Abstract
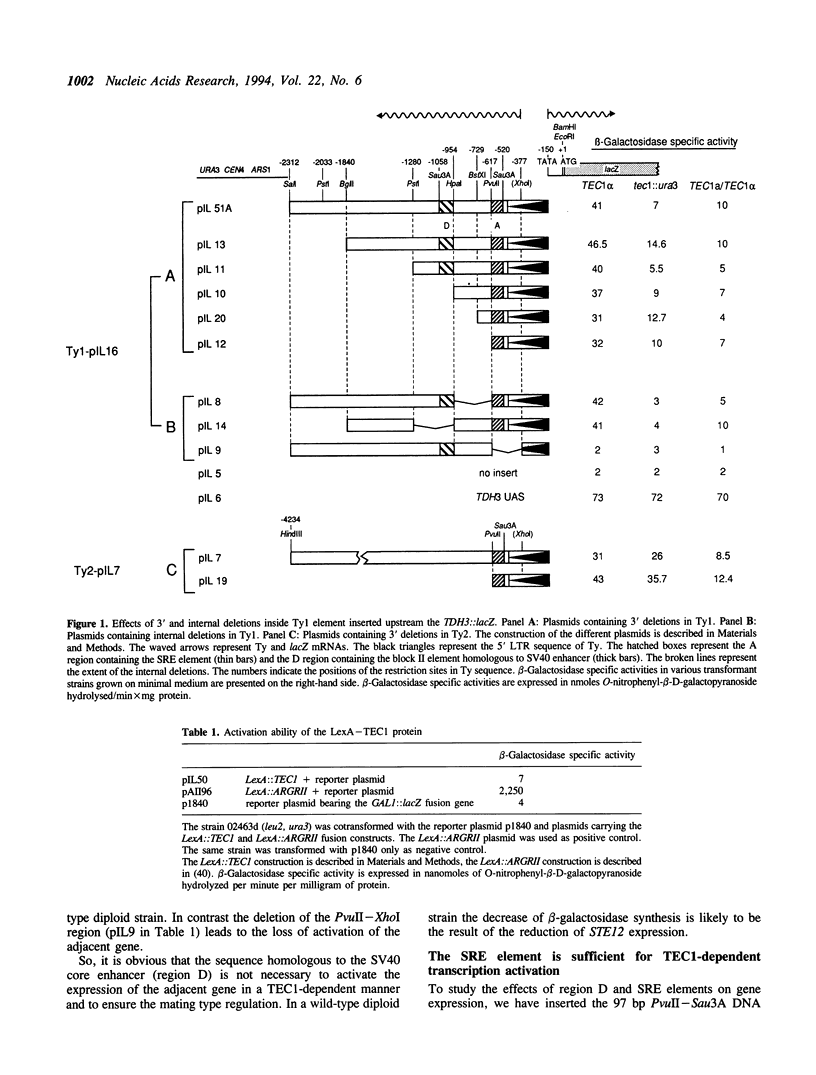
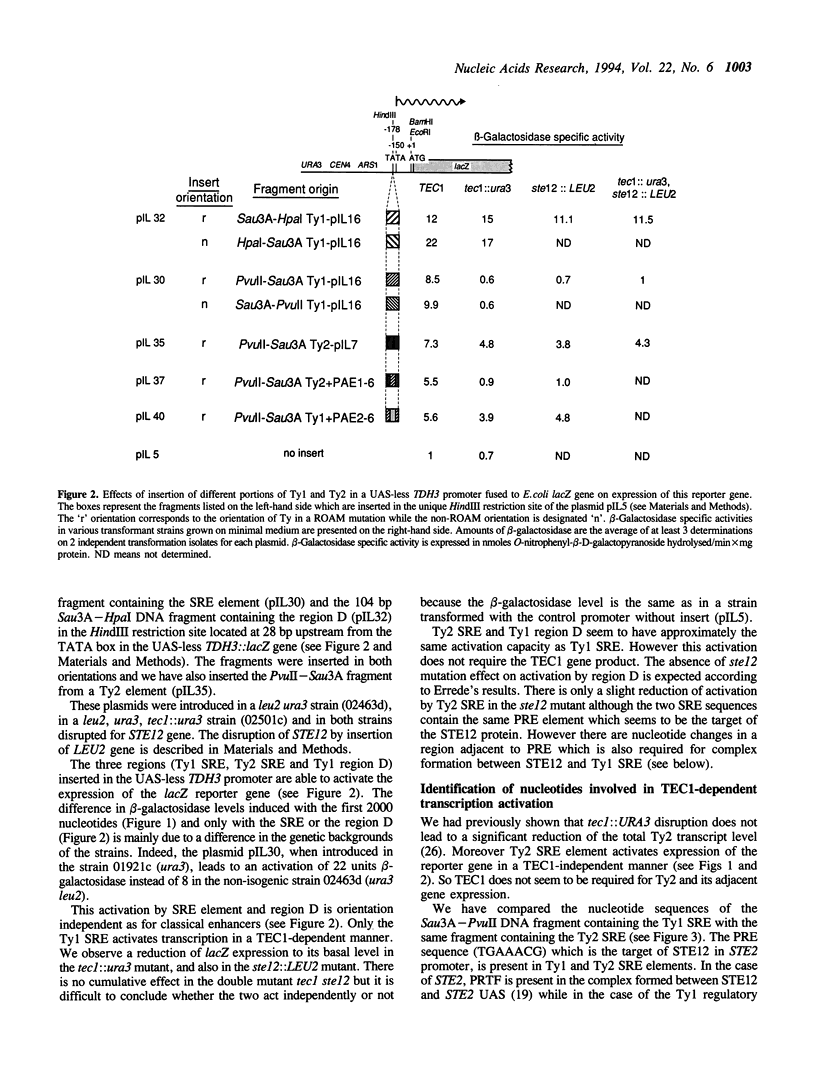
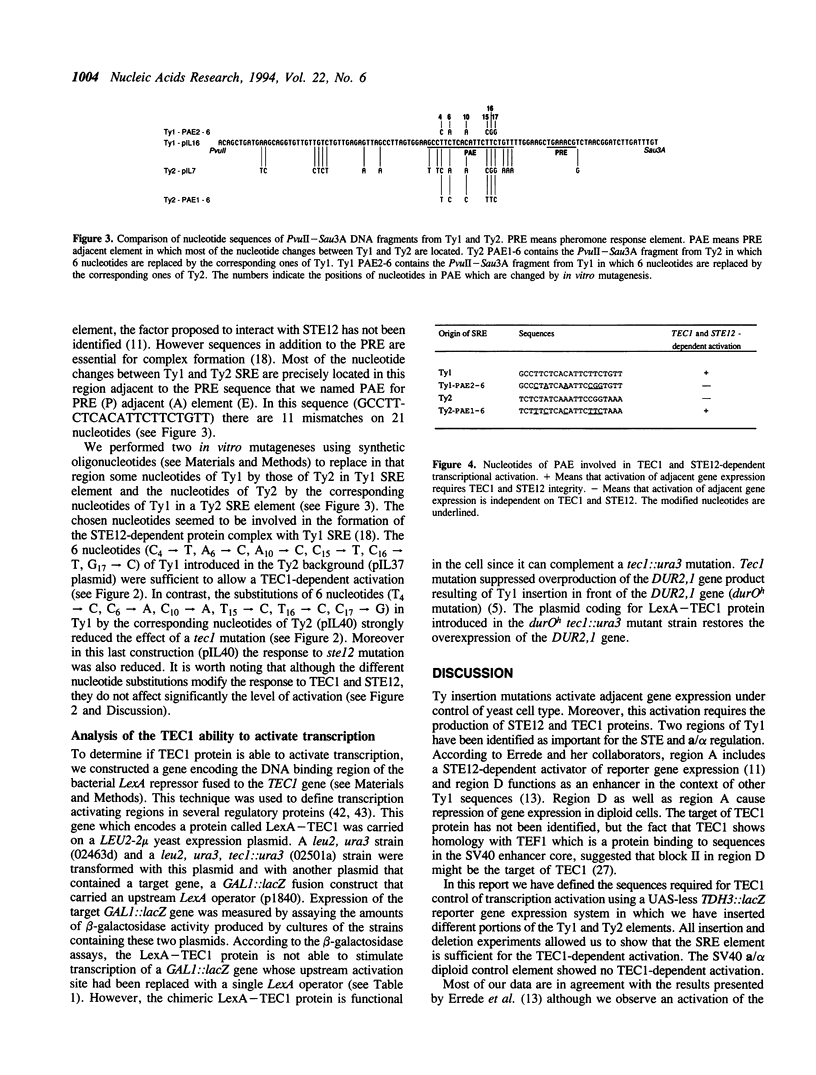
Some Ty1 transposable element insertion mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae activate transcription of adjacent genes in a cell-type dependent manner. This activation requires at least STE12 and TEC1 gene products. The binding site for the STE12 protein is located in the sterile responsive element (SRE), which is just downstream the 5' LTR of Ty1 and contains one copy of the pheromone response element (PRE). This report defines the sequences in Ty1 required for TEC1-dependent activation using a TDH3::lacZ reporter gene in which the UAS was replaced by different portions of a Ty1 or Ty2 element. The Ty1 SRE seems to be sufficient to ensure the TEC1 and STE12-mediated activation whereas Ty2 SRE can activate the expression of the adjacent genes in the absence of both proteins. Adjacent to the PRE element, there is a region (PAE) with extensive sequence divergence in Ty1 and Ty2 SREs. Swapping experiments between Ty1 and Ty2 sequences show that Ty1 PAE is required for the activation of adjacent gene expression in a TEC1 and STE12-dependent manner. The use of a LexA::TEC1 construct indicates that the chimeric protein has no activation ability suggesting that TEC1 could act in conjunction with another factor.
Full text
PDF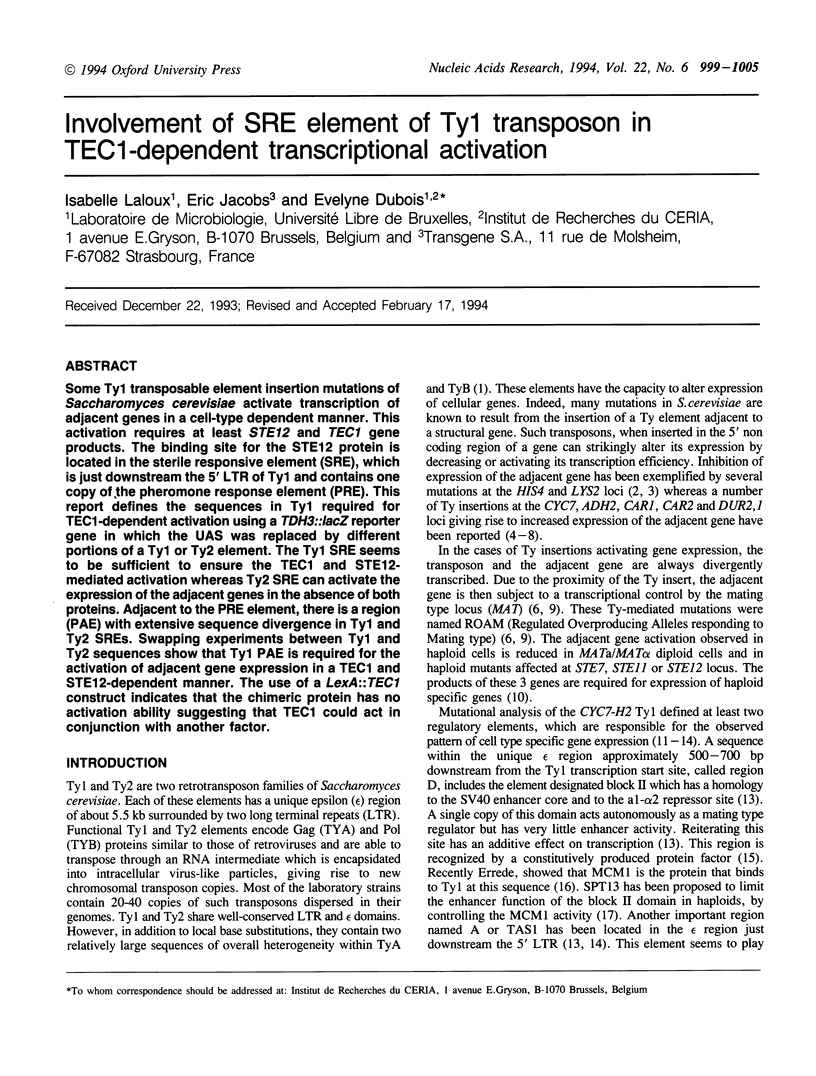



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter G. A., Egan K. M. Expression of heterologous genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from vectors utilizing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R. The TEA domain: a novel, highly conserved DNA-binding motif. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):11–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90132-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M., Freidel K., Löhning C. Characterization of trans-acting mutations affecting Ty and Ty-mediated transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1991 Dec;20(6):441–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00334769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriacy M., Williamson V. M. Analysis of mutations affecting Ty-mediated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):159–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00422784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Company M., Adler C., Errede B. Identification of a Ty1 regulatory sequence responsive to STE7 and STE12. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2545–2554. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Company M., Errede B. A Ty1 cell-type-specific regulatory sequence is a recognition element for a constitutive binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5299–5309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degols G., Jauniaux J. C., Wiame J. M. Molecular characterization of transposable-element-associated mutations that lead to constitutive L-ornithine aminotransferase expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):289–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Jacobs E., Jauniaux J. C. Expression of the ROAM mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: involvement of trans-acting regulatory elements and relation with the Ty1 transcription. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1133–1139. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibel H., Philippsen P. Preferential integration of yeast transposable element Ty into a promoter region. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):386–388. doi: 10.1038/307386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Ammerer G. STE12, a protein involved in cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast, is part of protein-DNA complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1349–1361. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Cardillo T. S., Sherman F., Dubois E., Deschamps J., Wiame J. M. Mating signals control expression of mutations resulting from insertion of a transposable repetitive element adjacent to diverse yeast genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Cardillo T. S., Wever G., Sherman F., Stiles J. I., Friedman L. R., Sherman F. Studies on transposable elements in yeast. I. ROAM mutations causing increased expression of yeast genes: their activation by signals directed toward conjugation functions and their formation by insertion of Ty1 repetitive elements. II. deletions, duplications, and transpositions of the COR segment that encompasses the structural gene of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):593–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Company M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Ty1 sequence with enhancer and mating-type-dependent regulatory activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):258–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B. MCM1 binds to a transcriptional control element in Ty1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P., Liao X. B., Belcourt M., Zhao H., Kapakos J., Clare J. Enhancer and silencerlike sites within the transcribed portion of a Ty2 transposable element of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4824–4834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laloux I., Dubois E., Dewerchin M., Jacobs E. TEC1, a gene involved in the activation of Ty1 and Ty1-mediated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning and molecular analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3541–3550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine Y., Dubois E., Wiame J. M. The regulation of urea amidolyase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mating type influence on a constitutivity mutation acting in cis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X. B., Clare J. J., Farabaugh P. J. The upstream activation site of a Ty2 element of yeast is necessary but not sufficient to promote maximal transcription of the element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8520–8524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A., Kinney D. M., Lusty C. J. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qui H. F., Dubois E., Messenguy F. Dissection of the bifunctional ARGRII protein involved in the regulation of arginine anabolic and catabolic pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2169–2179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen P. D., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. The yeast ROAM mutation--identification of the sequences mediating host gene activation and cell-type control in the yeast retrotransposon, Ty. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7309–7324. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Rose A. B., Pearlman R. E. Transposable element sequences involved in the enhancement of yeast gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5428–5432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Winston F., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty-mediated gene expression of the LYS2 and HIS4 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is controlled by the same SPT genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2431–2434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmington J. R., Waring R. B., Newlon C. S., Indge K. J., Oliver S. G. Nucleotide sequence characterization of Ty 1-17, a class II transposon from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6679–6693. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Young E. T., Ciriacy M. Transposable elements associated with constitutive expression of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chaleff D. T., Valent B., Fink G. R. Mutations affecting Ty-mediated expression of the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Jun;107(2):179–197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G., Fassler J. S. SPT13 (GAL11) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae negatively regulates activity of the MCM1 transcription factor in Ty1 elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


