Abstract
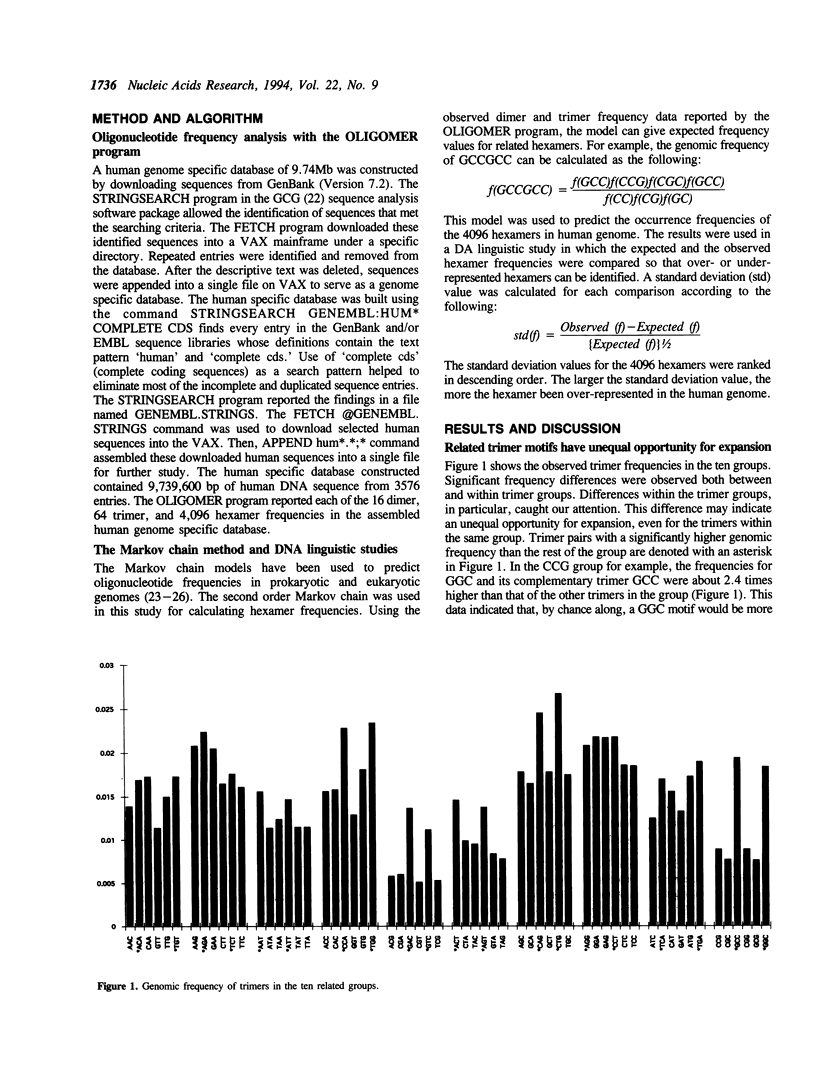
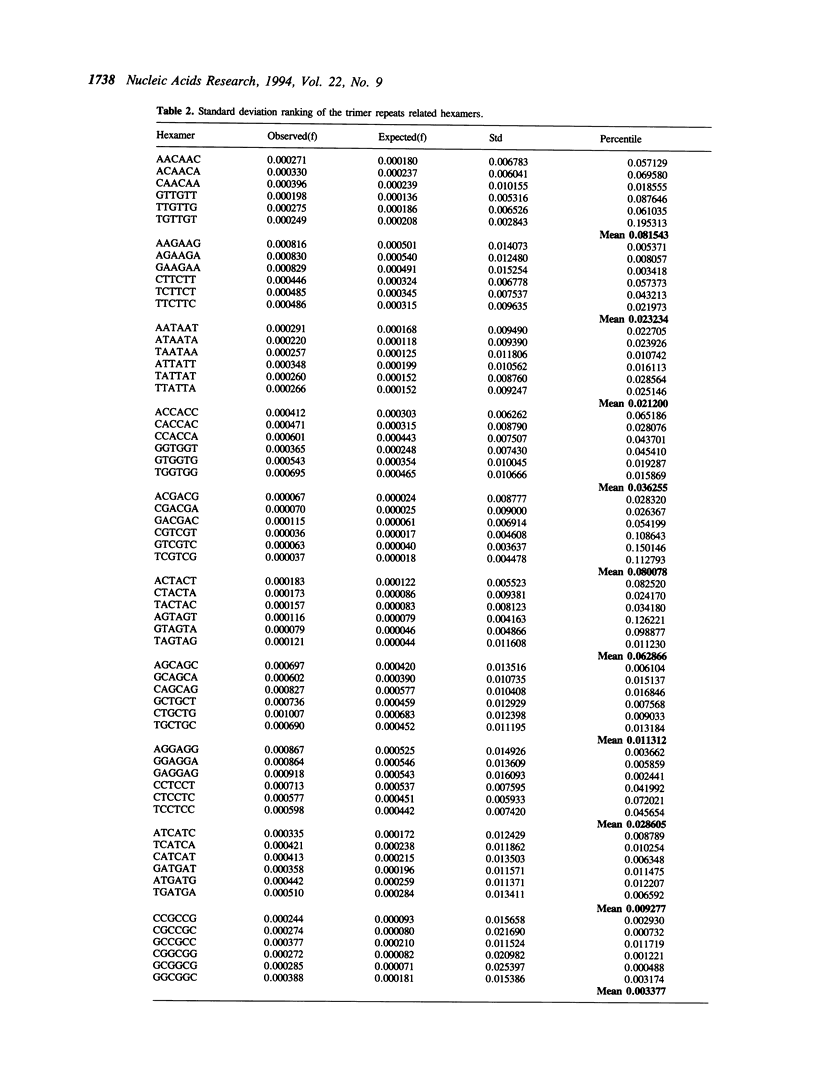
Expansion of trimer repeats has recently been described as a new type of human mutation. Of the 64 possible trimer compositions, only the CGG and CAG repeats have been implicated in genetic diseases. This study intends to address two questions: (1) What makes the CGG and CAG repeats unique? (2) Could other trimer repeats be involved in this type of mutation? By computer analysis of trimer and hexamer frequency distributions in approximately 10 Mb of human DNA, twenty trimer motifs (ten complementary pairs) have been identified that are the most likely to be expanded. The frequency distribution study also indicated that the expanded trimer motif in Fragile-X syndrome is GGC instead of CGG. DNA linguistics studies revealed that the GGC/GCC and CAG/CTG repeats were over-represented in the human genome. Further analysis of base composition suggested that the CCA/TGG repeats may be involved in the trimer expansion mutation since they possessed many similar characteristics to GGC/GCC and CAG/CTG. The computer aided sequence analysis studies reported here may help to understand the molecular mechanisms of trimer repeat expansion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslanidis C., Jansen G., Amemiya C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Chen C., Alleman J., Wormskamp N. G., Vooijs M. Cloning of the essential myotonic dystrophy region and mapping of the putative defect. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):548–551. doi: 10.1038/355548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell B. E. Markov chain analysis finds a significant influence of neighboring bases on the occurrence of a base in eucaryotic nuclear DNA sequences both protein-coding and noncoding. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(3):278–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02102360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge C., Campbell A. M., Karlin S. Over- and under-representation of short oligonucleotides in DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton J., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Jones C., Van Tongeren T., Aslanidis C., de Jong P., Jansen G., Anvret M., Riley B. Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):547–548. doi: 10.1038/355547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton J., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Jones C., Van Tongeren T., Aslanidis C., de Jong P., Jansen G., Anvret M., Riley B. Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):547–548. doi: 10.1038/355547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Zhu Z., Hsu C., Finley W. H. Selection of antisense oligonucleotides on the basis of genomic frequency of the target sequence. Antisense Res Dev. 1994 Spring;4(1):53–65. doi: 10.1089/ard.1994.4.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Brook J. D., Rundle S. A., Crow S., Reardon W., Buckler A. J., Harper P. S., Housman D. E., Shaw D. J. Expansion of an unstable DNA region and phenotypic variation in myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):545–546. doi: 10.1038/355545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert G., Kretz C., Johnson K., Mandel J. L. Origin of the expansion mutation in myotonic dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):72–76. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G., Willems P., Coerwinkel M., Nillesen W., Smeets H., Vits L., Höweler C., Brunner H., Wieringa B. Gonosomal mosaicism in myotonic dystrophy patients: involvement of mitotic events in (CTG)n repeat variation and selection against extreme expansion in sperm. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):575–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. J., Flannery A. V., Hirst M. C., Campbell L., Christodoulou Z., Phelps S. R., Pointon J., Middleton-Price H. R., Barnicoat A., Pembrey M. E. Trinucleotide repeat amplification and hypermethylation of a CpG island in FRAXE mental retardation. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90300-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide R., Ikeuchi T., Onodera O., Tanaka H., Igarashi S., Endo K., Takahashi H., Kondo R., Ishikawa A., Hayashi T. Unstable expansion of CAG repeat in hereditary dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA). Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):9–13. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer E. J., Pritchard M., Lynch M., Yu S., Holman K., Baker E., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1711–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.1675488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Spada A. R., Wilson E. M., Lubahn D. B., Harding A. E., Fischbeck K. H. Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):77–79. doi: 10.1038/352077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M. Selection against dam methylation sites in the genomes of DNA of enterobacteriophages. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF02115649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr H. T., Chung M. Y., Banfi S., Kwiatkowski T. J., Jr, Servadio A., Beaudet A. L., McCall A. E., Duvick L. A., Ranum L. P., Zoghbi H. Y. Expansion of an unstable trinucleotide CAG repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):221–226. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. J., Arnold J., Ivarie R. The effect of codon usage on the oligonucleotide composition of the E. coli genome and identification of over- and underrepresented sequences by Markov chain analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2627–2638. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Sutherland G. R. Heritable unstable DNA sequences. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):7–9. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M. Molecular evolution of bacteriophages: evidence of selection against the recognition sites of host restriction enzymes. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Jan;3(1):75–83. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Haan E. A., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M., Yu S., Richards R. I. Hereditary unstable DNA: a new explanation for some old genetic questions? Lancet. 1991 Aug 3;338(8762):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90426-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


