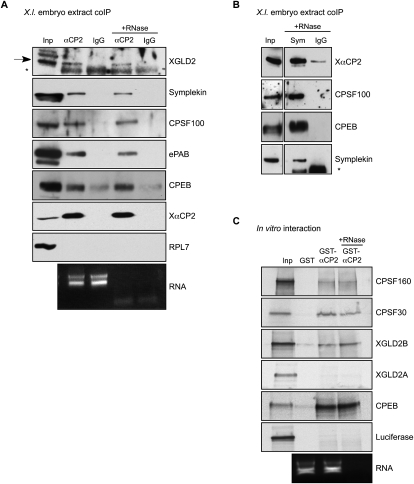
FIGURE 3.
XαCP2 interacts with proteins involved in the cytoplasmic polyadenylation pathway. (A) Co-IP analysis of XαCP2-associated proteins in Xenopus embryo extract. XαCP2 and associated proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-αCP2 antibody in the presence or absence of RNase. Protein enrichment was assessed relative to the input (2.5% of total) and to their content in a parallel immunoprecipitation carried out with preimmune sera (IgG). The enrichment for XαCP2 confirmed the effectiveness of the immunoprecipitation. The data reveal selective enrichment of the G-complex proteins XGLD2, symplekin, CPSF100, and CPEB, as well as the embryonic PABP isoform (ePAB). In each case, the association with XαCP2 was RNA independent. There was no appreciable enrichment of the ribosomal protein, RPL7, used as a non-interacting control. The black arrow in the XGLD2 Western denotes the XGLD2 band, while the asterisk (*) denotes the position of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain in the immunoprecipitates. Aliquots of total RNA extracted from the nonbinding supernatants of each co-IP were run on an Agarose gel to confirm effective RNase treatment as monitored by loss of 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA bands. (B) A reciprocal co-IP using anti-symplekin antibody confirms the interactions with XαCP2, CPSF100, and CPEB. The asterisk in the symplekin Western denotes unreduced immunoprecipitation antibody. (C) GST pull-down studies. Recombinant GST-XαCP2 and GST were used as the two affinity reagents. RRL in vitro translation reactions containing [35S]-met were charged with templates encoding CPSF160, CPSF30, XGLD2A, XGLD2B, CPEB, or Luciferase. Each in vitro translation reaction was incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads conjugated with recombinant GST or recombinant GST-XαCP2. One GST-XαCP2 pulldown was treated with RNase to distinguish RNA-dependent interactions. Each input lane represents 5% of total input. The bottom panel is a sample of total RNA from the supernatant of a representative GST pulldown; RNase treatment was monitored as described in A.