Abstract
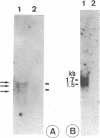
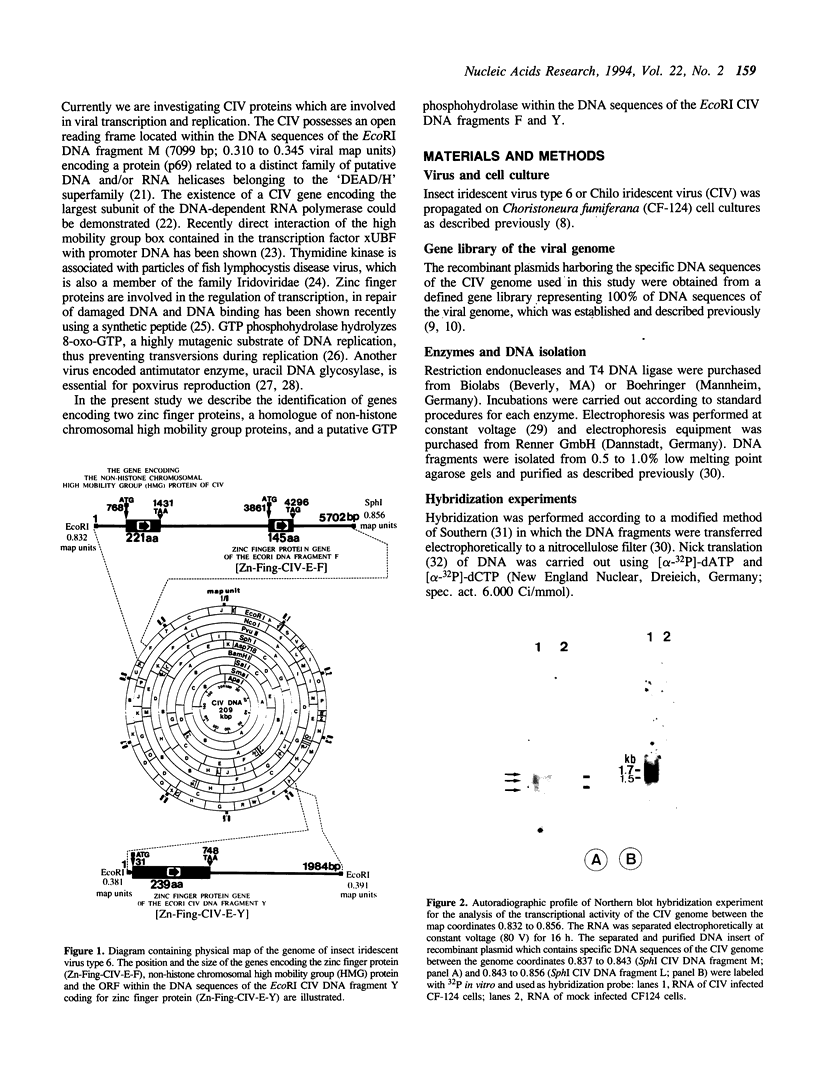
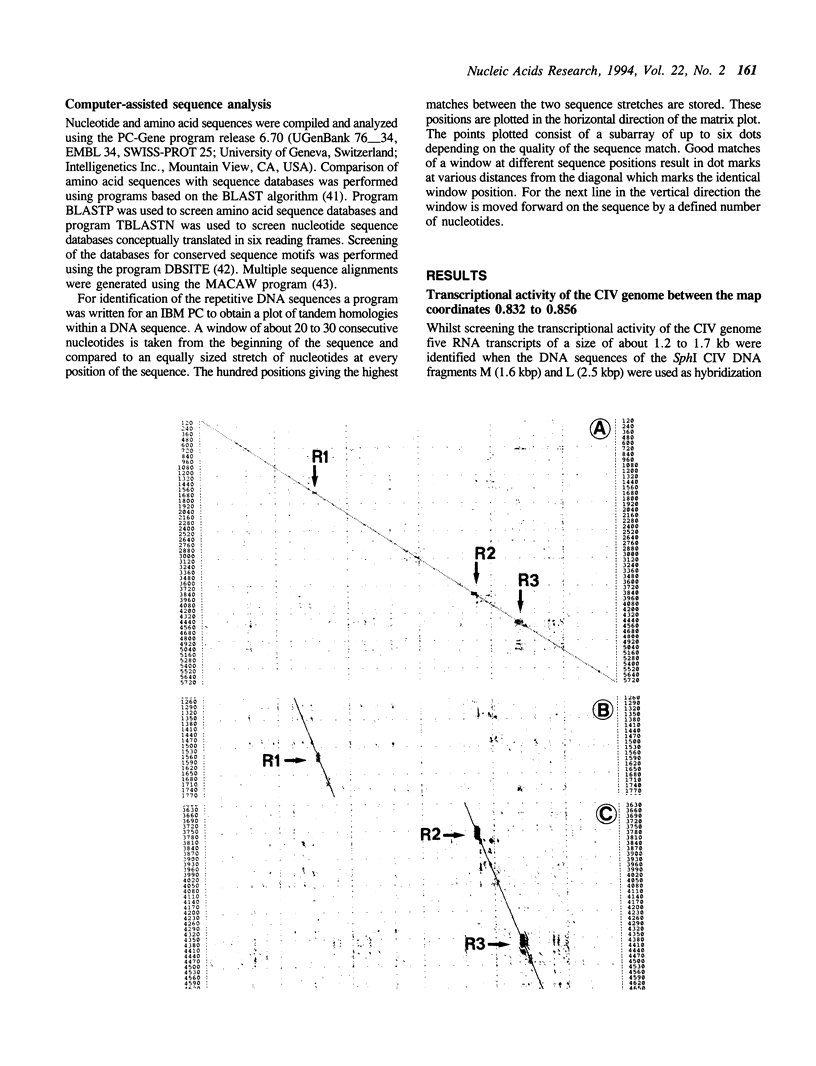
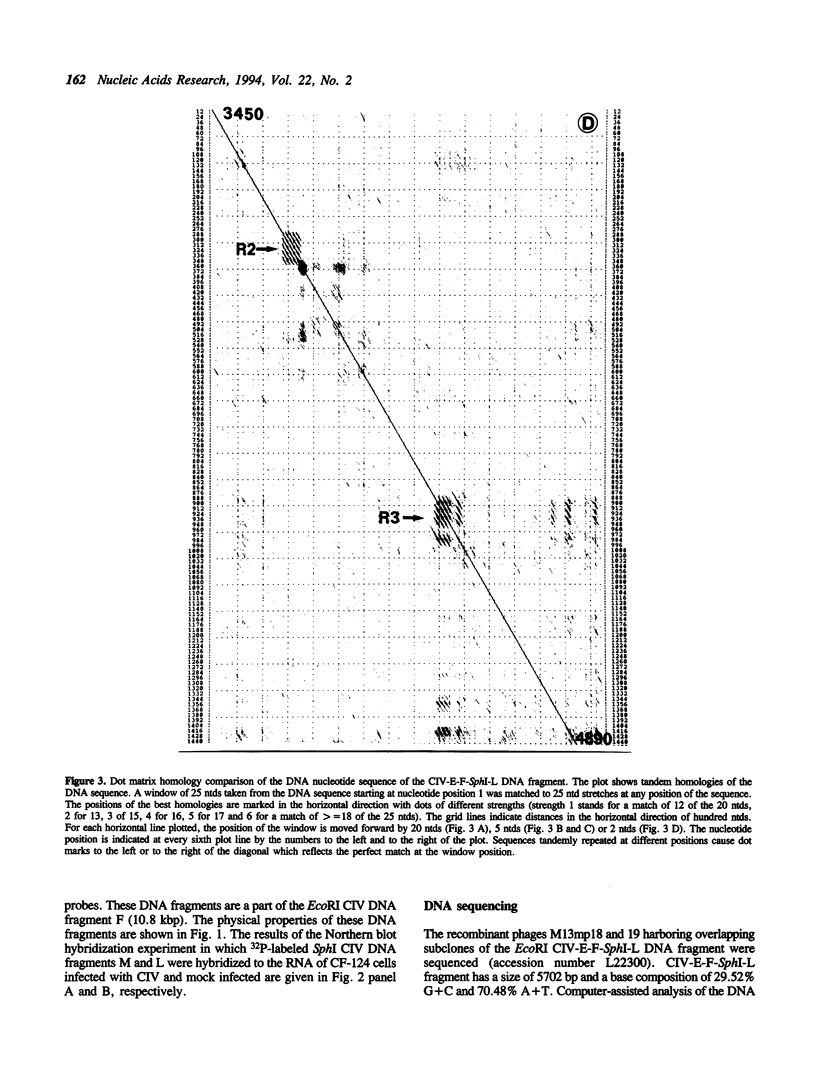
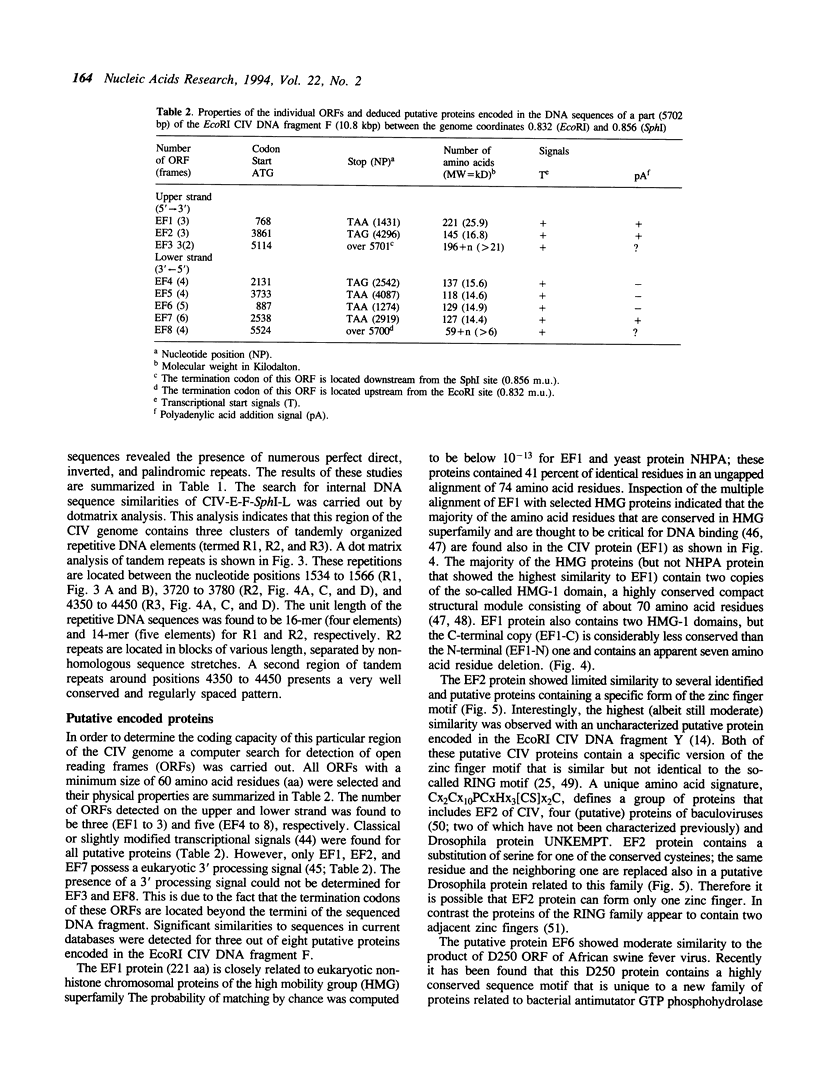
Five RNA transcripts of about 1.2 to 1.7 kilobases were mapped to a part of the genome of insect iridescent virus type 6 (Chilo iridescent virus; CIV) between genome coordinates 0.832 and 0.856 within the EcoRI DNA fragment F. The nucleotide sequence of this particular region (5702 base pairs) of the CIV genome was determined. The DNA sequence contains a number of perfect direct, inverted, and palindromic repeats including three clusters of tandemly organized repetitive DNA elements located between the nucleotide positions 1534 to 1566, 3720 to 3780, and 4350 to 4450. Eight long open reading frames (ORFs; EF1 to 8) were detected in the sequenced region of the CIV genome. ORF EF1 encodes a putative protein of 221 amino acid residues (aa) that is closely related to eukaryotic nonhistone chromosomal proteins of the high mobility group (HMG) superfamily. Virus encoded homologues of HMG proteins have not been reported so far. The EF2 gene product (145 aa) contains a specific zinc finger motif and belongs to a distinct group of identified and putative zinc finger proteins including a second putative protein (239 aa) of CIV encoded in the EcoRI DNA fragment Y (1984 bp; 0.381 to 0.391 viral map units). The product of EF6 (127 aa) is related to D250 ORF product of African swine fever virus (ASFV) and belongs to the recently described protein family sharing a highly conserved sequence motif with bacterial antimutator GTP phosphohydrolase MutT. Thus the sequenced region of the CIV genome encodes three putative proteins which may be directly involved in the replication and/or transcription of the viral DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama M., Horiuchi T., Sekiguchi M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the mutT mutator of Escherichia coli that causes A:T to C:G transversion. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jan;206(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00326530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M., Britton B. S., Mason C., Boursnell M. E. Analysis of the fowlpox virus genome region corresponding to the vaccinia virus D6 to A1 region: location of, and variation in, non-essential genes in poxviruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2873–2881. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunagel S. C., Daniel K. D., Reilly L. M., Guarino L. A., Hong T., Summers M. D. Sequence, genomic organization of the EcoRI-A fragment of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus, and identification of a viral-encoded protein resembling the outer capsid protein VP8 of rotavirus. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):1003–1008. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90281-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey G. P., Lescott T., Robertson J. S., Spencer L. K., Kelly D. C. Three African isolates of small iridescent viruses: type 21 from Heliothis armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), type 23 from Heteronychus arator (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae), and type 28 from Lethocerus columbiae (Hemiptera Heteroptera: Belostomatidae). Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):307–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti M., Devauchelle G. Inhibition of macromolecular synthesis in cells infected with an invertebrate virus (iridovirus type 6 or CIV). Arch Virol. 1980;63(3-4):297–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01315036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti M., Devauchelle G. Isolation and reconstitution of chilo iridescent virus membrane. Arch Virol. 1982;74(2-3):145–155. doi: 10.1007/BF01314708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. Initiation of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17721–17724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook N. E., Clem R. J., Miller L. K. An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2168–2174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2168-2174.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darai G., Delius H., Clarke J., Apfel H., Schnitzler P., Flügel R. M. Molecular cloning and physical mapping of the genome of fish lymphocystis disease virus. Virology. 1985 Oct 30;146(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. DNA analysis of insect iridescent virus 6: evidence for circular permutation and terminal redundancy. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):609–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.609-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M., Schnitzler P., Delius H., Darai G. Identification and characterization of the repetitive DNA element in the genome of insect iridescent virus type 6. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):485–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M., Schnitzler P., Scholz J., Rösen-Wolff A., Delius H., Darai G. DNA nucleotide sequence analysis of the PvuII DNA fragment L of the genome of insect iridescent virus type 6 reveals a complex cluster of multiple tandem, overlapping, and interdigitated repetitive DNA elements. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):497–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Lisowsky T., Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. DNA wrapping and bending by a mitochondrial high mobility group-like transcriptional activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3358–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Darai G., Gelderblom H. Viral proteins and adenosine triphosphate phosphohydrolase activity of fish lymphocystis disease virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard A. D., Borrow J., Freemont P. S., Solomon E. Characterization of a zinc finger gene disrupted by the t(15;17) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1720570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handermann M., Schnitzler P., Rösen-Wolff A., Raab K., Sonntag K. C., Darai G. Identification and mapping of origins of DNA replication within the DNA sequences of the genome of insect iridescent virus type 6. Virus Genes. 1992 Jan;6(1):19–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01703754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Itoh Y., Frank M. B. Protein heterogeneity in the human Ro/SSA ribonucleoproteins. The 52- and 60-kD Ro/SSA autoantigens are encoded by separate genes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):177–186. doi: 10.1172/JCI114968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. J., Duncan C. H. Full length cDNA sequence for bovine high mobility group 1 (HMG1) protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10375–10375. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodrubetz D., Burgum A. Duplicated NHP6 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encode proteins homologous to bovine high mobility group protein 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3234–3239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V. A highly conserved sequence motif defining the family of MutT-related proteins from eubacteria, eukaryotes and viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 11;21(20):4847–4847. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.20.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsman D., Bustin M. Assessment of the transcriptional activation potential of the HMG chromosomal proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4483–4489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc B., Read C., Moss T. Recognition of the Xenopus ribosomal core promoter by the transcription factor xUBF involves multiple HMG box domains and leads to an xUBF interdomain interaction. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):513–525. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. Y., Arif B., Dobos P., Krell P. Identification of bent DNA and ARS fragments in the genome of Choristoneura fumiferana nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virus Res. 1992 Aug;24(3):249–264. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90122-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovering R., Hanson I. M., Borden K. L., Martin S., O'Reilly N. J., Evan G. I., Rahman D., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J., Freemont P. S. Identification and preliminary characterization of a protein motif related to the zinc finger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki H., Sekiguchi M. MutT protein specifically hydrolyses a potent mutagenic substrate for DNA synthesis. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):273–275. doi: 10.1038/355273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merenmies J., Pihlaskari R., Laitinen J., Wartiovaara J., Rauvala H. 30-kDa heparin-binding protein of brain (amphoterin) involved in neurite outgrowth. Amino acid sequence and localization in the filopodia of the advancing plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16722–16729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J., Weiss N., Murli S., Mohammadi S., Vani K., Vasilakis G., Song C. H., Epstein A., Kuang T., English J. The embryonically active gene, unkempt, of Drosophila encodes a Cys3His finger protein. Genetics. 1992 Jun;131(2):377–388. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena L., Yáez R. J., Revilla Y., Viñuela E., Salas M. L. African swine fever virus guanylyltransferase. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):319–328. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentecost B. T., Wright J. M., Dixon G. H. Isolation and sequence of cDNA clones coding for a member of the family of high mobility group proteins (HMG-T) in trout and analysis of HMG-T-mRNA's in trout tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4871–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. L., Rohrmann G. F. The p6.5 gene region of a nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Orgyia pseudotsugata: DNA sequence and transcriptional analysis of four late genes. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):551–560. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzler P., Darai G. Characterization of the repetitive DNA elements in the genome of fish lymphocystis disease viruses. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):32–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzler P., Soltau J. B., Fischer M., Reisner H., Scholz J., Delius H., Darai G. Molecular cloning and physical mapping of the genome of insect iridescent virus type 6: further evidence for circular permutation of the viral genome. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):66–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. A workbench for multiple alignment construction and analysis. Proteins. 1991;9(3):180–190. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag K. C., Darai G. Characterization of the third origin of DNA replication of the genome of insect iridescent virus type 6. Virus Genes. 1992 Nov;6(4):333–342. doi: 10.1007/BF01703082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohwasser R., Raab K., Schnitzler P., Janssen W., Darai G. Identification of the gene encoding the major capsid protein of insect iridescent virus type 6 by polymerase chain reaction. J Gen Virol. 1993 May;74(Pt 5):873–879. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-5-873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer D. S., Jerng H. H., O'Connor K. Sequence and analysis of a portion of the genomes of Shope fibroma virus and malignant rabbit fibroma virus that is important for viral replication in lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90529-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. T., Upton C., Higman M. A., Niles E. G., McFadden G. A poxvirus-encoded uracil DNA glycosylase is essential for virus viability. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2503–2512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2503-2512.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton C., Stuart D. T., McFadden G. Identification of a poxvirus gene encoding a uracil DNA glycosylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4518–4522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk R., Köster M., Pöting A., Hartmann L., Knöchel W. An antisense transcript from the Xenopus laevis bFGF gene coding for an evolutionarily conserved 24 kd protein. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2983–2988. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08448.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Kraulis P. J., Hill C. S., Raine A. R., Laue E. D., Thomas J. O. Structure of the HMG box motif in the B-domain of HMG1. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sequence-specific interaction of the HMG box proteins TCF-1 and SRY occurs within the minor groove of a Watson-Crick double helix. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]