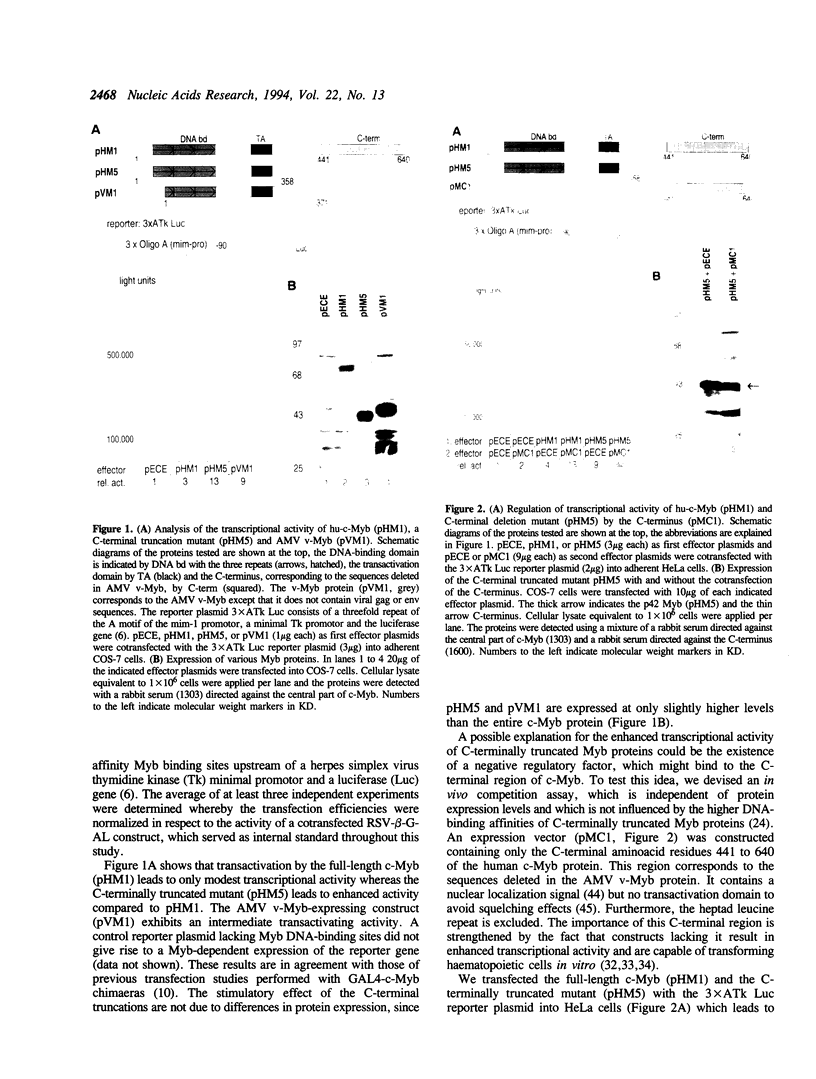
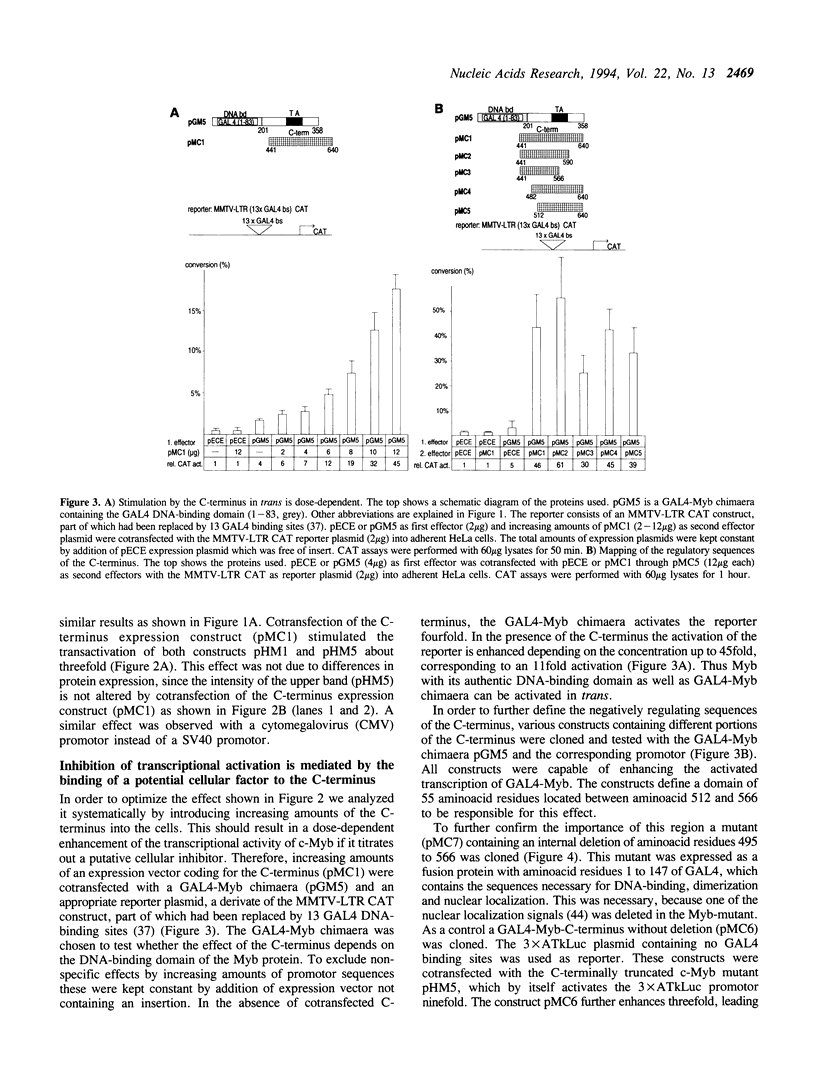
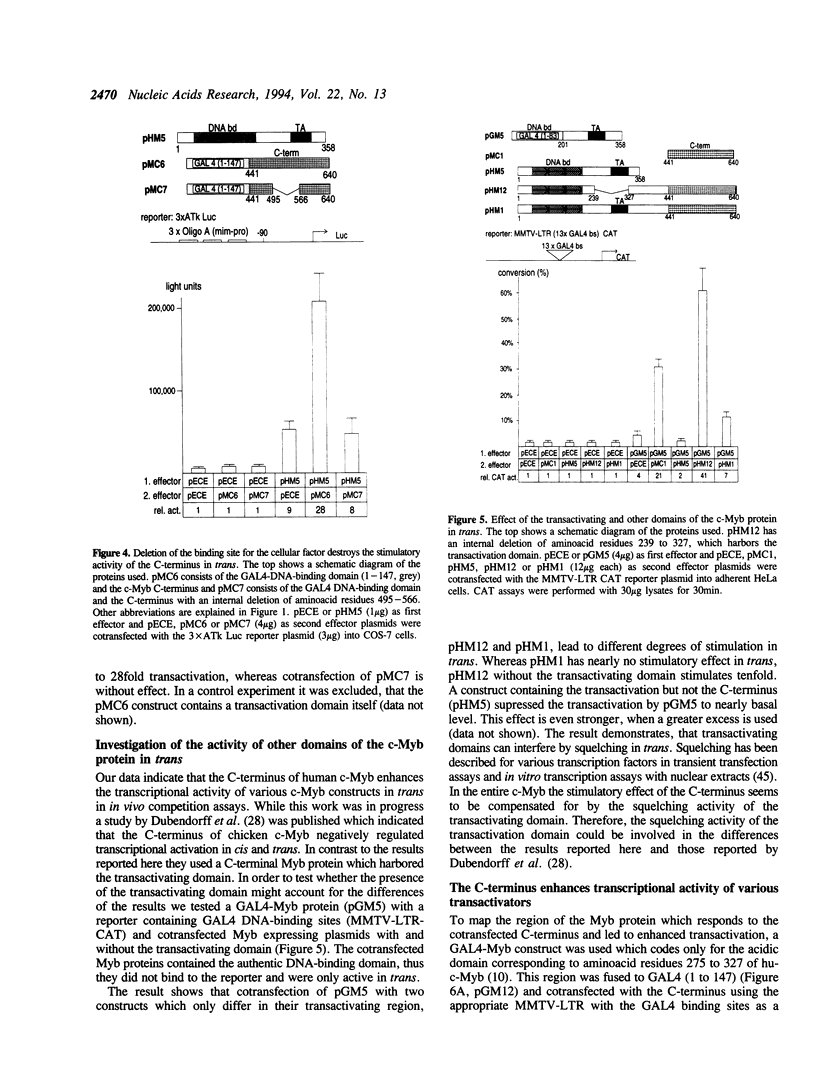
Abstract
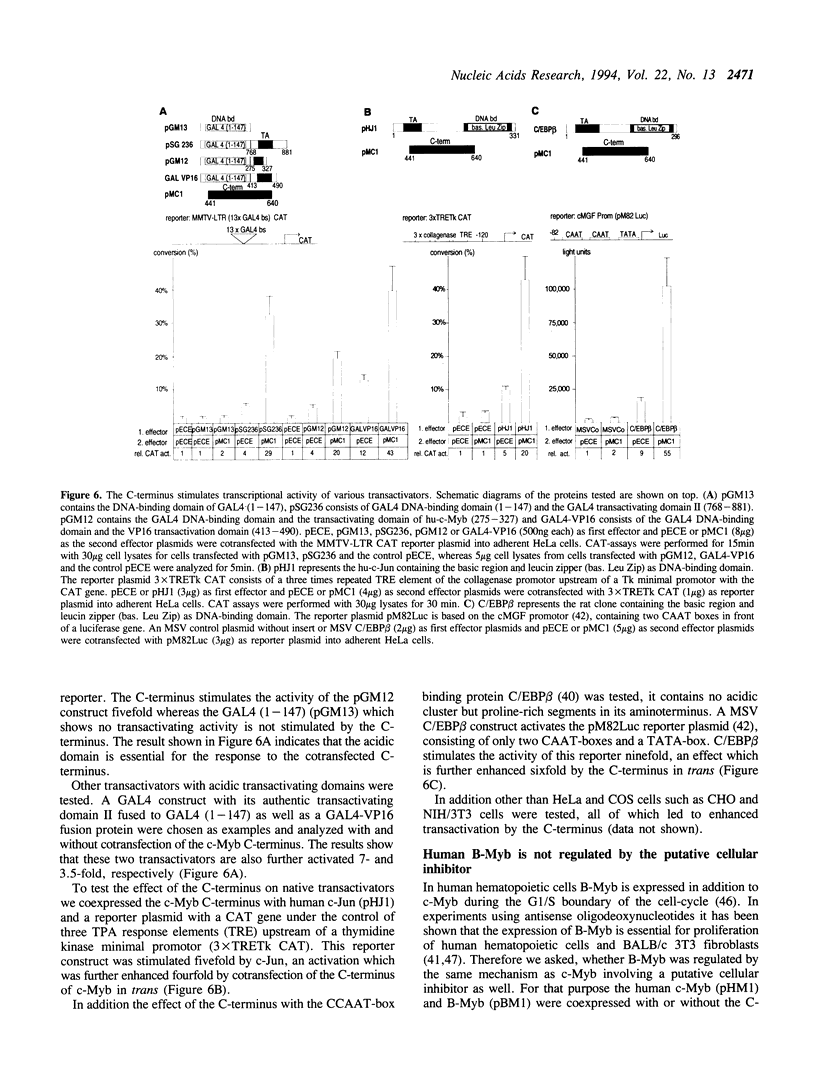
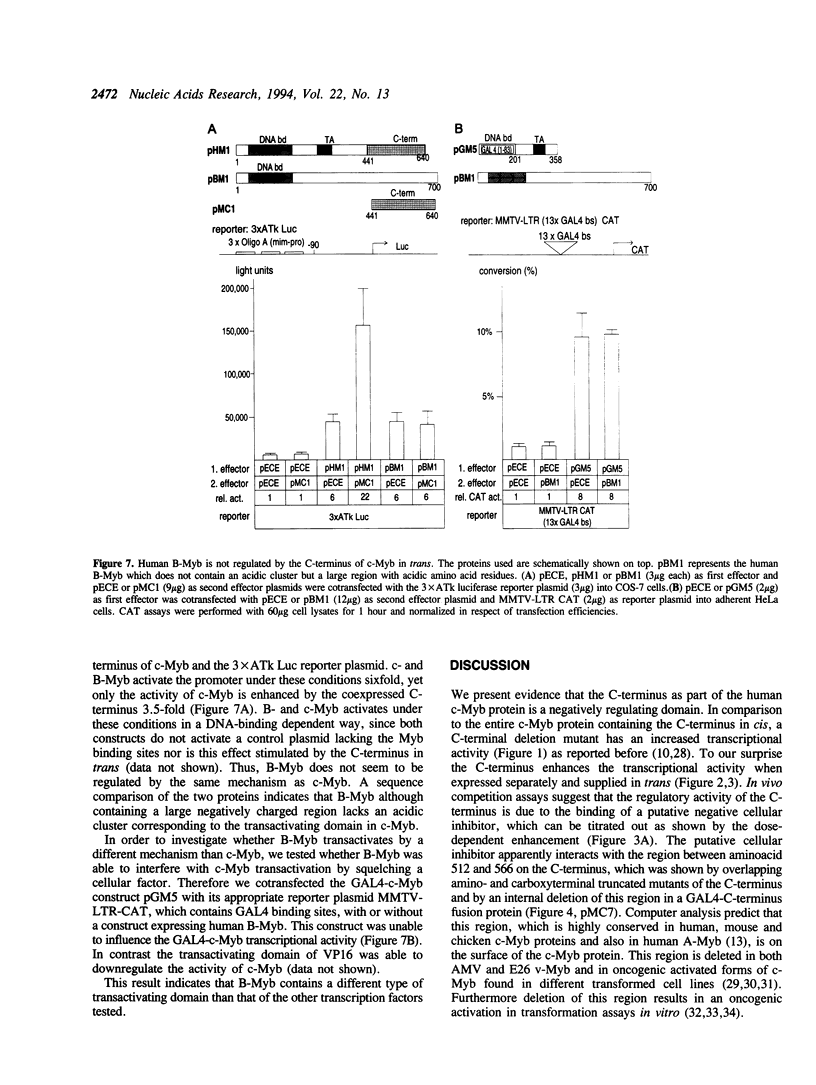
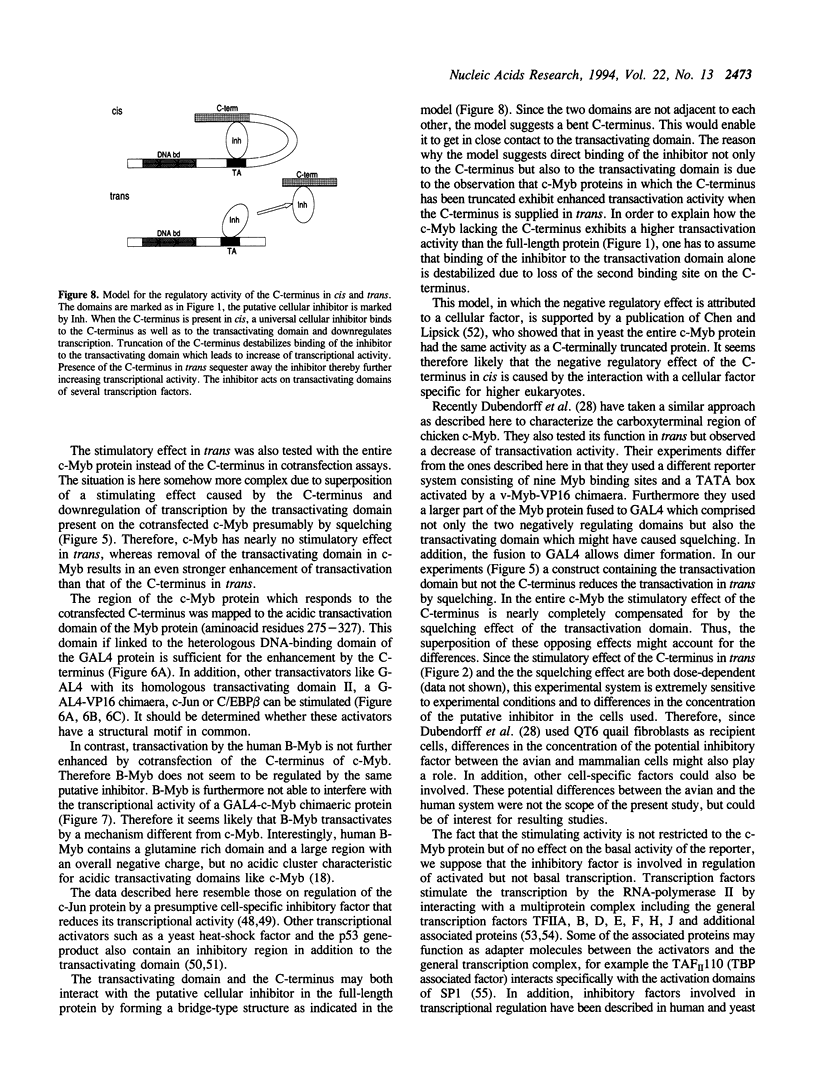
The cellular c-myb gene encodes a transcription factor composed of a DNA-binding domain, a transactivating domain and a regulatory domain located at its carboxy (C-) terminus. The latter one is deleted in the transforming viral protein v-Myb. Here we show that deletion of the C-terminus of c-Myb increases the transcriptional transactivation activity of c-Myb defining it as cis-acting negative regulatory domain. Cotransfection of the C-terminus in an in vivo competition assay causes stimulation of the transcriptional activity of various v- and c-Myb expression constructs in trans. The effect is dose-dependent and independent of the kind of DNA-binding domain, since c-Myb as well as GAL4-c-Myb chimaeras can be stimulated in trans. Other transcription factors, such as GAL4-VP16, GAL4, c-Jun or C/EBP beta are also stimulated by the cotransfected C-terminus. In contrast, human B-Myb is not stimulated by the c-Myb C-terminus in trans. The data suggest that the C-terminus of c-Myb may interact with a cellular inhibitor which is part of the protein complex mediating activated transcription and may stimulate in trans by sequestering away such an inhibitor. Binding of c-Myb to a putative inhibitor would explain differences between c-Myb in comparison to B- and v-Myb in transcriptional regulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsura M., Introna M., Passerini F., Mantovani A., Golay J. B-myb antisense oligonucleotides inhibit proliferation of human hematopoietic cell lines. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2708–2716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auble D. T., Hahn S. An ATP-dependent inhibitor of TBP binding to DNA. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):844–856. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Park A., Tjian R. The cell-type-specific activator region of c-Jun juxtaposes constitutive and negatively regulated domains. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1493–1502. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwmeester T., Güehmann S., el-Baradi T., Kalkbrenner F., van Wijk I., Moelling K., Pieler T. Molecular cloning, expression and in vitro functional characterization of Myb-related proteins in Xenopus. Mech Dev. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90015-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Lipsick J. S. Differential transcriptional activation by v-myb and c-myb in animal cells and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4423–4431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV tat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18019–18023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta P., Saikumar P., Reddy C. D., Reddy E. P. Myb protein binds to human immunodeficiency virus 1 long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences and transactivates LTR-mediated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8090–8094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubendorff J. W., Whittaker L. J., Eltman J. T., Lipsick J. S. Carboxy-terminal elements of c-Myb negatively regulate transcriptional activation in cis and in trans. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2524–2535. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foos G., Grimm S., Klempnauer K. H. Functional antagonism between members of the myb family: B-myb inhibits v-myb-induced gene activation. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4619–4629. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foos G., Natour S., Klempnauer K. H. TATA-box dependent trans-activation of the human HSP70 promoter by Myb proteins. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1775–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golay J., Capucci A., Arsura M., Castellano M., Rizzo V., Introna M. Expression of c-myb and B-myb, but not A-myb, correlates with proliferation in human hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):149–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Buckmaster C., Ramsay R. G. Activation of c-myb by carboxy-terminal truncation: relationship to transformation of murine haemopoietic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1777–1783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Cory S., Sobieszczuk P., Holtzman D., Adams J. M. Generation of altered transcripts by retroviral insertion within the c-myb gene in two murine monocytic leukemias. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2754–2763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2754-2763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Graf T., Lipsick J. S. Protein truncation is required for the activation of the c-myb proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3987–3996. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. TBP, a universal eukaryotic transcription factor? Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Watson R. J. Nucleotide preferences in sequence-specific recognition of DNA by c-myb protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3913–3919. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. L., Ramsay R. G., Kanei-Ishii C., Ishii S., Gonda T. J. Transformation by carboxyl-deleted Myb reflects increased transactivating capacity and disruption of a negative regulatory domain. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1549–1553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibanez C. E., Lipsick J. S. Structural and functional domains of the myb oncogene: requirements for nuclear transport, myeloid transformation, and colony formation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1981–1988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1981-1988.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Dr1, a TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrenner F., Guehmann S., Moelling K. Transcriptional activation by human c-myb and v-myb genes. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):657–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanei-Ishii C., MacMillan E. M., Nomura T., Sarai A., Ramsay R. G., Aimoto S., Ishii S., Gonda T. J. Transactivation and transformation by Myb are negatively regulated by a leucine-zipper structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3088–3092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Arnold H., Biedenkapp H. Activation of transcription by v-myb: evidence for two different mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1582–1589. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of proteins encoded by oncogenes of avian myeloblastosis virus and avian leukemia virus E26 and by chicken c-myb gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. W., Robinson C., Watson R. J. Characterization and cell cycle-regulated expression of mouse B-myb. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1885–1890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J. S., Ibanez C. E. env-encoded residues are not required for transformation by p48v-myb. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):933–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.933-936.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Miller C. W., Koeffler P. H., Berk A. J. The p53 activation domain binds the TATA box-binding polypeptide in Holo-TFIID, and a neighboring p53 domain inhibits transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3291–3300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Family of proteins that interact with TFIID and regulate promoter activity. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90530-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roy A. L., Lieu H. M., Roeder R. G. Activation of class II gene transcription by regulatory factors is potentiated by a novel activity. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):981–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi G., Nakagoshi H., Nagase T., Nomura N., Date T., Ueno Y., Ishii S. DNA binding activity and transcriptional activator function of the human B-myb protein compared with c-MYB. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9280–9284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagoshi H., Takemoto Y., Ishii S. Functional domains of the human B-myb gene product. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14161–14167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Graf T. Identification of genes differentially expressed in two types of v-myb-transformed avian myelomonocytic cells. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Marknell A., Graf T. The v-myb oncogene product binds to and activates the promyelocyte-specific mim-1 gene. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1115–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sotelo J., Wiederrecht G., Okuda A., Parker C. S. The yeast heat shock transcription factor contains a transcriptional activation domain whose activity is repressed under nonshock conditions. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina Y., Nakagoshi H., Imamoto F., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Trans-activation by the c-myb proto-oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):107–117. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura N., Takahashi M., Matsui M., Ishii S., Date T., Sasamoto S., Ishizaki R. Isolation of human cDNA clones of myb-related genes, A-myb and B-myb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11075–11089. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura T., Sakai N., Sarai A., Sudo T., Kanei-Ishii C., Ramsay R. G., Favier D., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Negative autoregulation of c-Myb activity by homodimer formation through the leucine zipper. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21914–21923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Beug H., Kornfeld S., Graf T. Transformation of both erythroid and myeloid cells by E26, an avian leukemia virus that contains the myb gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. G., Ishii S., Gonda T. J. Interaction of the Myb protein with specific DNA binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5656–5662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Nagase T., Nakagoshi H., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Delineation of three functional domains of the transcriptional activator encoded by the c-myb protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5758–5762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala A., Calabretta B. Regulation of BALB/c 3T3 fibroblast proliferation by B-myb is accompanied by selective activation of cdc2 and cyclin D1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10415–10419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterneck E., Müller C., Katz S., Leutz A. Autocrine growth induced by kinase type oncogenes in myeloid cells requires AP-1 and NF-M, a myeloid specific, C/EBP-like factor. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):115–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stober-Grässer U., Lipsick J. S. Specific amino acid substitutions are not required for transformation by v-myb of avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1093–1096. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1093-1096.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Ihle J. N., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Truncation of the c-myb gene by a retroviral integration in an interleukin 3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Bishop J. M. Transcriptional activation by the v-myb oncogene and its cellular progenitor, c-myb. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobel A., Kalkbrenner F., Guehmann S., Nawrath M., Vorbrueggen G., Moelling K. Interaction of the v-and c-Myb proteins with regulatory sequences of the human c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1397–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]