Abstract
A method is proposed to determine the fraction of the tautomeric forms of the imidazole ring of histidine in proteins as a function of pH, provided that the observed 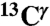 and
and 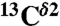 chemical shifts and the protein structure, or the fraction of H+ form, are known. This method is based on the use of quantum chemical methods to compute the 13C NMR shieldings of all the imidazole ring carbons (13Cγ,
chemical shifts and the protein structure, or the fraction of H+ form, are known. This method is based on the use of quantum chemical methods to compute the 13C NMR shieldings of all the imidazole ring carbons (13Cγ, 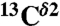 , and
, and 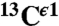 ) for each of the two tautomers, Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H, and the protonated form, H+, of histidine. This methodology enabled us (i) to determine the fraction of all the tautomeric forms of histidine for eight proteins for which the
) for each of the two tautomers, Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H, and the protonated form, H+, of histidine. This methodology enabled us (i) to determine the fraction of all the tautomeric forms of histidine for eight proteins for which the 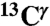 and
and 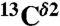 chemical shifts had been determined in solution in the pH range of 3.2 to 7.5 and (ii) to estimate the fraction of tautomeric forms of eight histidine-containing dipeptide crystals for which the chemical shifts had been determined by solid-state 13C NMR. Our results for proteins indicate that the protonated form is the most populated one, whereas the distribution of the tautomeric forms for the imidazole ring varies significantly among different histidines in the same protein, reflecting the importance of the environment of the histidines in determining the tautomeric forms. In addition, for ∼70% of the neutral histidine-containing dipeptides, the method leads to fairly good agreement between the calculated and the experimental tautomeric form. Coexistence of different tautomeric forms in the same crystal structure may explain the remaining 30% of disagreement.
chemical shifts had been determined in solution in the pH range of 3.2 to 7.5 and (ii) to estimate the fraction of tautomeric forms of eight histidine-containing dipeptide crystals for which the chemical shifts had been determined by solid-state 13C NMR. Our results for proteins indicate that the protonated form is the most populated one, whereas the distribution of the tautomeric forms for the imidazole ring varies significantly among different histidines in the same protein, reflecting the importance of the environment of the histidines in determining the tautomeric forms. In addition, for ∼70% of the neutral histidine-containing dipeptides, the method leads to fairly good agreement between the calculated and the experimental tautomeric form. Coexistence of different tautomeric forms in the same crystal structure may explain the remaining 30% of disagreement.
Keywords: histidine protonation, histidine tautomers, pH effect, side-chain conformation
Among all 20 naturally occurring amino acids, histidine (His) is a unique residue for a number of reasons, among others because ∼50% of all enzymes use His in their active sites (1). This is mainly because of the chemical versatility of its imidazole ring, which includes two neutral, chemically distinct forms, and a protonated form, referred to as Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H tautomers, and H+, respectively, with one form favored over the other by the protein environment and pH. Moreover, His with a pK° of 6.6 (2) titrates around neutral pH, allowing the deprotonated nitrogen of its imidazole ring to serve as an effective ligand for metal binding (3). In particular, it has been suggested that tautomerization and variations of χ1 of His are crucial parts of the proton-transfer process (4). In addition, it has also been recognized (5) that many imidazole-containing ligands could exhibit large chemical-shift variations when bound to a molecular target, such as a protein, offering valuable information about changes in the local structure of the ligand or target. Hence, characterization of the tautomers of drug molecules could have important consequence in the pharmaceutical industry. It is particularly interesting that the most abundant type of tautomers in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) correspond to derivatives of azoles, such as pyrazoles, imidazoles, etc. (6).
Since chemical shifts were first observed by Arnold et al. in 1951 (7), use of NMR spectroscopy to identify the different protonation states and the tautomeric states of the His residue has been the object of numerous experimental studies (4, 8–14). In addition, detailed theoretical analysis has been carried out, at the quantum chemical level of theory, to investigate the origin of the 13C NMR chemical shifts of the imidazole group of histidine (5, 15, 16). In particular, almost 40 years ago, Reynolds et al. (17) recommended “…the 13C chemical shift titration curves of the imidazole ring to determine the tautomeric form of histidyl residues in polypeptides and proteins….” Despite all this, determination of the fraction of the tautomeric forms of the imidazole ring of His in proteins in solution has been a long-standing problem in the biophysical chemistry of proteins, among other reasons because the tautomeric forms of the imidazole ring are coupled to the protonated state of His; hence, it is necessary, first, to obtain an accurate determination of the average degree of charge of His at the pH at which the NMR experiments are carried out and, second, to identify a nucleus or nuclei that could provide reliable information with which to determine the fraction of tautomers of the imidazole ring of His, unambiguously. The fact that protein structures are determined by NMR spectroscopy in the pH range of 5.8 to 7.5 (18) only exacerbates this problem because His can undergo variable states of protonation in this pH range.
In a seminal work, Cheng et al. (5) investigated the solid-state 13C NMR spectra of eight His-containing dipeptides at the quantum chemical level of theory, with the structure of all eight species obtained by X-ray crystallography, to determine the major contributions of the large chemical-shift ranges observed experimentally and the factors affecting such chemical-shift dispersion. Their study provides a physical basis for the origin of the 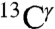 ,
, 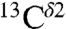 , and
, and 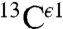 chemical-shift variation of His in peptides and shows how accurately the chemical shifts of His-containing dipeptides can be calculated by using quantum mechanical methods. For the eight dipeptide structures, investigated by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, the authors (5) determined that four structures exist only in the Nδ1-H tautomer, three in the Nϵ2-H tautomeric form and only one in the imidazolium, or protonated H+ form. Among many very interesting observations from their study (5) of His-containing dipeptides, which includes a shielding tensor-orientation analysis to understand the origin of the shielding changes associated with the tautomeric forms and hydrogen-bond formation, the authors found that (i) incorporation of a “lattice-partner” effect (or, in a protein, a “neighboring-residue” effect) would enable them to reproduce imidazole Cγ, Cδ2, and Cϵ1 NMR chemical shifts in dipeptides and (ii) knowledge of
chemical-shift variation of His in peptides and shows how accurately the chemical shifts of His-containing dipeptides can be calculated by using quantum mechanical methods. For the eight dipeptide structures, investigated by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography, the authors (5) determined that four structures exist only in the Nδ1-H tautomer, three in the Nϵ2-H tautomeric form and only one in the imidazolium, or protonated H+ form. Among many very interesting observations from their study (5) of His-containing dipeptides, which includes a shielding tensor-orientation analysis to understand the origin of the shielding changes associated with the tautomeric forms and hydrogen-bond formation, the authors found that (i) incorporation of a “lattice-partner” effect (or, in a protein, a “neighboring-residue” effect) would enable them to reproduce imidazole Cγ, Cδ2, and Cϵ1 NMR chemical shifts in dipeptides and (ii) knowledge of 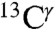 and
and 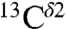 shifts would enable them, in most cases, to obtain good predictions of the tautomeric state. Despite the latter conclusion, and the availability of the structure and the 13C chemical shifts for all carbons of the imidazole rings of His for eight proteins (Table S1 and SI Text), seven of them solved by X-ray crystallography, a computation of the distribution of the tautomeric forms of these proteins, was not carried out.
shifts would enable them, in most cases, to obtain good predictions of the tautomeric state. Despite the latter conclusion, and the availability of the structure and the 13C chemical shifts for all carbons of the imidazole rings of His for eight proteins (Table S1 and SI Text), seven of them solved by X-ray crystallography, a computation of the distribution of the tautomeric forms of these proteins, was not carried out.
Regarding conclusion (i) above, even if a single structure is determined accurately, as in X-ray crystallography, the coexistence of protein conformations in solution (from which the 13C chemical shifts are observed) requires the evaluation of the chemical shifts of each member of an ensemble, rather than a single conformation, making the computational task of considering the lattice-partner effect, e.g., hydrogen-bond effects for each imidazole ring of His during the computation of the chemical shifts at the quantum chemical level of theory, almost impossible. To solve this problem, some approximation must be adopted. Considering that the shielding variations observed for the 13C carbons of the imidazole ring of His are determined mainly by their tautomeric forms (5), it is reasonable to assume that other contributions, such as those that arise from hydrogen-bond effects, can be considered as minor contributions because such effects are likely to be averaged out in the ensemble of conformations. Evidence for the validity of this assumption for the nuclei of interest, Cγ, Cδ2 and Cϵ1, is provided in Results and Discussion by comparing the variation of the computed shielding ranges with observed chemical-shift data for proteins, from the Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank (BMRB) (19), and for eight dipeptide structures listed in Table S2.
Therefore, the goal of this investigation is to develop a method to determine the fraction of tautomeric forms of His in proteins in solution as a function of the pH. This is an important problem for a number of reasons: (i) Proteins in solution exist as an ensemble of conformations with a population of rapidly interconverting tautomers, at a given fixed pH; (ii) the chemical shifts for proteins are usually determined in neutral or acidic solutions in which His may be protonated, e.g., the chemical shifts of the above-mentioned set of eight proteins listed in Table S1 were obtained in the pH range of 3.2 to 7.5 (5), and, hence, the protonation of each His residue in a given protein may vary significantly with the environment; (iii) determination of the tautomeric content of His, at a given pH, will be useful for assigning the location of hydrogen atoms in protein structures; (iv) because the exchange between different protonation states is assumed to occur in the fast exchange regime (4), the NMR resonances of a given nucleus, which include rotation, protonation, and tautomerization, merge into a single average signal. As to whether the information from these exchange processes can be decoded offers the possibility to determine the extent to which the His residues in proteins behave as free His, where the Nϵ2-H tautomer is favored over the Nδ1-H tautomer in a ratio of 4∶1 (17); and (v) the existing solid-state NMR data for His-containing dipeptides offer the possibility to analyze the tautomeric content in crystals.
Results and Discussion
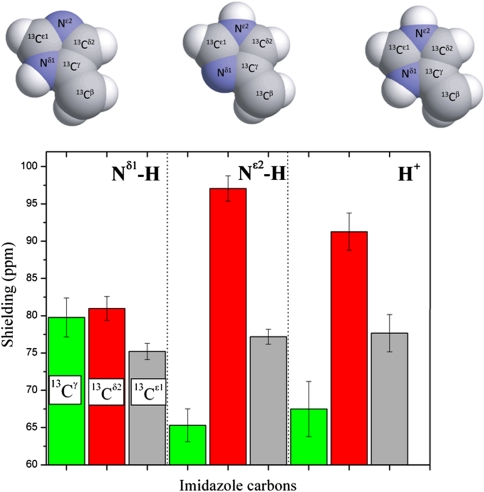
Fig. 1 shows the computed shielding values for each form of the imidazole ring of His in a model tripeptide. Focusing on the computed relative heights of the bars in Fig. 1, it can be seen that the 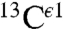 nucleus (gray bars in Fig. 1) is not sensitive to changes in the form of the imidazole ring. Therefore, we confine our interest to those nuclei that are sensitive to such changes, namely
nucleus (gray bars in Fig. 1) is not sensitive to changes in the form of the imidazole ring. Therefore, we confine our interest to those nuclei that are sensitive to such changes, namely 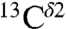 and
and 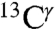 (red and green bars, respectively, in Fig. 1), for each of the two tautomeric forms of the imidazole ring of His and the H+ form. Hence, we carry out a validation analysis of the computed ranges of shielding variations only for
(red and green bars, respectively, in Fig. 1), for each of the two tautomeric forms of the imidazole ring of His and the H+ form. Hence, we carry out a validation analysis of the computed ranges of shielding variations only for 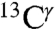 and
and 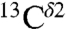 , using chemical-shift data deposited in the BMRB (19), and data from solid-state NMR (5). This is accomplished by comparing the histogram of the computed shielding distribution to the histogram of the observed chemical-shift distribution obtained from the BMRB. Then, a series of applications to eight different proteins listed in Table S1 and to eight His-containing dipeptides (5) are discussed.
, using chemical-shift data deposited in the BMRB (19), and data from solid-state NMR (5). This is accomplished by comparing the histogram of the computed shielding distribution to the histogram of the observed chemical-shift distribution obtained from the BMRB. Then, a series of applications to eight different proteins listed in Table S1 and to eight His-containing dipeptides (5) are discussed.
Fig. 1.
(Top) Space-filling-sphere representation of the forms of the imidazole ring of His: Nδ1-H, Nϵ2-H, and H+. (Bottom) Bar diagram of the computed shielding values for each carbon of the imidazole ring of His for each of the two tautomers: Nδ1-H, Nϵ2-H, and for the H+ form in the model tripeptide Ac-GHG-NMe. For each carbon of the imidazole ring, the height of the bar represents the mean value, σ∘, of the Gaussian function that fits the histogram of the computed shielding distribution for each of ∼35,000 conformations of histidine in the model tripeptide, and the vertical lines at the top of the bars the corresponding standard deviations (see Materials and Methods). Green, red, and gray colors indicate the results obtained for the 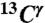 ,
, 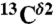 , and
, and 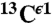 nuclei, respectively.
nuclei, respectively.
Validation Using BMRB-Obtained Data.
The deposited chemical shifts for His residues in proteins in the BMRB are a very important source of data for comparison with the computed range of shielding variations of the 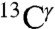 (green bars) and
(green bars) and 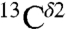 (red bars) nuclei of the imidazole ring of His in Fig. 1. For each of these nuclei, 84 and 2,267 observed chemical shifts, respectively, were deposited in the BMRB (as of October 2010). The range of the observed chemical-shift variations, computed as the difference between maximum and minimum chemical shifts, are 14.5 ppm and 18.6 ppm, for the
(red bars) nuclei of the imidazole ring of His in Fig. 1. For each of these nuclei, 84 and 2,267 observed chemical shifts, respectively, were deposited in the BMRB (as of October 2010). The range of the observed chemical-shift variations, computed as the difference between maximum and minimum chemical shifts, are 14.5 ppm and 18.6 ppm, for the 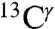 and
and 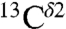 nucleus, respectively. It is important to note that these values were obtained after excluding outliers, i.e., those observed chemical shifts that are greater or smaller than 3 standard deviations from the BMRB-reported mean average value.
nucleus, respectively. It is important to note that these values were obtained after excluding outliers, i.e., those observed chemical shifts that are greater or smaller than 3 standard deviations from the BMRB-reported mean average value.
The largest difference in shielding between any of the two tautomers and the H+ form, for each of the 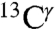 (green bars) and the
(green bars) and the 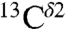 (red bars) nuclei, occurs between the Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H tautomers (Fig. 1). For any pair of these two 13C nuclei, the difference between shielding computed for these two tautomers was fit with a Gaussian function characterized by a mean value and a standard deviation. By this criterion, the following results are obtained for the largest range of computed shielding variations of the
(red bars) nuclei, occurs between the Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H tautomers (Fig. 1). For any pair of these two 13C nuclei, the difference between shielding computed for these two tautomers was fit with a Gaussian function characterized by a mean value and a standard deviation. By this criterion, the following results are obtained for the largest range of computed shielding variations of the 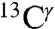 and
and 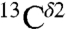 nuclei: 14.4 ± 3.5 ppm and 16.2 ± 2.5 ppm, respectively. These ranges of shielding are in good agreement with the above observed range of variation for the chemical shifts from the BMRB data, although caution must be exercised in interpreting the very good agreement for the
nuclei: 14.4 ± 3.5 ppm and 16.2 ± 2.5 ppm, respectively. These ranges of shielding are in good agreement with the above observed range of variation for the chemical shifts from the BMRB data, although caution must be exercised in interpreting the very good agreement for the 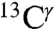 nucleus because of the low number, 84, of observed values.
nucleus because of the low number, 84, of observed values.
Validation Using Solid-State NMR Data for His-Containing Dipeptides.
As for proteins, there is a wide range of variations for the observed 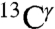 and
and 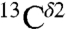 chemical shifts among all tautomeric forms of the His-containing dipeptides studied by Cheng et al. (5), namely 12.7 ppm and 13.8 ppm, respectively. These values are within the range of variations computed above for these two nuclei in the model tripeptides, namely 14.4 ± 3.5 ppm and 16.2 ± 2.5 ppm.
chemical shifts among all tautomeric forms of the His-containing dipeptides studied by Cheng et al. (5), namely 12.7 ppm and 13.8 ppm, respectively. These values are within the range of variations computed above for these two nuclei in the model tripeptides, namely 14.4 ± 3.5 ppm and 16.2 ± 2.5 ppm.
The good agreement obtained for the computed range of shielding variations compared to the chemical-shift data from both the BMRB and solid-state NMR validates our hypothesis that, from a statistical point of view, the main contribution to the observed chemical shifts, for the 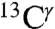 and
and 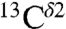 nuclei, is dominated by the tautomeric equilibria, with other contributions in the observed data, such as those arising from “local interactions,” averaged-out in an ensemble of conformations. This assumption is important because we are interested only in properties of the ensemble of conformations in solution and in the solid state, not for individual conformers (see discussion of the physical meaning of Eqs. 1 and 2 in Materials and Methods).
nuclei, is dominated by the tautomeric equilibria, with other contributions in the observed data, such as those arising from “local interactions,” averaged-out in an ensemble of conformations. This assumption is important because we are interested only in properties of the ensemble of conformations in solution and in the solid state, not for individual conformers (see discussion of the physical meaning of Eqs. 1 and 2 in Materials and Methods).
Analysis of the Histogram of the Computed Shielding Distribution in a Model Tripeptide.
We consider here the shielding distribution for each of the carbon nuclei of the imidazole ring of His.
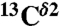 Nucleus.
Nucleus.
A plot of the histogram for the 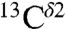 nucleus for all the imidazole ring forms of His without distinction among them shows three peaks (indicated as I, II, and III in the blue-line profile of Fig. S1A). Each of these three peaks corresponds to the most highly populated computed shielding (red bars in Fig. 1) of the Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H tautomers, and the H+ form, respectively. The histogram, given by the blue-line profile shown in Fig. S1A, is the one that would be observed if all imidazole ring tautomers of His and the H+ form were equally probable for a protein in solution. But they are not. In fact, an analysis of the histogram of the distribution of 2,267 observed
nucleus for all the imidazole ring forms of His without distinction among them shows three peaks (indicated as I, II, and III in the blue-line profile of Fig. S1A). Each of these three peaks corresponds to the most highly populated computed shielding (red bars in Fig. 1) of the Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H tautomers, and the H+ form, respectively. The histogram, given by the blue-line profile shown in Fig. S1A, is the one that would be observed if all imidazole ring tautomers of His and the H+ form were equally probable for a protein in solution. But they are not. In fact, an analysis of the histogram of the distribution of 2,267 observed 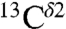 chemical shifts, from the BMRB, indicates (Fig. S1B) the existence of only two rather than three major peaks, with the peak centered at ∼119 ppm having a significantly higher frequency of the chemical-shift distribution than the other peak centered at ∼127 ppm. This observation is a clear indication that there is an imbalance in the distribution of the imidazole ring forms of His in proteins in solution and, hence, deserves further analysis.
chemical shifts, from the BMRB, indicates (Fig. S1B) the existence of only two rather than three major peaks, with the peak centered at ∼119 ppm having a significantly higher frequency of the chemical-shift distribution than the other peak centered at ∼127 ppm. This observation is a clear indication that there is an imbalance in the distribution of the imidazole ring forms of His in proteins in solution and, hence, deserves further analysis.
There is an ∼8-ppm difference between these two observed peaks in the histogram of the chemical-shift distribution for the 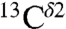 nucleus in Fig. S1B. On the other hand, the computed average shielding difference for the
nucleus in Fig. S1B. On the other hand, the computed average shielding difference for the 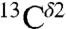 nucleus between (Nδ1-H and H+), (Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H), and (Nϵ2-H and H+) forms, respectively, are ∼10 ppm, ∼16 ppm, and ∼6 ppm, respectively (Fig. 1). Certainly, the tautomeric forms are not dominant in solution; otherwise, the observed difference, ∼8 ppm, between peaks in Fig. S1B should be larger, i.e., close to ∼16 ppm for (Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H) as in Fig. 1. This result also provides evidence that the observed peak centered at ∼127 ppm (Fig. S1B), showing lower frequency of the chemical-shift distribution, contains contributions mainly from the Nδ1-H tautomer (low shielding peak I, in Fig. S1A), whereas the observed peak centered at ∼119 ppm, showing higher frequency of the chemical-shift distribution, contains contributions from both the H+ and the Nϵ2-H form (high-shielding peaks II and III in Fig. S1A).
nucleus between (Nδ1-H and H+), (Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H), and (Nϵ2-H and H+) forms, respectively, are ∼10 ppm, ∼16 ppm, and ∼6 ppm, respectively (Fig. 1). Certainly, the tautomeric forms are not dominant in solution; otherwise, the observed difference, ∼8 ppm, between peaks in Fig. S1B should be larger, i.e., close to ∼16 ppm for (Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H) as in Fig. 1. This result also provides evidence that the observed peak centered at ∼127 ppm (Fig. S1B), showing lower frequency of the chemical-shift distribution, contains contributions mainly from the Nδ1-H tautomer (low shielding peak I, in Fig. S1A), whereas the observed peak centered at ∼119 ppm, showing higher frequency of the chemical-shift distribution, contains contributions from both the H+ and the Nϵ2-H form (high-shielding peaks II and III in Fig. S1A).
The above conclusion, that the highest frequency of the chemical-shift distribution contains contributions from both the H+ form and the Nϵ2-H tautomer, is not surprising given that the structures of most of the proteins in solution are determined in a pH range where His is mostly protonated, rather than neutral. To illustrate this qualitatively, we arbitrarily assume that 70% of the total computed 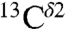 shielding in Fig. S1A came from the H+ form with the remaining 30% provided by the Nδ1-H (15%) and Nϵ2-H (15%) tautomers, respectively. With this assumption, the histogram of the shielding distribution shows a profile given by the red line in Fig. S1A, which exhibits two rather than three peaks and resembles the one observed from the histogram of the
shielding in Fig. S1A came from the H+ form with the remaining 30% provided by the Nδ1-H (15%) and Nϵ2-H (15%) tautomers, respectively. With this assumption, the histogram of the shielding distribution shows a profile given by the red line in Fig. S1A, which exhibits two rather than three peaks and resembles the one observed from the histogram of the 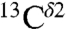 chemical-shift distribution (centered at ∼119 ppm) obtained from the BMRB (Fig. S1B). On the whole, the peak showing the high frequency of the chemical-shift distribution (centered at ∼119 ppm) appears to contain contributions from two forms, rather than one.
chemical-shift distribution (centered at ∼119 ppm) obtained from the BMRB (Fig. S1B). On the whole, the peak showing the high frequency of the chemical-shift distribution (centered at ∼119 ppm) appears to contain contributions from two forms, rather than one.
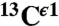 Nucleus.
Nucleus.
Even though the 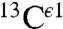 nucleus is not considered in our method, an analysis of the histogram of the shielding distribution for this nucleus shows the existence of essentially a single peak (Fig. S2A). Not surprising, a single peak is also seen for the histogram of the distribution of 1,754 observed
nucleus is not considered in our method, an analysis of the histogram of the shielding distribution for this nucleus shows the existence of essentially a single peak (Fig. S2A). Not surprising, a single peak is also seen for the histogram of the distribution of 1,754 observed 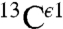 chemical shifts, from the BMRB (Fig. S2B). In general, the existence of a single peak validates the idea (4) that the
chemical shifts, from the BMRB (Fig. S2B). In general, the existence of a single peak validates the idea (4) that the 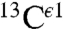 nucleus is not a very sensitive indicator of the changes of forms of the imidazole ring of His, as already seen by the similar heights of the gray bars in Fig. 1.
nucleus is not a very sensitive indicator of the changes of forms of the imidazole ring of His, as already seen by the similar heights of the gray bars in Fig. 1.
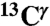 Nucleus.
Nucleus.
An analysis of all computed 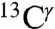 shieldings shows the existence of two peaks, rather than three or one computed for the
shieldings shows the existence of two peaks, rather than three or one computed for the 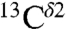 and
and 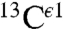 nuclei, respectively (blue-line profile in Fig. S3A). This peak distribution for the
nuclei, respectively (blue-line profile in Fig. S3A). This peak distribution for the 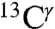 nucleus reflects the fact that the most-probable shielding value for the Nϵ2-H and the protonated, H+, forms are comparable but differ from that of the Nδ1-H tautomer (green bars in Fig. 1). An analysis of the histogram of the distribution of only the 84 observed
nucleus reflects the fact that the most-probable shielding value for the Nϵ2-H and the protonated, H+, forms are comparable but differ from that of the Nδ1-H tautomer (green bars in Fig. 1). An analysis of the histogram of the distribution of only the 84 observed 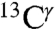 chemical shifts, from the BMRB, also appears to indicate the existence of two peaks (Fig. S3B). However, the low number of observed
chemical shifts, from the BMRB, also appears to indicate the existence of two peaks (Fig. S3B). However, the low number of observed 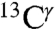 chemical shifts, which is ∼30 times smaller than that for the
chemical shifts, which is ∼30 times smaller than that for the 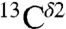 chemical shifts, prevents us from carrying out a more accurate analysis.
chemical shifts, prevents us from carrying out a more accurate analysis.
Overall, the analysis of the computed shielding distributions enables us to rationalize the origin of the peaks in the histograms of the chemical shifts for all three 13C carbons of the imidazole ring of His, although correspondence with the observed chemical-shift peak values was possible only for 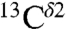 and
and 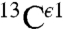 but not for
but not for 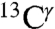 , because the number of observed chemical shifts for
, because the number of observed chemical shifts for 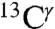 is not large enough to be statistically representative of proteins in solution.
is not large enough to be statistically representative of proteins in solution.
Computation of the Tautomeric Distribution of the Imidazole Ring of His in Proteins.
Among all eight proteins from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) (20) analyzed in this study, one of them, namely 1E1A (21), was chosen as an example to discuss the application of our methodology in detail to assess the fraction of His tautomers in solution, as a function of pH. This protein was selected because (i) among all eight proteins, it contains the largest number (namely six) of His residues in the sequence; (ii) biophysical and site-directed mutagenesis evidence indicates that one histidine (H289) is essential for enzymatic activity (21); (iii) at the pH at which the chemical shifts were determined, namely pH 6.5, several of the His residues show a significantly different average degree of protonation and, hence, a different distribution of the tautomeric forms; and (iv) among all eight proteins it is the only one for which the method was not applicable for one of the His residues (H183), as explained below.
Analysis of Protein 1E1A.
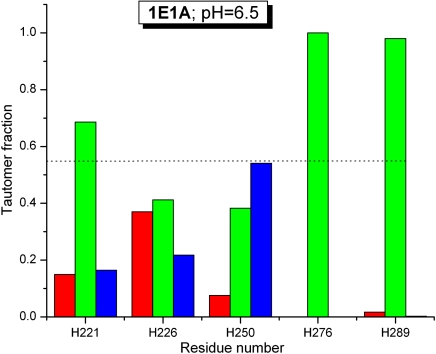
The structure of 1E1A, a 314-residue calcium-binding protein, has been determined by X-ray crystallography at 1.8-Å resolution (21), and the chemical shifts for all six His residues have been obtained at pH 6.5 and their values deposited in the BMRB. The distribution of average degrees of charge, computed by the method of ref. 22 with the Fast Adaptive Multigrid Boundary Element (FAMBE-pH) method, for the six His residues are shown in Table S1, and the corresponding fraction of H+ forms are represented by green bars in Fig. 2, except for H183. The resulting patterns of the tautomer distributions for most of the five His (shown by red and blue bars in Fig. 2) are different. Among all five His residues, the tautomeric distribution obtained for H226 and H250 are the most interesting because these two His residues show very similar degrees of ionization, namely 0.41 and 0.38, respectively, but very different distributions of the fraction of tautomers (Fig. 2), in line with the different Δobs values, where 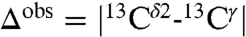 , namely 18.9 ppm and 3.7 ppm for H226 and H250, respectively (Table S1).
, namely 18.9 ppm and 3.7 ppm for H226 and H250, respectively (Table S1).
Fig. 2.
Fraction of tautomeric distribution for each of five out of six His residues of protein 1E1A, for which the chemical shifts were determined in solution at pH 6.5. Red and blue bars represent the fraction of the Nϵ2-H and Nδ1-H tautomer, respectively, and the green bars the fraction of the protonated form, H+. The dotted horizontal line indicates the fraction of the H+ form that a free His residue would have in solution at pH 6.5.
Regarding the charge distribution of these two His residues, the imidazole ring of H250 has a charge of 〈ρ〉 = 0.38 because it is surrounded completely by R264 and R266 (Fig. S4A) which, at the computed pH 6.5, are fully protonated (〈ρ〉 = 1). H226 also has a low degree of protonation (〈ρ〉 = 0.41); its imidazole ring is mostly buried and without favorable interactions with the nearest backbone oxygen groups, such as for H183 discussed below, and, hence, preventing it from being protonated.
As regards the different tautomeric distributions computed for H226 and H250, we analyze the environment of each nitrogen in the imidazole ring of these His residues. On one hand, the Nδ1 nucleus of H250 is located only 2.9 Å from the carbonyl backbone oxygen of S248, presumably forming a hydrogen bond, whereas the Nϵ2 nucleus is exposed to the solvent but the imidazole ring is surrounded by fully protonated R264 and R266 (Fig. S4A) and, hence, lowering the probability that a proton binds to Nϵ2, in good agreement with the tautomeric distribution in Fig. 2. On the other hand, the Nϵ2 nucleus but not Nδ1 of the imidazole ring of H226 is at 3.3 Å from a backbone carbonyl oxygen, namely that of W246. As a result, a preference of Nϵ2-H over the Nδ1-H tautomeric form is expected, as indicated by the computed fractions in Fig. 2.
Two residues show a high degree of protonation at pH 6.5, namely H276 and H289 (1.00 and 0.98, respectively). Residue H276 makes favorable electrostatic interactions with the deprotonated side-chain carboxyl groups of Asp234 and Glu309 (Fig. S4B), whereas the protonated H289 interacts with the deprotonated E39 (Fig. S5).
H183 (not shown in Fig. 2) is buried but, in contrast to H226, it is almost fully protonated, namely 〈ρ〉 = 0.85. This can be explained by the existence of a favorable electrostatic environment around the imidazole H183 ring; e.g., the distances between the Nϵ2 nucleus and the backbone oxygens of V179 and F124 are 4.0 Å and 4.4 Å, respectively, and the distances between the Nδ1 nucleus and the backbone oxygens of G185 and R186 are 3.5 Å and 4.1 Å, respectively. Nevertheless, 〈ρ〉 = 0.85, as computed from the X-ray-determined structure, is incompatible with the observed chemical shifts in solution by NMR spectroscopy, namely Δobs ∼ 1 ppm. In other words, the Δobs value (red entries in Table S1) is ≪ Δcutoff = approximately 9 ppm and, hence, our method does not apply (see Materials and Methods). The origin of the discrepancy may possibly be found in different conformations for residue H183 in solution and in the crystal structure.
On the whole, the analysis of the distribution of the forms of His for all remaining seven proteins (Figs. S6–S12) show, as for 1E1A, that the H+ form is the most populated one, whereas the tautomeric distribution of the imidazole ring, namely for Nδ1-H and Nϵ2-H, respectively, varies significantly among different histidines in the same protein. This conclusion is valid for a wide range of pH, even for pH > pK°. This is an important conclusion because it is common practice to assume that, for pH > pK°, the dominant His form would be that of the neutral species. On the contrary, our results indicate that this practice may be inaccurate. For example, for H34 of protein 1RCF, and H142 of protein 5FX2, the protonated H+ form is the most populated one, i.e., representing more than 50% of all imidazole forms of the His ring, even though the chemical shifts were determined at pH 7.5 and 7.0, respectively (Figs. S6 and S11).
Computation of the Tautomeric Distribution of the His-Containing Dipeptides.
Using the observed values, Δobs, obtained from solid-state NMR of eight His-containing dipeptides (5), listed in column 3 of Table S2, we have determined the tautomeric fractions of the imidazole ring of His for each of these eight compounds with Eqs. 1 and 2 (see columns 4 and 5 of Table S2). By adopting the fact (5) that the His in none of the compounds labeled 5–8 or 10–12 (in Table S2) is protonated, there is no need to know the crystal structure of these compounds in order to apply our method.
Consider these seven compounds with neutral His listed in Table S2. An analysis of the agreement between the experimental (column 2 of Table S2) and the computed tautomeric forms (columns 4 and 5 of Table S2) for each of these seven compounds leads to the following results, after considering a 10% error in the calculations: for the first three compounds, namely 5, 6, and 7 in Table S2, the imidazole ring of His is predicted to be in the Nδ1-H tautomeric form, in very good agreement with the experimental tautomeric form (5). For compounds 8 and 12 fairly good agreement is obtained; i.e., the method predicted the experimental tautomeric forms (5) as the most populated ones within ∼20% accuracy. Finally, poor agreement is found for compounds 10 and 11 (Table S2); i.e., less than 50% of the computed tautomers agree with the experimental one.
The poor agreement between experimental and computed tautomeric forms for compound 10 may be caused by use of the idea that a given crystal structure can be represented by a single dominant form, whereas, in fact, different forms can coexist (statically or dynamically) in the same crystal (23, 24). For example, the structure of compound 10 (His-Ala) was originally solved by Steiner (25) and confirmed by Cheng et al. (5) who reported His to be in the Nϵ2-H tautomeric form (Fig. S13A). However, His-Ala molecules in the crystal (25) are connected by a network of hydrogen bonds mediated by water molecules. Because the positions of the hydrogen atoms were not reported (25), it is clear from Fig. S13A that the same crystal packing can be achieved by assuming an Nδ1-H rather than an Nϵ2-H tautomeric form by rotation of the water molecules. On the other hand, because the hydrogen bond in His-Met (compound 6) is intramolecular, the imidazole ring of His is not allowed to adopt any tautomeric form in the crystal other than Nδ1-H (Fig. S13B). Conceivably, this observation may explain the good agreement obtained for compound 6 and the poor one obtained for compound 10. On the other hand, visual analysis of the crystal structure of compound 11 does not enable us to explain the disagreement between experimental and computed tautomeric forms (Table S2). Nevertheless, because the tautomeric arrangement for the dipeptide crystals was determined (5), presumably, on the basis of data on only the heavy atoms, the possibility of coexistence of tautomers (statically or dynamically) should not be ruled out.
Overall, we have obtained from good to moderately good agreement between calculated and experimental (5) tautomeric forms for five of seven compounds, i.e., for ∼70% of the neutral His-containing dipeptides, with poor agreement for the remaining two compounds, which, likely, originates from the presence of more than one tautomeric form in the crystal.
For the only protonated compound, namely His-Asp (Table S2), the observed difference, Δobs, between 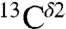 and
and 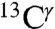 chemical shifts, is only 8 ppm. This Δobs value is far lower than the observed values in a protein (1E1A) for which two His residues are almost fully protonated, namely H289 and H276, with each of them showing Δobs values of ∼26 ppm and ∼22 ppm, respectively (Table S1). Even more important, the value of Δobs = 8 ppm is less than Δcutoff = ∼ 9 ppm and, hence, our method does not apply (see Materials and Methods). Conceivably, the low Δobs value for His-Asp may indicate that an important fraction of the dipeptides in the crystal are in the Nδ1-H rather than in the H+ form that is shown in Fig. S14, because the value of Δobs for the Nδ1-H tautomer is expected to be small (Table S2). To consider this option, based on the positions of the non-hydrogen atoms, we analyzed the crystal structure of the His-Asp dipeptide (5) in which both the imidazole ring of His and the Asp side chain are charged (Fig. S14). Visual analysis of the imidazole ring of His in Fig. S14 suggests that the Nδ1 atom forms a hydrogen bond with the C-terminal carboxylate group of a neighboring dipeptide and, hence, Nδ1 must be protonated (23). On the other hand, the Nϵ1 atom forms a hydrogen bond with the side-chain carboxylate of Asp of a neighboring dipeptide and, hence, Nϵ1 could be deprotonated. This rearrangement of charges would transform the imidazole H+ form, shown in Fig. S14, to an Nδ1-H tautomer and, hence, leave both residues (His and Asp) neutral, without any significant change in the crystal packing, i.e., the positions of the non-hydrogen atoms; it would also reduce potential electrostatic interactions between the H+ form of His and the N-terminal
chemical shifts, is only 8 ppm. This Δobs value is far lower than the observed values in a protein (1E1A) for which two His residues are almost fully protonated, namely H289 and H276, with each of them showing Δobs values of ∼26 ppm and ∼22 ppm, respectively (Table S1). Even more important, the value of Δobs = 8 ppm is less than Δcutoff = ∼ 9 ppm and, hence, our method does not apply (see Materials and Methods). Conceivably, the low Δobs value for His-Asp may indicate that an important fraction of the dipeptides in the crystal are in the Nδ1-H rather than in the H+ form that is shown in Fig. S14, because the value of Δobs for the Nδ1-H tautomer is expected to be small (Table S2). To consider this option, based on the positions of the non-hydrogen atoms, we analyzed the crystal structure of the His-Asp dipeptide (5) in which both the imidazole ring of His and the Asp side chain are charged (Fig. S14). Visual analysis of the imidazole ring of His in Fig. S14 suggests that the Nδ1 atom forms a hydrogen bond with the C-terminal carboxylate group of a neighboring dipeptide and, hence, Nδ1 must be protonated (23). On the other hand, the Nϵ1 atom forms a hydrogen bond with the side-chain carboxylate of Asp of a neighboring dipeptide and, hence, Nϵ1 could be deprotonated. This rearrangement of charges would transform the imidazole H+ form, shown in Fig. S14, to an Nδ1-H tautomer and, hence, leave both residues (His and Asp) neutral, without any significant change in the crystal packing, i.e., the positions of the non-hydrogen atoms; it would also reduce potential electrostatic interactions between the H+ form of His and the N-terminal 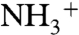 group of the dipeptide. A solution to the proper assignment of protons, which could lead to many possible combinations of forms compatible with the observed value of Δobs, lies beyond this work, and, hence, the reported values for fϵ and fδ of the His-Asp dipeptide in Table S2 are denoted as “unknown.”
group of the dipeptide. A solution to the proper assignment of protons, which could lead to many possible combinations of forms compatible with the observed value of Δobs, lies beyond this work, and, hence, the reported values for fϵ and fδ of the His-Asp dipeptide in Table S2 are denoted as “unknown.”
Conclusions
We have presented a methodology to determine the tautomeric fractions of the imidazole ring of His for proteins in solution as a function of pH, based on the observed 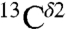 and
and 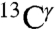 chemical shifts and either the structure or alternatively the fraction of the protonated form. Results for eight proteins indicate that the protonated form is the most populated one, whereas the distribution of the tautomeric forms for the imidazole ring of His varies significantly among different His in the same protein, reflecting the importance of the environment of His in determining the tautomeric forms. Consequently, this method could be used to extend an important solid-state NMR study of the mechanism of His-mediated proton conduction of the M2 protein (26) to the pH region of 4.5 to 8.5 in which protonation/deprotonation of His occurs. In particular, our method can also be used to cross-validate 13C- and 15N-based tautomeric distributions for His (26) at pH 8.5 (see Cross-Validation Test).
chemical shifts and either the structure or alternatively the fraction of the protonated form. Results for eight proteins indicate that the protonated form is the most populated one, whereas the distribution of the tautomeric forms for the imidazole ring of His varies significantly among different His in the same protein, reflecting the importance of the environment of His in determining the tautomeric forms. Consequently, this method could be used to extend an important solid-state NMR study of the mechanism of His-mediated proton conduction of the M2 protein (26) to the pH region of 4.5 to 8.5 in which protonation/deprotonation of His occurs. In particular, our method can also be used to cross-validate 13C- and 15N-based tautomeric distributions for His (26) at pH 8.5 (see Cross-Validation Test).
We have provided evidence that the range of the computed shieldings of the 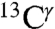 and
and 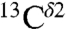 nuclei of the imidazole ring of His are within the range of values observed for chemical shifts of proteins in solution and for His-containing dipeptides. Using the computed shielding values, we have been able to rationalize the frequencies of chemical-shift distributions observed in proteins for all the imidazole carbon atoms. We also have provided evidence that the number of peaks in the histogram of the frequency of the chemical-shift distribution, and their relative separation, when more than one peak is observed, is a fingerprint to enable a given nucleus to sense tautomeric changes.
nuclei of the imidazole ring of His are within the range of values observed for chemical shifts of proteins in solution and for His-containing dipeptides. Using the computed shielding values, we have been able to rationalize the frequencies of chemical-shift distributions observed in proteins for all the imidazole carbon atoms. We also have provided evidence that the number of peaks in the histogram of the frequency of the chemical-shift distribution, and their relative separation, when more than one peak is observed, is a fingerprint to enable a given nucleus to sense tautomeric changes.
For seven out of eight proteins analyzed in this work, use has been made of the structure solved by X-ray crystallography, although the observed chemical shifts were determined in solution, at pH 3.2 to 7.5. Because determination of the fraction of tautomers for the imidazole ring of His, as a function of pH, is very sensitive to the degree of protonation of the His residue, interpretation of the results may differ significantly if the structure of the protein solved by X-ray crystallography disagrees with the structure that it could have in solution, because the observed pKa’s of the ionizable groups depend on the conformation of the molecule and on the environment of these groups in the macromolecule (27).
For ∼70% of the neutral His-containing dipeptides, i.e., five out of seven in Table S2, our method leads to fairly good agreement between computed and experimental (5) tautomeric forms. The disagreement obtained for the remaining 30% of the remaining dipeptides with the neutral His, as for the dipeptide with the protonated His, may originate in the approximation that the experimental crystal structure is assumed to be represented by a single dominant form, i.e., without the static or dynamic coexistence of different tautomeric forms.
Materials and Methods
Computations of both the 13C shielding (28–31) and the average degree of charge (〈ρ〉), as a function of pH (22), were carried out according to previously published methods, and, hence, they are discussed here only briefly. In addition, in this section, the methodology adopted to compute the tautomeric fractions of the imidazole ring of His are described in detail.
Computation of the 13C Shielding for the Imidazole Ring of His.
We represent each form of His as a terminally blocked model tripeptide with the sequence Ac-GHξG-NMe (28), with Hξ in the Nδ1-H, the Nϵ2-H tautomer form or the protonated form H+, respectively. For the Nϵ2-H tautomer and the H+ form, a set of more than ∼35,000 conformations each, representing a uniform sampling of the whole Ramachandran map as a function of ϕ, ψ, ω, χ1, and χ2 torsional angles, was generated. For each of the ∼35,000 conformations, the gas-phase, isotropic shielding value of the His residue was calculated with the Gaussian 03 package (32) by using a small basis set (6-31G/3-21G) and then extrapolating the shielding values to those for a large basis set [6-311+G(2d,p)/3-21G], following the identical procedure that was already used for the generation of the Nδ1-H tautomer database (29). Finally, the distribution of the computed shielding for each 13C of the imidazole ring of His was analyzed. For all 13C nuclei, namely 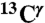 ,
, 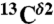 , and
, and 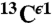 , the histogram of the shielding distribution, among all ∼35,000 conformations, was fit by a Gaussian function with a mean value σ0 and standard deviation as shown in Fig. 1.
, the histogram of the shielding distribution, among all ∼35,000 conformations, was fit by a Gaussian function with a mean value σ0 and standard deviation as shown in Fig. 1.
Method to Compute the Tautomeric Forms of His as a Function of pH.
Determination of the average degree of charge (〈ρ〉) of a given His residue in a protein (22) enables us to determine the fraction of remaining neutral imidazole rings (f0) in solution as f0 + f+ = 1, with f+ = 〈ρ〉 and the fraction of tautomer (f0) given by f0 = fϵ + fδ, with fϵ and fδ representing the fraction of Nϵ2-H and Nδ1-H tautomers, respectively.
Use of first-order shielding differences for a pair of selected nuclei, namely 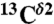 and
and 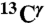 (red and green bars, respectively, in Fig. 1), rather than chemical shifts, is a very convenient approach because the experimental referencing problem may be a source of errors (5). Consequently, we define the first-order shielding difference, Δξ, as
(red and green bars, respectively, in Fig. 1), rather than chemical shifts, is a very convenient approach because the experimental referencing problem may be a source of errors (5). Consequently, we define the first-order shielding difference, Δξ, as 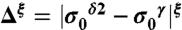 , with ξ denoting the form of the imidazole ring, and
, with ξ denoting the form of the imidazole ring, and 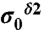 and
and 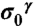 the computed mean values of the shielding distribution for the
the computed mean values of the shielding distribution for the 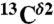 and
and 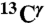 nuclei, respectively (given by the height of the red and green bars, respectively, in Fig. 1). In other words, the following convention is adopted: ξ = δ, ϵ, or + to designate the Nδ1-H, Nϵ2-H, or H+ form, respectively.
nuclei, respectively (given by the height of the red and green bars, respectively, in Fig. 1). In other words, the following convention is adopted: ξ = δ, ϵ, or + to designate the Nδ1-H, Nϵ2-H, or H+ form, respectively.
From Fig. 1, it can be seen that the following inequality holds: Δϵ > Δ+ > Δδ, and Δδ ∼ 0. Therefore, once the fraction of protonated H+ form, f+ = 〈ρ〉, and 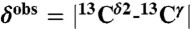 , with
, with 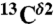 and
and 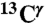 being the observed chemical shifts in solution, at a given pH, are known, the fraction of the Nϵ2-H tautomer (fϵ ) can be obtained assuming (i) that all forms are in fast exchange on the NMR chemical-shift time scale (4), i.e., Δobs = fϵΔϵ + f+Δ+ + fδΔδ, and (ii) that Δδ ≡ 0. To assure that fϵ≥0 for any 〈ρ〉, the following condition must be satisfied: [1 - 〈ρ〉(Δ+/Δobs)]≥0, which means that ((Δ+/Δobs) ≤ (1/〈ρ〉)). By definition Δ+ is a single value, i.e., the first-order shielding difference computed for the protonated form. But, because Δobs exhibits a large dispersion, e.g., for 〈ρ〉 ∼ 1.0 (see Table S1), this relation would imply a large variation, rather than a single value, of Δ+. To assure that fϵ≥0 for any 〈ρ〉, we introduce the constraint that (Δ+/Δobs) = 1. Consequently, fϵ can be computed from the following equation:
being the observed chemical shifts in solution, at a given pH, are known, the fraction of the Nϵ2-H tautomer (fϵ ) can be obtained assuming (i) that all forms are in fast exchange on the NMR chemical-shift time scale (4), i.e., Δobs = fϵΔϵ + f+Δ+ + fδΔδ, and (ii) that Δδ ≡ 0. To assure that fϵ≥0 for any 〈ρ〉, the following condition must be satisfied: [1 - 〈ρ〉(Δ+/Δobs)]≥0, which means that ((Δ+/Δobs) ≤ (1/〈ρ〉)). By definition Δ+ is a single value, i.e., the first-order shielding difference computed for the protonated form. But, because Δobs exhibits a large dispersion, e.g., for 〈ρ〉 ∼ 1.0 (see Table S1), this relation would imply a large variation, rather than a single value, of Δ+. To assure that fϵ≥0 for any 〈ρ〉, we introduce the constraint that (Δ+/Δobs) = 1. Consequently, fϵ can be computed from the following equation:
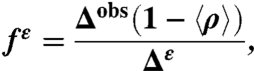 |
[1] |
with Δϵ the single-valued first-order shielding difference computed for the Nϵ2-H tautomer, namely Δϵ = 31.7 ppm (Fig. 1). In contrast to the solution proposed for Δ+, we rely on adoption of a fixed value of Δϵ, which was validated by the results obtained for the tautomeric fraction of distributions of five out of seven neutral dipeptides (see Table S2) as well as from a cross-validation of our method with results obtained for a neutral His (see Cross-Validation Test). The fraction of the fδ tautomer is obtained straightforwardly as
| [2] |
For each His residue i of a single conformation, as for an X-ray structure, determination of the average degree of charge, 〈ρ〉, can lead to a noninteger number, although we know that a noninteger charge does not make physical sense. Because of the Boltzmann nature of the averaged value computed by the FAMBE-pH method (22), a fractional charge should physically be interpreted as follows: For a given single conformation, there are many replicas (33) of such a conformation and, hence, a fractional charge, e.g., 0.60, means that, for 60% of these replicas, the imidazole ring of His of residue i is in the H+ form with an integer charge, whereas for the remaining 40% of the replicas, the imidazole ring of His of residue i is in a neutral form, i.e., represented by fractions of Nϵ2-H and Nδ1-H tautomers, as determined by Eqs. 1 and 2.
In this work we assume that the calculated fraction of each of the two tautomeric forms of the imidazole ring of His and the H+ form, at a given pH, is affected by an estimated error of ∼ ± 10% (see Assessing the Accuracy of the Calculations). Moreover, if 〈ρ〉 ∼ 1.0 and the value of Δobs is lower than a certain cutoff, namely Δcutoff ∼ 9 ppm, the method cannot be applied (see Determine an Applicability Limit).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We thank Kent R. Wenger (BMRB, Madison, WI) for providing the observed histograms of the chemical shifts, shown in Figs. S1B, S2B, and S3B. We also thank all spectroscopists and crystallographers who have deposited their coordinates at the PDB, and chemical shifts at the BMRB; without their effort, this work would not be possible. This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (GM-14312 and GM-24893) and the National Science Foundation (MCB05-41633). Support was also received from CONICET, Fondo para la investigación Científica y Tecnológica-Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Técnica (PAV 22642/22672), from the Universidad Nacional de San Luis (P-328402), Argentina, and from the Russian Ministry of Science (02.740.11.0079, SS-3185.2010.4, and RFBR-09-04-00136). The research was conducted by using the resources of Pople, a facility of the National Science Foundation Terascale Computing System at the Pittsburgh Supercomputer Center.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1102373108/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Shimba N, et al. Quantitative identification of the protonation state of histidine in vitro and in vivo. Biochemistry. 2003;42:9227–9234. doi: 10.1021/bi0344679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Demchuk E, Wade RC. J Phys Chem. 1996;100:17373–17387. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jensen MR, Has MAS, Hansen DF, Led JJ. Investigating metal-binding in proteins by nuclear magnetic resonance. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:1085–1104. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-6447-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hass MAS, Hansen DF, Christensen HEM, Led JJ, Kay LE. Characterization of conformational exchange of a histidine side chain: protonation, rotamerization, and tautomerization of His61 plastocyanin from Anabaena variabilis. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:8460–8470. doi: 10.1021/ja801330h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cheng F, Sun H, Zhang Y, Mukkamala D, Oldfield E. A solid state 13C NMR, crystallographic, and quantum chemical investigation of chemical shifts and hydrogen bonding in histidine dipeptides. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:12544–12554. doi: 10.1021/ja051528c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cruz-Cabeza AJ, Groom CR. Identification, classification and relative stability of tautomers in the Cambridge structural database. Cryst Eng Comm. 2011;13:93–98. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Arnold JT, Dharmatti SS, Packard ME. Chemical effects on nuclear induction signals from organic compounds. J Chem Phys. 1951;19:507. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meadows DH, Jardetzky O, Epand RM, Ruterjans HH, Scheraga HA. Assignment of the histidine peaks in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of ribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1968;60:766–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wüthrich K. NMR in Biological Research: Peptides and Proteins. Amsterdam: North-Holland; 1976. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harbison G, Herzfeld J, Griffin RGJ. Nitrogen-15 chemical shifts tensors in L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate. J Am Chem Soc. 1981;103:4752–4754. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pelton JG, Torchia DA, Meadow ND, Roseman S. Tautomeric states of the active-site histidines of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated IIIClc a signal-transducing protein from Escherichia coli, using two-dimensional heteronuclear. Protein Sci. 1993;2:543–558. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shimba N, Takahashi H, Sakakura M, Fuji I, Shimada I. Determination of protonation and deprotonation forms and tautomeric states of histidine residues in large proteins using nitrogen-carbon J couplings in imidazole ring. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:10988–10989. [Google Scholar]
-
13.Sudmeier JL, et al. Identification of histidine tautomers in proteins by 2D
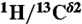 one-bond correlated NMR. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:8430–8431. doi: 10.1021/ja034072c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
one-bond correlated NMR. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:8430–8431. doi: 10.1021/ja034072c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] - 14.Hass MAS, Yilmaz A, Christensen HEM, Led JJ. Histidine side-chain dynamics and protonation monitored by 13C CPMG NMR relaxation dispersion. J Biomol NMR. 2009;44:225–233. doi: 10.1007/s10858-009-9332-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Strohmeier M, Stueber D, Grant DM. Accurate 13C and 15N chemical shift and 14N quadrupolar coupling constant calculations in amino acid crystals: Zwitterionic, hydrogen-bonded systems. J Phys Chem A. 2003;107:7629–7642. doi: 10.1021/jp0350114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen X, Zhan CG. First-principles studies of C-13 NMR chemical shift tensors of amino acids in crystal state. J Mol Struct-THEOCHEM. 2004;682:73–82. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Reynolds WF, Peat IR, Freedman MH, Lyerla JR., Jr Determination of the tautomeric form of the imidazole ring of L-Histidine in basic solution by carbon-13 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 1973;95:328–331. doi: 10.1021/ja00783a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spera S, Bax A. Empirical correlation between protein backbone conformation and Cα and Cβ 13C nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts. J Am Chem Soc. 1991;113:5490–5492. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ulrich EL, et al. BioMagResBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;36:D402–D408. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Berman HM, et al. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:235–242. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Scharff EI, Koepke GF, Lücke C, Rüterjans H. Crystal structure of diisopropylfluorophosphatase from Loligo vulgaris. Structure. 2001;9:493–502. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00610-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vorobjev YA, Vila JA, Scheraga HA. FAMBE-pH: A fast and accurate method to compute the total solvation free energies of proteins. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112:11122–11136. doi: 10.1021/jp709969n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Steiner T, Koellner G. Coexistence of both histidine tautomers in the solid state and stabilization of the unfavorable Nδ-H form by intramolecular hydrogen bonding: Crystalline L-His-Gly hemihydrates. Chem Commun. 1997;(13):1207–1208. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sayle RA. So you think you understand tautomerism? J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2010;24:485–496. doi: 10.1007/s10822-010-9329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Steiner T. L-Histidyl-L-alanine dihydrate. Acta Crystallogr C. 1996;52:2554–2556. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hu F, Wenbin L, Hong M. Mechanism of proton conduction and gating in influenza M2 proton channels from solid-state NMR. Science. 2010;330:505–508. doi: 10.1126/science.1191714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Laskowski M, Jr, Scheraga HA. Thermodynamic considerations of protein reactions. I. Modified reactivity of polar groups. J Am Chem Soc. 1954;76:6305–6319. [Google Scholar]
-
28.Vila JA, Villegas ME, Baldoni HA, Scheraga HA. Predicting
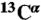 chemical shifts for validation of protein structures. J Biomol NMR. 2007;38:221–235. doi: 10.1007/s10858-007-9162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
chemical shifts for validation of protein structures. J Biomol NMR. 2007;38:221–235. doi: 10.1007/s10858-007-9162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] -
29.Vila JA, Arnautova YA, Martin OA, Scheraga HA. Quantum-mechanics-derived
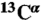 chemical shift server (CheShift) for protein structure validation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:16972–16977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908833106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
chemical shift server (CheShift) for protein structure validation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:16972–16977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908833106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] -
30.Vila JA, Baldoni HA, Scheraga HA. Performance of density functional models to reproduce observed
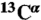 chemical shifts of proteins in solution. J Comput Chem. 2009;30:884–892. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
chemical shifts of proteins in solution. J Comput Chem. 2009;30:884–892. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] -
31.Vila JA, Scheraga HA. Assessing the accuracy of protein structures by quantum mechanical computations of
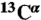 chemical shifts. Acc Chem Res. 2009;42:1545–1553. doi: 10.1021/ar900068s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
chemical shifts. Acc Chem Res. 2009;42:1545–1553. doi: 10.1021/ar900068s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] - 32.Frisch MJ, et al. Gaussian 03, Revision E.01. Wallingford, CT: Gaussian, Inc; 2004. [Google Scholar]
-
33.Arnautova YA, Vila JA, Martin OA, Scheraga HA. What can we learn by computing
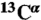 chemical shifts for X-ray protein models? Acta Crystallogr D. 2009;65:697–703. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909012086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
chemical shifts for X-ray protein models? Acta Crystallogr D. 2009;65:697–703. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909012086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.