Abstract
Inhibitors of human transglutaminase 2 (TG2) are anticipated to be useful in the therapy of a variety of diseases including celiac sprue as well as certain CNS disorders and cancers. A class of 3-acylidene-2-oxoindoles was identified as potent reversible inhibitors of human TG2. Structure-activity relationship analysis of a lead compound led to the generation of several potent, competitive inhibitors. Analogues with significant non-competitive character were also identified, suggesting that the compounds bind at one or more allosteric regulatory sites on this multidomain enzyme. The most active compounds had Ki values below 1.0 µM in two different kinetic assays for human TG2, and may therefore be suitable for investigations into the role of TG2 in physiology and disease in animals.
Keywords: transglutaminase 2, oxoindole, celiac sprue, structure-activity relationships, allostery
Transglutaminase 2 (TG2), a ubiquitous member of the mammalian transglutaminase enzyme family, is found in intracellular as well as extracellular environments of many organs. In the presence of Ca2+ and the absence of guanine nucleotides, TG2 adopts an open, catalytically competent conformation, which activates γ-glutaminyl residues on proteins as acyl donors and cross-links these to ε-amino groups of lysyl residues. As a result, proteolytically resistant isopeptide bonds are formed between proteins. Hydrolysis of the γ-glutamyl acyl-enzyme intermediate results in deamidation of the substrate.1,2 TG2 is implicated in the pathogenesis of disorders including neurological diseases such as Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, certain types of cancers and renal diseases, cystic fibrosis and celiac sprue,3–8 and may therefore be a suitable therapeutic target for one or more of these conditions.9 Consequently, small molecule modulators of in vivo TG2 activity are of pharmacological and medicinal interest.
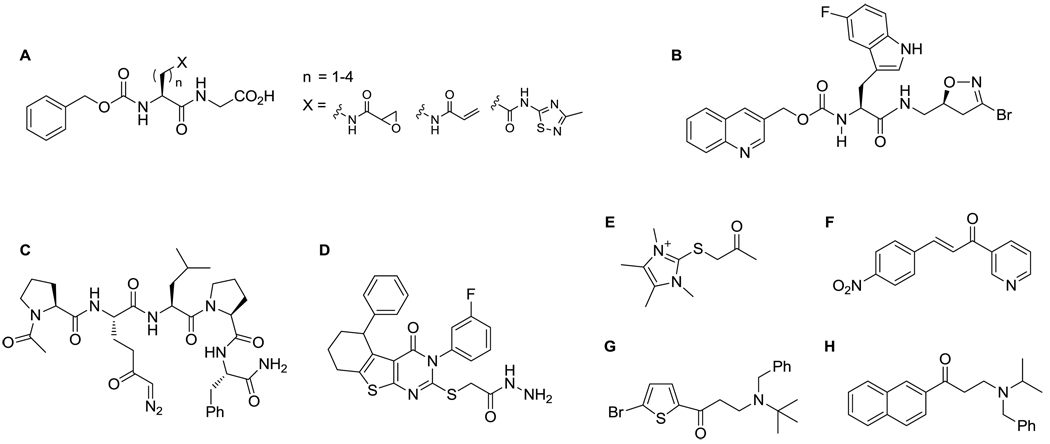
Several classes of irreversibleinhibitors of TG2 have been described thus far (Figure 1).2,10–15 More recently, three classes of reversible inhibitors have also been reported.16–18 Here, we present a structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis for a new class of reversible inhibitors of human TG2, the acylidene oxoindoles.
Figure 1.
Selected TG2 inhibitors – irreversible dipeptide inhibitors (A)11, irreversible DHI-based inhibitors (B)10, irreversible DON-based substrate mimics (C)2, reversible thienopyrimidinones (D)16, irreversible imidazolium salts (E)12,13, reversible azachalcones (F)17 and aryl-β-aminoethyl ketones (G, H)14,15
Isatin (indoline-2,3-dione) is an endogenous indole in mammals with a range of biological activities.19,20 Our motivation to screen this natural product as a candidate TG2 inhibitor was guided by the hypothesis that the cyclic α-keto amide structure of isatin may mimic the γ-carboxamide group of TG2 substrates. α-Keto amides, including isatin analogues, are widely utilized as reversible inhibitors of cysteine-dependent proteases.21 This led us to propose that isatin analogues may also be reversible inhibitors of the cysteine transglutaminase TG2. In preliminary screening efforts, isatin was found to be a weak, reversible inhibitor of human TG2 (IC50 > 0.25 mM), and certain 5-substituted analogues with electron-withdrawing functional groups were somewhat more active (IC50 = 65–450 µM for 5-chloro, 5-bromo, 5-iodo and 5,7-difluoroisatin).
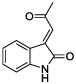
Using this information and data available for other classes of TG2 inhibitors, we built a ligand-based statistical model with which to identify new TG2 inhibitors. This model was used to screen ChemNavigator’s iResearch library of commercially available compounds, and to prioritize compounds for acquisition and testing. Among these were a series of symmetrical isatin dimers (1–6), as well as three 3-acylidene-2-oxoindoles: indirubin (7), isoindigotin (8) and methyl ketone (9) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Structures and TG2 inhibitory characteristics of isatin dimers and analogues. Enzyme inhibition was measured using the coupled GDH assay ([TG2] = 0.5 µM). For IC50 values, the substrate was used at its Km = 10 mM. The errors were typically less than 10 %.
| cpd | IC50 [µM] | Ki [µM] | |
|---|---|---|---|
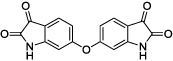 |
1 | 30–40 | --- |
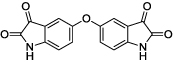 |
2 | 25 | 3 |
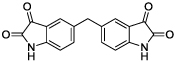 |
3 | 30 | 15 |
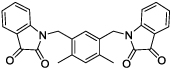 |
4 | 40 | 11 |
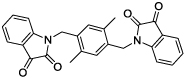 |
5 | > 250 | --- |
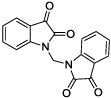 |
6 | 18 | 10 |
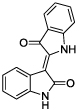 |
7 | > 100 | --- |
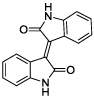 |
8 | 8 | 41 |
 |
9 | 11 | 10 |
Using a standard glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)-coupled deamidation assay with Cbz-Gln-Gly (ZQG) as the acyl donor substrate,22 isatin dimers linked 6,6’ (1), 5,5’ (2, 3) and 1,1’ (4, 5) were found to display inhibition constants in the range of 18–40 µM, approximately 10-fold more potent than the simple 5-haloisatins. The linker can play a role in determining the activity of isatin dimers: the m-xylyl and methylene-linked analogues 4 and 6 were active whereas the p-xylyl linked analogue 5, a constitutional isomer of 4, was not. Among the 3-acylidene oxoindoles, indirubin (7) was inactive, but isoindigotin (8) and the E-methyl ketone 9 proved to be promising inhibitors.
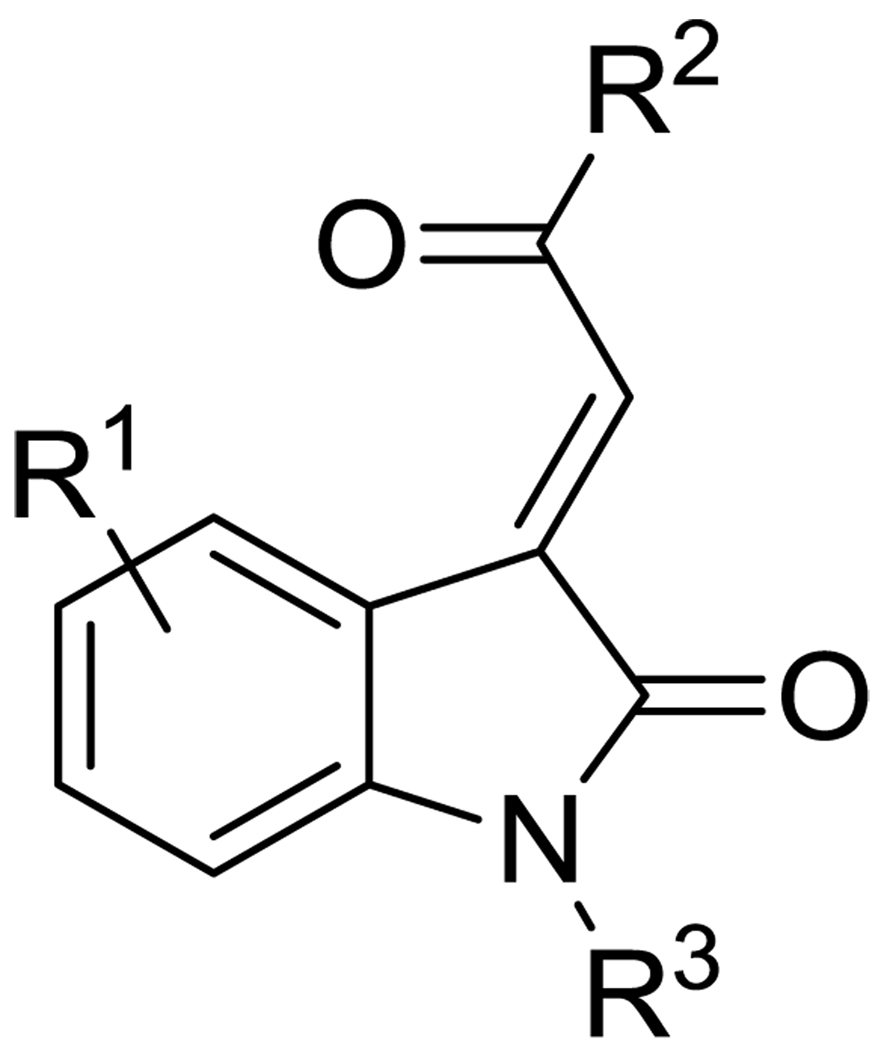
To explore the potential of acylidene oxoindoles as TG2 inhibitors, we undertook the synthesis of analogues of compound 9 bearing substitution in 3 regions – on the aromatic oxoindole ring (R1), at the methyl position of the ketone (R2), and on the amide nitrogen (R3) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
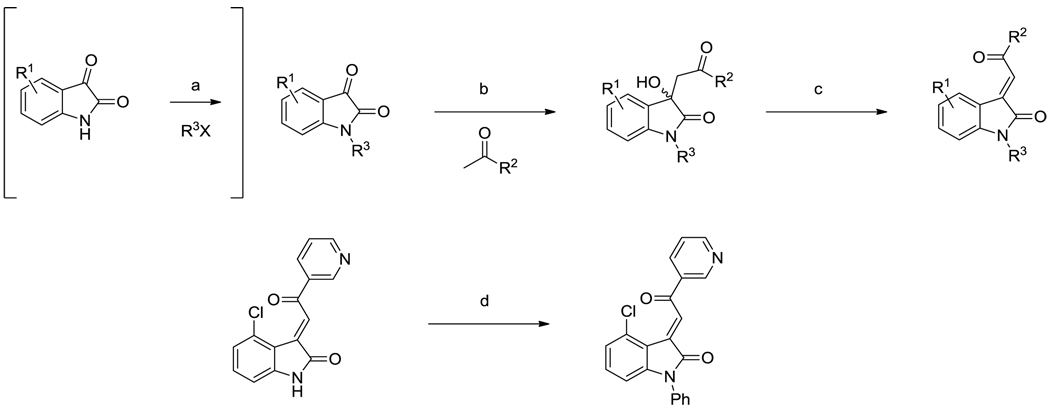
The acylidene oxoindoles were prepared by a two-step condensation-dehydration sequence from isatin or a substituted isatin along with acetone or an aryl methyl ketone (Scheme 1). The first step, performed under basic conditions, afforded β-hydroxy ketones which were isolated and then dehydrated under acidic conditions, or via the agency of methanesulfonyl chloride in pyridine, to produce the acylidene oxoindole.23 All compounds were obtained as a single stereoisomer, which was assigned as the (E)-diastereomer based on the 1H NMR spectra, which displayed downfield chemical shifts for the aromatic C-4 proton resonances.24,25 N-substituted compounds were prepared either via condensation-dehydration starting from the corresponding N-substituted isatin or via copper-mediated N-arylation of an acylidene oxoindole.26
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of 3-acylidene-2-oxoindoles. Top: Synthesis of N1-H or N1-substituted analogues via condensation-dehydration of N1-H or N1-substituted isatins. Bottom: Synthesis of N1-substituted analogues via N-arylation of N1-H compounds. a) R3X (alkyl bromide or iodide), K2CO3, DMF, 16–48 h. b) acetone, NHEt2, 60 °C, 16 h or aryl methyl ketone, NHEt2, EtOH, RT, 2–48 h. c) HCl, AcOH, reflux, 0.5 h or HCl, AcOH, RT, 16 h. d) PhB(OH)2, CuSO4·5H2O, pyridine, DCM, 16 h.
The inhibitory properties of the acylidene oxoindoles toward TG2-catalyzed deamidation of ZQG were initially characterized using the GDH-coupled assay (Table 2). We first examined a small series of analogues of parent compound 9 bearing fluoro, chloro or ether substituents at the 4-, 5-, 6- or 7-position of the oxoindole system (compounds 10–14). Here, the 4-chloro analogue 10 exhibited the highest potency, with an IC50 value of 1.5 µM and a Ki value of 0.7 µM.
Table 2.
Structures and activities of 3-acylidene-2-oxoindole inhibitors modified in all regions. Their inhibitory characteristics against TG2 were measured in the GDH assay ([TG2] = 0.5 µM). For IC50 values, the substrate was used at its Km = 10 mM. The errors were typically less than 10 %.
| cpd | R = | IC50 [µM] | Ki [µM] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
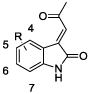 |
10 | 4-Cl | 1.5 | 0.7 |
| 11 | 5-Cl | 4.3 | 0.9 | |
| 12 | 6-F | 11 | 5.4 | |
| 13 | 6-OCF3 | 3.6 | ||
| 14 | 7-Cl | 4.7 | ||
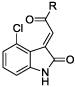 |
15 | 2’-pyridyl | 1.1 | |
| 16 | 3’-pyridyl | 0.9 | 1.3 | |
| 17 | 4’-pyridyl | 1.2 | ||
| 18 | 3’-pyr-5’-Br | 1.4 | ||
| 19 | 3’-pyr-4’-OMe | 1.4 | ||
| 20 | Ph | 2.8 | 3.3 | |
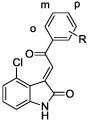 |
21 | m-Cl | 0.7 | |
| 22 | p-Cl | 0.8 | ||
| 23 | o-OMe | 0.9 | ||
| 24 | m-OMe | 1.0 | ||
| 25 | p-OMe | 1.1 | ||
| 26 | m-NH2 | 1.4 | ||
| 27 | p-NH2 | 1.1 | ||
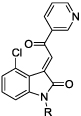 |
28 | Me | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 29 | iPr | 1.4 | ||
| 30 | iBu | 1.0 | ||
| 31 | Ph | 0.8 | ||
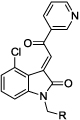 |
32 | cyclohexyl | 2.1 | |
| 33 | Ph | 1.5 | 0.41 | |
| 34 | CH2Ph | 1.5 | ||
| 35 | (CH2)2Ph | 1.3 | ||
| 36 | CONMe2 | 5.5 | ||
| 37 | CO2Et | 1.8 | ||
| 38 | (m-CO2Me)Ph | 1.1 | ||
| 39 | (p-CO2Me)Ph | 1.2 | ||
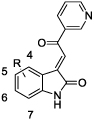 |
40 | H | 22 | 12 |
| 41 | 4-Br | 0.9 | 0.4 | |
| 42 | 5-Cl | 6.0 | ||
| 43 | 5-Br | 4.8 | 3.0 | |
| 44 | 5-Me | 6.3 | ||
| 45 | 5-NO2 | 7.9 | ||
| 46 | 6-Cl | 2.1 (70%)# | 5.3 | |
| 47 | 6-Br | 1.5 (35%)# | ||
| 48 | 7-Cl | 7.3 | ||
| 49 | 7-Br | 2.9 |
If partial inhibition was observed, the maximum inhibition effect is shown in parentheses.
Using compound 10 as a new lead, we next examined the effects of replacing the methyl group on the ketone moiety with aromatic groups (compounds 15–27). We observed that phenyl, substituted phenyl, pyridinyl and substituted pyridinyl groups were well-tolerated at this position, affording compounds with IC50 values very similar to that of compound 10. Negligible differences in TG2 inhibitory potency were observed among regioisomeric pyridin-2-yl, -3-yl or -4-yl analogues (15–17), 4’-or 5’-substituted pyridine-3-yl analogues (18, 19), phenyl analogue 20, or phenyl analogues substituted at the 2’-, 3’- or 4’-positions with chloro, methoxy or amino groups (21–27).
The 4-chloro-pyridin-3’-yl analogue 16 was used as a scaffold to examine the effects of substitution at the oxoindole nitrogen (compounds 28–39). While methyl and dimethylacetamido substituents led to 4- and 6-fold losses in potency for compounds 28 and 36, respectively, a range of other substituents afforded analogues that were essentially equipotent to 16. These substituents included primary and secondary alkyl (29, 30, 32), phenyl (31), 2-phenylethyl (34), 3-phenylpropyl (35) benzyl (33, 38, 39) and ethyl acetyl (37) groups.
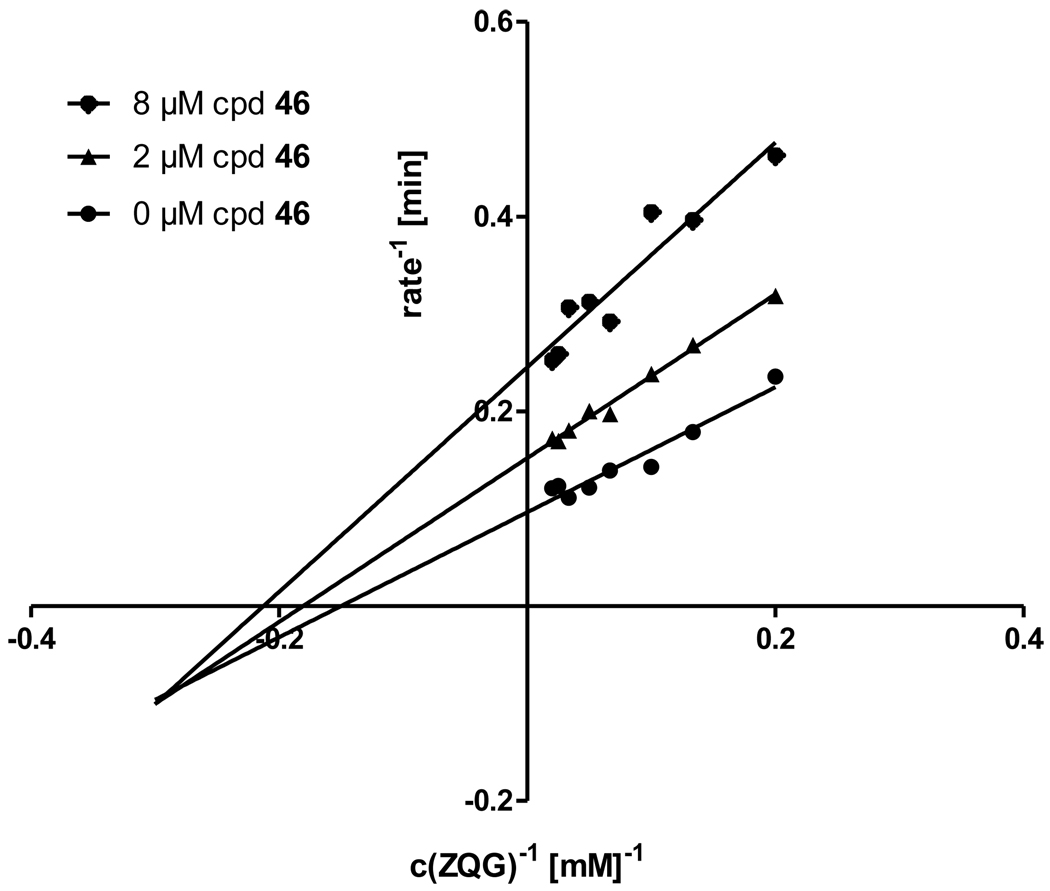
We also used compound 16 as a starting point from which to examine more systematically the effects of substitution on the oxoindole benzene ring (compounds 40–49). Removal of the 4-chloro substituent led to a >20-fold loss in potency for compound 40, but replacing chlorine with bromine at the 4-position afforded the sub-micromolar inhibitor 41. Analogues bearing chloro, bromo, methyl or nitro groups at the 5-position (42–45), or with chloro or bromo groups in the 7-position (48, 49), displayed IC50 values in the range of 2.9–7.9 µM, some 3- to 9-fold less potent than compound 16. The 6-chloro and 6-bromo analogues 46 and 47 were nearly as potent as compound 16. Interestingly, these compounds were only partial inhibitors of TG2, achieving maximal inhibition of only 70% and 30%, respectively. This behavior suggests a non-competitive, allosteric mode of action, a hypothesis that was confirmed for compound 46 via Lineweaver-Burk analysis (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Lineweaver-Burk analysis of the 6-chloro substituted compound 46, confirming its non-competitive inhibitory character. Reversibility was assigned based on the observation that preincubation of TG2 with inhibitors in the presence of 4 mM Ca+2 for 40 min did not appreciably alter the outcome of inhibition experiments (data not shown).
The GDH-coupled assay for TG2 activity became problematic as the potencies of acylidene oxoindole inhibitors increased. The typical enzyme concentration used in this assay is 0.5 µM, which precludes measurement of Ki values below this concentration. Therefore, a more sensitive direct fluorometric assay was implemented, which follows the TG2-catalyzed release of 7-hydroxycoumarin from an ester substrate and allows the use of enzyme concentrations below 100 nM.27 Table 3 presents the IC50 values obtained for 43 acylidene oxoindole inhibitors with this method and with the GDH-coupled assay, where it may be seen that the fluorometric assay indeed allowed us to determine lower IC50 values (range 0.090 – 20 µM) than did the GDH-coupled assay (range 0.8 – 22 µM). The fluorometric assay also uncovered partial inhibition activity with a larger subset of compounds, including compounds 19, 22, 27, 47 and 48. Furthermore, using a mixed inhibition model for analyzing the observed inhibition kinetic behavior, non-competitive binding character could be detected for a number of compounds that did not exhibit partial inhibition towards TG2, including compounds 33, 41 and 43 (Table 4).
Table 3.
Comparison of IC50 concentrations as determined by the widely used coupled GDH assay and the coumarin-based fluorescence assay with a better dynamic range for submicromolar values. For IC50 values in the GDH-coupled assay, the substrate was used at its Km = 10 mM with 500 nM TG2. In the fluorescent assay, IC50 values were measured at 10 µM substrate concentration (= 2 * Km) with 15 nM TG2. The errors were typically less than 10 %.
| cpd | GDH | Fluoresc. |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 [µM] | IC50 [µM] | |
| 9 | 11 | 19 |
| 10 | 1.5 | -- |
| 11 | 4.3 | 3.7 |
| 12 | 11 | 20 |
| 13 | 3.6 | 2.6 |
| 14 | 4.7 | 3.9 |
| 15 | 1.1 | 0.89 |
| 16 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| 17 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| 18 | 1.4 | 0.97 |
| 19 | 1.4 | 0.95 (50%)# |
| 20 | 2.8 | 20 |
| 21 | 0.7 | 2.8 |
| 22 | 0.8 | 0.09 (60%)# |
| 23 | 0.9 | 0.74 |
| 24 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| 25 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| 26 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
| 27 | 1.1 | 3.0 (65%)# |
| 28 | 4.0 | 11 |
| 29 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| 30 | 1.0 | 4.1 |
| 31 | 0.8 | 0.57 |
| 32 | 2.1 | 6.7 |
| 33 | 1.5 | 0.36 |
| 34 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
| 35 | 1.3 | 1.0 |
| 36 | 5.5 | 9.2 |
| 37 | 1.8 | 2.5 |
| 38 | 1.1 | 5.6 |
| 39 | 1.2 | 0.66 |
| 40 | 22 | 8.5 |
| 41 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| 42 | 6.0 | 1.2 |
| 43 | 4.8 | 0.56 |
| 44 | 6.3 | 4.5 |
| 45 | 7.9 | 1.7 |
| 46 | 2.1 (70%)# | 20 |
| 47 | 1.5 (35%)# | 0.36 (65%)# |
| 48 | 7.3 | 1.6 (70%)# |
| 49 | 2.9 | 3.2 |
Table 4.
Analysis of inhibition constants of selected 3-acylidene-2-oxoindoles in the GDH assay ([TG2] = 0.5 µM) and the fluorescent assay ([TG2] = 15 nM), α is the ratio Ki’/Ki in a mixed inhibition model. The larger α, the more competitive is the inhibition; when α = 1, the inhibition is simple non-competitive and when α < 1, the inhibition is increasingly un-competitive.
| cpd # | GDH-coupled assay | Fluorescent assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki [µM] | α | Ki [µM] | α | |
| 10 | 0.7 | > 100 | ||
| 11 | 0.9 | > 100 | ||
| 12 | 5.4 | > 100 | ||
| 16 | 1.3 | > 100 | ||
| 20 | 3.3 | > 100 | ||
| 28 | 4.0 | > 100 | ||
| 33 | 0.41 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 3.6 |
| 40 | 12 | > 100 | ||
| 41 | 0.4 | > 100 | 0.25 | 2.6 |
| 43 | 3.0 | > 100 | 0.68 | 4.4 |
| 46 | 5.3 | 0.86 | ||
Acylidene oxoindoles have been widely utilized as synthetic intermediates, e.g., in the synthesis of stereochemically rich and diverse spirocycles,28–32 natural products33 and chemical libraries.34 Acylidene oxoindoles have also shown biological activity, for example, as kinase inhibitors,35,36 phosphatase inhibitors,37 promoters of vasodilatation,38 antifungal agents,39 and activators of TRP1 ion channels.40 As described in this communication, we have identified in 3-acylidene-2-oxoindoles a new class of reversible inhibitors of human TG2. Through synthesis and biochemical characterization of analogues substituted on the oxoindole benzene ring, at the exocyclic ketone group and on the oxoindole nitrogen, we have demonstrated that 1) TG2 inhibitory potency is increased by substitution of chlorine or bromine at position C-4, and 2) a range of aryl substituents may be attached to the ketone group, and a range of substituents may be added to oxoindole nitrogen with minimal impact on TG2 inhibitory potency. We have furthermore provided kinetic evidence that some acylidene oxoindoles are allosteric inhibitors of TG2 with a non-competitive inhibition mechanism. The most active compounds in this series inhibit TG2 at submicromolar concentrations, and may therefore be suitable for investigations into the role of TG2 in physiology and disease.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by an STTR grant from the NIH (DK 1 R41 DK081244).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Fesus L, Piacentini M. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:534–539. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(02)02182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pinkas DM, Strop P, Brunger AT, Khosla C. PLoS Biol. 2007;5:2788–2796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bailey CDC, Tucholski J, Johnson GVW. Progress in experimental tumor research. 2005;38:139–157. doi: 10.1159/000084238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sollid LM. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:647–655. doi: 10.1038/nri885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ruan Q, Johnson GVW. Front. Biosci. 2007;3:891–904. doi: 10.2741/2111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Verma A, Mehta K. Drug Resist. Updat. 2007;10:144–151. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2007.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shweke N, Boulos N, Jouanneau C, Vandermeersch S, Melino G, Dussaule J-C, Chatziantoniou C, Ronco P, Boffa J-J. Am. J. Pathol. 2008;173:631–642. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.080025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Maiuri L, Luciani A, Giardino I, Raia V, Villella VR, D’Apolito M, Pettoello-Mantovani M, Guido S, Ciacci C, Cimmino M, Cexus ON, Londei M, Quaratino S. J. Immunol. 2008;180:7697–7705. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.11.7697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Siegel M, Khosla C. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007;115:232–245. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Watts RE, Siegel M, Khosla C. J. Med. Chem. 2006;49:7493–7501. doi: 10.1021/jm060839a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Marrano C, Macédo Pde, Keillor JW. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001;9:1923–1928. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Freund KF, Doshi KP, Gaul SL, Claremon DA, Remy DC, Baldwin JJ, Pitzenberger SM, Stern AM. Biochemistry. 1994;33:10109–10119. doi: 10.1021/bi00199a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hausch F, Halttunen T, Mäki M, Khosla C. Chem. Biol. 2003;10:225–231. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(03)00045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lai T-S, Liu Y, Tucker T, Daniel KR, Sane DC, Toone E, Burke JR, Strittmatter WJ, Greenberg CS. Chem. Biol. 2008;15:969–978. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ozaki S, Ebisui E, Hamada K, Goto J-I, Suzuki AZ, Terauchi A, Mikoshiba K. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010;20:1141–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Duval E, Case A, Stein RL, Cuny GD. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005;15:1885–1889. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pardin C, Pelletier JN, Lubell WD, Keillor JW. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:5766–5775. doi: 10.1021/jo8004843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schaertl S, Prime M, Wityak J, Dominguez C, Munoz-Sanjuan I, Pacifici RE, Courtney S, Scheel A, Macdonald D. J. Biomol. Screen. 2010;15:478–487. doi: 10.1177/1087057110366035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pandeya SN, Smitha S, Jyoti M, Sridhar SK. Acta Pharm. (Zagreb, Croatia) 2005;55:27–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vine KL, Matesic L, Locke JM, Ranson M, Skropeta D. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009;9:397–414. doi: 10.2174/1871520610909040397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee D, Long SA, Murray JH, Adams JL, Nuttall ME, Nadeau DP, Kikly K, Winkler JD, Sung CM, Ryan MD, Levy MA, Keller PM, DeWolf WE. J. Med. Chem. 2001;44:2015–2026. doi: 10.1021/jm0100537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Piper JL, Gray GM, Khosla C. Biochemistry. 2002;41:386–393. doi: 10.1021/bi011715x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Popp F, Parson R, Donigan B. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980;69:1235. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600691035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Autrey RL, Tahk FC. Tetrahedron. 1967;23:901–917. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Faita G, Mella M, Righetti P, Tacconi G. Tetrahedron. 1994;50:10955–10962. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chan D, Monaco K, Wang R, Winters M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:2933–2936. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gillet SMFG, Pelletier JN, Keillor JW. Anal. Biochem. 2005;347:221–226. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2005.09.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Babu ARS, Raghunathan R. Synth. Commun. 2008;38:1433–1438. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bencivenni G, Wu L-Y, Mazzanti A, Giannichi B, Pesciaioli F, Song M-P, Bartoli G, Melchiorre P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009;48:7200–7203. doi: 10.1002/anie.200903192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Galliford CV, Martenson JS, Stern C, Scheidt KA. Chem. Commun. 2007:631–633. doi: 10.1039/b609155e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jiang K, Jia Z-J, Yin X, Wu L, Chen Y-C. Org. Lett. 2010;12:2766–2769. doi: 10.1021/ol100857s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Trost BM, Cramer N, Silverman SM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:12396–12397. doi: 10.1021/ja075335w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sebahar PR, Williams RM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:5666–5667. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lo MM-C, Neumann CS, Nagayama S, Perlstein EO, Schreiber SL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:16077–16086. doi: 10.1021/ja045089d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Adams C, Aldous DJ, Shelley A, Bamborough P, Bright C, Crowe S, Eastwood P, Fenton G, Foster M, Harrison TKP, King S, Lai J, Lawrence C, Letallec J-P, McCarthy C, Moorcroft N, Page K, Rao S, Redford J, Sadiq S, Smith K, Souness JE, Thurairatnam S, Vine M, Wyman B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003;13:3105–3110. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(03)00657-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Woodard CL, Li Z, Kathcart AK, Terrell J, Gerena L, Lopez-Sanchez M, Kyle DE, Bhattacharjee AK, Nichols DA, Ellis W, Prigge ST, Geyer JA, Waters NC. J. Med. Chem. 2003;46:3877–3882. doi: 10.1021/jm0300983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shimazawa R, Kuriyama M, Shirai R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008;18:3350–3353. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.04.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Maroñas PA, Sudo RT, Corrêa MB, Pinto AC, Garden SJ, Trachez MM, Zapata-Sudo G. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008;35:1091–1096. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Strigácová J, Hudecová D, Mikulášová M, Varečka L, Lásiková A, Végh D. Folia Microbiol. 2001;46:187–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02818531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Macpherson LJ, Dubin AE, Evans MJ, Marr F, Schultz PG, Cravatt BF, Patapoutian A. Nature. 2007;445:541–545. doi: 10.1038/nature05544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.