Abstract
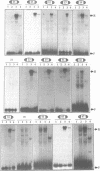
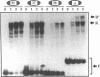
We have used the technique known as selected and amplified binding (SAAB) to isolate binding sites for the yeast transcription factor RAP1 from a degenerate pool of oligonucleotides. A total of 47 sequences were isolated, of which two were shown to be contaminating non-RAP1 binding sites. After excluding these two sequences the remainder of the sequences were used to derive a new consensus binding site for RAP1. The new consensus 5' A/G T A/G C A C C C A N N C C/A C C 3' is a significant extension of the existing consensus (4). It is longer by two base pairs at the 5' end and is significantly more constrained at the 3' end. An analysis of the combinations of mis-matches in individual SAAB sequences, compared to the consensus RAP1 binding site, has allowed us to analyse the structure of the RAP1 binding site in some detail. The binding site can be sub-divided into three regions; a core binding site, a 5' flanking region and a 3' flanking region. The core binding site, consisting of the sequence 5'CACCCA3', is critical for recognition by RAP1. The less conserved flanking regions are not as important. Interactions between RAP1 and these regions probably stabilise the interaction between RAP1 and the core binding site. Each of the sequences isolated in the SAAB analysis was used to search release 78 of the EMBL+GenBank DNA data base. The searches identified 102 potential binding sites for RAP1 within promoters of yeast genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capieaux E., Vignais M. L., Sentenac A., Goffeau A. The yeast H+-ATPase gene is controlled by the promoter binding factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7437–7446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Stanway C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. The UAS of the yeast PGK gene is composed of multiple functional elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8245–8260. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A., Tsang J. S., Stanway C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Transcriptional control of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene by RAP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5516–5524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin C., Tice-Baldwin K., Shore D., Arndt K. T. RAP1 is required for BAS1/BAS2- and GCN4-dependent transcription of the yeast HIS4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3642–3651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Marguet D., Lauquin G. J. Downstream activating sequence within the coding region of a yeast gene: specific binding in vitro of RAP1 protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Dec;236(1):65–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00279644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F., Sussel L., Shore D. A RAP1-interacting protein involved in transcriptional silencing and telomere length regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):801–814. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry Y. A., Chambers A., Tsang J. S., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Characterisation of the DNA binding domain of the yeast RAP1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2617–2623. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A. TUF, the yeast DNA-binding factor specific for UASrpg upstream activating sequences: identification of the protein and its DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3648–3652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz S., Shore D. RAP1 protein activates and silences transcription of mating-type genes in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):616–628. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrion G., Liu K., Liu C., Lustig A. J. RAP1 and telomere structure regulate telomere position effects in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1146–1159. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., Wilson N. M., Petracek M. E., Berman J. A yeast telomere binding activity binds to two related telomere sequence motifs and is indistinguishable from RAP1. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):225–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00422108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay V. L. Cloning of yeast STE genes in 2 microns vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:325–343. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. E., Stanway C., Kim S., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene depends on an upstream activation sequence but does not require TATA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4335–4343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D., Courey A. J. The same dorsal binding site mediates both activation and repression in a context-dependent manner. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. A sensitive method for the determination of protein-DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6197–6204. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussel L., Shore D. Separation of transcriptional activation and silencing functions of the RAP1-encoded repressor/activator protein 1: isolation of viable mutants affecting both silencing and telomere length. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7749–7753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Sentenac A. Asymmetric DNA bending induced by the yeast multifunctional factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Woudt L. P., Wassenaar G. M., Mager W. H., Sentenac A., Planta R. J. Specific binding of TUF factor to upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1451–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne J., Treisman R. SRF and MCM1 have related but distinct DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3297–3303. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]