Abstract
A panel of cytochrome c maturation (ccm) mutants of Legionella pneumophila displayed a loss of siderophore (legiobactin) expression, as measured by both the chrome azurol S assay and a Legionella-specific bioassay. These data, coupled with the finding that ccm transcripts are expressed by wild-type bacteria grown in deferrated medium, indicate that the Ccm system promotes siderophore expression by L. pneumophila. To determine the basis of this newfound role for Ccm, we constructed and tested a set of mutants specifically lacking individual c-type cytochromes. Whereas ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase (petC) mutants specifically lacking cytochrome c1 and cycB mutants lacking cytochrome c5 had normal siderophore expression, cyc4 mutants defective for cytochrome c4 completely lacked legiobactin. These data, along with the expression pattern of cyc4 mRNA, indicate that cytochrome c4 in particular promotes siderophore expression. In intracellular infection assays, petC mutants and cycB mutants, but not cyc4 mutants, had a reduced ability to infect both amoebae and macrophage hosts. Like ccm mutants, the cycB mutants were completely unable to grow in amoebae, highlighting a major role for cytochrome c5 in intracellular infection. To our knowledge, these data represent both the first direct documentation of the importance of a c-type cytochrome in expression of a biologically active siderophore and the first insight into the relative importance of c-type cytochromes in intracellular infection events.
INTRODUCTION
Legionella pneumophila is an aerobic, Gram-negative bacterium that is best known as the agent of Legionnaires' disease, a potentially fatal form of pneumonia (Diederen, 2008). In its aquatic habitat, L. pneumophila survives planktonically, within biofilms, and as an intracellular parasite of protozoa (Taylor et al., 2009). Human infection occurs after inhalation of contaminated droplets that originate from a variety of aerosol-generating devices. In the lung, L. pneumophila grows in macrophages, and bacterial persistence may also involve growth in epithelia and extracellular survival (Allard et al., 2009; Newton et al., 2010). Iron acquisition is a key component of L. pneumophila growth, intracellular infection and virulence (Cianciotto, 2007; Cianciotto, 2008a, b). Factors involved in Legionella Fe2+ assimilation include an inner-membrane Fe2+ transport (FeoB) system and a secreted pyomelanin pigment that has Fe3+ reductase activity (Chatfield & Cianciotto, 2007; Robey & Cianciotto, 2002). L. pneumophila feoB mutants are impaired in lung infection, confirming the importance of Fe2+ assimilation for pathogenesis (Robey & Cianciotto, 2002). The principal aspect of L. pneumophila Fe3+ uptake is legiobactin. When L. pneumophila strains are grown in a low-iron, chemically defined medium (CDM), the siderophore is detected by the chrome azurol S (CAS) assay (Allard et al., 2006; Liles et al., 2000). Legiobactin is also detected in a bioassay, in which CDM culture supernatants or purified siderophore stimulate the growth of iron-starved legionellae (Allard et al., 2006, 2009). Some but not all other Legionella species appear to make legiobactin (Allard et al., 2006; Starkenburg et al., 2004). Two linked genes, lbtA and lbtB, have been implicated in the production of legiobactin. LbtA, required for the synthesis of siderophore, has sequence similarity to several other siderophore synthetases (Allard et al., 2006). LbtB is believed to be an inner-membrane transporter that promotes the secretion of legiobactin (Allard et al., 2006). Importantly, lbtA mutants, but not their complemented derivatives, are defective for infection of the murine lung, documenting a role for legiobactin in L. pneumophila virulence (Allard et al., 2009).
In addition to characterizing FeoB, ferric reductase and legiobactin, we previously determined that the ccm locus promotes L. pneumophila growth in low-iron conditions, suggesting that the cytochrome c maturation system has a role in iron acquisition (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004; Viswanathan et al., 2002). In L. pneumophila and a variety of other bacteria, the ccm locus is an eight-gene operon (ccmA through ccmH) that encodes a multi-protein complex which transports haem across the inner membrane and then attaches it to apocytochromes in the periplasm as the final step in the maturation of c-type cytochromes (Cianciotto et al., 2005; Kranz et al., 2009; Sanders et al., 2010). Also important for the maturation of c-type cytochromes are the Sec translocon, which delivers (reduced) apocytochromes across the inner membrane, and the extracytoplasmic DsbA/DsbB pathway, which converts the reduced apocytochromes to the oxidized forms that are acted on by the Ccm system (Sanders et al., 2010). Initially, we found that mutations in ccmC reduced the plating efficiency of L. pneumophila on low-iron buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar (Pope et al., 1996; Viswanathan et al., 2002). The ccmC mutants were also impaired for infection of Hartmannella vermiformis amoebae, human macrophage-like cells (U937 and THP-1 lines) and the murine lung (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004; Viswanathan et al., 2002). The infectivity defect was exacerbated when the host cells were treated with the Fe3+ chelator desferrioxamine but ameliorated when supplementary iron was added, suggesting that the ccmC mutants are impaired for both extracellular and intracellular iron acquisition (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004; Viswanathan et al., 2002). Complementation analysis confirmed that ccmC is required for L. pneumophila growth on low-iron media and during infection (Viswanathan et al., 2002). By characterizing additional ccmB, ccmC and ccmF mutants, we confirmed that the entire Ccm system is required for L. pneumophila growth in low-iron conditions (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004). We now report that L. pneumophila Ccm and more specifically cytochrome c4 are required for the expression of legiobactin.
METHODS
Bacterial strains.
L. pneumophila 130b (ATCC strain BAA-74, also known as AA100 or Wadsworth) served as our wild-type (Allard et al., 2009). This serogroup 1 strain is a virulent clinical isolate. Previously described mutants of 130b used in this study were as follows: NU257 and NU295 are ccmC mutants, NU292 and NU293 ccmB mutants, NU296 and NU297 ccmF mutants, NU269 an feoB mutant, and NU302 an lbtA mutant (Allard et al., 2006; Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004; Robey & Cianciotto, 2002; Viswanathan et al., 2002). Escherichia coli DH5α (Invitrogen) was the host for recombinant plasmids.
Bacteriological media and extracellular growth experiments.
L. pneumophila strains were routinely cultured at 37 °C on BCYE agar, which has an iron supplement consisting of 0.25 g of ferric pyrophosphate per litre (Allard et al., 2006). When appropriate, the agar was supplemented with chloramphenicol at 6 μg ml−1, kanamycin at 25 μg ml−1 or gentamicin at 2.5 μg ml−1. To judge the basic extracellular growth capacity of L. pneumophila, bacteria grown on BCYE agar were inoculated into buffered yeast extract (BYE) broth, and then the optical density of the cultures was determined at 660 nm (OD660) (Hickey & Cianciotto, 1997; Liles et al., 2000; Viswanathan et al., 2000). To assess the extracellular growth of L. pneumophila in iron-limiting conditions, strains were inoculated in deferrated CDM and growth was monitored spectrophotometrically (Allard et al., 2006). To judge growth on iron-limited solid medium, legionellae were tested for their ability to form colonies on BCYE agar that lacked its iron supplement (Allard et al., 2006; Robey & Cianciotto, 2002; Viswanathan et al., 2002). Bacteria were pre-cultured for 3 days on standard BCYE agar, suspended in PBS at 1×109 c.f.u. ml−1, and then 10 μl aliquots taken from 10-fold serial dilutions in PBS were spotted on the assay medium. Growth was recorded after 4 days of incubation at 37 °C. E. coli was grown in Luria–Bertani medium, containing kanamycin (50 μg ml−1), gentamicin (2.5 μg ml−1), chloramphenicol (30 μg ml−1) or ampicillin (100 μg ml−1).
Siderophore assays.
Legiobactin production, secretion and utilization were examined as described previously (Allard et al., 2006, 2009). Briefly, L. pneumophila strains were grown in BYE to an OD660 of 1.0, inoculated into deferrated CDM to an OD660 of 0.3, and then incubated at 37 °C. At 24 h post-inoculation, siderophore activity in supernatants was quantified using the CAS assay as previously done, with desferrioxamine serving as the standard (Allard et al., 2006, 2009; Liles et al., 2000; Starkenburg et al., 2004). Supernatants were tested for siderophore biological activity by examining their ability to promote the growth of the NU269 feoB mutant on non-iron-supplemented BCYE agar (Allard et al., 2006, 2009). NU269 lacks an inner-membrane Fe2+ permease and thus is defective for uptake of Fe2+ but not Fe3+ (Robey & Cianciotto, 2002). To compare wild-type and mutant L. pneumophila for their ability to use legiobactin, bacteria were pre-cultured for 3 days on BCYE agar, suspended in PBS, and then 1×104 c.f.u. were spread onto non-iron-supplemented BCYE agar containing 400 μM 2,2′-dipyridyl (Allard et al., 2006). Small wells cut in the centre of the agar were filled with 75 μl of supernatants obtained from deferrated CDM cultures. Control wells contained deferrated CDM, 5 μM Fe3+ pyrophosphate or 20 μM Fe2+ ammonium sulfate. Growth around the wells was assessed after incubation at 25 °C for 8–10 days.
DNA, RNA and protein analysis.
DNA was isolated from L. pneumophila as before (Cianciotto & Fields, 1992). DNA sequencing was done at the Northwestern University Biotech Lab, with primers from Integrated DNA Tech. Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR was done as previously described (Allard et al., 2006; Liles et al., 1998). RNA was isolated from 18 h CDM or BYE cultures of L. pneumophila using RNA STAT-60 according to the manufacturer's instructions (TEL-TEST B, Inc.). Total cDNA was amplified with random hexamers (Invitrogen) and detected using standard PCR. Primer pairs used for amplifying the ccm, petC (encoding cytochrome c1 of ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase), cyc4 (cytochrome c4), cycB (cytochrome c5), lbtA and dsbA genes are listed in Table 1. Control experiments lacking reverse transcriptase were done to rule out contributions from contaminating DNA in the DNase-treated samples. PCR products obtained from genomic DNA confirmed that the mRNAs observed were of the appropriate length. PCR products were separated by agarose-gel electrophoresis and detected with ethidium bromide (Allard et al., 2006; Liles et al., 1998). Homology searches were done through the National Center for Biotechnology Information at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ and L. pneumophila databases at http://genolist.pasteur.fr/LegioList/, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/data/view/FR687201 and http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomeprj/48801.
Table 1.
Primers used in this study
| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| ccmB-F (orf1-5—F) | TATTAATCCAGGTGCGGCAA |
| ccmB-R (ccmB5′-R) | GGATATCCACACTAATCCGGGAGC |
| ccmC-F (orf2-1—F) | TGATGCGTGGTAGAATCCTT |
| ccmC-R (ccmC5′-R) | GCATCCCCTTGCTGGATATCTG |
| ccmD-F (ccmD3′-F) | CGTTGGTTTAAGAGATAGGATATCTG |
| ccmD-R (ccmC-R) | ACCTCCAACTCGGATGTGGTGTTT |
| ccmF-F (ccmF12-F) | ATGAAGGTTCCATGCTGTTA |
| ccmF-R (ccmE-R) | AAAGCCAGGATCTTGCAGCAATGG |
| ccmG-F (ccmH-F) | TCCTCATCATTTGCCTTCAGCTCG |
| ccmG-R (ccmF-R) | TCTCGCGTGCTCTGGATTGTCTTT |
| ccmH-F (ccmG3′-F) | TCCGCTACAGGGATATCGGGATA |
| ccmH-R (ccmH5′-R) | TCTGCGATATCCTGATTTTGGCAT |
| petC-F (c1-F) | GCCCGCTAATCCAATGGTG |
| petC-R (c1-R) | CTTCCGCACGGGCTACTG |
| cyc4-F (c4-F) | GGTGTTTTGCTGGTTCTTGC |
| cyc4-R (c4-R) | CGATTGTTTCGTTGCCAGTG |
| cycB-F (c5-F) | GCTCCAGCCTGATTGAGTG |
| cycB-R (c5-R) | GTTCATTCGCAGAAACGGC |
| lbtA-F | CATTTGATCGATGGCCTCTT |
| lbtA-R | GCGCGGAAATTAGGATGATA |
| dsbA-F | GCCAAAGCCTATTACACAGC |
| dsbA-R | CTCCCTGCCATTTGTAAGTC |
Mutant constructions.
To obtain a cytochrome c1 mutant, the petC gene was amplified from the genomic DNA of strain 130b by PCR using primers c1-F and c1-R (Table 1), and the resulting 1.6 kb fragment was cloned into pGEM-T Easy (Promega). The resultant plasmid, pGpetC, was digested with SspI and ligated to a fragment of pMB2190 that carries a kanamycin-resistance gene (Kmr) (Rossier et al., 2004). This final construct, pGpetC : : Kmr, was then introduced into 130b by transformation (Allard et al., 2006; Rossier et al., 2004; Stewart et al., 2009), and transformants were selected on antibiotic-containing BCYE agar. Mutation of petC was confirmed by PCR using c1-F and c1-R. Two independently derived petC mutants were designated NU375 and NU376. To make a cytochrome c4 mutant, the cyc4 gene was PCR-amplified from 130b DNA using primers c4-F and c4-R (Table 1), and the resultant 1.2 kb fragment was cloned into pGEM-T Easy to yield pGcyc4. This plasmid was digested with NaeI, and Kmr was cloned into cyc4. The resulting pGcyc4 : : Kmr was digested with SphI/SpeI, filled in, and subcloned into pRE112. Electroporation was used to introduce the plasmid containing the mutated gene into 130b. Two independently derived cyc4 mutants, NU379 and NU380, were obtained after antibiotic selection and PCR confirmation. To make a cytochrome c5 mutant, the cycB gene was amplified by PCR using primers c5-F and c5-R (Table 1). The 1.6 kb product was cloned into pGEM-T Easy, yielding pGcycB. The new plasmid was then digested with EcoRI, and Kmr was inserted into cycB. The resulting plasmid, pGcycB : : Kmr, was introduced into 130b by transformation, and mutants NU381 and NU382 were obtained.
Intracellular infection assays.
To examine the ability of L. pneumophila strains to grow intracellularly, Hartmannella vermiformis and Acanthamoeba castellanii amoebae and human U937 macrophages were infected as previously described (Allard et al., 2006, 2009; Pearce & Cianciotto, 2009; Rossier et al., 2008).
RESULTS
L. pneumophila ccm promotes the expression of legiobactin
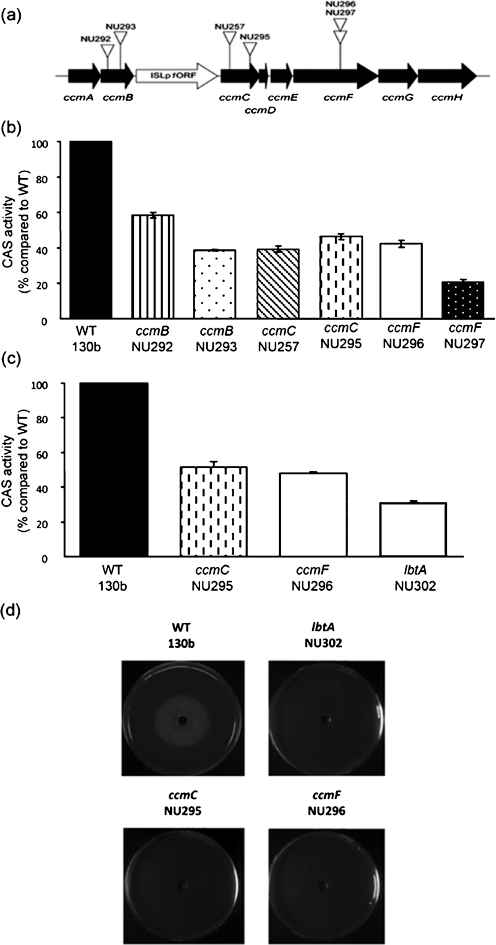
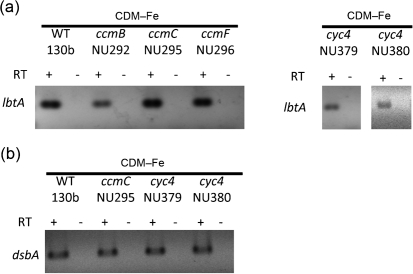
Since our initial studies on ccm mutants (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004; Viswanathan et al., 2002), we have improved our ability to produce and detect L. pneumophila siderophore (Allard et al., 2006, 2009). Therefore, as a next step toward understanding the mechanistic connection between Ccm and Legionella growth in low-iron conditions, we examined anew six of our ccm mutants for their expression of legiobactin. Two mutants (NU292, NU293) contained an inactivated ccmB, two (NU257, NU295) had mutations in ccmC, and two (NU296, NU297) were defective for ccmF (Fig. 1a). The mutants were grown in deferrated CDM, and then cell-free culture supernatants were tested in the CAS assay. All of these ccm mutants displayed a significant reduction in CAS reactivity when compared to their wild-type parent, strain 130b (Fig. 1b). Over the course of multiple experiments, the siderophore activity of the mutants ranged from 20 to 50 % of that of wild-type. Further trials confirmed that the reduction in CAS reactivity exhibited by the ccm mutants was comparable to that of an lbtA mutant (Allard et al., 2006) that is known to not make legiobactin (Fig. 1c). To confirm the impact of the ccm mutations on siderophore production, we tested the supernatants from these mutants in a legiobactin-specific bioassay. Like the samples derived from the lbtA mutant, supernatants obtained from the ccm mutants were unable to stimulate the growth of iron-starved legionellae (Fig. 1d). Ccm mutants were, however, capable of using supplied legiobactin obtained from wild-type supernatants in order to stimulate their growth on iron-deplete media (data not shown). Taken together, these data indicated that an intact ccm locus is required for the production but not utilization of legiobactin. In support of this conclusion, RT-PCR analysis confirmed that genes within the ccm locus are expressed when wild-type 130b is grown in deferrated CDM (Fig. 2a). This analysis additionally indicated that ccm gene transcripts also occur when 130b is grown in BYE broth (Fig. 2a), indicating that ccm expression occurs in both minimal, iron-depleted conditions and rich, iron-replete medium, compatible with its having significance for multiple facets of bacterial growth besides siderophore expression. When RT-PCR analysis was extended to include lbtA, we found that the legiobactin synthesis gene was expressed in the ccm mutants (Fig. 3a, left panel), implying that the absence of a Ccm system (in ccm mutants) did not trigger some sort of feedback that shut down lbtA and legiobactin synthesis. Based on these data and coupled with the fact that Ccm operates within the inner membrane and periplasm, we posited that Ccm is promoting the maturation or secretion of legiobactin.
Fig. 1.
Legiobactin production by L. pneumophila wild-type and ccm mutants. (a) The region of the L. pneumophila chromosome containing the ccm locus. Horizontal black arrows depict the relative sizes and orientation of the eight ccm genes (i.e. ccmA–ccmH) in strain 130b. The white horizontal arrow denotes the insertion sequence element between ccmB and ccmC (Viswanathan et al., 2002). The vertical arrowheads point to the locations of the KmR insertion in six ccm mutants. (b) CAS activity of the ccmB, ccmC and ccmF mutants compared to wild-type 130b. The CAS values are the means and standard deviations from duplicate cultures. The results presented are representative of at least three independent experiments. (c) CAS activity of the ccm mutants compared to an lbtA mutant. In (b) and (c), the CAS activities of the various ccm mutants were significantly less than that of wild-type (Student's t-test, P<0.05). In (c), the CAS activities for the ccm mutants were not significantly different from that of the lbtA mutant (P>0.05). (d) Siderophore biological activity of wild-type and mutants. We plated approx. 105 c.f.u. of feoB mutant legionellae onto non-iron-supplemented BCYE agar and a centre well was filled with a supernatant sample obtained from deferrated CDM cultures of wild-type 130b, lbtA mutant NU302, ccmC mutant NU295 and ccmF mutant NU296, as indicated. After 5 days, the growth of the bacteria was recorded. The results shown are representative of at least three experiments. Although not shown here for the sake of space, ccmB mutants NU292 and NU293, ccmC mutant NU257 and ccmF mutant NU297 also lacked siderophore biological activity.
Fig. 2.
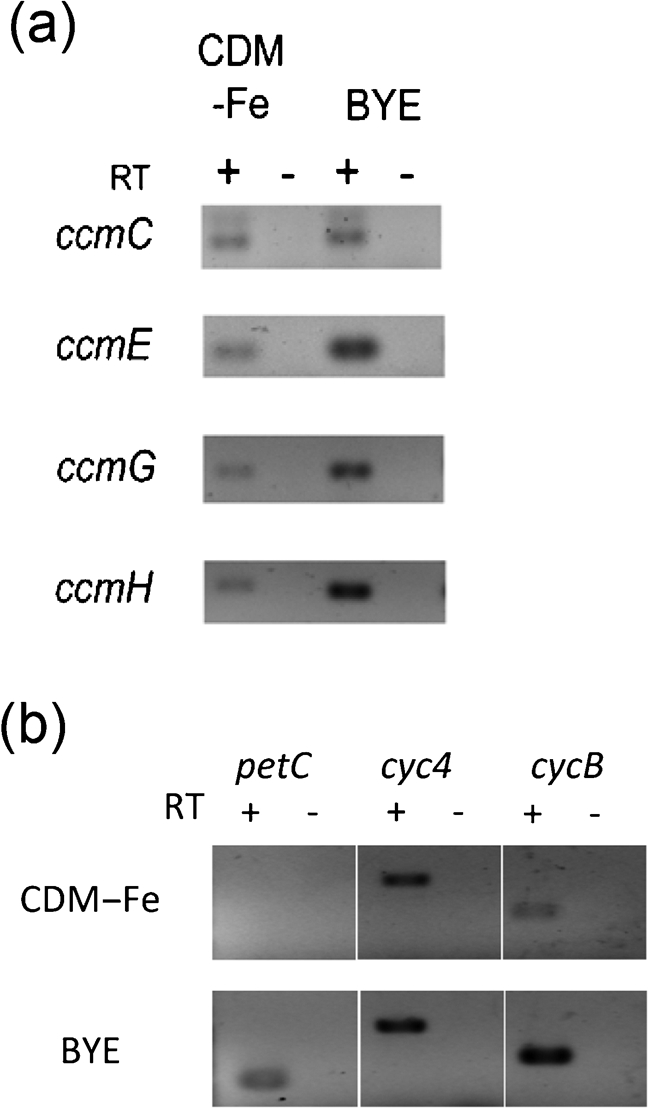
Transcription of the ccm, petC, cyc4 and cycB genes. (a) Expression of ccm transcripts. Wild-type 130b was grown in deferrated CDM (CDM–Fe) or standard BYE broth (BYE), and then RNA was analysed by RT-PCR utilizing primers specific to ccmC, ccmE, ccmG or ccmH. That the PCR products obtained resulted from mRNA templates was confirmed by the lack of product obtained when the reaction did not incorporate RT (–RT lanes). In additional experiments, ccmB and ccmF transcripts were detected in 130b growing in CDM–Fe (data not shown). (b) Expression of the c-type cytochrome genes. RNA from the wild-type was analysed by RT-PCR utilizing primers specific to petC, cyc4 or cycB. The results presented are representative of three independent experiments.
Fig. 3.
Expression of lbtA and dsbA by ccm and cyc4 mutants and wild-type L. pneumophila. (a) Wild-type 130b, ccmB mutant NU292, ccmC mutant NU295, ccmF mutant NU296, and cyc4 mutants NU379 and NU380 were inoculated into deferrated CDM (CDM–Fe), and then RNA was analysed by RT-PCR utilizing primers specific to lbtA. (b) Wild-type 130b, ccmC mutant NU295, and cyc4 mutants NU379 and NU380 were inoculated into CDM–Fe, and then RNA was analysed by RT-PCR utilizing primers specific to dsbA. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
Cytochrome c4 is required for the expression of legiobactin
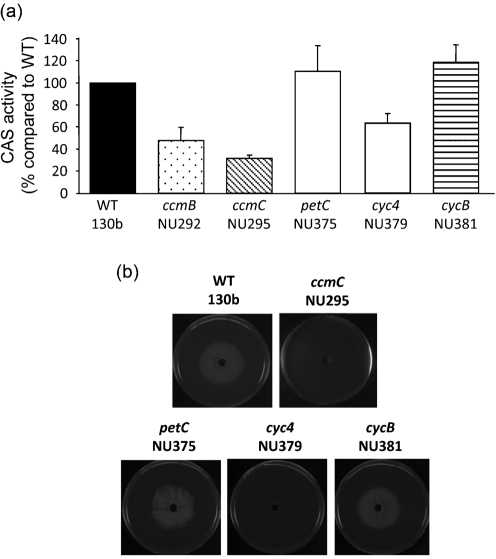
Since the Ccm system is best known for its role in the maturation of c-type cytochromes (Sanders et al., 2010), we sought to determine the importance of individual c-type cytochromes for legiobactin expression. After examining the genomes of all five sequenced strains of L. pneumophila (strains Philadelphia-1, Paris, Lens, Corby, Alcoy and 130b) (Cazalet et al., 2004; Chien et al., 2004; D'Auria et al., 2010; Glöckner et al., 2008; Schroeder et al., 2010), we targeted the three genes encoding c-type cytochromes. The first gene (petC) encodes cytochrome c1, which is 28 kDa in size and possesses one haem-attachment site (the motif CXXCH) (Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry, 1992; Sanders et al., 2010). As is typical in other bacteria (Davidson & Daldal, 1987; Thöny-Meyer et al., 1991), L. pneumophila petC is the last gene in an operon with the other two genes (petA and petB) encoding the Rieske iron–sulfur protein and cytochrome b (Rossier & Cianciotto, 2005). The second gene (cyc4) that we targeted encodes cytochrome c4, which is 21 kDa in size and a di-haem (i.e. with two CXXCH motifs) protein (Chang et al., 2010; Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry, 1992; Deeudom et al., 2008; Giudici-Orticoni et al., 2000). The third gene (cycB) gene encodes a 15 kDa, mono-haem cytochrome c5 (Chang et al., 2010; Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry, 1992; Klarskov et al., 1998; Li et al., 2010). Both cyc4 and cycB are in a two-gene operon, with the gene downstream of cyc4 being dsbA, and the gene downstream of cycB being dsbB. As noted earlier, DsbA and DsbB mediate the oxidative folding of apocytochrome c molecules prior to their interaction with the Ccm system (Heras et al., 2009; Sanders et al., 2010). In the strain 130b database, petC, cyc4 and cycB are also denoted by the ORF designations lpw_29591, lpw_01241 and lpw_29881, respectively (Schroeder et al., 2010). Using allelic exchange, as we have done many times to make other L. pneumophila mutants of strain 130b (Allard et al., 2006; Pearce & Cianciotto, 2009; Stewart et al., 2009), we constructed multiple mutants inactivated for either petC (NU375, NU376), cyc4 (NU379, NU380) or cycB (NU381, NU382) and then tested them in the legiobactin assays. Whereas the petC mutants and cycB mutants behaved as the wild-type did, the cyc4 mutants displayed a reduction in CAS activity that was comparable to that of the ccm mutants (Fig. 4a). In a similar vein, supernatants from the cyc4 mutants were unable to stimulate the growth of iron-starved legionellae, whereas supernatants from the petC mutants and cycB mutants did stimulate growth (Fig. 4b). Because multiple independently derived cyc4 mutants had the same phenotype, the loss of siderophore activity in these strains was due to the cyc4 mutation rather than a spontaneous second-site mutation. Furthermore, because the cyc4 mutants continued to express dsbA transcripts (Fig. 3b), this mutant phenotype was not due to polarity on the downstream dsbA. The fact that Ccm− mutants were also impaired for legiobactin also strongly argues that this mutant phenotype involves the loss of cytochrome c4 as opposed to being only due to a possible polar effect on dsbA and the loss of activities of DsbA that are unrelated to cytochrome maturation. Compatible with a role for cytochrome c4 in siderophore expression, cyc4 transcripts were detected in L. pneumophila grown in deferrated CDM (Fig. 2b). Like the ccm genes, this cytochrome gene was also expressed when bacteria were grown in BYE broth (Fig. 2b). The cycB transcripts were also detected in bacteria grown in either medium, whereas petC mRNA was only evident in bacteria cultured in BYE (Fig. 2b). Together, these data indicate that cytochrome c4, but not cytochromes c1 and c5, is required for legiobactin expression, and the importance of Ccm for siderophore expression is tied to its role in producing a certain c-type cytochrome. Given the cellular location of c-type cytochromes as well as the fact that lbtA expression is evident in the cyc4 mutants (Fig. 3a, right panel), we posit that cytochrome c4 promotes the maturation or secretion of the Legionella siderophore.
Fig. 4.
Legiobactin production by L. pneumophila wild-type and mutants lacking c-type cytochromes. (a) CAS activity of petC, cyc4 and cycB mutants compared to that of wild-type 130b and the ccmB and ccmC mutants. The CAS values are the means and standard deviations from duplicate cultures, and the results presented are representative of at least three independent experiments. The levels of CAS activity displayed by the cyc4 mutants were significantly less than that of wild-type (Student's t-test, P<0.05). They were not, however, different from that of the ccm mutants, nor were the levels of CAS activity displayed by the petC and cycB mutants different from that of wild-type (P>0.05). (b) We plated approx. 105 c.f.u. of the feoB mutant onto non-iron-supplemented BCYE agar and a centre well was filled, as indicated, with supernatant obtained from deferrated CDM cultures of wild-type 130b, ccmC mutant NU295, petC mutant NU375, cyc4 mutant NU379 or cycB mutant NU381. After 5 days, the growth of the bacteria was recorded. The results shown are representative of at least three experiments. Although not shown here for the sake of space, cyc4 mutant NU380 also lacked siderophore activity in its culture supernatants, whereas petC mutant NU376 and cycB mutant NU382 behaved like the wild-type in this regard.
Effect of c-type cytochromes on L. pneumophila extracellular growth and intracellular infection
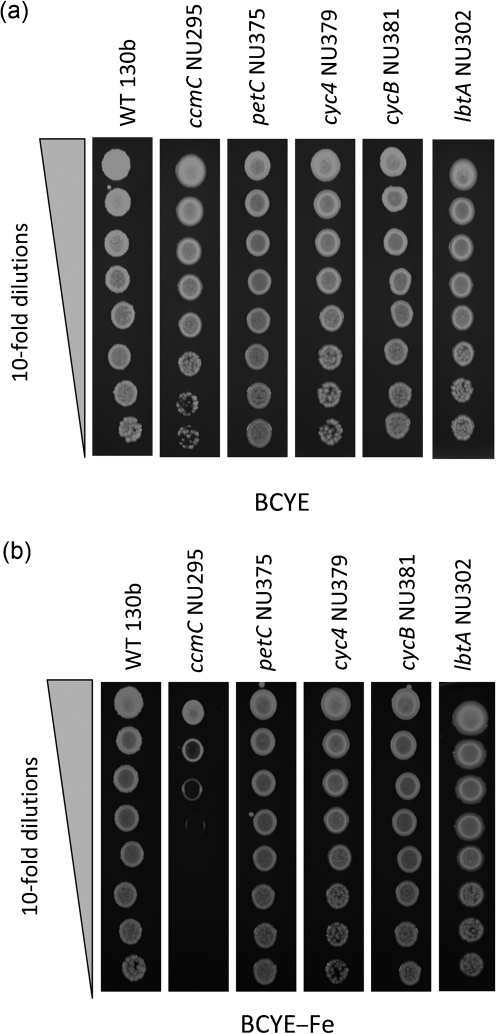
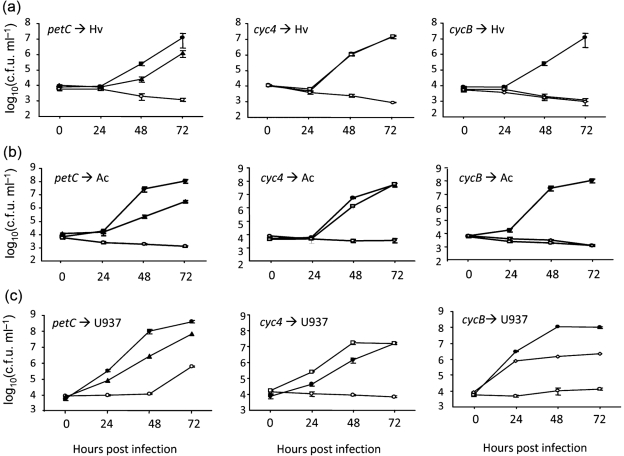
None of the newly made cytochrome mutants displayed a growth defect in standard BYE broth (data not shown) or on standard BCYE agar (Fig. 5a), indicating that they do not have a generalized growth defect. As noted above, L. pneumophila ccm mutants show a reduced ability to grow on BCYE agar that lacks an iron supplement (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004; Viswanathan et al., 2002). However, none of the new mutants showed this defect (Fig. 5b), indicating that the growth defect of the ccm mutants on non-iron-supplemented media is not due to the loss of one of the c-type cytochromes. This is compatible with the fact that lbtA mutants grow normally on non-iron-supplemented BCYE agar (Allard et al., 2006) (Fig. 5b). Turning to intracellular growth assessments, the petC mutants and cycB mutants, but not the cyc4 mutants, exhibited a reduced ability to grow in amoebal hosts (Fig. 6a, b). That cyc4 mutants grew like the wild-type did was not at odds with their lack of siderophore and impaired growth on iron-depleted media, because as we previously determined, legiobactin is not needed for intracellular infection under standard conditions (Allard et al., 2006). The defects of the petC mutants and cycB mutants were noted in H. vermiformis and A. castellanii (Fig. 6a, b). Whereas the petC mutants displayed a relatively modest infectivity defect of 10- to 100-fold, depending upon the time post-inoculation, the cycB mutants appeared completely unable to infect the protozoa. Indeed, the cycB mutants were as defective as the ccmC mutants were (Fig. 6a, b), implying that the importance of Ccm for L. pneumophila infection of amoebae is due largely to a need for cytochrome c5. Mirroring the results obtained from the amoebal assays, the petC mutants and cycB mutants, but not the cyc4 mutants, were impaired for growth in macrophages (Fig. 6c). One difference was the fact that the cycB mutant was not nearly as defective as a ccm mutant was, suggesting that the importance of Ccm has a more complex basis in macrophages than it does in amoebae. Because multiple independently derived petC mutants had impaired growth in host cells and because there is no transcriptionally linked gene downstream of petC, the loss of infectivity by the petC mutants was due to the loss of PetC rather than any second-site mutation or polarity. Given that multiple cycB mutants showed impaired intracellular infection, the loss of infectivity in these mutants was due to the mutation in cycB as opposed to a second-site mutation. Since cycB mutants and the ccm mutants (which lack c-type cytochromes because of a mutation in a distinct chromosomal locus) had similar infectivity defects, we further conclude that these mutant phenotypes resulted from the loss of cytochrome c5 as opposed to being only due to a possible polar effect on dsbB and the loss of DsbB activities that are unrelated to cytochromes. In sum, these data indicate that cytochromes c1 and c5 are required for the optimal intracellular growth of L. pneumophila.
Fig. 5.
Growth of L. pneumophila wild-type and c-type cytochrome mutants on BCYE agar. We spotted 10 μl aliquots from 10-fold serial dilutions of wild-type 130b, ccmC mutant NU295, petC mutant NU375, cyc4 mutant NU379, cycB mutant NU381 and lbtA mutant NU302 onto standard BCYE agar (a) or BCYE lacking its usual iron supplement (b). After 4 days, growth was recorded. Each strain (i.e. each column of growth depicted here) was spotted on its own plate, to prevent diffusible factors produced by some strains from stimulating the growth of others nearby and thereby confounding mutant analysis. The results shown are representative of three experiments.
Fig. 6.
Intracellular infection by L. pneumophila wild-type and c-type cytochrome mutants. H. vermiformis (Hv, a), A. castellanii (Ac, b), and U937 cell macrophages (c) were infected with wild-type 130b (•) and ccmC mutant NU295 (○) (all panels in a–c) as well as the petC mutant NU375 (▴) (left panels), cyc4 mutant NU379 (□) (centre panels), and cycB mutant NU381 (◊) (right panels), and then at the indicated times, the c.f.u. in the infected wells were determined by plating. Data are the mean and standard deviations from four infected wells (error bars not shown where smaller than symbols). In (a) and (b), the recovery of the petC and cycB mutants was significantly less than that of wild-type at 48 and 72 h (Student's t-test, P<0.05). In (c), the recovery of the petC and cycB mutants was less than that of wild-type at 24, 48, and 72 h (Student's t-test, P<0.05). Each of the cytochrome mutants was tested on at least two occasions, with the results obtained being comparable to those depicted here. Although not shown here for the sake of space, additional experiments using NU376 and NU382 confirmed the infectivity defects of the petC mutant and cycB mutant.
DISCUSSION
For multiple reasons, we conclude that the Ccm system is required for full expression of legiobactin. First, a variety of independent ccm mutants of a virulent strain of L. pneumophila lack siderophore expression. Second, multiple, independently derived cyc4 mutants lacking a particular c-type cytochrome exhibit a similar lack of siderophore. Third, the loss of siderophore was documented by both the CAS assay and a legiobactin-specific bioassay. Fourth, transcription of the ccm and cyc4 genes occurs in legionellae growing in deferrated media. Our data bring to four the number of cases in which a Ccm system is linked to siderophore. Past examples include pyoverdine production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Baert et al., 2008), pyoverdine and thioquinolobactin synthesis by Pseudomonas fluorescens (Baysse et al., 2002, 2003; Gaballa et al., 1996; Matthijs et al., 2007) and siderophore expression by Paracoccus denitrificans and Rhizobium leguminosarum (Pearce et al., 1998; Yeoman et al., 1997). The fact that Legionella, Pseudomonas, Paracoccus and Rhizobium are quite distinct from each other, as are the structures of their siderophores (Allard et al., 2009), suggests that the connection between Ccm and siderophores likely also exists in a variety of other bacteria, including both environmental and pathogenic strains.
The molecular basis for the role of Ccm in siderophore expression has been the subject of speculation. We and others had theorized that Ccm might be facilitating siderophore production through its role in the maturation of c-type cytochromes, the delivery of haem into the periplasm for purposes other than its ligation to apocytochromes, or the export of a molecule besides haem (Cianciotto et al., 2005). An early report had suggested the involvement of a cyc4-like gene (pvcD) in the production of pyoverdine chromophore by P. aeruginosa (Baysse et al., 2001; Stintzi et al., 1999); however, it was later determined that the pvc locus aids in the production of isonitrile-functionalized coumarin and pseudoverdine, which do not have siderophore biological activity (Clarke-Pearson & Brady, 2008; Stintzi et al., 1996). By specifically targeting individual c-type cytochromes for mutation and using both chemical and biological assays for detection of legiobactin, we can now conclude that the role of Ccm in siderophore production by L. pneumophila is linked to c-type cytochromes, i.e. cytochrome c4. One hypothesis to explain the newfound importance for the c-type cytochrome is that the biosynthesis of legiobactin requires an electron-transfer step within the periplasm, e.g. shuttling electrons, possibly from an electron-transport chain, to a substrate or enzyme that is needed for legiobactin synthesis and/or secretion. In support of this hypothesis, periplasmic enzymes have been shown to be necessary for the completion of siderophore synthesis in some other bacteria (Yeterian et al., 2010). It does remain formally possible however that cytochrome c4 indirectly promotes the processing of legiobactin by helping to maintain a certain redox homeostasis in the periplasm or acting as a signalling molecule. Regardless, the fact that cytochrome c4, but not cytochromes c1 and c5, is critical for legiobactin expression suggests that there is specificity to the interaction between the siderophore and cytochrome pathways.
To our knowledge, the current study represents the first investigation into the relative importance of c-type cytochromes for L. pneumophila growth. Since all of our ccm mutants grew normally on standard media, c-type cytochromes are not essential for L. pneumophila extracellular growth. That the mutants lacking petC, cyc4 or cycB also grew normally on BCYE agar and in BYE broth supports this conclusion. These data are compatible with the fact that L. pneumophila also has a-, b- and d-type cytochromes, with at least d-type cytochromes supporting respiration via a quinol-oxidizing branch that is independent of cytochrome c (Cazalet et al., 2004; Hoffman & Pine, 1982; Miller & Hammel, 1985; Thöny-Meyer, 1997). In contrast, under conditions of moderate iron limitation (i.e. non-iron-supplemented BCYE agar without iron chelator), ccm mutants exhibited a growth defect that was not recapitulated by the cytochrome mutants nor ascribed to lack of siderophore. Three basic scenarios can be envisioned to explain these data. In the first case, there is a functional redundancy among cytochromes c1, c4 and c5, such that impaired growth under these conditions requires the absence of more than one of the cytochromes. In the second scenario, there is an additional c-type cytochrome(s) expressed by L. pneumophila. In support of this possibility, when examining the database, we did find several ORFs that might encode cytochrome c-like proteins (unpublished results). As to how c-type cytochromes (be they c1, c4, c5 or encoded by an uncharacterized ORF) might facilitate growth in moderately low-iron conditions, it is possible that they promote Fe3+ reduction as has been documented for some of the c-type cytochromes produced by species of Geobacter and Shewanella (Dale et al., 2007; Londer et al., 2002; Mehta et al., 2005; Shi et al., 2007). That L. pneumophila can utilize Fe2+ transport to grow on low-iron media (Robey & Cianciotto, 2002) gives support to this possibility. In the final case, the importance of Ccm under extracellular conditions of moderate iron-depletion is independent of its role in cytochrome maturation and may involve an alternate use of Ccm-exported haem.
As to the role of cytochromes in intracellular growth, cytochromes c1 and c5 vs cytochrome c4 proved to be the most important. Remarkably, the cycB mutants, like the ccm mutants, were completely unable to grow in amoebae, indicating a critical role for this cytochrome c5. We believe that the current study is the first to discern the relative importance of different c-type cytochromes during an intracellular infection event. Since our experiments testing the cycB and petC mutants utilized host cells that were not iron-stressed, and since mutants lacking Fe3+ (legiobactin) or Fe2+ (FeoB) uptake do not have this level of impairment, the key function of these c-type cytochromes during infection may involve their roles in respiration. On the other hand, there is a growing list of cases where Ccm or a cytochrome is linked to processes that are distinct from respiration and iron acquisition (Cianciotto et al., 2005; El-Naggar et al., 2010; Yurgel et al., 2007). In light of the importance of Ccm in lung infection by L. pneumophila (Naylor & Cianciotto, 2004), particularly intriguing is a recent report demonstrating that two c-type cytochromes regulate virulence factor (toxin) gene regulation in Bacillus anthracis (Wilson et al., 2009). Thus, studies on L. pneumophila Ccm and its c-type cytochromes should provide new insights into bacterial iron acquisition, intracellular infection and virulence.
Acknowledgments
We thank present and past members of the Cianciotto lab for their help and support, including Christa Chatfield and Brendan Mulhern for assisting with siderophore bioassays. E. S. Y. and D. M. B. were partly supported by NIH training grant T32 AI0007476. This study was funded by NIH grant AI034937 awarded to N. P. C.
Abbreviations
CAS, chrome azurol S
Ccm, cytochrome c maturation
References
- Allard, K. A., Viswanathan, V. K. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2006). lbtA and lbtB are required for production of the Legionella pneumophila siderophore legiobactin. J Bacteriol 188, 1351–1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allard, K. A., Dao, J., Sanjeevaiah, P., McCoy-Simandle, K., Chatfield, C. H., Crumrine, D. S., Castignetti, D. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2009). Purification of legiobactin and importance of this siderophore in lung infection by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun 77, 2887–2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baert, B., Baysse, C., Matthijs, S. & Cornelis, P. (2008). Multiple phenotypic alterations caused by a c-type cytochrome maturation ccmC gene mutation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 154, 127–138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baysse, C., Matthijs, S., Pattery, T. & Cornelis, P. (2001). Impact of mutations in hemA and hemH genes on pyoverdine production by Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC17400. FEMS Microbiol Lett 205, 57–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baysse, C., Budzikiewicz, H., Uría Fernández, D. & Cornelis, P. (2002). Impaired maturation of the siderophore pyoverdine chromophore in Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC 17400 deficient for the cytochrome c biogenesis protein CcmC. FEBS Lett 523, 23–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baysse, C., Matthijs, S., Schobert, M., Layer, G., Jahn, D. & Cornelis, P. (2003). Co-ordination of iron acquisition, iron porphyrin chelation and iron-protoporphyrin export via the cytochrome c biogenesis protein CcmC in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Microbiology 149, 3543–3552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalet, C., Rusniok, C., Brüggemann, H., Zidane, N., Magnier, A., Ma, L., Tichit, M., Jarraud, S., Bouchier, C. & other authors (2004). Evidence in the Legionella pneumophila genome for exploitation of host cell functions and high genome plasticity. Nat Genet 36, 1165–1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Y., Ahn, Y., Pace, L. A., Lin, M. T., Lin, Y. H. & Gennis, R. B. (2010). The diheme cytochrome c4 from Vibrio cholerae is a natural electron donor to the respiratory cbb3 oxygen reductase. Biochemistry 49, 7494–7503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, C. H. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2007). The secreted pyomelanin pigment of Legionella pneumophila confers ferric reductase activity. Infect Immun 75, 4062–4070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien, M., Morozova, I., Shi, S., Sheng, H., Chen, J., Gomez, S. M., Asamani, G., Hill, K., Nuara, J. & other authors (2004). The genomic sequence of the accidental pathogen Legionella pneumophila. Science 305, 1966–1968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto, N. P. (2007). Iron acquisition by Legionella pneumophila. Biometals 20, 323–331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto, N. P. (2008a). Iron assimilation and type II protein secretion. In Legionella pneumophila: Pathogenesis and Immunity, pp. 33–48. Edited by Hoffman, P. S., Friedman, H. & Bendinelli, M.. New York. : Springer.
- Cianciotto, N. P. (2008b). Secretion and export in Legionella. In Legionella Molecular Microbiology, pp. 153–166. Edited by Huener, K. & Swanson, M. S.. Norwich, UK. : Horizon Biosciences.
- Cianciotto, N. P. & Fields, B. S. (1992). Legionella pneumophila mip gene potentiates intracellular infection of protozoa and human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89, 5188–5191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto, N. P., Cornelis, P. & Baysse, C. (2005). Impact of the bacterial type I cytochrome c maturation system on different biological processes. Mol Microbiol 56, 1408–1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke-Pearson, M. F. & Brady, S. F. (2008). Paerucumarin, a new metabolite produced by the pvc gene cluster from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 190, 6927–6930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale, J. R., Wade, R., Jr & Dichristina, T. J. (2007). A conserved histidine in cytochrome c maturation permease CcmB of Shewanella putrefaciens is required for anaerobic growth below a threshold standard redox potential. J Bacteriol 189, 1036–1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Auria, G., Jiménez-Hernández, N., Peris-Bondia, F., Moya, A. & Latorre, A. (2010). Legionella pneumophila pangenome reveals strain-specific virulence factors. BMC Genomics 11, 181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E. & Daldal, F. (1987). Primary structure of the bc1 complex of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Nucleotide sequence of the pet operon encoding the Rieske cytochrome b, and cytochrome c1 apoproteins. J Mol Biol 195, 13–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeudom, M., Koomey, M. & Moir, J. W. (2008). Roles of c-type cytochromes in respiration in Neisseria meningitidis. Microbiology 154, 2857–2864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederen, B. M. (2008). Legionella spp. and Legionnaires' disease. J Infect 56, 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar, M. Y., Wanger, G., Leung, K. M., Yuzvinsky, T. D., Southam, G., Yang, J., Lau, W. M., Nealson, K. H. & Gorby, Y. A. (2010). Electrical transport along bacterial nanowires from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107, 18127–18131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaballa, A., Koedam, N. & Cornelis, P. (1996). A cytochrome c biogenesis gene involved in pyoverdine production in Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC 17400. Mol Microbiol 21, 777–785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudici-Orticoni, M. T., Leroy, G., Nitschke, W. & Bruschi, M. (2000). Characterization of a new dihemic c4-type cytochrome isolated from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biochemistry 39, 7205–7211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glöckner, G., Albert-Weissenberger, C., Weinmann, E., Jacobi, S., Schunder, E., Steinert, M., Hacker, J. & Heuner, K. (2008). Identification and characterization of a new conjugation/type IVA secretion system (trb/tra) of Legionella pneumophila Corby localized on two mobile genomic islands. Int J Med Microbiol 298, 411–428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heras, B., Shouldice, S. R., Totsika, M., Scanlon, M. J., Schembri, M. A. & Martin, J. L. (2009). DSB proteins and bacterial pathogenicity. Nat Rev Microbiol 7, 215–225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey, E. K. & Cianciotto, N. P. (1997). An iron- and Fur-repressed Legionella pneumophila gene that promotes intracellular infection and encodes a protein with similarity to the Escherichia coli aerobactin synthetases. Infect Immun 65, 133–143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, P. S. & Pine, L. (1982). Respiratory physiology and cytochrome content of Legionella pneumophila. Curr Microbiol 7, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Klarskov, K., Van Driessche, G., Backers, K., Dumortier, C., Meyer, T. E., Tollin, G., Cusanovich, M. A. & Van Beeumen, J. J. (1998). Ligand binding and covalent structure of an oxygen-binding heme protein from Rhodobacter sphaeroides, a representative of a new structural family of c-type cytochromes. Biochemistry 37, 5995–6002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz, R. G., Richard-Fogal, C., Taylor, J. S. & Frawley, E. R. (2009). Cytochrome c biogenesis: mechanisms for covalent modifications and trafficking of heme and for heme-iron redox control. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 73, 510–528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y., Hopper, A., Overton, T., Squire, D. J., Cole, J. & Tovell, N. (2010). Organization of the electron transfer chain to oxygen in the obligate human pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae: roles for cytochromes c4 and c5, but not cytochrome c2, in oxygen reduction. J Bacteriol 192, 2395–2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liles, M. R., Viswanathan, V. K. & Cianciotto, N. P. (1998). Identification and temperature regulation of Legionella pneumophila genes involved in type IV pilus biogenesis and type II protein secretion. Infect Immun 66, 1776–1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liles, M. R., Scheel, T. A. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2000). Discovery of a nonclassical siderophore, legiobactin, produced by strains of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol 182, 749–757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londer, Y. Y., Pokkuluri, P. R., Tiede, D. M. & Schiffer, M. (2002). Production and preliminary characterization of a recombinant triheme cytochrome c7 from Geobacter sulfurreducens in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1554, 202–211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthijs, S., Tehrani, K. A., Laus, G., Jackson, R. W., Cooper, R. M. & Cornelis, P. (2007). Thioquinolobactin, a Pseudomonas siderophore with antifungal and anti-Pythium activity. Environ Microbiol 9, 425–434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, T., Coppi, M. V., Childers, S. E. & Lovley, D. R. (2005). Outer membrane c-type cytochromes required for Fe(III) and Mn(IV) oxide reduction in Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl Environ Microbiol 71, 8634–8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R. D. & Hammel, J. M. (1985). Biochemistry and physiology of Legionella. In Legionellosis, pp. 83–106. Edited by Katz, S. M.. Boca Raton, FL. : CRC Press.
- Naylor, J. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2004). Cytochrome c maturation proteins are critical for in vivo growth of Legionella pneumophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett 241, 249–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton, H. J., Ang, D. K., van Driel, I. R. & Hartland, E. L. (2010). Molecular pathogenesis of infections caused by Legionella pneumophila. Clin Microbiol Rev 23, 274–298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry (1992). Nomenclature of electron-transfer proteins. Recommendations 1989. J Biol Chem 267, 665–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, M. M. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2009). Legionella pneumophila secretes an endoglucanase that belongs to the family-5 of glycosyl hydrolases and is dependent upon type II secretion. FEMS Microbiol Lett 300, 256–264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, D. A., Page, M. D., Norris, H. A., Tomlinson, E. J. & Ferguson, S. J. (1998). Identification of the contiguous Paracoccus denitrificans ccmF and ccmH genes: disruption of ccmF, encoding a putative transporter, results in formation of an unstable apocytochrome c and deficiency in siderophore production. Microbiology 144, 467–477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope, C. D., O'Connell, W. & Cianciotto, N. P. (1996). Legionella pneumophila mutants that are defective for iron acquisition and assimilation and intracellular infection. Infect Immun 64, 629–636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey, M. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2002). Legionella pneumophila feoAB promotes ferrous iron uptake and intracellular infection. Infect Immun 70, 5659–5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier, O. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2005). The Legionella pneumophila tatB gene facilitates secretion of phospholipase C, growth under iron-limiting conditions, and intracellular infection. Infect Immun 73, 2020–2032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier, O., Starkenburg, S. R. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2004). Legionella pneumophila type II protein secretion promotes virulence in the A/J mouse model of Legionnaires' disease pneumonia. Infect Immun 72, 310–321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier, O., Dao, J. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2008). The type II secretion system of Legionella pneumophila elaborates two aminopeptidases, as well as a metalloprotease that contributes to differential infection among protozoan hosts. Appl Environ Microbiol 74, 753–761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, C., Turkarslan, S., Lee, D. W. & Daldal, F. (2010). Cytochrome c biogenesis: the Ccm system. Trends Microbiol 18, 266–274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, G. N., Petty, N. K., Mousnier, A., Harding, C. R., Vogrin, A. J., Wee, B., Fry, N. K., Harrison, T. G., Newton, H. J. & other authors (2010). Legionella pneumophila strain 130b possesses a unique combination of type IV secretion systems and novel Dot/Icm secretion system effector proteins. J Bacteriol 192, 6001–6016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L., Squier, T. C., Zachara, J. M. & Fredrickson, J. K. (2007). Respiration of metal (hydr)oxides by Shewanella and Geobacter: a key role for multihaem c-type cytochromes. Mol Microbiol 65, 12–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkenburg, S. R., Casey, J. M. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2004). Siderophore activity among members of the Legionella genus. Curr Microbiol 49, 203–207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, C. R., Rossier, O. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2009). Surface translocation by Legionella pneumophila: a form of sliding motility that is dependent upon type II protein secretion. J Bacteriol 191, 1537–1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzi, A., Cornelis, P., Hohnadel, D., Meyer, J. M., Dean, C., Poole, K., Kourambas, S. & Krishnapillai, V. (1996). Novel pyoverdine biosynthesis gene(s) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Microbiology 142, 1181–1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzi, A., Johnson, Z., Stonehouse, M., Ochsner, U., Meyer, J. M., Vasil, M. L. & Poole, K. (1999). The pvc gene cluster of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: role in synthesis of the pyoverdine chromophore and regulation by PtxR and PvdS. J Bacteriol 181, 4118–4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M., Ross, K. & Bentham, R. (2009). Legionella, protozoa, and biofilms: interactions within complex microbial systems. Microb Ecol 58, 538–547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny-Meyer, L. (1997). Biogenesis of respiratory cytochromes in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61, 337–376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny-Meyer, L., James, P. & Hennecke, H. (1991). From one gene to two proteins: the biogenesis of cytochromes b and c1 in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88, 5001–5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, V. K., Edelstein, P. H., Pope, C. D. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2000). The Legionella pneumophila iraAB locus is required for iron assimilation, intracellular infection, and virulence. Infect Immun 68, 1069–1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, V. K., Kurtz, S., Pedersen, L. L., Abu-Kwaik, Y., Krcmarik, K., Mody, S. & Cianciotto, N. P. (2002). The cytochrome c maturation locus of Legionella pneumophila promotes iron assimilation and intracellular infection and contains a strain-specific insertion sequence element. Infect Immun 70, 1842–1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A. C., Hoch, J. A. & Perego, M. (2009). Two small c-type cytochromes affect virulence gene expression in Bacillus anthracis. Mol Microbiol 72, 109–123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeoman, K. H., Delgado, M. J., Wexler, M., Downie, J. A. & Johnston, A. W. (1997). High affinity iron acquisition in Rhizobium leguminosarum requires the cycHJKL operon and the feuPQ gene products, which belong to the family of two-component transcriptional regulators. Microbiology 143, 127–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeterian, E., Martin, L. W., Guillon, L., Journet, L., Lamont, I. L. & Schalk, I. J. (2010). Synthesis of the siderophore pyoverdine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involves a periplasmic maturation. Amino Acids 38, 1447–1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurgel, S. N., Berrocal, J., Wilson, C. & Kahn, M. L. (2007). Pleiotropic effects of mutations that alter the Sinorhizobium meliloti cytochrome c respiratory system. Microbiology 153, 399–410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]