Abstract
The control of translation is a critical aspect of gene regulation. It is often inversely related to mRNA degradation and is typically controlled during initiation. The Stm1 protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been shown to interact with ribosomes, affect the interaction of eEF3 with ribosomes, and promote the decapping of a subclass of mRNAs. We demonstrate that in vitro Stm1 inhibits translation after formation of an 80S complex. This suggests that Stm1 modulates translation and mRNA decapping by controlling translation elongation.
Keywords: Stm1, ribosomes, translation elongation, Dhh1, Pat1
INTRODUCTION
The proper control of gene expression involves the modulation of mRNA translation and degradation. The general pathways of mRNA degradation occur by deadenylation followed by 3′-to-5′ degradation, or more commonly by decapping and 5′-to-3′ degradation (Parker and Song 2004; Garneau et al. 2007). Decapping is enhanced by inhibition of translation initiation and loss of the eIF4F cap-binding complex suggesting an inverse relationship with translation initiation (Schwartz and Parker 1999, 2000). Consistent with that mechanism, the Dhh1 and Pat1 proteins, which promote decapping in vivo, function in part to directly repress translation initiation (Coller and Parker 2005; Nissan et al. 2010). However, how an mRNA engaged in translation initially recruits Dhh1 or Pat1 and is thereby targeted for translation repression and/or decapping is unknown.
The Stm1 protein has been identified as functioning in mRNA decapping in yeast by being a high-copy suppressor of the temperature-sensitive phenotype of a pat1Δ strain, inhibiting the growth of a dhh1Δ strain when overexpressed, and being required for the decay of a subset of yeast mRNAs (Balagopal and Parker 2009). An unresolved question is how Stm1 affects the processes of translation and mRNA degradation.
Earlier work has suggested that Stm1 can influence translation. Stm1 binds ribosomes (Inada et al. 2002; Van Dyke et al. 2004, 2006, 2009). Stm1 also influences the binding of eEF3 to 80S complexes since stm1Δ strains show increased eEF3 binding to ribosomes and strains with increased levels of Stm1 show decreased levels of eEF3 associated with ribosomes (Van Dyke et al. 2009). This has led to the suggestion that Stm1 might function with eEF3 to promote translation elongation (Van Dyke et al. 2009), although a direct effect on translation by Stm1 has never been examined. In this study, we examine the function of Stm1 in vitro and demonstrate that Stm1 can inhibit translation after formation of an 80S complex. Moreover, this inhibition is dependent on regions in Stm1 that affect its function in vivo. These observations suggest that Stm1 is a translational repressor that functions by stalling ribosomes after formation of 80S complexes.
RESULTS
Mutational analysis of Stm1
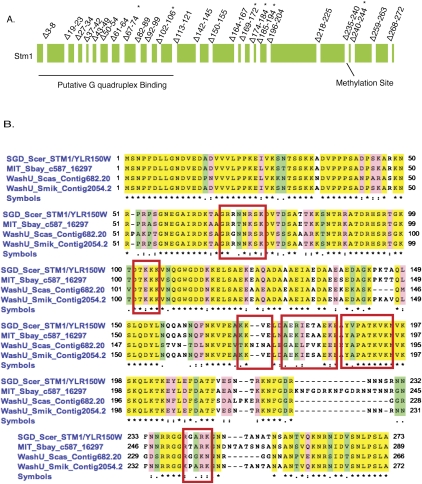
As a first step in understanding the function of Stm1, we desired to identify mutations in STM1 that affected its function in vivo, which we could then use to evaluate the significance of any biochemical activities in vitro. To identify functional domains of STM1, we deleted three to 10 amino acids from throughout the protein (Fig. 1). These Stm1 mutants were expressed under their own promoter on a 2μ plasmid, and their function was examined in vivo by examining Stm1 overexpression suppression of the temperature-sensitive growth defect of pat1Δ strains, and the inhibition of growth seen in a dhh1Δ strain, when Stm1 is overexpressed (Balagopal and Parker 2009).
FIGURE 1.
Mutational analysis of Stm1. (A) Schematic of the Stm1 protein, its known motifs, and the positions of the deletions generated in this study. (*) The mutations that showed in vivo phenotypes. (B) Stm1 is a highly conserved protein within the fungal genomes. Shown is the protein sequence alignment of Stm1 between closely related Saccharomyces species. (Red boxes) Locations of the mutations that displayed in vivo phenotypes.
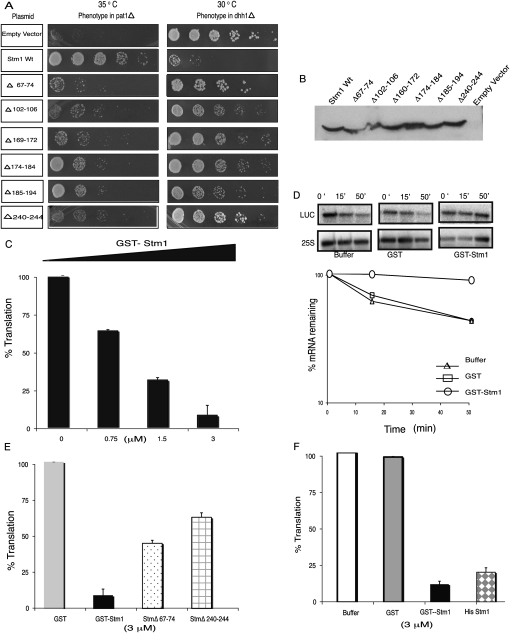
We observed that six deletions in Stm1 (Δ67-74, Δ102-106, Δ169-172, Δ174-184, and Δ188-194, and Δ240-244) failed to rescue the temperature-sensitive phenotype of the pat1Δ (Fig. 2A). Moreover, those same six alleles failed to inhibit the growth of a dhh1Δ strain (Fig. 2A). By Western analysis, these six STM1 deletion alleles were expressed similarly to the wild-type STM1 (Fig. 2B). The mutations are spread throughout the protein (Fig. 1), indicating that the entire protein is required for optimal function. Since the same mutations affect both the suppression of pat1Δ and the inhibition of growth in the dhh1Δ strain, it demonstrates that the suppression of pat1Δ growth defects and decreased growth in a dhh1Δ are due to a related function of Stm1.
FIGURE 2.
Stm1 functions as a translation repressor. (A) Mutational analysis of Stm1. In vivo phenotypes of overexpressing the relevant STM1 mutations in pat1Δ and dhh1Δ strains. (B) Western analysis showing the expression levels of the deletion mutants of STM1 using a rabbit antibody generated against Stm1 produced in E. coli. (C) Dose-dependent repression of translation by GST Stm1 in vitro in yeast extracts. (D) The percentage luciferase mRNA remaining during the reaction at 0, 20, and 50 min normalized to 25S rRNA levels. The amount of mRNA remaining during the time course of reaction in the presence of buffer (open triangle), GST (open square), and GST Stm1 (open circle) is also plotted using a logarithmic scale. (E) Comparison of translation repression abilities of wild-type (solid black bar) and two mutant Stm1Δ67-74 (dotted bar) and Δ240–244 (grid bar) proteins in vitro. (F) Stm1 can repress translation in vitro independent of the tag used. Shown is the effect of GST (solid black bar) and His-tagged Stm1 (diamond bar) on the translation of luciferase mRNA.
Stm1 represses translation in vitro
The genetic interaction of STM1 with pat1Δ and dhh1Δ and the stabilization of some mRNAs in an stm1Δ strain indicate that Stm1 promotes mRNA degradation, either by direct interactions with mRNA degradation factors or by inhibition of translation, which would then enhance mRNA degradation. Since Stm1 has been demonstrated to interact with ribosomes (Inada et al. 2002; Van Dyke et al. 2004, 2006, 2009) and no interactions have been reported between Stm1 and mRNA decay factors from genomic analyses, we hypothesized that Stm1 might function by inhibiting translation. To examine if Stm1 directly affects translation, we purified a GST-Stm1 fusion protein from Escherichia coli and examined how it affected translation of a capped poly-adenylated luciferase reporter mRNA (LUC) in yeast translation extracts.
An important result was that the addition of recombinant GST-Stm1 inhibited luciferase production in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2C). Similar results with His-tagged Stm1 showed that inhibition of protein production is independent of the tag (Fig. 2F). In principle, the reduction in protein production by Stm1 could be due either to an inhibition of translation or destabilization of the reporter mRNA. However, Northern analysis of Luciferase mRNA (LUC) over a time course showed that GST-Stm1 did not destabilize the mRNA (Fig. 2D). These results indicate that Stm1 can inhibit translation in vitro.
To determine if the inhibition of translation by Stm1 in vitro was related to its function in vivo, we purified GST-tagged recombinant versions of Stm1Δ67-74 and Stm1Δ240-244 proteins (two of the mutants that disrupted function in vivo) and tested their effect on translation in vitro (Fig. 2E). These partial-loss-of-function alleles showed reduced ability to repress translation in vitro as compared to the wild-type protein. This observation indicates that the repression of translation in vitro by Stm1 is related to its in vivo function.
Stm1 inhibits translation after 80S formation
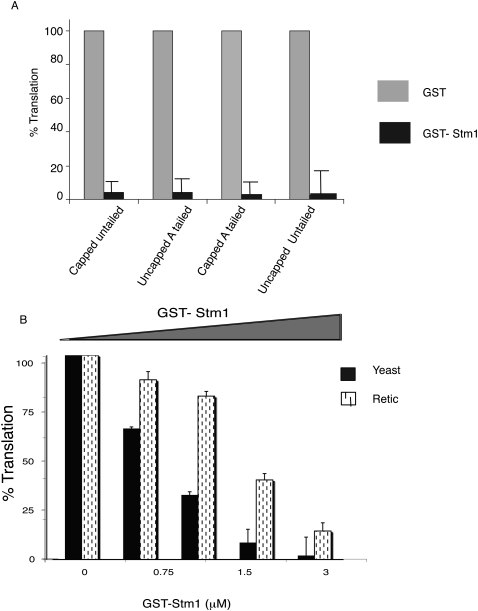
Stm1's interaction with ribosomes (Inada et al. 2002; Van Dyke et al. 2004, 2006, 2009) suggests that ribosomes might be the target of Stm1's inhibition of translation. Consistent with that possibility, examination of reporter mRNAs lacking a cap or poly(A) tail or both indicated that Stm1 could repress translation independent of these structures (Fig. 3A). We interpret this observation to suggest that the target of Stm1 inhibition of translation is not the cap or poly(A) tail.
FIGURE 3.
Stm1's translation repression activity is independent of Cap or poly(A) tail or eEF3. (A) Shown is the effect of GST (gray bars) or GST-Stm1 (black bars) on the translation of luciferase mRNA with or without methyl G7 cap and/or poly(A) tail. (B) Stm1 is able to repress translation in reticulocyte lysates system where eEF3 is absent. Dose-dependent repression of translation by Stm1 in vitro in yeast extracts (solid black bars) and reticulocyte lysates (dashed bars).
Based on earlier experiments on Stm1, two models for Stm1 inhibition of translation can be envisioned, which can be distinguished by the examination of Stm1's effect on translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. First, Stm1 might bind ribosomes and directly inhibit their function. Since ribosomes are highly conserved, this model predicts that Stm1 would inhibit translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Alternatively, since Stm1 limits the interaction of eEF3 with ribosomes (Van Dyke et al. 2009), Stm1 might indirectly block translation through inhibition of eEF3 function. Since eEF3 is a fungal-specific translation factor (Kovalchuke and Chakraburtty 1994; Chakraburtty and Triana-Alonso 1998; Blakely et al. 2001), this latter model predicts that Stm1 should have no effect on translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates, which is independent of eEF3.
To distinguish between these models, we examined the effect of Stm1 on translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Following addition of Stm1 to rabbit reticulocyte lysates, translation was repressed, although the magnitude of repression was reduced as compared to yeast extracts (Fig. 3B). These results indicate that the target of Stm1 repression is conserved between yeast and mammals and argue that Stm1 does not inhibit translation by blocking eEF3 function.
To determine how Stm1 inhibits translation, we examined the types of complexes formed on a radiolabeled reporter mRNA based on the yeast MFA2 mRNA using sucrose gradient analysis when Stm1 inhibited translation. Translation initiation proceeds by the formation of an mRNP, which then recruits the multifactor complex, which includes eIF3, eIF2, the initiator tRNA, and the 40S subunit, to form a 48S complex. Subsequently, the 48S complex recognizes the AUG start codon, leading to recruitment of the 60S subunit to form an 80S complex that enters elongation (for review, see Acker and Lorsch 2008; Jackson et al. 2010).
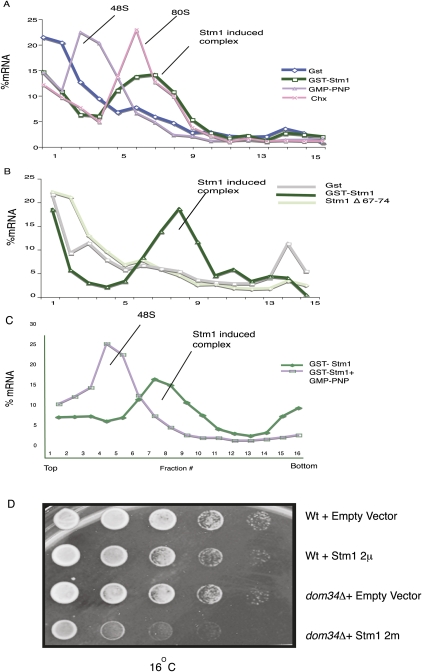
A striking result was that the addition of Stm1 led to the accumulation of the MFA2 mRNA in a high-molecular-weight complex (Fig. 4A). This complex was larger than a 48S complex, which accumulates in the presence of GMP-PNP (Gray and Hentze 1994), and comigrated with an 80S complex, which accumulates in the presence of the elongation blocker cycloheximide (Fig. 4A; Thermann and Hentze 2007). The formation of the 80S complex is related to Stm1 repression of translation since the Stm1Δ67-74 protein, which is defective in translation repression (Fig. 2E), shows reduced accumulation of the 80S complex (Fig. 4B). The accumulation of an 80S complex is not limited to the MFA2 mRNA as Stm1's inhibition of translation also led to the accumulation of the luciferase mRNA in a large complex (data not shown), although this complex was slightly larger than the 80S complex formed with the MFA2 mRNA, presumably due to the larger size of the luciferase mRNA (1751 nt as compared to 330 nt). These results indicate that Stm1 inhibits translation by blocking the function of the 80S complex.
FIGURE 4.
Stm1 can stall 80S ribosome on mRNAs. (A) Sedimentation of radiolabeled MFA2 mRNA in sucrose gradients, when translation reactions are assembled with GST (blue curve), GST-Stm1 (green curve), GMP-PNP (purple curve), or cycloheximide (pink curve). The location of the 48S, 80S, and Stm1 complexes is indicated in the figures. (B) Comparison of 80S complex formation between GST (gray curve), GST-Stm1 (dark green curve), and GST-Stm1Δ67-74 (light green curve) recombinant proteins. (C) Stm1 complex formation depends on 60S subunit joining. Shown is the sedimentation of radiolabeled MFA2 mRNA in sucrose gradients, when translation reactions are assembled with GST-Stm1 alone (green curve) or GST-Stm1 in combination with GMP-PNP (purple curve). (D) STM1 shows genetic interaction with DOM34. Stm1 was overexpressed using a 2μ plasmid in wild-type and dom34Δ strains. Growth at 16°C was monitored over a period of 5 d.
The ability of Stm1 to trap an 80S complex predicts that inhibiting translation upstream of 80S complex formation should reduce the Stm1-induced 80S complex. To test this possibility, we examined if Stm1 induced 80S complex formation in the presence of GMP-PNP (Gray and Hentze 1994; Coller and Parker 2005; Nissan et al. 2010), a non-hydrolysable GTP analog that prevents 60S subunit, leading to the accumulation of the 48S complex. Addition of GMP-PNP blocked the ability of Stm1 to induce an 80S complex and led to the accumulation of a 48S complex as expected (Fig. 4C). This provides further evidence that the 80S complex accumulating in the presence of Stm1 requires subunit joining and is formed by the normal process of translation initiation.
Recent results have shown that the Dom34/Hbs1 complex functions analogously to a termination codon at prolonged elongation stalls to disassemble the translation complex (Chen et al. 2010; Shoemaker et al. 2010). Since Stm1 can induce translational stalls in vitro, we examined if there was any genetic interaction of STM1 and DOM34 in vivo. We observed that at low temperatures (16°C), Stm1 overexpression showed a stronger growth inhibition in dom34Δ strains as compared to wild-type strains (Fig. 4D). This provides additional genetic evidence that Stm1 stalls ribosomes in vivo and suggests that the Dom34/Hbs1 complex may play a role in releasing ribosomes stalled by Stm1.
DISCUSSION
Three observations indicate that Stm1 can inhibit translation in vitro by blocking function of the 80S ribosome. First, Stm1 inhibits translation in vitro (Fig. 2). Second, during Stm1-mediated repression, the mRNA accumulates in an 80S complex (Fig. 4). Moreover, formation of this 80S complex depends on 60S joining since it is blocked by the addition of GMP-PNP (Fig. 4). In principle, Stm1 could be inhibiting a late step in translation initiation (after 80S joining), or Stm1 could generally inhibit any elongation event.
Several observations suggest that the inhibition of translation by Stm1 in extracts is related to its function in vivo. First, we observed that mutations in STM1 that inactivated its genetic interactions with decapping activators in vivo also reduced the ability of Stm1 to inhibit translation in vitro (Fig. 2). It should be noted that since translation and mRNA decapping are typically inversely related (Coller and Parker 2004), the ability of Stm1 to inhibit translation would be consistent with the requirement of Stm1 for the normal degradation of some yeast mRNAs (Balagopal and Parker 2009). Moreover, overexpression of Stm1 inhibits the growth of dom34Δ strains at low temperature (Fig. 4D), which could be explained by Stm1 promoting ribosome stalling in a manner that was resolved by the Dom34/Hbs1 complex (Chen et al. 2010; Shoemaker et al. 2010).
Given the interaction of Stm1 with ribosomes, two general models for Stm1 function can be envisioned. First, Stm1 might bind ribosomes and inhibit a substep in the translation elongation cycle. Second, since Stm1 limits the interaction of eEF3 with ribosomes, the reduction in translation could be due to eEF3 no longer interacting sufficiently with the ribosome. Because Stm1 can also inhibit translation in mammalian cell extracts (Fig. 3), which lack eEF3, we favor the interpretation that Stm1 binds ribosomes independently of eEF3 and directly inhibits their function. Consistent with that possibility, Stm1 binding to ribosomes is not influenced by the levels of ribosome-bound eEF3 (Van Dyke et al. 2009). However, it remains a possibility that Stm1 also affects eEF3 function.
Stm1 has been proposed to promote substeps in the translation elongation cycle, based in part on the hypersensitivity of stm1Δ strains to translation elongation inhibitors, and a subtle increase in polysomes and a decrease in the 80S monosome peak as compared to wild-type strains when grown in galactose-containing media (Van Dyke et al. 2009). However, in our strain background, we have not observed a hypersensitivity of the stm1Δ strain to translation elongation inhibitors or a reproducible difference in polysome profiles between wild-type and stm1Δ strains even when the polysome analysis is performed with or without added cycloheximide (data not shown). This suggests that these phenotypes might be strain- or condition-dependent, which is consistent with stm1Δ strains showing no difference in polysome profiles when grown in the presence of glucose (see Fig. 2 of Van Dyke et al. 2009). Future biochemical and structural work will be required to determine the precise mode of Stm1 function.
The ability of Stm1 to stall ribosomes after formation of an 80S complex raises the intriguing possibility that some mRNAs will be controlled at this step either for their targeting to decapping or for holding them in a paused state of elongation to allow for rapid resumption of translation. This could serve as a sharp on/off switch for control of translation in a manner analogous to the regulation of transcription at a postinitiation stage (Wu and Snyder 2008; Chopra et al. 2009; Nechaev et al. 2010).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Yeast strains, growth conditions, and plasmids
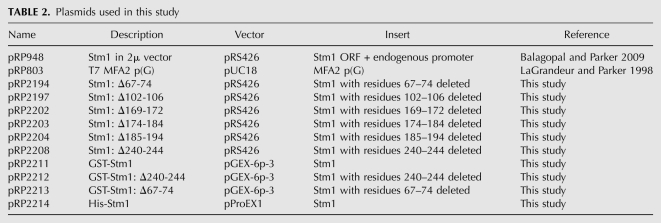
Yeast strains are grown in either standard yeast extract/peptone (YP) or synthetic medium (SC) supplemented with appropriate amino acids and 2% dextrose. Strains were grown at 30°C unless otherwise stated. The genotypes of all strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. All the plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 2. All mutant variations of the parental wild-type plasmids were made by Quick Change mutagenesis (Stratagene) and verified by sequencing.
TABLE 1.
Yeast strains used in this study
TABLE 2.
Plasmids used in this study
Purification of recombinant Stm1
GST or HIS-tagged Stm1 expression plasmids were transformed into BL21 cells and grown to an OD of 0.6. Protein expression was induced for 4 h using IPTG and purified from E. coli using glutathione-Sepharose beads (GE) or Talon IMAC resin (Clontech) according to standard protocols. Purified protein was concentrated and dialyzed into 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), and 2 mM DTT with 50% glycerol and stored at 20°C.
In vitro translation assays
Yeast extracts were prepared as described previously with minor modifications (Iizuka and Sarnow 1997; Wu et al. 2007). Briefly, yRP930 cells were grown to saturation overnight, lysed using a Retsch PM200 mill with cells frozen in liquid nitrogen, and lysed twice at 300 rpm in canisters cooled with liquid nitrogen for 3 min. After thawing, gel filtration and extract preparation were similar to the published protocols.
In vitro translation reactions were conducted using 200 ng of uncapped poly(A)+ (Promega) or Capped A tailed luciferase mRNA. The capped message was transcribed using Megascript (Ambion) from T7 luciferase control plasmid (Promega #L4821) linearized with Ecl136II, and A-tailed using the poly(A) tailing kit (Ambion). Reactions were assembled at room temperature, started with the addition of mRNA, and incubated for 50 min. Translation was monitored using luciferase enzymatic assay (Promega). To assess the stability of luciferase mRNA, translation reactions were assembled as above, with aliquots removed at 0, 20, and 50 min of incubation. The mRNA was purified using MegaClear columns (Ambion) and run on a 1.25% formaldehyde agarose gel. mRNA was analyzed by Northern blot with an end-labeled probe to luciferase mRNA (oRP1435: 5′-caatttggactttccgccctt-3′) or to 25S rRNA (Leeds et al. 2006) as an internal control. Quantitation of blots was done by PhosphorImager scanning and ImageQuant software (Amersham Biosciences).
In Figure 4, translation was performed using capped radiolabeled MFA2pG poly(A)+ RNA transcribed from Xba1-linearized pRP803 (LaGrandeur and Parker 1998) with MAXIScript (Ambion) and incubated for 15 min. These reactions were supplemented with 5 mM GMP-PNP and 7.5 mM MgOAc or 0.5 mg/mL cycloheximide as appropriate. The extracts were loaded on a 15%–50% sucrose gradient and sedimented in a SW41 rotor at 39,000 rpm for 2.5 h at 4°C. Radioactivity was assayed by Cerenkov counting.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank all members of the Parker laboratory, especially Tracy Nissan, Saumya Jain, Kylie Swisher, Sarah Mitchell, Denise Muhlrad, and Anne Webb for valuable input and useful discussions. Thanks to Amma and Vivek for moral support and encouragement. This work was supported by funds from the National Institutes of Health (Grant R37 GM45443) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
Article published online ahead of print. Article and publication date are at http://www.rnajournal.org/cgi/doi/10.1261/rna.2677311.
REFERENCES
- Acker MG, Lorsch JR 2008. Mechanism of ribosomal subunit joining during eukaryotic translation initiation. Biochem Soc Trans 36: 653–657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balagopal V, Parker R 2009. Stm1 modulates mRNA decay and Dhh1 function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 181: 93–103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely G, Hekman J, Chakraburtty K, Williamson PR 2001. Evolutionary divergence of an elongation factor 3 from Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol 183: 2241–2248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brachmann CB, Davies A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: A useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14: 115–132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraburtty K, Triana-Alonso FJ 1998. Yeast elongation factor 3: structure and function. Biol Chem 379: 831–840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L, Muhlrad D, Hauryliuk V, Cheng Z, Lim MK, Shyp V, Parker R, Song H 2010. Structure of the Dom34–Hbs1 complex and implications for no-go decay. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 1233–1240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra VS, Hong JW, Levine M 2009. Regulation of Hox gene activity by transcriptional elongation in Drosophila. Curr Biol 19: 688–693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller J, Parker R 2004. Eukaryotic mRNA decapping. Annu Rev Biochem 73: 861–890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller J, Parker R 2005. General translational repression by activators of mRNA decapping. Cell 122: 875–886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garneau NL, Wilusz J, Wilusz CJ 2007. The highways and byways of mRNA decay. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 113–126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray NK, Hentze MW 1994. Iron regulatory protein prevents binding of the 43S translation pre-initiation complex to ferritin and eALAS mRNAs. EMBO J 13: 3882–3891 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka N, Sarnow P 1997. Translation-competent extracts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Effects of L-A RNA, 5′ cap, and 3′ poly(A) tail on translational efficiency of mRNAs. Methods 11: 353–360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada T, Winstall E, Tarun SZ Jr, Yates JR III, Schieltz D, Sachs AB 2002. One-step affinity purification of the yeast ribosome and its associated proteins and mRNAs. RNA 8: 948–958 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson RJ, Hellen CU, Pestova TV 2010. The mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation and principles of its regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11: 113–127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovalchuke O, Chakraburtty K 1994. Comparative analysis of ribosome-associated adenosinetriphosphatase (ATPase) from pig liver and the ATPase of elongation factor 3 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 226: 133–140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGrandeur TE, Parker R 1998. Isolation and characterization of Dcp1p, the yeast mRNA decapping enzyme. EMBO J 17: 1487–1496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeds NB, Small EC, Hiley SL, Hughes TR, Staley JP 2006. The splicing factor Prp43p, a DEAH box ATPase, functions in ribosome biogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26: 513–522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nechaev S, Fargo DC, dos Santos G, Liu L, Gao Y, Adelman K 2010. Global analysis of short RNAs reveals widespread promoter-proximal stalling and arrest of Pol II in Drosophila. Science 327: 335–338 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissan T, Rajyaguru P, She M, Song H, Parker R 2010. Decapping activators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae act by multiple mechanisms. Mol Cell 39: 773–783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R, Song H 2004. The enzymes and control of eukaryotic mRNA turnover. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 121–127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz DC, Parker R 1999. Mutations in translation initiation factors lead to increased rates of deadenylation and decapping of mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 19: 5247–5256 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz DC, Parker R 2000. mRNA decapping in yeast requires dissociation of the cap binding protein, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E. Mol Cell Biol 20: 7933–7942 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker CJ, Eyler DE, Green R 2010. Dom34:Hbs1 promotes subunit dissociation and peptidyl-tRNA drop-off to initiate no-go decay. Science 330: 369–372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharun S, He W, Mayes AE, Lennertz P, Beggs JD, Parker R 2000. Yeast Sm-like proteins function in mRNA decapping and decay. Nature 404: 515–518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thermann R, Hentze MW 2007. Drosophila miR2 induces pseudo-polysomes and inhibits translation initiation. Nature 447: 875–878 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke MW, Nelson LD, Weilbaecher RG, Mehta DV 2004. Stm1p, a G4 quadruplex and purine motif triplex nucleic acid-binding protein, interacts with ribosomes and subtelomeric Y′ DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 279: 24323–24333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke N, Baby J, Van Dyke MW 2006. Stm1p, a ribosome-associated protein, is important for protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under nutritional stress conditions. J Mol Biol 358: 1023–1031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke N, Pickering BF, Van Dyke MW 2009. Stm1p alters the ribosome association of eukaryotic elongation factor 3 and affects translation elongation. Nucleic Acids Res 37: 6116–6125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winzeler EA, Shoemaker DD, Astromoff A, Liang H, Anderson K, Andre B, Bangham R, Benito R, Boeke JD, Bussey H, et al. 1999. Functional characterization of the S. cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 285: 901–906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu JQ, Snyder M 2008. RNA polymerase II stalling: loading at the start prepares genes for a sprint. Genome Biol 9: 220 doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-5-220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C, Amrani N, Jacobson A, Sachs MS 2007. The use of fungal in vitro systems for studying translational regulation. Methods Enzymol 429: 203–225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]