Abstract
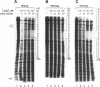
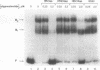
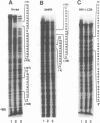
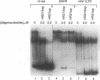
A region of the human Ha-ras promoter (-8 to -28) which contains two of the three Sp1 binding sites essential for transcriptional activity forms a sequence specific oligonucleotide-directed pur*pur:pyr triple helix. The relative binding of oligonucleotides containing different substitutions, including an abasic propanediol linker, over three potentially destabilizing C:G interruptions in the otherwise poly G:poly C target was examined. DNase I footprint titrations reveal that substitution of the positively charged abasic propanediol linker results in approximately ten fold greater binding than cytosine substitution which in turn provides greater sequence specific binding than substitution of a guanine in the third strand oligonucleotide over the C:G interruptions. Protein binding assays demonstrate that triplex formation by the linker substituted oligomer (HR21Xap) is less effective in inhibiting Sp1 binding than the cytosine substituted oligomer (HR21ap) both to the target sequence as well as an upstream sequence. As an indication of the effect of linker substitution and targeting consensus Sp1 sites on triplex specificity, the relative ability of the Ha-ras promoter targeted oligonucleotides to interact with non-target Sp1 sequences within the Ha-ras promoter as well as in the DHFR promoter and HIV-1 LTR was also investigated. At concentrations which afford complete DNase I protection of the target sequence, HR21ap does not bind to the non-target sequences while HR21Xap interacts weakly only at a distal site in the DHFR promoter. Also, HR21ap as well as HR21Xap are specific in their inhibition of Sp1 binding. These results suggest that the propanediol linker is able to skip over interruptions in a target sequence thereby stabilizing triplex but, slightly compromises sequence specificity and the ability to inhibit Sp1 binding to the Ha-ras promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. The influence of single base triplet changes on the stability of a pur.pur.pyr triple helix determined by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2773–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume S. W., Gee J. E., Shrestha K., Miller D. M. Triple helix formation by purine-rich oligonucleotides targeted to the human dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1777–1784. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durland R. H., Kessler D. J., Gunnell S., Duvic M., Pettitt B. M., Hogan M. E. Binding of triple helix forming oligonucleotides to sites in gene promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9246–9255. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorova O. S., Knorre D. G., Podust L. M., Zarytova V. F. Complementary addressed modification of double-stranded DNA within a ternary complex. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehler B. C., Terhorst T., Shaw J. P., McCurdy S. N. Triple-helix formation and cooperative binding by oligodeoxynucleotides with a 3'-3' internucleotide junction. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1603–1609. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee J. E., Blume S., Snyder R. C., Ray R., Miller D. M. Triplex formation prevents Sp1 binding to the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11163–11167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. E., Beckman C. A., Cowan K. H. 5' Nucleotide sequences influence serum-modulated expression of a human dihydrofolate reductase minigene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):878–886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Recognition of thymine adenine.base pairs by guanine in a pyrimidine triple helix motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2549639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wells R. D. Site-specific inhibition of EcoRI restriction/modification enzymes by a DNA triple helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):157–161. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D. A., Dervan P. B. Effects of an abasic site on triple helix formation characterized by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4963–4965. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R., Brady J. N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Binding of the Sp1 transcription factor by the human Harvey ras1 proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1410–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3012774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena S. D., Johnston B. H. Oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation at adjacent oligopurine and oligopyrimidine DNA tracts by alternate strand recognition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5279–5288. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Cantor C. R. A stable complex between homopyrimidine oligomers and the homologous regions of duplex DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2165–2178. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McShan W. M., Rossen R. D., Laughter A. H., Trial J., Kessler D. J., Zendegui J. G., Hogan M. E., Orson F. M. Inhibition of transcription of HIV-1 in infected human cells by oligodeoxynucleotides designed to form DNA triple helices. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5712–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergny J. L., Sun J. S., Rougée M., Montenay-Garestier T., Barcelo F., Chomilier J., Hélène C. Sequence specificity in triple-helix formation: experimental and theoretical studies of the effect of mismatches on triplex stability. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9791–9798. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono A., Chen C. N., Kan L. S. DNA triplex formation of oligonucleotide analogues consisting of linker groups and octamer segments that have opposite sugar-phosphate backbone polarities. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):9914–9912. doi: 10.1021/bi00105a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Perrouault L., Le Doan T., Chassignol M., Thuong N., Hélène C. Sequence-specific binding and photocrosslinking of alpha and beta oligodeoxynucleotides to the major groove of DNA via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Collier D. A., Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wohlrab F. The chemistry and biology of unusual DNA structures adopted by oligopurine.oligopyrimidine sequences. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2939–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Krawczyk S. H., Matteucci M. D., Toole J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10023–10026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]