Abstract
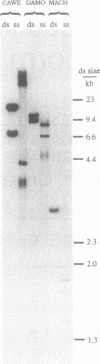
Minisatellite isoallelism, i.e. the occurrence of minisatellite alleles with different internal sequence composition but indistinguishable length, is a common limitation of minisatellite allele length analysis. Internal sequence variation can be used to distinguish such isoalleles, provided that detailed sequence knowledge of its basis is available. We now show that minisatellite isoalleles can also be simply resolved by single-stranded conformational polymorphisms (SSCP) arising during agarose gel electrophoresis. SSCP on agarose gels can be used to distinguish minisatellite isoalleles either after PCR amplification, or by standard Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armour J. A., Harris P. C., Jeffreys A. J. Allelic diversity at minisatellite MS205 (D16S309): evidence for polarized variability. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1137–1145. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray I. C., Jeffreys A. J. Evolutionary transience of hypervariable minisatellites in man and the primates. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Mar 22;243(1308):241–253. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., MacLeod A., Tamaki K., Neil D. L., Monckton D. G. Minisatellite repeat coding as a digital approach to DNA typing. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):204–209. doi: 10.1038/354204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Neumann R., Wilson V. Repeat unit sequence variation in minisatellites: a novel source of DNA polymorphism for studying variation and mutation by single molecule analysis. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):473–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monckton D. G., Jeffreys A. J. Minisatellite "isoallele" discrimination in pseudohomozygotes by single molecule PCR and variant repeat mapping. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):465–467. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90158-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monckton D. G., Tamaki K., MacLeod A., Neil D. L., Jeffreys A. J. Allele-specific MVR-PCR analysis at minisatellite D1S8. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 May;2(5):513–519. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.5.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Aagaard L. Analysis of a 1963-bp polymorphic region flanking the human insulin gene. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):475–479. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle N. J., Armour J. A., Webb M., Thomas A., Jeffreys A. J. A hypervariable locus D16S309 located at the distal end of 16p. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1164–1164. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Patel I., Povey S., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a panel of highly variable minisatellites cloned from human DNA. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;51(Pt 4):269–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]