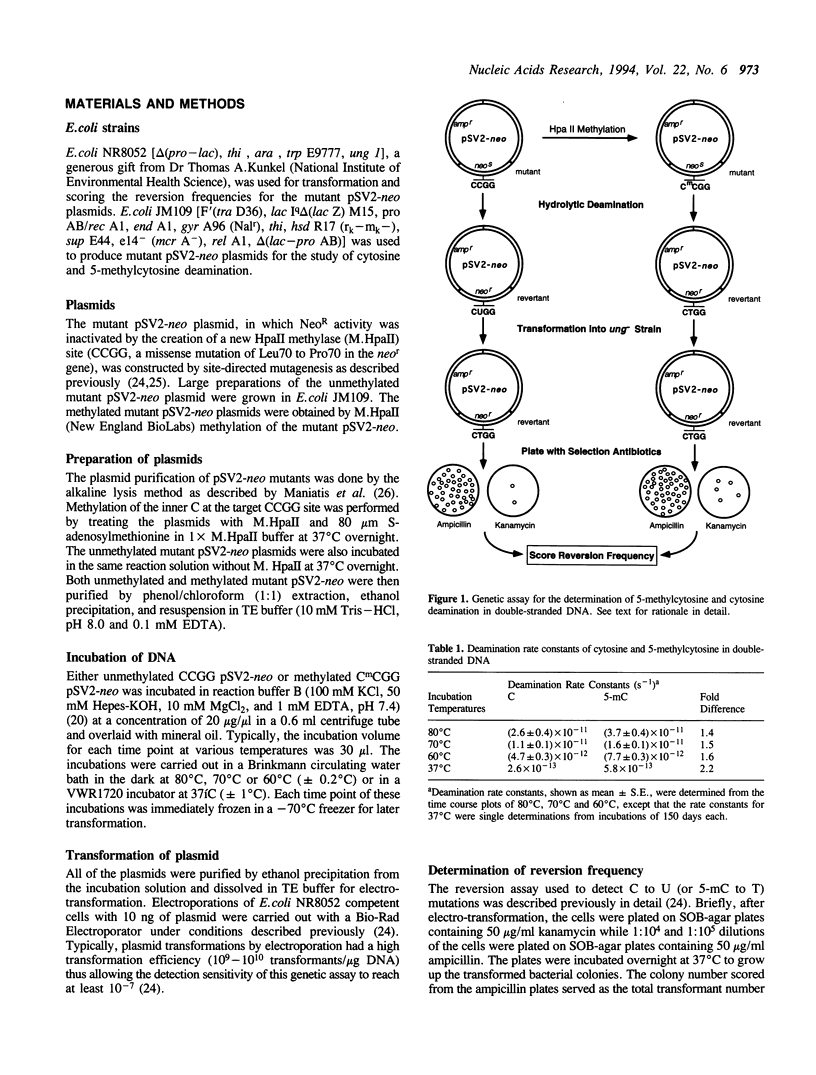
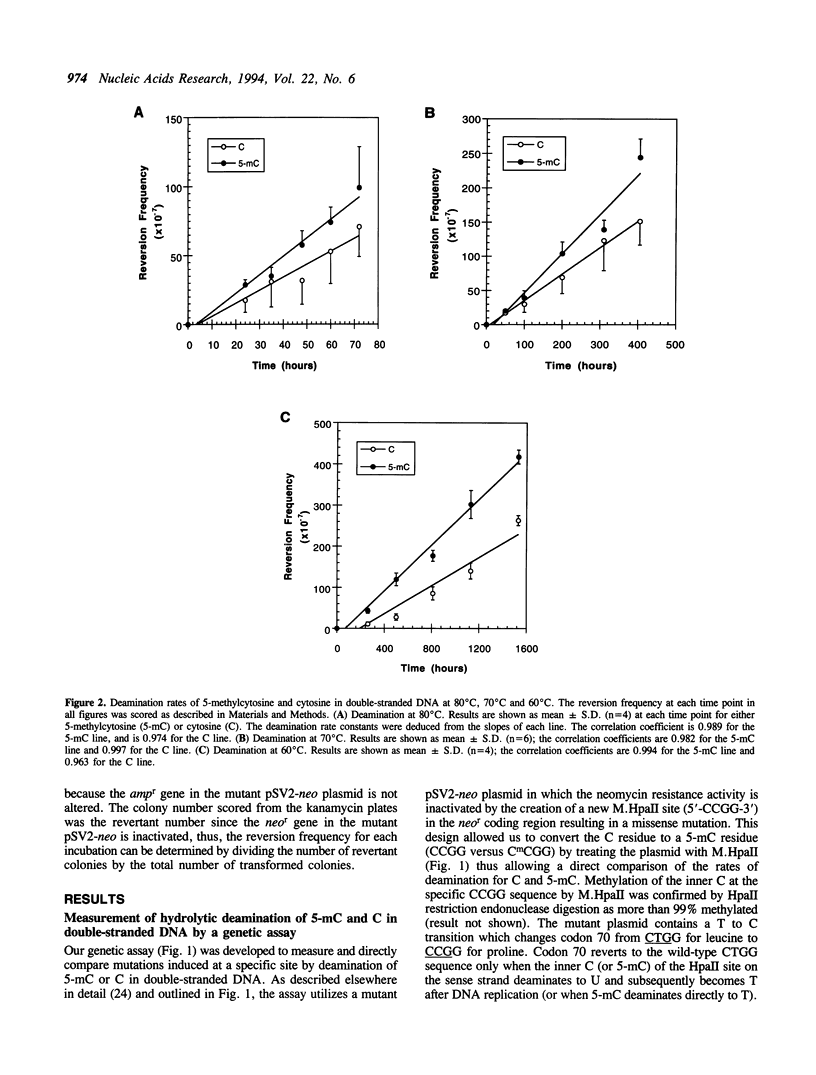
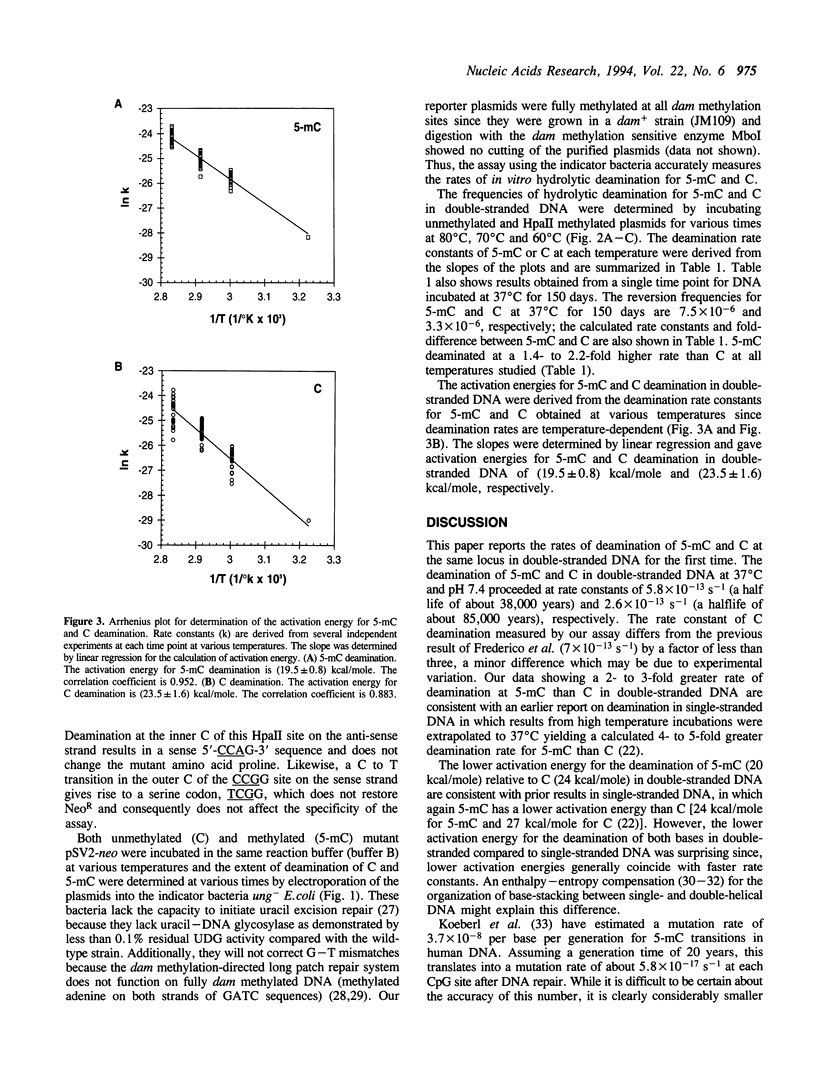
Abstract
The modified base, 5-methylcytosine, constitutes approximately 1% of human DNA, but sites containing 5-methylcytosine account for at least 30% of all germline and somatic point mutations. A genetic assay with a sensitivity of 1 in 10(7), based on reversion to neomycin resistance of a mutant pSV2-neo plasmid, was utilized to determine and compare the deamination rates of 5-methylcytosine and cytosine in double-stranded DNA for the first time. The rate constants for spontaneous hydrolytic deamination of 5-methylcytosine and cytosine in double-stranded DNA at 37 degrees C were 5.8 x 10(-13) s-1 and 2.6 x 10(-13) s-1, respectively. These rates are more than sufficient to explain the observed frequency of mutation at sites containing 5-methylcytosine and emphasize the importance of hydrolytic deamination as a major source of human mutations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breslauer K. J., Remeta D. P., Chou W. Y., Ferrante R., Curry J., Zaunczkowski D., Snyder J. G., Marky L. A. Enthalpy-entropy compensations in drug-DNA binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8922–8926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. C., Jiricny J. A specific mismatch repair event protects mammalian cells from loss of 5-methylcytosine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):945–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90521-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. C., Jiricny J. Different base/base mispairs are corrected with different efficiencies and specificities in monkey kidney cells. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):705–711. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caradonna S. J., Cheng Y. C. Uracil DNA-glycosylase. Purification and properties of this enzyme isolated from blast cells of acute myelocytic leukemia patients. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2293–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Youssoufian H. The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00278187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby B., Prakash L., Davis H., Hinkle D. C. Purification and characterization of a uracil-DNA glycosylase from the yeast. Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5797–5809. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Miller J. H. Mutagenic deamination of cytosine residues in DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):560–561. doi: 10.1038/287560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Norris K. F., Wang R. Y., Kuo K. C., Gehrke C. W. DNA cytosine methylation and heat-induced deamination. Biosci Rep. 1986 Apr;6(4):387–393. doi: 10.1007/BF01116426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederico L. A., Kunkel T. A., Shaw B. R. A sensitive genetic assay for the detection of cytosine deamination: determination of rate constants and the activation energy. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2532–2537. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M., Wagner R., Radman M. Mismatch repair of deaminated 5-methyl-cytosine. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Rideout W. M., 3rd, Shen J. C., Spruck C. H., Tsai Y. C. Methylation, mutation and cancer. Bioessays. 1992 Jan;14(1):33–36. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeberl D. D., Bottema C. D., Ketterling R. P., Bridge P. J., Lillicrap D. P., Sommer S. S. Mutations causing hemophilia B: direct estimate of the underlying rates of spontaneous germ-line transitions, transversions, and deletions in a human gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):202–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Bacterial genes mutL, mutS, and dcm participate in repair of mismatches at 5-methylcytosine sites. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5241–5246. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5241-5246.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Specific mismatch correction in bacteriophage lambda crosses by very short patch repair. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):118–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00330898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Spontaneous mutation at a 5-methylcytosine hotspot is prevented by very short patch (VSP) mismatch repair. Genetics. 1991 May;128(1):23–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA glycosylases, endonucleases for apurinic/apyrimidinic sites, and base excision-repair. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1979;22:135–192. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60800-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):709–715. doi: 10.1038/362709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Ljungquist S., Siegert W., Nyberg B., Sperens B. DNA N-glycosidases: properties of uracil-DNA glycosidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3286–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Heat-induced deamination of cytosine residues in deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3405–3410. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Chlebek J. Uracil-DNA glycosylase in insects. Drosophila and the locust. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9911–9914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukkila P. J., Peterson J., Herman G., Modrich P., Meselson M. Effects of high levels of DNA adenine methylation on methyl-directed mismatch repair in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1983 Aug;104(4):571–582. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radman M., Wagner R. Mismatch repair in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:523–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rideout W. M., 3rd, Coetzee G. A., Olumi A. F., Jones P. A. 5-Methylcytosine as an endogenous mutagen in the human LDL receptor and p53 genes. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1288–1290. doi: 10.1126/science.1697983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal G., Arenaz P., Sirover M. A. Purification and properties of the human placental uracil DNA glycosylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 13;925(2):226–233. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle M. S., Williams D. H. On the stability of nucleic acid structures in solution: enthalpy-entropy compensations, internal rotations and reversibility. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2051–2056. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Klein R. S. The deamination of cytidine and cytosine by acidic buffer solutions. Mutagenic implications. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2358–2362. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen J. C., Rideout W. M., 3rd, Jones P. A. High frequency mutagenesis by a DNA methyltransferase. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. C. Spontaneous mutagenesis: experimental, genetic and other factors. Mutat Res. 1992 Aug;277(2):139–162. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(92)90002-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S. Assessing the underlying pattern of human germline mutations: lessons from the factor IX gene. FASEB J. 1992 Jul;6(10):2767–2774. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.10.1634040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved J., Bird A. The expected equilibrium of the CpG dinucleotide in vertebrate genomes under a mutation model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4692–4696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebauer K., Jiricny J. In vitro correction of G.T mispairs to G.C pairs in nuclear extracts from human cells. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):234–236. doi: 10.1038/339234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



