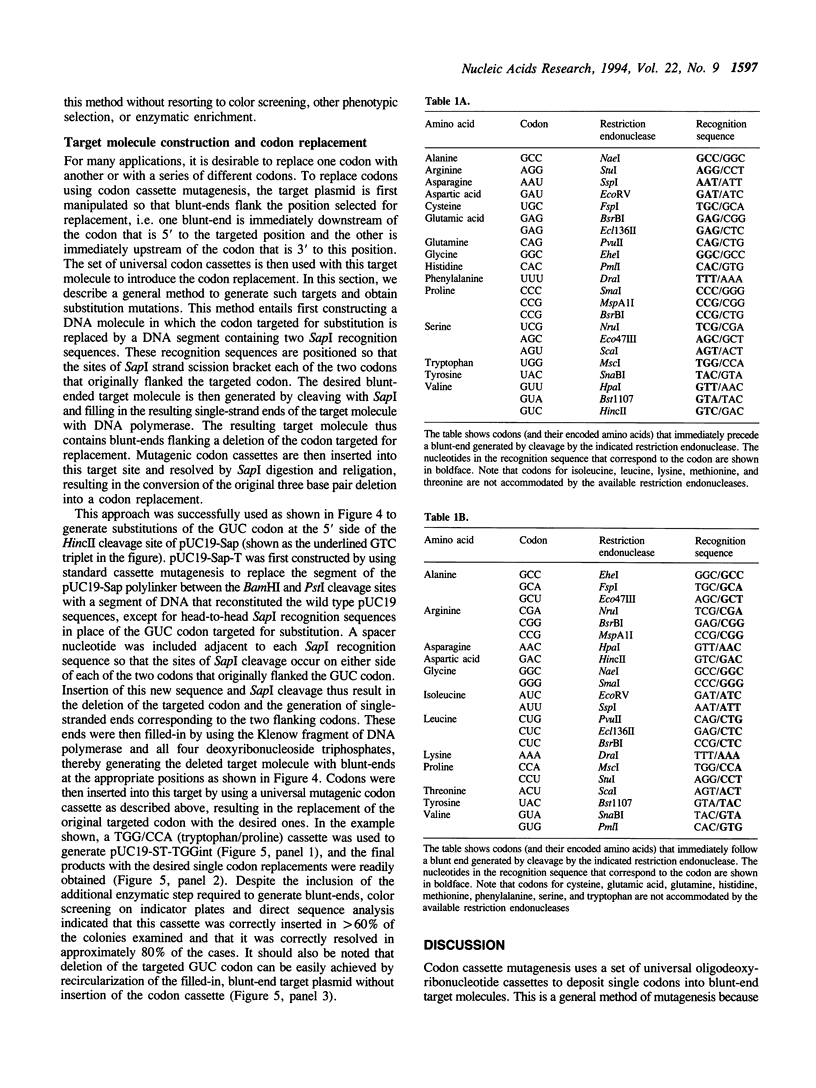
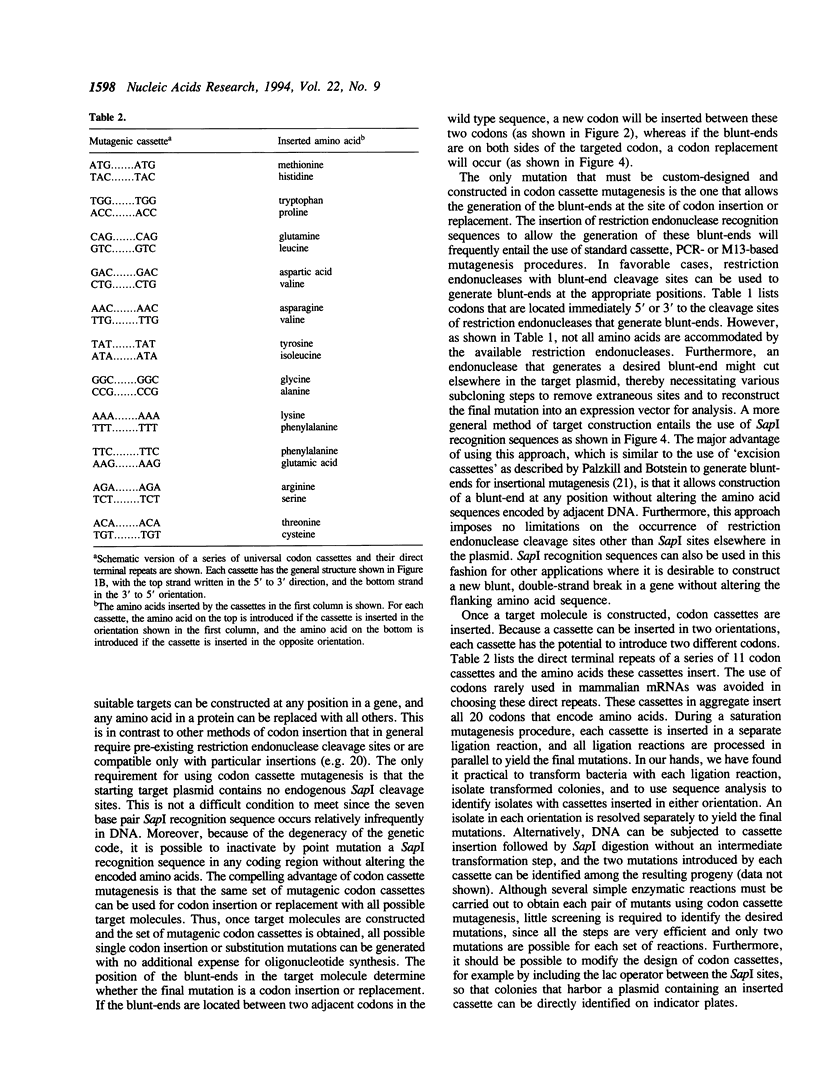
Abstract
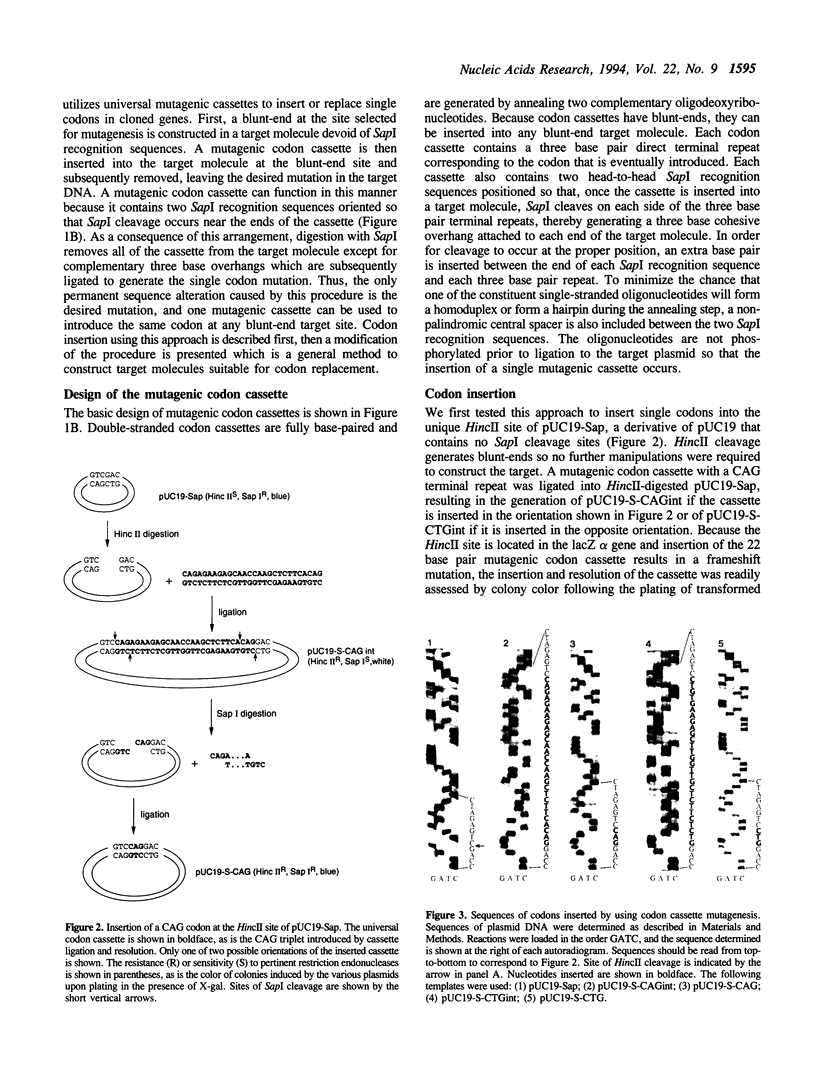
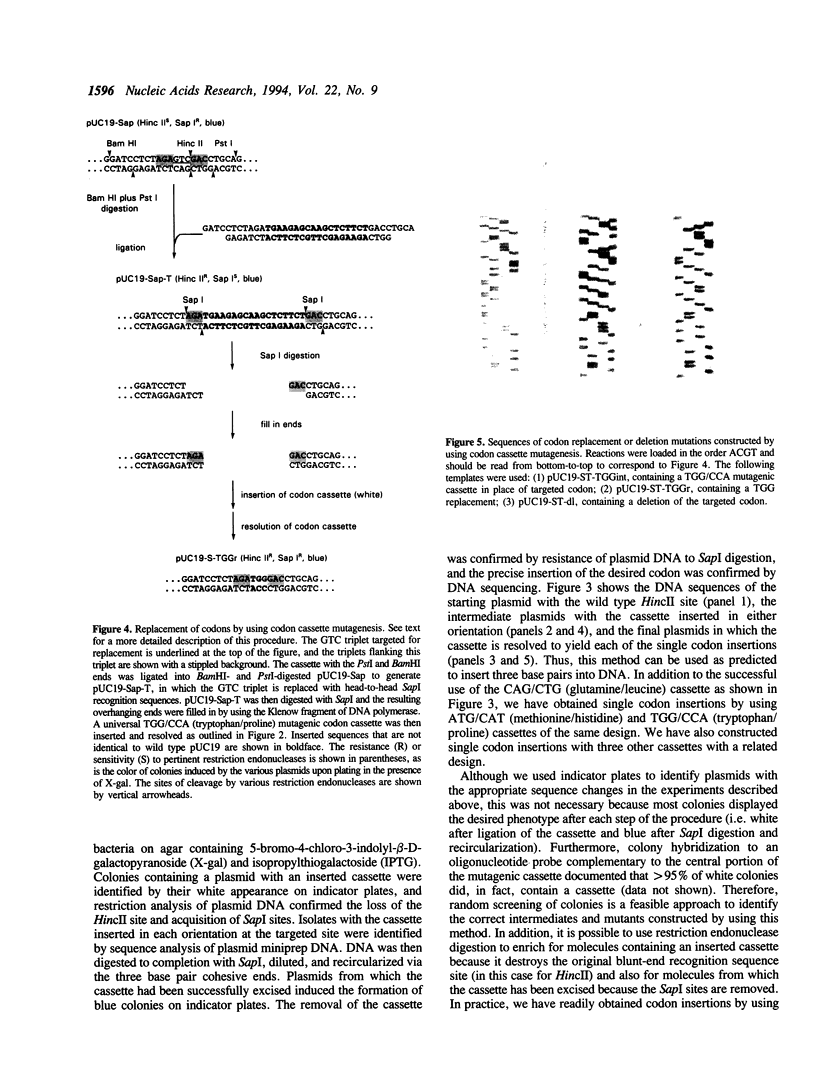
We describe codon cassette mutagenesis, a simple method of mutagenesis that uses universal mutagenic cassettes to deposit single codons at specific sites in double-stranded DNA. A target molecule is first constructed that contains a blunt, double-strand break at the site targeted for mutagenesis. A double-stranded mutagenic codon cassette is then inserted at the target site. Each mutagenic codon cassette contains a three base pair direct terminal repeat and two head-to-head recognition sequences for the restriction endonuclease Sapl, an enzyme that cleaves outside of its recognition sequence. The intermediate molecule containing the mutagenic cassette is then digested with Sapl, thereby removing most of the mutagenic cassette, leaving only a three base cohesive overhang that is ligated to generate the final insertion or substitution mutation. A general method for constructing blunt-end target molecules suitable for this approach is also described. Because the mutagenic cassette is excised during this procedure and alters the target only by introducing the desired mutation, the same cassette can be used to introduce a particular codon at all target sites. Each cassette can deposit two different codons, depending on the orientation in which it is inserted into the target molecule. Therefore, a series of eleven cassettes is sufficient to insert all possible amino acids at any constructed target site. Thus codon cassettes are 'off-the-shelf' reagents, and this methodology should be a particularly useful and inexpensive approach for subjecting multiple different positions in a protein sequence to saturation mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2043–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D. One and two codon insertion mutants of bacteriophage f1. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):288–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00425599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Shortle D. Strategies and applications of in vitro mutagenesis. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1193–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.2994214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire K. M., Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. A simple and efficient procedure for saturation mutagenesis using mixed oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode B. L., Feinstein S. C. "Speedprep" purification of template for double-stranded DNA sequencing. Biotechniques. 1992 Mar;12(3):374–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., DiMaio D. Saturation mutagenesis using mixed oligonucleotides and M13 templates containing uracil. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:599–611. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85047-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung H., Inouye S., West J., Sturm B., Inouye M. Further improvements on the phosphotriester synthesis of deoxyribooligonucleotides and the oligonucleotide directed site-specific mutagenesis of E. coli lipoprotein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3227–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Rossi J. J., Wallace R. B. Synthesis and use of synthetic oligonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:323–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteucci M. D., Heyneker H. L. Targeted random mutagenesis: the use of ambiguously synthesized oligonucleotides to mutagenize sequences immediately 5' of an ATG initiation codon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3113–3121. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Colby W. W., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Biological properties of human c-Ha-ras1 genes mutated at codon 12. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):71–75. doi: 10.1038/312071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. In vitro mutagenesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:423–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Vass W. C., Willumsen B. M., Lowy D. R. p21-ras effector domain mutants constructed by "cassette" mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3565–3569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Vasser M., Powers D. B. Cassette mutagenesis: an efficient method for generation of multiple mutations at defined sites. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]