Abstract
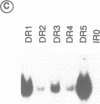
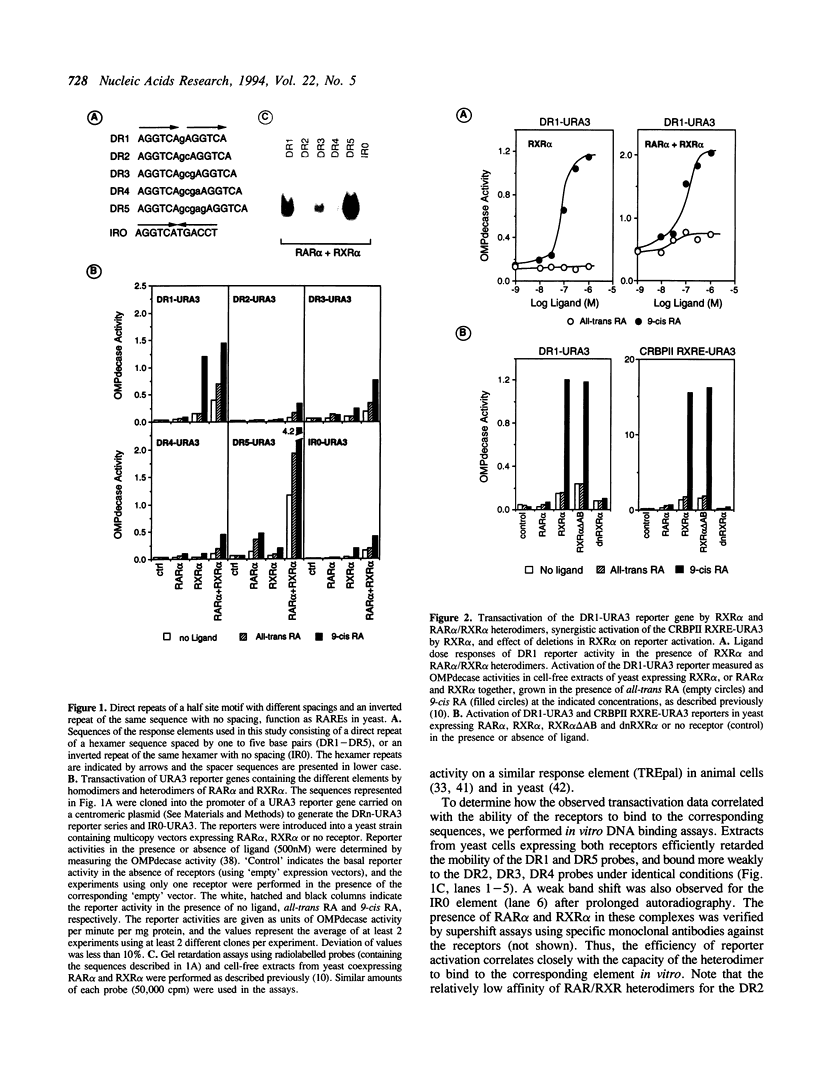
The polymorphic nature of sequences which act as retinoic acid response elements (RAREs and RXREs) in transactivation assays in mammalian cells, suggests that elements consisting of a direct repetition of a half site motif, separated by 1 to 5 base pairs (DR1 to DR5), are targets for retinoic acid (RA) signalling. In a previous report we showed that in yeast cells, heterodimers of the retinoic acid receptors RAR alpha and RXR alpha were required for efficient transcription of a reporter gene containing a DR5 element [Heery et al., (1993); Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90: 4281-4285]. Here we report that DR1 to DR5 elements containing a direct repeat of the 5'-AGGTCA-3' motif, and an inverted repeat of the same sequence with no spacer (IR0), behave as RAREs in yeast cells coexpressing RAR alpha and RXR alpha, albeit with different efficacies. Heterodimer activity was strongest on a DR5 reporter gene, and the strength of activation of the reporter series (DR5 > DR1 > DR3 > DR2 = IR0 = DR4) correlated with the ability of the heterodimer to bind to the corresponding sequences in vitro. Significantly, a reporter containing a DR1 element was selectively and efficiently activated in yeast cells expressing only RXR alpha. This activity was dependent on the induction by 9-cis retinoic acid of an activation function (AF-2) located in the RXR alpha ligand binding domain. In addition, a strong synergistic activity of RXR alpha was observed on a reporter containing the putative RXR element (RXRE) from the rat CRBPII gene promoter. Thus, RXR alpha can function independently as a transcription factor, in the absence of RARs or other heteromeric partners. Similarly, homodimers of RAR alpha selectively stimulated the transcription of a DR5 reporter in a ligand-dependent manner, but less efficiently than RAR alpha/RXR alpha heterodimers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrodin T. J., Marks M. S., Ozato K., Linney E., Lazar M. A. Heterodimerization among thyroid hormone receptor, retinoic acid receptor, retinoid X receptor, chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor, and an endogenous liver protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Sep;6(9):1468–1478. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.9.1331778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N. J., Petkovich M., Chambon P. Characterization of a functional promoter for the human retinoic acid receptor-alpha (hRAR-alpha). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6799–6806. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca L. M. Retinoids and their receptors in differentiation, embryogenesis, and neoplasia. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2924–2933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Shean M. L., McBride M. S., Stewart M. J. Retinoic acid response element in the human alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH3: implications for regulation of retinoic acid synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1638–1646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand B., Saunders M., Leroy P., Leid M., Chambon P. All-trans and 9-cis retinoic acid induction of CRABPII transcription is mediated by RAR-RXR heterodimers bound to DR1 and DR2 repeated motifs. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90267-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Dimerization among nuclear hormone receptors. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. Nuclear hormone receptors. Promiscuous liaisons. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):590–591. doi: 10.1038/361590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. L., Smit-McBride Z., Privalsky M. L. Reconstitution of retinoid X receptor function and combinatorial regulation of other nuclear hormone receptors in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heery D. M., Zacharewski T., Pierrat B., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P., Losson R. Efficient transactivation by retinoic acid receptors in yeast requires retinoid X receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor-COUP-TF interactions modulate retinoic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. RAR gamma 2 expression is regulated through a retinoic acid response element embedded in Sp1 sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2976–2985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. Mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha 2 isoform is transcribed from a promoter that contains a retinoic acid response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10138–10142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loison G., Vidal A., Findeli A., Roitsch C., Balloul J. M., Lemoine Y. High level of expression of a protective antigen of schistosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1989 Nov-Dec;5(6):497–507. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., Granner D. K. Hormone response domains in gene transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1131–1173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Leroy P., Chen J. Y., Chambon P. Multiple parameters control the selectivity of nuclear receptors for their response elements. Selectivity and promiscuity in response element recognition by retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Friant S., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. RARs and RXRs: evidence for two autonomous transactivation functions (AF-1 and AF-2) and heterodimerization in vivo. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2349–2360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Saunders M., Kastner P., Durand B., Nakshatri H., Chambon P. Promoter context- and response element-dependent specificity of the transcriptional activation and modulating functions of retinoic acid receptors. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90250-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrat B., Heery D. M., Lemoine Y., Losson R. Functional analysis of the human estrogen receptor using a phenotypic transactivation assay in yeast. Gene. 1992 Oct 1;119(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90277-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisher B. D., Gulick T., Zhang Z., Strauss A. W., Moore D. D., Kelly D. P. Identification of a novel retinoid-responsive element in the promoter region of the medium chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20264–20269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman J. N., Widom R. L., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V., Karathanasis S. K. A retinoic acid-responsive element in the apolipoprotein AI gene distinguishes between two different retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3814–3820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Nakshatri H., Leroy P., Rees J., Chambon P. A retinoic acid response element is present in the mouse cellular retinol binding protein I (mCRBPI) promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2223–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G., Mader S., Gold J. D., Leid M., Lutz Y., Gaub M. P., Chambon P., Gudas L. The late retinoic acid induction of laminin B1 gene transcription involves RAR binding to the responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]