Abstract
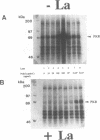
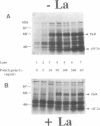
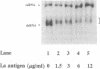
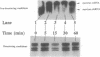
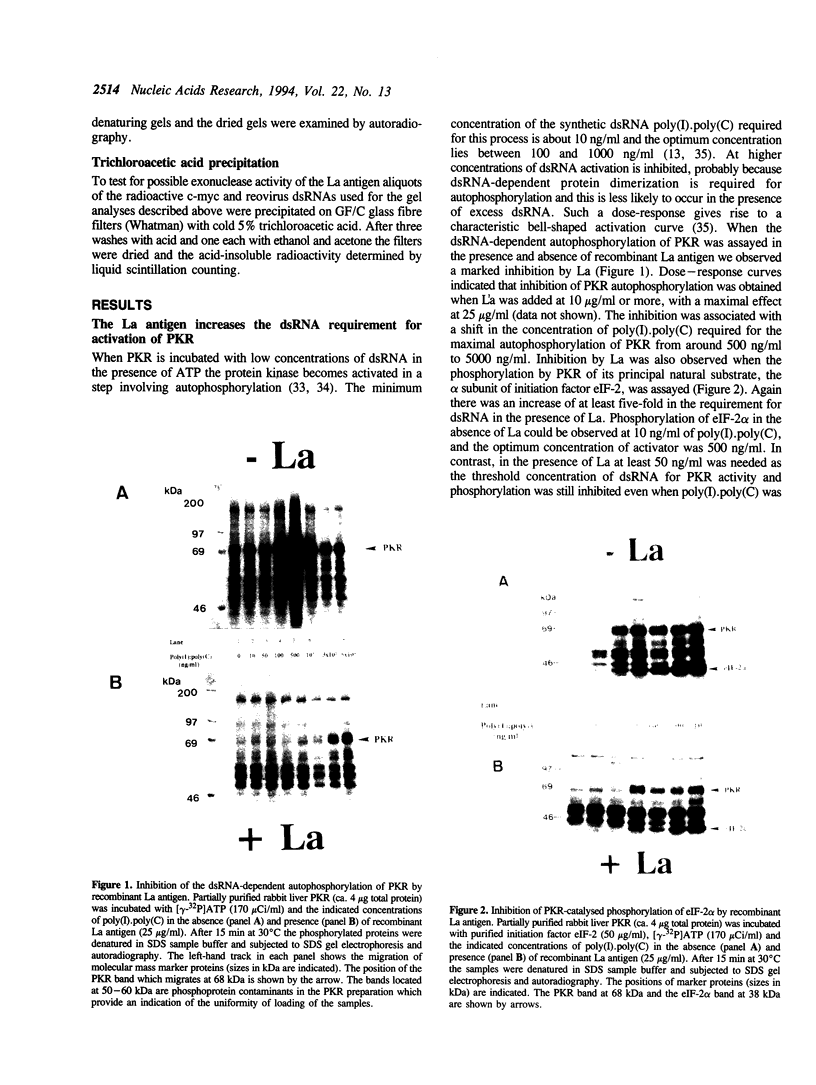
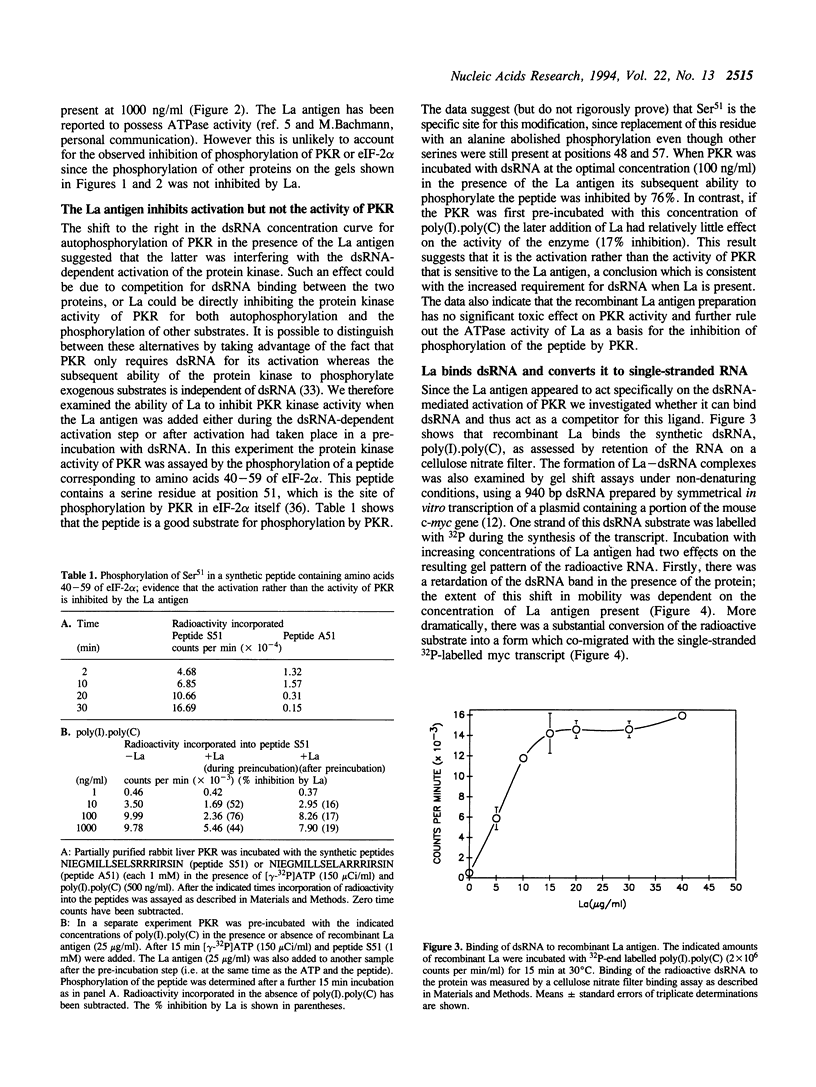
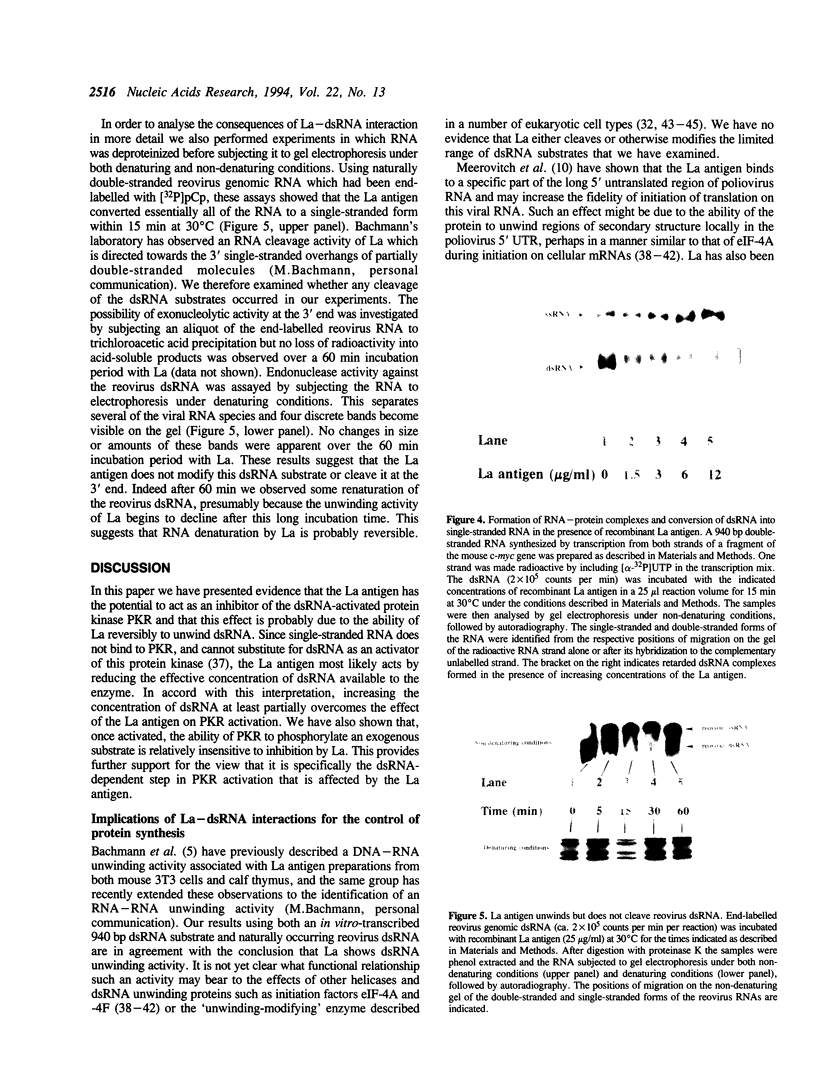
The La (SS-B) autoimmune antigen is an RNA-binding protein that is present in both nucleus and cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. The spectrum of RNAs that interact with the La antigen includes species which also bind to the interferon-inducible protein kinase PKR. We have investigated whether the La antigen can regulate the activity of PKR and have observed that both the autophosphorylation of the protein kinase that accompanies its activation by dsRNA and the dsRNA-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of polypeptide chain initiation factor eIF-2 by PKR are inhibited in the presence of recombinant La antigen. This inhibition is partially relieved at higher concentrations of dsRNA. Once activated by dsRNA the protein kinase activity of PKR is insensitive to the La antigen. We have demonstrated by a filter binding assay that La is a dsRNA binding protein. Furthermore, when recombinant La is incubated with a 900 bp synthetic dsRNA or with naturally occurring reovirus dsRNA it converts these substrates to single-stranded forms. We conclude that the La antigen inhibits the dsRNA-dependent activation of PKR by binding and unwinding dsRNA and that it may therefore play a role in the regulation of this protein kinase in interferon-treated or virus-infected cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baboonian C., Venables P. J., Booth J., Williams D. G., Roffe L. M., Maini R. N. Virus infection induces redistribution and membrane localization of the nuclear antigen La (SS-B): a possible mechanism for autoimmunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):454–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Falke D., Preuhs J., Schröder H. C., Pfeifer K., Müller W. E. Occurrence of novel small RNAs with concomitant inhibition of host cellular U small nuclear RNA synthesis in Vero cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2587–2594. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Falke D., Schröder H. C., Müller W. E. Intracellular distribution of the La antigen in CV-1 cells after herpes simplex virus type 1 infection compared with the localization of U small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Gen Virol. 1989 Apr;70(Pt 4):881–891. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-4-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Pfeifer K., Schröder H. C., Müller W. E. Characterization of the autoantigen La as a nucleic acid-dependent ATPase/dATPase with melting properties. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90718-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Pfeifer K., Schröder H. C., Müller W. E. The La antigen shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in CV-1 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb 21;85(2):103–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00577106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. An unwinding activity that covalently modifies its double-stranded RNA substrate. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1089–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum S., Schmid S. R., Pause A., Buser P., Linder P., Sonenberg N., Trachsel H. ATP hydrolysis by initiation factor 4A is required for translation initiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Fox R. I., Tan E. M. Sjögren's syndrome nuclear antigen B (La): cDNA cloning, structural domains, and autoepitopes. J Autoimmun. 1989 Aug;2(4):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. Ribonucleoprotein SS-B/La belongs to a protein family with consensus sequences for RNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2233–2244. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Watson J. C., Jacobs B. L. The E3L gene of vaccinia virus encodes an inhibitor of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4825–4829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. L., Feng L., Schappert K., Meurs E., Donahue T. F., Friesen J. D., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1553–1562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. A., Sharp N. A., Clemens M. J. Translational control by the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER-1. Reversal of the double-stranded RNA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Anderson W. F., London I. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates by double-stranded RNA and oxidized glutathione: indirect mode of action on polypeptide chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J. The small RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Feb;17(2):81–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00996215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colthurst D. R., Campbell D. G., Proud C. G. Structure and regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2. Sequence of the site in the alpha subunit phosphorylated by the haem-controlled repressor and by the double-stranded RNA-activated inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 15;166(2):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Hovanessian A. G. Modified subcellular localization of interferon-induced p68 kinase during encephalomyocarditis virus infection. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90126-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Mathews M. B. Interaction between VA RNA and the lupus antigen La: formation of a ribonucleoprotein particle in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Katze M. G., Robert N., Hovanessian A. G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman J. N., Howe J. G., Steitz J. A. Structural analyses of EBER1 and EBER2 ribonucleoprotein particles present in Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):902–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.902-911.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. Function of the mammalian La protein: evidence for its action in transcription termination by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):851–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The RNA binding protein La influences both the accuracy and the efficiency of RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Two RNA-binding motifs in the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, DAI. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2478–2490. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelin R., Chan E. K., Tan E. M., Arlinghaus R. B. Antibodies against small nuclear ribonucleoproteins immunoprecipitate complexes containing ts110 Moloney murine sarcoma virus genomic and messenger RNAs. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo M., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. RNA unwinding in translation: assembly of helicase complex intermediates comprising eukaryotic initiation factors eIF-4F and eIF-4B. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5992–5997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Green S. R., Mathews M. B., Spector D. L. Organization of the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase DAI and virus-associated VA RNAI in adenovirus-2-infected HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):11–22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judware R., Petryshyn R. Mechanism of action of a cellular inhibitor of the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase from 3T3-F442A cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21685–21690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G. The war against the interferon-induced dsRNA-activated protein kinase: can viruses win? J Interferon Res. 1992 Aug;12(4):241–248. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Purification and activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1576–1586. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Cabradilla C. D., Holloway B. P., Keene J. D. Nucleotide sequence and host La protein interactions of rabies virus leader RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):773–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.773-778.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Characterization and regulation of the 58,000-dalton cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14238–14243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. M., Shatkin A. J. Translational stimulation by reovirus polypeptide sigma 3: substitution for VAI RNA and inhibition of phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6878–6884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6878-6884.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Francoeur A. M. La antigen recognizes and binds to the 3'-oligouridylate tail of a small RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1134–1140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Svitkin Y. V., Lee H. S., Lejbkowicz F., Kenan D. J., Chan E. K., Agol V. I., Keene J. D., Sonenberg N. La autoantigen enhances and corrects aberrant translation of poliovirus RNA in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3798–3807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3798-3807.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Galabru J., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Hovanessian A. G. Tumor suppressor function of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Watanabe Y., Kadereit S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Constitutive expression of human double-stranded RNA-activated p68 kinase in murine cells mediates phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and partial resistance to encephalomyocarditis virus growth. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5805–5814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5805-5814.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundschau L. J., Faller D. V. Oncogenic ras induces an inhibitor of double-stranded RNA-dependent eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha-kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23092–23098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K. Modulation of double-stranded RNAs in vivo by RNA duplex unwindase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Oct 28;660:240–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb21076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Méthot N., Sonenberg N. The HRIGRXXR region of the DEAD box RNA helicase eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A is required for RNA binding and ATP hydrolysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6789–6798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of a DEAD box RNA helicase: the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2643–2654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peek R., Pruijn G. J., van der Kemp A. J., van Venrooij W. J. Subcellular distribution of Ro ribonucleoprotein complexes and their constituents. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):929–935. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Slobbe R. L., Van Venrooij W. J. Structure and function of La and Ro RNPs. Mol Biol Rep. 1990;14(2-3):43–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00360410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Slobbe R. L., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of protein--RNA interactions within Ro ribonucleoprotein complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5173–5180. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Melton D. A. Antisense RNA injections in fertilized frog eggs reveal an RNA duplex unwinding activity. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Tan E., Busch H. Identification of a La protein binding site in a RNA polymerase III transcript (4.5 I RNA). J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8352–8356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D., Gottlieb E., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus-encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus-associated ribonucleic acids VAI and VAII. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):785–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother R. P., Thomas P. S. La/SSB ribonucleoprotein levels increased in transformed cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):369–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito S., Kawakita M. Inhibitor of interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and its relevance to alteration of cellular protein kinase activity level in response to external stimuli. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(12):1105–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwemmle M., Clemens M. J., Hilse K., Pfeifer K., Tröster H., Müller W. E., Bachmann M. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 in interphase and mitotic Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10292–10296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T. V., Schwemmle M., Jeffrey I., Laing K., Mellor H., Proud C. G., Hilse K., Clemens M. J. Comparative analysis of the regulation of the interferon-inducible protein kinase PKR by Epstein-Barr virus RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 and adenovirus VAI RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4483–4490. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T. V., Xiao Q., Jeffrey I., Gewert D. R., Clemens M. J. Reversal of the double-stranded-RNA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis by a catalytically inactive mutant of the protein kinase PKR. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 15;214(3):945–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobbe R. L., Pluk W., van Venrooij W. J., Pruijn G. J. Ro ribonucleoprotein assembly in vitro. Identification of RNA-protein and protein-protein interactions. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90890-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Brown N. H., Gall J. G., Jantsch M. A conserved double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10979–10983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3' termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. W., Nishikura K. Cell cycle expression of RNA duplex unwindase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):770–777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. C., Chang H. W., Jacobs B. L. Characterization of a vaccinia virus-encoded double-stranded RNA-binding protein that may be involved in inhibition of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):206–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90768-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Keene J. D. Interactions of plus and minus strand leader RNAs of the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus with the cellular La protein. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. A host protein (La) binds to a unique species of minus-sense leader RNA during replication of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5827–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]