Abstract
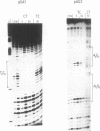
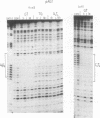
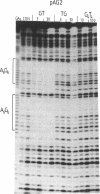
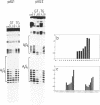
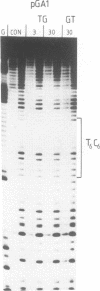
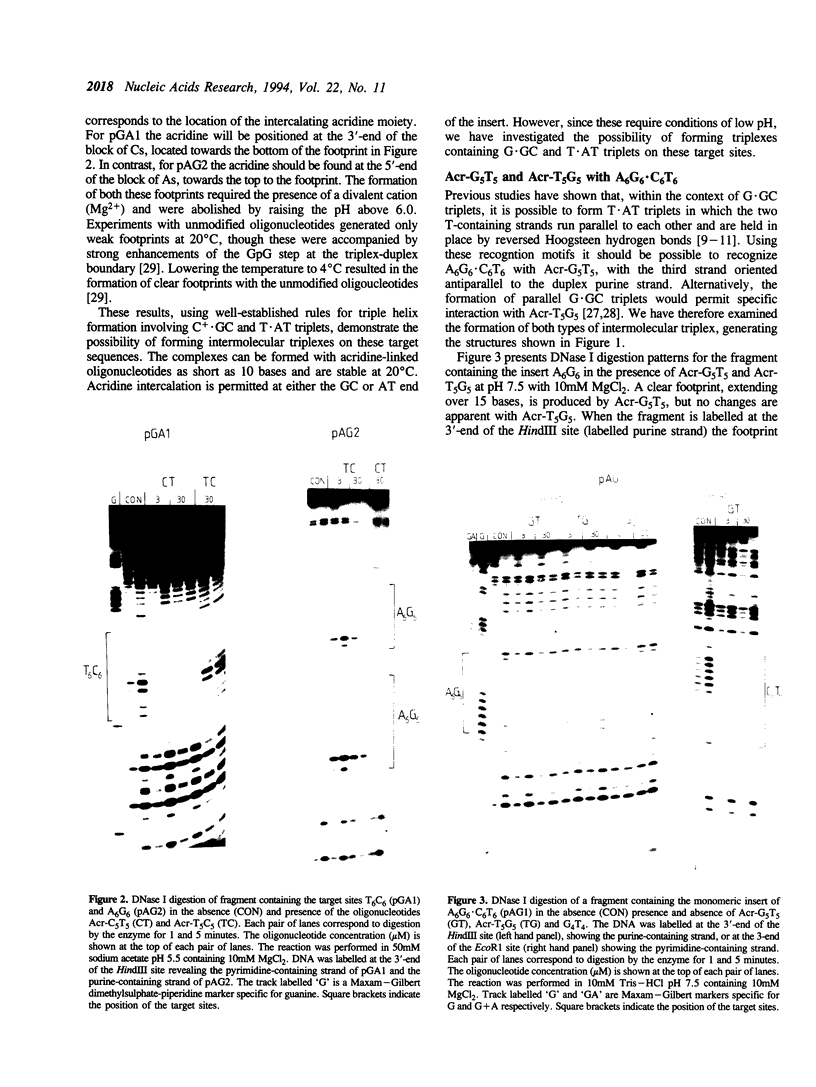
We have used DNase I footprinting to assess triple helix formation at target sites containing the sequences A6G6.C6T6 and G6A6.T6C6. These sequences can be recognized by the acridine-linked oligopyrimidines Acr-T5C5 and Acr-C5T5 respectively at low pH, using well-characterised T.AT and C+.GC triplets. At pH 7.5 A6G6.C6T6 is specifically bound by Acr-G5T5, utilising G.GC and T.AT triplets in which the third strand runs antiparallel to the purine strand of the duplex. This interaction requires the presence of magnesium ions. No interaction was detected with Acr-T5G5, an oligonucleotide designed to form parallel G.GC and T.AT triplets. In contrast neither Acr-T5G5 nor Acr-G5T5 produced DNase I footprints with the target sequence G6A6.T6C6. These results suggest that, in an antiparallel R.RY triple helix, the T.AT triplet is weaker than the G.GC triplet. We find no evidence for the formation of structures containing parallel G.GC triplets.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baguley B. C., Falkenhaug E. M. The interaction of ethidium with synthetic double-stranded polynucleotides at low ionic strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):161–171. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. The influence of single base triplet changes on the stability of a pur.pur.pyr triple helix determined by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2773–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birg F., Praseuth D., Zerial A., Thuong N. T., Asseline U., Le Doan T., Hélène C. Inhibition of simian virus 40 DNA replication in CV-1 cells by an oligodeoxynucleotide covalently linked to an intercalating agent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2901–2908. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresloff J. L., Crothers D. M. Equilibrium studies of ethidium--polynucleotide interactions. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3547–3553. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broitman S. L., Im D. D., Fresco J. R. Formation of the triple-stranded polynucleotide helix, poly(A.A.U). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler S. P., Fox K. R. Triple helix formation at A8XA8.T8YT8. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 11;332(1-2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. M. Intramolecular triplex formation of the purine.purine.pyrimidine type. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4472–4479. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb J. M., Hogan M. E. Human therapeutics based on triple helix technology. Trends Biotechnol. 1992 Apr;10(4):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(92)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durland R. H., Kessler D. J., Gunnell S., Duvic M., Pettitt B. M., Hogan M. E. Binding of triple helix forming oligonucleotides to sites in gene promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9246–9255. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD G., RICH A. Studies on the formation of two- and three-stranded polyribonucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Dec;26(3):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Helene C. Sequence-targeted cleavage of single- and double-stranded DNA by oligothymidylates covalently linked to 1,10-phenanthroline. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5891–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease cleavage via triple helix formation by homopyrimidine oligonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9617–9619. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannangéli C., Rougée M., Garestier T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Triple-helix formation by oligonucleotides containing the three bases thymine, cytosine, and guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8631–8635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena S. D., Johnston B. H. Intramolecular triple-helix formation at (PunPyn).(PunPyn) tracts: recognition of alternate strands via Pu.PuPy and Py.PuPy base triplets. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):320–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letai A. G., Palladino M. A., Fromm E., Rizzo V., Fresco J. R. Specificity in formation of triple-stranded nucleic acid helical complexes: studies with agarose-linked polyribonucleotide affinity columns. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9108–9112. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkov V. A., Voloshin O. N., Soyfer V. N., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Cation and sequence effects on stability of intermolecular pyrimidine-purine-purine triplex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):585–591. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat A. S. Triplex DNA finally comes of age. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1374–1375. doi: 10.1126/science.2047850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch D. S., Levenson C., Shafer R. H. Structure, stability, and thermodynamics of a short intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple helix. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6081–6088. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan I., de los Santos C., Patel D. J. Nuclear magnetic resonance structural studies of intramolecular purine.purine.pyrimidine DNA triplexes in solution. Base triple pairing alignments and strand direction. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1403–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Specificity and stringency in DNA triplex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9397–9401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. Inhibition of gene transcription by purine rich triplex forming oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2845–2852. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., De Bizemont T., Duval-Valentin G., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Extension of the range of recognition sequences for triple helix formation by oligonucleotides containing guanines and thymines. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;313(13):585–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., Giovannangeli C., François J. C., Kurfurst R., Montenay-Garestier T., Asseline U., Saison-Behmoaras T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Triple-helix formation by alpha oligodeoxynucleotides and alpha oligodeoxynucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K., Hobbs C. A., Koch J., Sardaro M., Kutny R., Weis A. L. Elucidation of the sequence-specific third-strand recognition of four Watson-Crick base pairs in a pyrimidine triple-helix motif: T.AT, C.GC, T.CG, and G.TA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]