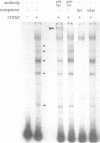
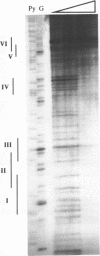
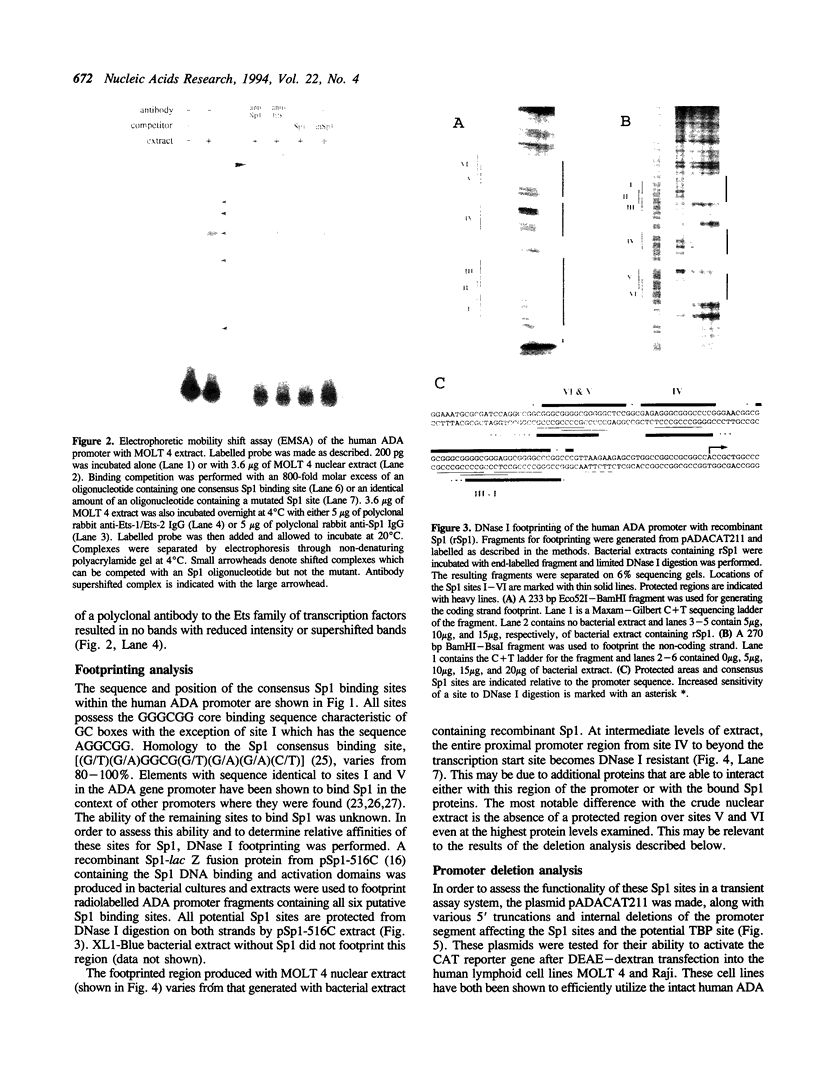
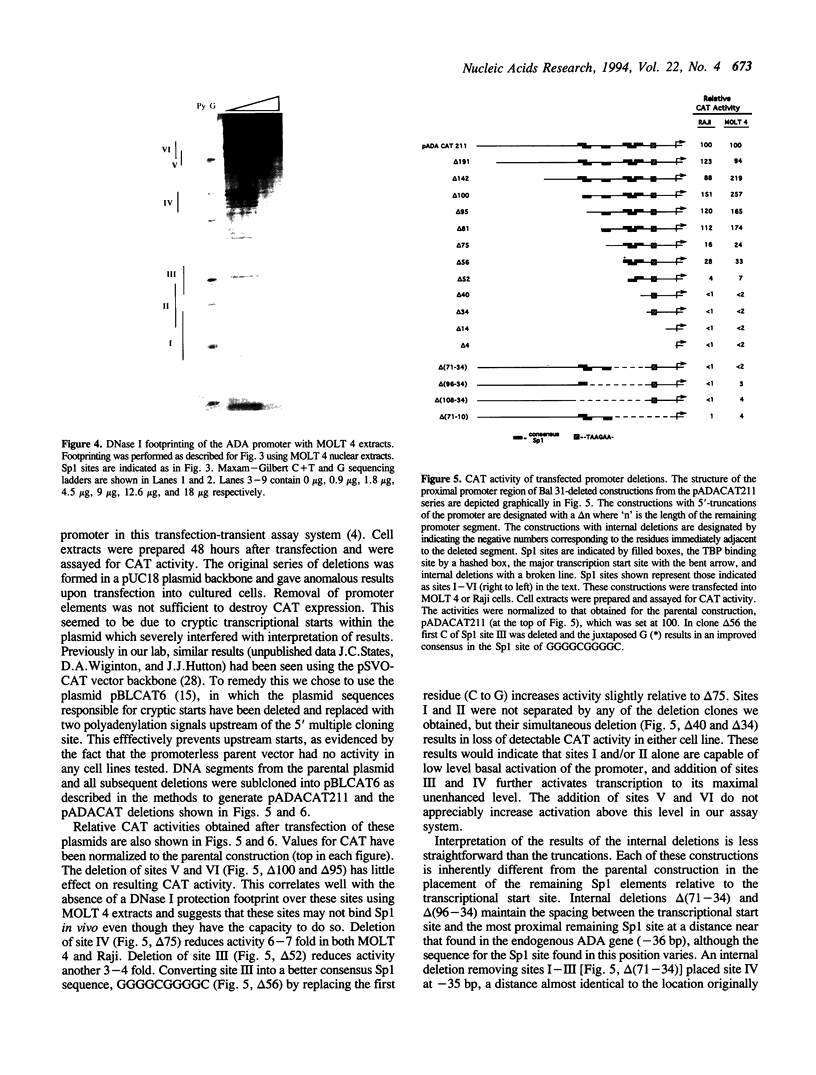
Abstract
Tissue-specific expression of the human adenosine deaminase (ADA) gene is mediated by transcriptional activation over a thousand-fold range. Cis-regulatory regions responsible for high and basal levels of activation include an enhancer and the proximal promoter region. While analyses of the T-cell specific enhancer have been carried out, detailed studies of the the promoter region or promoter-enhancer interactions have not. Examination of the promoter region by homology searches revealed six putative Sp1 binding sites. DNase I footprinting showed that Sp1 is able to bind these sites. Deletion analysis indicated that the proximal Sp1 site is required for activation of a reporter gene to detectable levels and that the more distal Sp1 sites further activate the level of expression. Inclusion of an ADA enhancer-containing fragment in these deletion constructions demonstrated that Sp1 sites are also essential for enhancer function. Apparently Sp1 controls not only low level expression but is also an integral part of the mechanism by which the enhancer achieves high level ADA expression. Mutagenesis of a potential TBP binding site at base pairs -21 to -26 decreased activity only two-fold indicating that it is not essential for transcriptional activation or enhancement.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. L., Minden A. G., Williams G. T., Bobonis C., Yeung C. Y. Functional significance of an overlapping consensus binding motif for Sp1 and Zif268 in the murine adenosine deaminase gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7523–7527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams A., Harkness R. A. Adenosine deaminase activity in thymus and other human tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):647–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. M., Freytag S. O. Synergistic activation of a human promoter in vivo by transcription factor Sp1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1935–1943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronow B. J., Silbiger R. N., Dusing M. R., Stock J. L., Yager K. L., Potter S. S., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A. Functional analysis of the human adenosine deaminase gene thymic regulatory region and its ability to generate position-independent transgene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4170–4185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronow B., Lattier D., Silbiger R., Dusing M., Hutton J., Jones G., Stock J., McNeish J., Potter S., Witte D. Evidence for a complex regulatory array in the first intron of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1384–1400. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADY T. G., O'DONOVAN C. I. A STUDY OF THE TISSUE DISTRIBUTION OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE IN SIX MAMMAL SPECIES. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Jan;14:101–120. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. Deletions covering the putative promoter region of early mRNAs of simian virus 40 do not abolish T-antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3865–3869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Jambou R. C., Swick A. G., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Transcriptional initiation is controlled by upstream GC-box interactions in a TATAA-less promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6632–6641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Klüppel M., Schmidt A., Schütz G., Luckow B. Reporter constructs with low background activity utilizing the cat gene. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):129–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90456-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Azizkhan J. C., Lee D. C. The binding of transcription factor Sp1 to multiple sites is required for maximal expression from the rat transforming growth factor alpha promoter. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1805–1815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Harless M. L., Wright D. A., Kellems R. E. Identification and characterization of transcriptional arrest sites in exon 1 of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4555–4564. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Innis J. W., Sun M. H., Wright D. A., Kellems R. E. Sequence requirements for transcriptional arrest in exon 1 of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6248–6256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinsky J. M., Maa M. C., Ramamurthy V., Kellems R. E. Adenosine deaminase gene expression. Tissue-dependent regulation of transcriptional elongation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14561–14565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinsky J. M., Ramamurthy V., Fanslow W. C., Ingolia D. E., Blackburn M. R., Shaffer K. T., Higley H. R., Trentin J. J., Rudolph F. B., Knudsen T. B. Developmental expression of adenosine deaminase in the upper alimentary tract of mice. Differentiation. 1990 Feb;42(3):172–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciudad C. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Deletion analysis of the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16274–16282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan J., Manley J. L. TFIID can be rate limiting in vivo for TATA-containing, but not TATA-lacking, RNA polymerase II promoters. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):304–315. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Tjian R. Eukaryotic coactivators associated with the TATA box binding protein. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Yeast TATA-binding protein TFIID binds to TATA elements with both consensus and nonconsensus DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5718–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Martiniuk F., Rosen F. S. Adenosine deaminase activity in normal tissues and tissues from a child with severe combined immunodeficiency and adenosine deaminase deficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Mar;9(3):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia D. E., Al-Ubaidi M. R., Yeung C. Y., Bigo H. A., Wright D., Kellems R. E. Molecular cloning of the murine adenosine deaminase gene from a genetically enriched source: identification and characterization of the promoter region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4458–4466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis J. W., Kellems R. E. A heat-labile factor promotes premature 3' end formation in exon 1 of the murine adenosine deaminase gene in a cell-free transcription system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5398–5409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis J. W., Moore D. J., Kash S. F., Ramamurthy V., Sawadogo M., Kellems R. E. The murine adenosine deaminase promoter requires an atypical TATA box which binds transcription factor IID and transcriptional activity is stimulated by multiple upstream Sp1 binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21765–21772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kash S. F., Innis J. W., Jackson A. U., Kellems R. E. Functional analysis of a stable transcription arrest site in the first intron of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2718–2729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley C., Winoto A. Cloning of GT box-binding proteins: a novel Sp1 multigene family regulating T-cell receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4251–4261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen T. B., Green J. D., Airhart M. J., Higley H. R., Chinsky J. M., Kellems R. E. Developmental expression of adenosine deaminase in placental tissues of the early postimplantation mouse embryo and uterine stroma. Biol Reprod. 1988 Nov;39(4):937–951. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod39.4.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriwacki R. W., Schultz S. C., Steitz T. A., Caradonna J. P. Sequence-specific recognition of DNA by zinc-finger peptides derived from the transcription factor Sp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9759–9763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattier D. L., States J. C., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A. Cell type-specific transcriptional regulation of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1061–1076. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa M. C., Chinsky J. M., Ramamurthy V., Martin B. D., Kellems R. E. Identification of transcription stop sites at the 5' and 3' ends of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12513–12519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Jr, Gelfand E. W. Biochemistry of diseases of immunodevelopment. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:845–877. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Courey A. J., Wall J. S., Jackson S. P., Hough P. V. DNA looping and Sp1 multimer links: a mechanism for transcriptional synergism and enhancement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5670–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Roles of TATA and initiator elements in determining the start site location and direction of RNA polymerase II transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1391–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogulis R. J., Freytag S. O. Contribution of specific cis-acting elements to activity of the mouse pro-alpha 2(I) collagen enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2493–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Lee B. A., Monks J. Multiple SP1 binding sites confer enhancer-independent, replication-activated transcription of HIV-1 and globin gene promoters. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):369–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Diverse transcriptional functions of the multisubunit eukaryotic TFIID complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthy V., Maa M. C., Harless M. L., Wright D. A., Kellems R. E. Sequence requirements for transcriptional arrest in exon 1 of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1484–1491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. An enhancer/locus control region is not sufficient to open chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3990–3998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasanen K., Oikarinen J., Kivirikko K. I., Pihlajaniemi T. Interaction of transcription factor Sp1 with the promoter of the gene for the multifunctional protein disulphide isomerase polypeptide. Biochem J. 1993 May 15;292(Pt 1):41–45. doi: 10.1042/bj2920041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerio D., Duyvesteyn M. G., Dekker B. M., Weeda G., Berkvens T. M., van der Voorn L., van Ormondt H., van der Eb A. J. Adenosine deaminase: characterization and expression of a gene with a remarkable promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):437–443. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weyden M. B., Kelley W. N. Human adenosine deaminase. Distribution and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5448–5456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiginton D. A., Kaplan D. J., States J. C., Akeson A. L., Perme C. M., Bilyk I. J., Vaughn A. J., Lattier D. L., Hutton J. J. Complete sequence and structure of the gene for human adenosine deaminase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8234–8244. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley S. R., Kraus R. J., Mertz J. E. Functional binding of the "TATA" box binding component of transcription factor TFIID to the -30 region of TATA-less promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5814–5818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston J. H., Hanten G. R., Overbeek P. A., Kellems R. E. 5' flanking sequences of the murine adenosine deaminase gene direct expression of a reporter gene to specific prenatal and postnatal tissues in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13472–13479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte D. P., Wiginton D. A., Hutton J. J., Aronow B. J. Coordinate developmental regulation of purine catabolic enzyme expression in gastrointestinal and postimplantation reproductive tracts. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):179–190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenzie-Gregory B., Khachi A., Garraway I. P., Smale S. T. Mechanism of initiator-mediated transcription: evidence for a functional interaction between the TATA-binding protein and DNA in the absence of a specific recognition sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3841–3849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Ubaidi M. R., Ramamurthy V., Maa M. C., Ingolia D. E., Chinsky J. M., Martin B. D., Kellems R. E. Structural and functional analysis of the murine adenosine deaminase gene. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):476–485. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]