cobalt was demonstrated, and regeneration of the binding sites was shown. These results suggest that with properly selected recognition elements with intermediate binding affinities, reversible nanopore sensors can be developed. A significant challenge, however, lies in the development of selective sensors that bind reversibly. Future efforts aim to develop a renewable nanopipette sensor which displays high selectivity for different species of metal ions and further explores titrations, limits of detection and analytical performance of these interesting electrochemical devices.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The support of the American Heart Association, Research Corporation and National Institutes of Health are gratefully acknowledged.
References
- 1.Hille B. Ion channels of excitable membranes. Sinauer Assocates Inc; Sunderland, MA: 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cheng LJ, Guo LJ. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:923–938. doi: 10.1039/b822554k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vlassiouk I, Kozel TR, Siwy ZS. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:8211–8220. doi: 10.1021/ja901120f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Siwy ZS, Howorka S. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:1115–1132. doi: 10.1039/b909105j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Howorka S, Siwy Z. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:2360–2384. doi: 10.1039/b813796j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ying LM. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37:702–706. doi: 10.1042/BST0370702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mak AC, Osterfeld SJ, Yu H, Wang SX, Davis RW, Jejelowo OA, Pourmand N. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;25:1635–1639. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2009.11.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Song LZ, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE. Science. 1996;274:1859–1866. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5294.1859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Braha O, Gu LQ, Zhou L, Lu XF, Cheley S, Bayley H. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:1005–1007. doi: 10.1038/79275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.White RJ, Ervin EN, Yang T, Chen X, Daniel S, Cremer PS, White HS. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:11766–11775. doi: 10.1021/ja073174q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li JL, Gershow M, Stein D, Brandin E, Golovchenko JA. Nat Mater. 2003;2:611–615. doi: 10.1038/nmat965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Storm AJ, Storm C, Chen JH, Zandbergen H, Joanny JF, Dekker C. Nano Lett. 2005;5:1193–1197. doi: 10.1021/nl048030d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang B, Galusha J, Shiozawa PG, Wang GL, Bergren AJ, Jones RM, White RJ, Ervin EN, Cauley CC, White HS. Anal Chem. 2007;79:4778–4787. doi: 10.1021/ac070609j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.White RJ, Ervin EN, Yang T, Chen X, Daniel S, Cremer PS, White HS. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:11766–11775. doi: 10.1021/ja073174q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.White HS, Bund A. Langmuir. 2008;24:2212–2218. doi: 10.1021/la702955k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shim JH, Kim J, Cha GS, Nam H, White RJ, White HS, Brown RB. Anal Chem. 2007;79:3568–3574. doi: 10.1021/ac061984z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ding S, Gao CL, Gu LQ. Anal Chem. 2009;81:6649–6655. doi: 10.1021/ac9006705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Heins EA, Baker LA, Siwy ZS, Mota M, Martin CR. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109:18400–18407. doi: 10.1021/jp052341a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Heins EA, Siwy ZS, Baker LA, Martin CR. Nano Lett. 2005;5:1824–1829. doi: 10.1021/nl050925i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mara A, Siwy Z, Trautmann C, Wan J, Kamme F. Nano Lett. 2004;4:497–501. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Siwy Z, Trofin L, Kohli P, Baker LA, Trautmann C, Martin CR. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:5000–5001. doi: 10.1021/ja043910f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Odom DJ, Baker LA, Martin CR. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109:20887–20894. doi: 10.1021/jp0524983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huang GS, Wu XL, Yang LW, Shao XF, Siu GG, Chu PK. Appl Phys A. 2005;81:1345–1349. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shan YH, Kalkan AK, Peng CY, Fonash SJ. Nano Lett. 2004;4:2085–2089. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen Y, Wang X, Hong MK, Erramilli S, Mohanty P, Rosenberg C. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91:243511–4. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wei C, Bard AJ, Feldberg SW. Anal Chem. 1997;69:4627–4633. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Karhanek M, Kemp JT, Pourmand N, Davis RW, Webb CD. Nano Lett. 2005;5:403–407. doi: 10.1021/nl0480464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Umehara S, Karhanek M, Davis RW, Pourmand N. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:4611–4616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900306106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Umehara S, Pourmand N, Webb CD, Davis RW, Yasuda K, Karhanek M. Nano Lett. 2006;6:2486–2492. doi: 10.1021/nl061681k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Piper JD, Clarke RW, Korchev YE, Ying LM, Klenerman D. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:16462–16463. doi: 10.1021/ja0650899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fu YQ, Tokuhisa H, Baker LA. Chem Commun (Cambridge, U K) 2009:4877–4879. doi: 10.1039/b910511e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kececi K, Sexton LT, Buyukserin F, Martin CR. Nanomedicine. 2008;3:787–796. doi: 10.2217/17435889.3.6.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yameen B, Ali M, Neumann R, Ensinger W, Knoll W, Azzaroni O. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:2070–2071. doi: 10.1021/ja8086104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Siwy Z, Heins E, Harrell CC, Kohli P, Martin CR. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:10850–10851. doi: 10.1021/ja047675c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ali M, Ramirez P, Mafe S, Neumann R, Ensinger W. ACS Nano. 2009;3:603–608. doi: 10.1021/nn900039f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fischer BE, Spohr R. Rev Mod Phys. 1983;55:907. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jin P, Mukaibo H, Horne LP, Bishop GW, Martin CR. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:2118–2119. doi: 10.1021/ja909335r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Siwy Z, Fulinski A. Phys Rev Lett. 2002;89:198103–4. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.198103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Karnik R, Duan CH, Castelino K, Daiguji H, Majumdar A. Nano Lett. 2007;7:547–551. doi: 10.1021/nl062806o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Miller SA, Kelly KC, Timperman AT. Lab Chip. 2008;8:1729–1732. doi: 10.1039/b808179d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wanunu M, Meller A. Nano Lett. 2007;7:1580–1585. doi: 10.1021/nl070462b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nilsson J, Lee JRI, Ratto TV, Letant SE. Adv Mater (Weinheim, Ger) 2006;18:427–431. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Parks GA. Chem Rev (Washington, DC, U S) 1965;65:177–198. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Daiguji H, Oka Y, Shirono K. Nano Lett. 2005;5:2274–2280. doi: 10.1021/nl051646y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Siwy Z, Apel P, Dobrev D, Neumann R, Spohr R, Trautmann C, Voss K. Nucl Instr and Meth B. 2003;208:143–148. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Taewook Kang YP, Choi Kyunghee, Lee Jeong Sang, Yi Jongheop. J Mater Chem. 2004;14:1043–1049. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Park HJ, Tavlarides LL. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2008;47:3401–3409. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ito T, Citterio D, Buhlmann P, Umezawa Y. Langmuir. 1999;15:2788–2793. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Canham SM, Bass JY, Navarro O, Lim SG, Das N, Blum SA. Organometallics. 2008;27:2172–2175. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Powell MR, Sullivan M, Vlassiouk I, Constantin D, Sudre O, Martens CC, Eisenberg RS, Siwy ZS. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3:51–57. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Innes L, Powell MR, Vlassiouk I, Martens C, Siwy ZS. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114:8126–8134. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.