Abstract
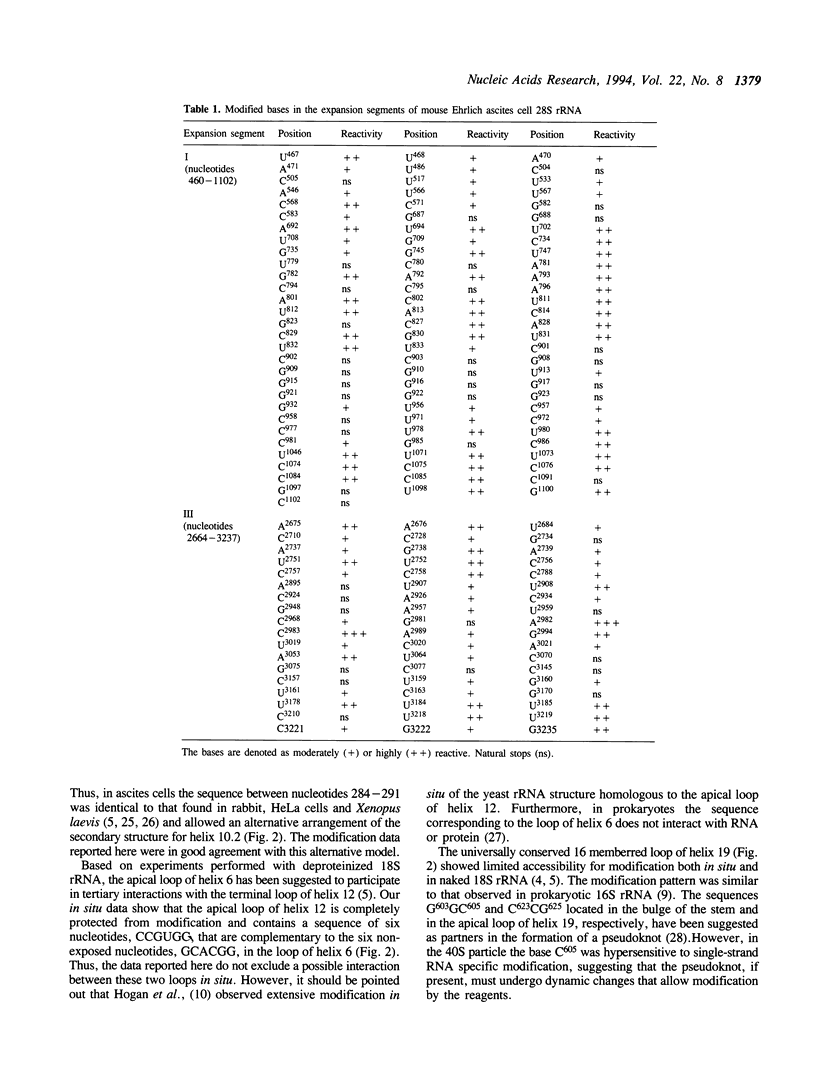
The secondary structure of mouse Ehrlich ascites 18S, 5.8S and 28S ribosomal RNA in situ was investigated by chemical modification using dimethyl sulphate and 1-cyclohexyl-3-(morpholinoethyl) carbodiimide metho-p-toluene sulphonate. These reagents specifically modify unpaired bases in the RNA. The reactive bases were localized by primer extension followed by gel electrophoresis. The three rRNA species were equally accessible for modification i.e. approximately 10% of the nucleotides were reactive. The experimental data support the theoretical secondary structure models proposed for 18S and 5.8/28S rRNA as almost all modified bases were located in putative single-strand regions of the rRNAs or in helical regions that could be expected to undergo dynamic breathing. However, deviations from the suggested models were found in both 18S and 28S rRNA. In 18S rRNA some putative helices in the 5'-domain were extensively modified by the single-strand specific reagents as was one of the suggested helices in domain III of 28S rRNA. Of the four eukaryote specific expansion segments present in mouse Ehrlich ascites cell 28S rRNA, segments I and III were only partly available for modification while segments II and IV showed average to high modification.
Full text
PDF

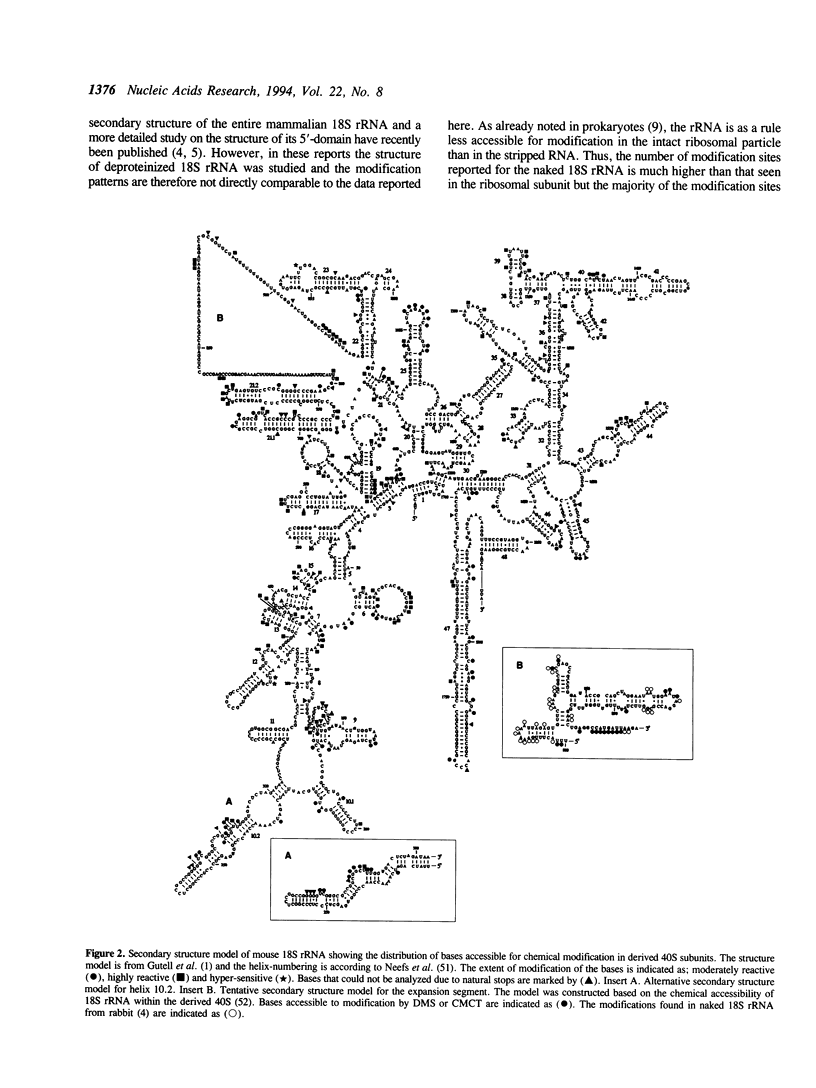
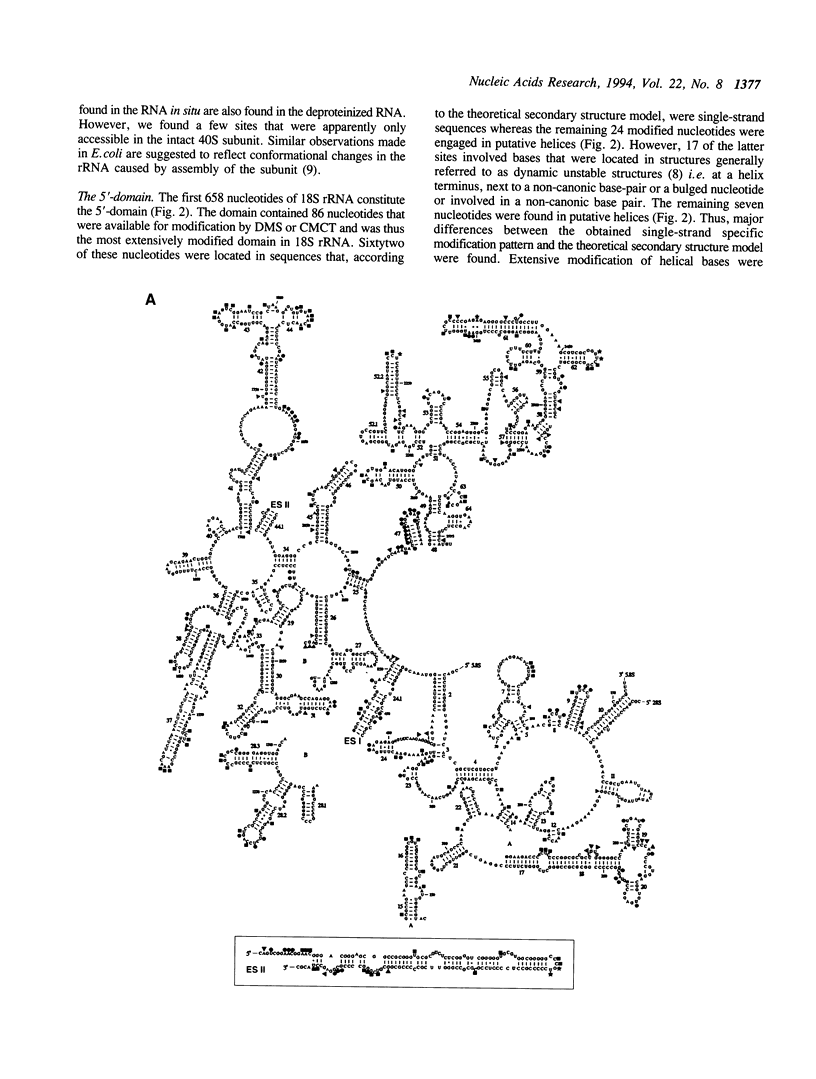
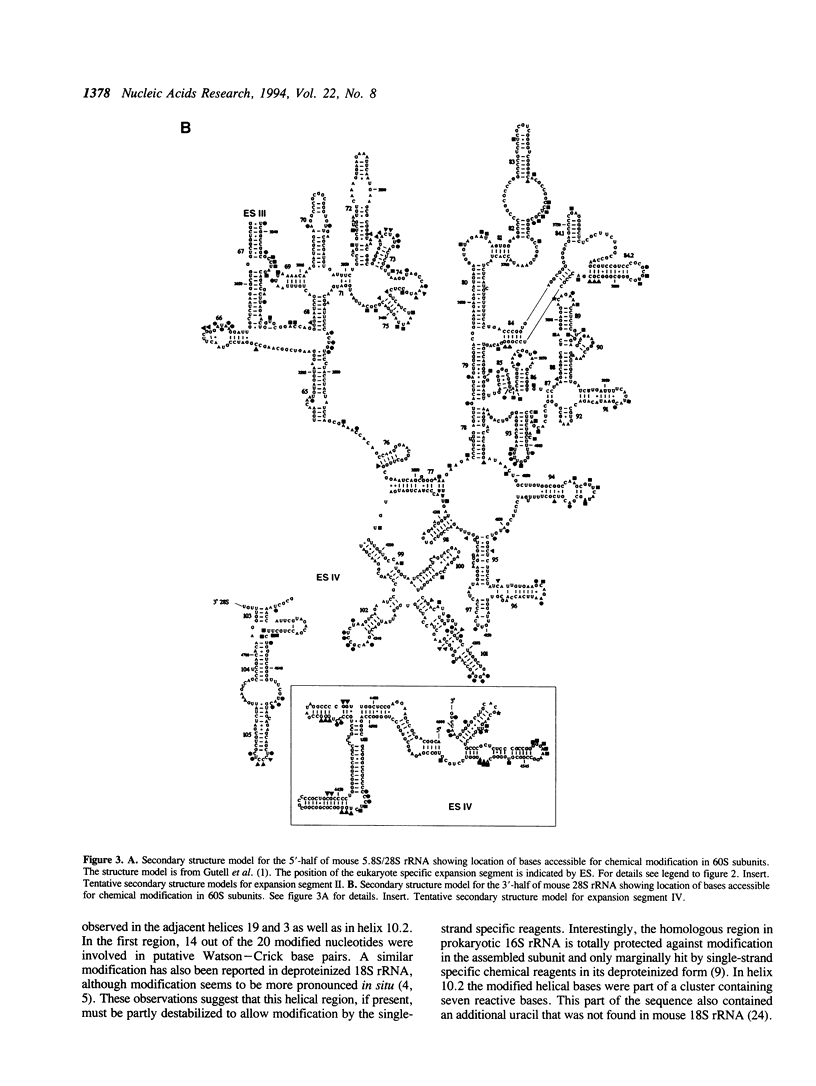



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J., Delihas N., Hanas J. S., Wu C. W. 5S RNA structure and interaction with transcription factor A. 1. Ribonuclease probe of the structure of 5S RNA from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5752–5759. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauclerk A. A., Cundliffe E. The binding site for ribosomal protein L2 within 23S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3589–3594. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G., Mendecki J., Lee S. Y. A procedure for the isolation of mammalian messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):637–641. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruthers M. H., Beaton G., Wu J. V., Wiesler W. Chemical synthesis of deoxyoligonucleotides and deoxyoligonucleotide analogs. Methods Enzymol. 1992;211:3–20. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)11003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Paz V., Olvera J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein S16. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80711-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein S20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 24;1049(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90088-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton J. F., Rairkar A., Lockard R. E., Kumar A. Primary structure of rabbit 18S ribosomal RNA determined by direct RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4731–4745. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Douthwaite S. R., Liljas A., Garrett R. A. Characterization of the binding sites of protein L11 and the L10.(L12)4 pentameric complex in the GTPase domain of 23 S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 20;213(2):275–288. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80190-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Leffers H., Christensen A., Andersen H., Garrett R. A. Structure and accessibility of domain I of Escherichia coli 23 S RNA in free RNA, in the L24-RNA complex and in 50 S subunits. Implications for ribosomal assembly. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90515-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. A compilation of large subunit (23S- and 23S-like) ribosomal RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2095–2109. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna N., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3563–3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Atmadja J., Nierhaus K. H. Evidence that the G2661 region of 23S rRNA is located at the ribosomal binding sites of both elongation factors. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):911–923. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan J. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Probing the conformation of 18S rRNA in yeast 40S ribosomal subunits with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3322–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Melander Y., Nygård O. Ribosome-bound eukaryotic elongation factor 2 protects 5 S rRNA from modification. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21906–21910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano Y., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 31;187(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Egebjerg J., Andersen A., Christensen T., Garrett R. A. Domain VI of Escherichia coli 23 S ribosomal RNA. Structure, assembly and function. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):507–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Kjems J., Ostergaard L., Larsen N., Garrett R. A. Evolutionary relationships amongst archaebacteria. A comparative study of 23 S ribosomal RNAs of a sulphur-dependent extreme thermophile, an extreme halophile and a thermophilic methanogen. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W., Lo A. C., Nazar R. N. Structure of the ribosome-associated 5.8 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 5;171(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo A. C., Liu W. Y., Culham D. E., Nazar R. N. Effects of ribosome dissociation on the structure of the ribosome-associated 5.8S RNA. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;65(6):536–542. doi: 10.1139/o87-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandiyan V., Boublik M. Structural analysis of the 5' domain of the HeLa 18S ribosomal RNA by chemical and enzymatic probing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7055–7062. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. A 5.8 S rRNA-like sequence in prokaryotic 23 S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., De Wachter R. A proposal for the secondary structure of a variable area of eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit RNA involving the existence of a pseudoknot. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5695–5704. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Ribosomal RNA and translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:191–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygård O., Nilsson L. Characterization of the ribosomal properties required for formation of a GTPase active complex with the eukaryotic elongation factor 2. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;179(3):603–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygård O., Westermann P. Purification of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-3 from rat liver microsomes by affinity chromatography on rRNA-cellulose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 30;697(3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz V., Chan Y. L., Glück A., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein S14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9484–9484. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rairkar A., Rubino H. M., Lockard R. E. Chemical probing of adenine residues within the secondary structure of rabbit 18S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):582–592. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal F., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 18 S rRNA gene: comparison with other available homologs. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 27;167(2):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbins-Boaz B., Gerbi S. A. Structural analysis of the peptidyl transferase region in ribosomal RNA of the eukaryote Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 5;217(1):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90614-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Moazed D., Noller H. F. Structural analysis of RNA using chemical and enzymatic probing monitored by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:481–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. RNA-protein interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):783–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2658053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundkvist I. C., Staehelin T. Structure and function of free 40 S ribosome subunits: Characterization of initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):401–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann P., Nygård O., Bielka H. Cross-linking of Met-tRNAf to eIF-2 beta and to the ribosomal proteins S3a and S6 within the eukaryotic inhibition complex, eIF-2 .GMPPCP.Met-tRNAf.small ribosomal subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2387–2396. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R. R. Evidence for several higher order structural elements in ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3119–3122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Winker S., Gutell R. R. Architecture of ribosomal RNA: constraints on the sequence of "tetra-loops". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]