Abstract
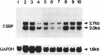
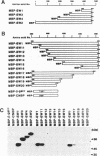
We previously identified a G-rich silencer element involved in negative regulation of catalase gene expression in some hepatoma cells (Mol. Cell. Biol., (1992), 12, 2525-2533). To study a nuclear binding protein for this element, we screened cDNA libraries from a rat ascites hepatoma cell line by binding with a synthetic oligonucleotide probe and obtained several clones. One of them, designated SW, was studied in detail. A clone (SW2) of this series contained a near full length cDNA encoding a putative peptide with 463 amino acid residues. We isolated this peptide as a fusion protein. It was found that the protein strongly bound to the C-stretch of the DNA sequence in a single strand specific fashion, but absolutely did not to G-rich sequence. The protein bound weakly to the corresponding double-stranded DNA as well as to C-rich RNA sequence. This protein, though not the expected one, was found to be a novel protein whose DNA binding domain was located on the region containing at least 75 amino acid residues of the carboxyl terminus. A proline rich region was also observed in the middle part of the protein. Northern blot profiles indicated extensive and slight expression of both 2.0 kb and 2.7 kb mRNA species in some hepatoma cell lines and in the rat liver, respectively.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bause E. Structural requirements of N-glycosylation of proteins. Studies with proline peptides as conformational probes. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):331–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2090331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel F., Alzari P. M., Ferrara P., Zakin M. M. Cloning and sequencing of PYBP, a pyrimidine-rich specific single strand DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5237–5245. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael E. P., Roome J. M., Wahl A. F. Binding of a sequence-specific single-stranded DNA-binding factor to the simian virus 40 core origin inverted repeat domain is cell cycle regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):408–420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleghon V., Klessig D. F. Characterization of the nucleic acid binding region of adenovirus DNA binding protein by partial proteolysis and photochemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17872–17881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Protein phosphorylation and hormone action. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 22;234(1275):115–144. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Identification of the human c-myc protein nuclear translocation signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4048–4054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann W., Kröger B., Goller M., Horak I. A recombination hotspot in the LTR of a mouse retrotransposon identified in an in vitro system. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):937–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdile L. F., Heyer W. D., Kolodner R., Kelly T. J. Characterization of a cDNA encoding the 70-kDa single-stranded DNA-binding subunit of human replication protein A and the role of the protein in DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12090–12098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavin M., Strauss F. Multiple sequence-specific single-strand-binding proteins for the promoter region of the rat albumin gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;10(2):113–118. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Strauss F. Sequence-specific single-strand-binding protein for the simian virus 40 early promoter stimulates transcription in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Boshart M., Lupp B., Bosserhoff A., Frank R. W., Schütz G. The rat poly pyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) interacts with a single-stranded DNA motif in a liver-specific enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1243–1249. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C., Snyder R. O., Wold M. S. Binding properties of replication protein A from human and yeast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3050–3059. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraiso T., Nomoto S., Yamazaki H., Mishima Y., Kominami R. A single-stranded DNA binding protein from mouse tumor cells specifically recognizes the C-rich strand of the (AGG:CCT)n repeats that can alter DNA conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6631–6635. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Taylor A. K., Andalibi A., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J. Identification of a zinc finger protein that binds to the sterol regulatory element. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):640–643. doi: 10.1126/science.2562787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ito K., Kohara H., Yamaguchi Y., Adachi K., Endo H. Negative regulation of catalase gene expression in hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2525–2533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliet P. R., Hall F. L., Mitchell J. P., Hardie D. G. Identification of a novel proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinase in rat pheochromocytoma. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16292–16298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkison W. O., Min H. Y., Claffey K. P., Satterberg B. L., Spiegelman B. M. Control of the adipsin gene in adipocyte differentiation. Identification of distinct nuclear factors binding to single- and double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):477–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Nomoto S., Mishima Y., Kominami R. A 35-kDa protein binding to a cytosine-rich strand of hypervariable minisatellite DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12311–12316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee H. A., Wong A. K., van de Sande J. H., Rattner J. B. Identification of novel single-stranded d(TC)n binding proteins in several mammalian species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):949–953. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]