Abstract
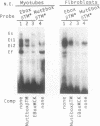
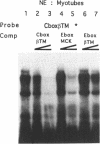
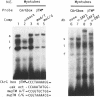
The chicken beta tropomyosin (beta TM) gene has two alternative transcription start sites (sk and nmCAP sites) which are used in muscle or non muscle tissues respectively. In order to understand the mechanisms involved in the tissue-specific and developmentally-regulated expression of the beta TM gene, we have analyzed the 5' regions associated with each CAP site. Truncated regions 5' to the nmCAP site were inserted upstream to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene and these constructs were transfected into avian myogenic and non myogenic cells. The maximum transcription is driven by the CAT construct (-168/ + 216 nt) in all cell types. Previous deletion analysis of the region 5' to the beta TMskCAP site has indicated that 805 nt confer myotube-specific transcription. In this work, we characterized an enhancer element (-201/-68 nt) which contains an E box (-177), a variant CArG box (-104) and a stretch of 7Cs (-147). Mutation of any of these motifs results in a decrease of the myotube-specific transcriptional activity. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays indicate that these cis-acting sequences specifically bind nuclear proteins. This enhancer functions in an orientation-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessereau J. L., Mendelzon D., LePoupon C., Fiszman M., Changeux J. P., Piette J. Muscle-specific expression of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene requires both positive and negative interactions between myogenic factors, Sp1 and GBF factors. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):443–449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. S., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. The complete sequence of the chicken alpha-cardiac actin gene: a highly conserved vertebrate gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1223–1237. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubas P., Klarsfeld A., Garner I., Pinset C., Cox R., Buckingham M. Functional activity of the two promoters of the myosin alkali light chain gene in primary muscle cell cultures: comparison with other muscle gene promoters and other culture systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1251–1271. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge J., Zehner Z., Paterson B. M. Nucleotide sequence of the chicken cardiac alpha actin gene: absence of strong homologies in the promoter and 3'-untranslated regions with the skeletal alpha actin sequence. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell F. X., Sax C. M., Zehner Z. E. A negative element involved in vimentin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2349–2358. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M. Y., Fuchs P. Temperature-sensitive expression of differentiation in transformed myoblasts. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):429–431. doi: 10.1038/254429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Nabeshima Y., Komiya T., Uetsuki T., Asakura A., Nabeshima Y. Differential trans-activation of muscle-specific regulatory elements including the mysosin light chain box by chicken MyoD, myogenin, and MRF4. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10031–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier-Rouvière C., Cavadore J. C., Blanchard J. M., Lamb N. J., Fernandez A. p67SRF is a constitutive nuclear protein implicated in the modulation of genes required throughout the G1 period. Cell Regul. 1991 Jul;2(7):575–588. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.7.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier-Rouvière C., Caï Q. Q., Lautredou N., Fernandez A., Blanchard J. M., Lamb N. J. Expression and purification of the DNA-binding domain of SRF: SRF-DB, a part of a DNA-binding protein which can act as a dominant negative mutant in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Dec;209(2):208–215. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Cheley S., Kuismanen E., Finn L. A., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y. Nonmuscle and muscle tropomyosin isoforms are expressed from a single gene by alternative RNA splicing and polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3582–3595. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier M., Balvay L., Mouly V., Libri D., Fiszman M. Y. The chicken gene encoding the alpha isoform of tropomyosin of fast-twitch muscle fibers: organization, expression and identification of the major proteins synthesized. Gene. 1991 Nov 15;107(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Camp S., Rachinsky T. L., Bongiorno C., Taylor P. Promoter elements and transcriptional control of the mouse acetylcholinesterase gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3563–3572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Balvay L., Fiszman M. Y. In vivo splicing of the beta tropomyosin pre-mRNA: a role for branch point and donor site competition. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3204–3215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Lemonnier M., Meinnel T., Fiszman M. Y. A single gene codes for the beta subunits of smooth and skeletal muscle tropomyosin in the chicken. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2935–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Marie J., Brody E., Fiszman M. Y. A subfragment of the beta tropomyosin gene is alternatively spliced when transfected into differentiating muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6449–6462. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Mouly V., Lemonnier M., Fiszman M. Y. A nonmuscle tropomyosin is encoded by the smooth/skeletal beta-tropomyosin gene and its RNA is transcribed from an internal promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3471–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinnel T., Libri D., Mouly V., Gros D., Fiszman M. Y., Lemonnier M. Tissue-specific transcriptional control of alpha- and beta-tropomyosins in chicken muscle development. Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;131(2):430–438. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montarras D., Fiszman M. Y. A new muscle phenotype is expressed by subcultured quail myoblasts isolated from future fast and slow muscles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3883–3888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Bessereau J. L., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Two adjacent MyoD1-binding sites regulate expression of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):353–355. doi: 10.1038/345353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro I. M., Walsh K. Natural and synthetic DNA elements with the CArG motif differ in expression and protein-binding properties. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6296–6305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. M., Burden S. J. An E box mediates activation and repression of the acetylcholine receptor delta-subunit gene during myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5133–5140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Tanimoto K., Murakami K., Fukamizu A. A combination of upstream and proximal elements is required for efficient expression of the mouse renin promoter in cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3617–3623. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Fiszman M. Y., Lemonnier M. The muscle specific promoter of chick beta tropomyosin gene requires helix-loop-helix myogenic regulatory factors and ubiquitous transcription factors. C R Acad Sci III. 1993 Aug;316(8):711–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Toutant J. P., Montarras D., Fiszman M. Y. Potential phasic and tonic muscles express a common set of fast and slow myosin light chains and fast tropomyosin during early development of chick embryo. Biochimie. 1983 Nov-Dec;65(11-12):637–642. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(84)80027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. M., Tsay H. J., Schmidt J. Expression of the acetylcholine receptor delta-subunit gene in differentiating chick muscle cells is activated by an element that contains two 16 bp copies of a segment of the alpha-subunit enhancer. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):783–790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08174.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Lockshon D., Lassar A. MyoD binds cooperatively to two sites in a target enhancer sequence: occupancy of two sites is required for activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Engert J. C., Berglund E. B., Rosenthal N. Paired MyoD-binding sites regulate myosin light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1242–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Binder M., Funk W. Cyclic amplification and selection of targets (CASTing) for the myogenin consensus binding site. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4104–4110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]