Abstract
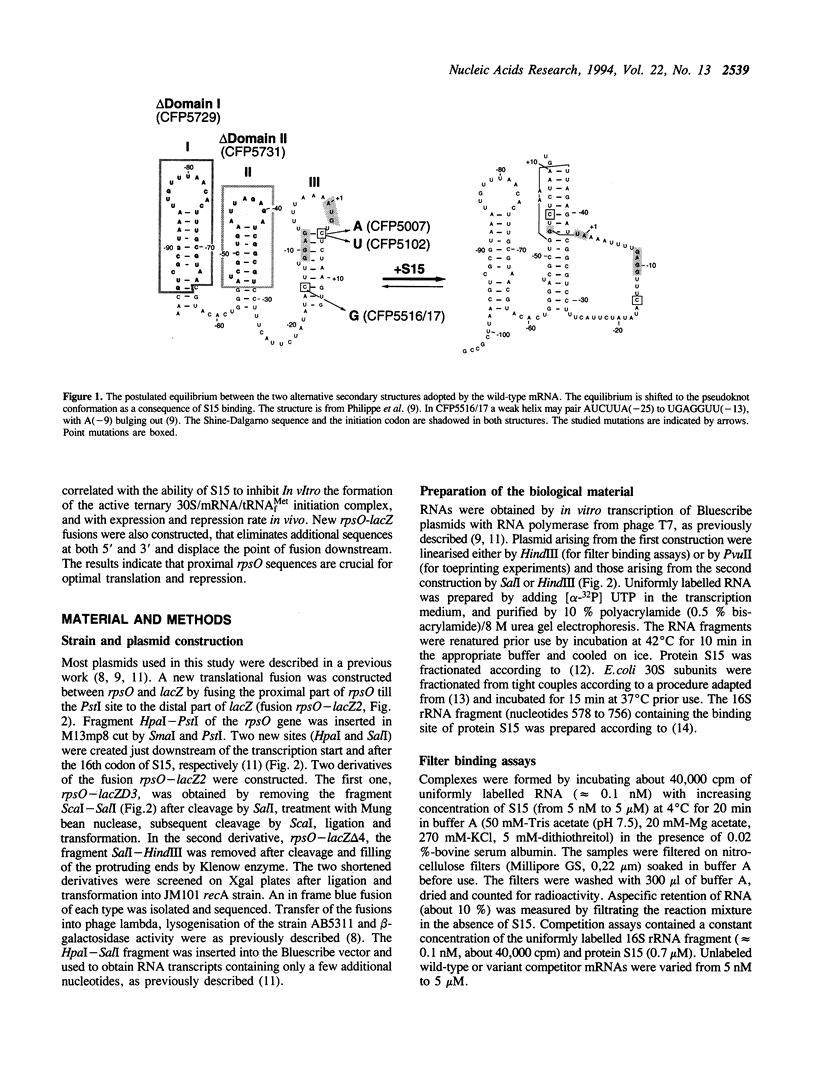
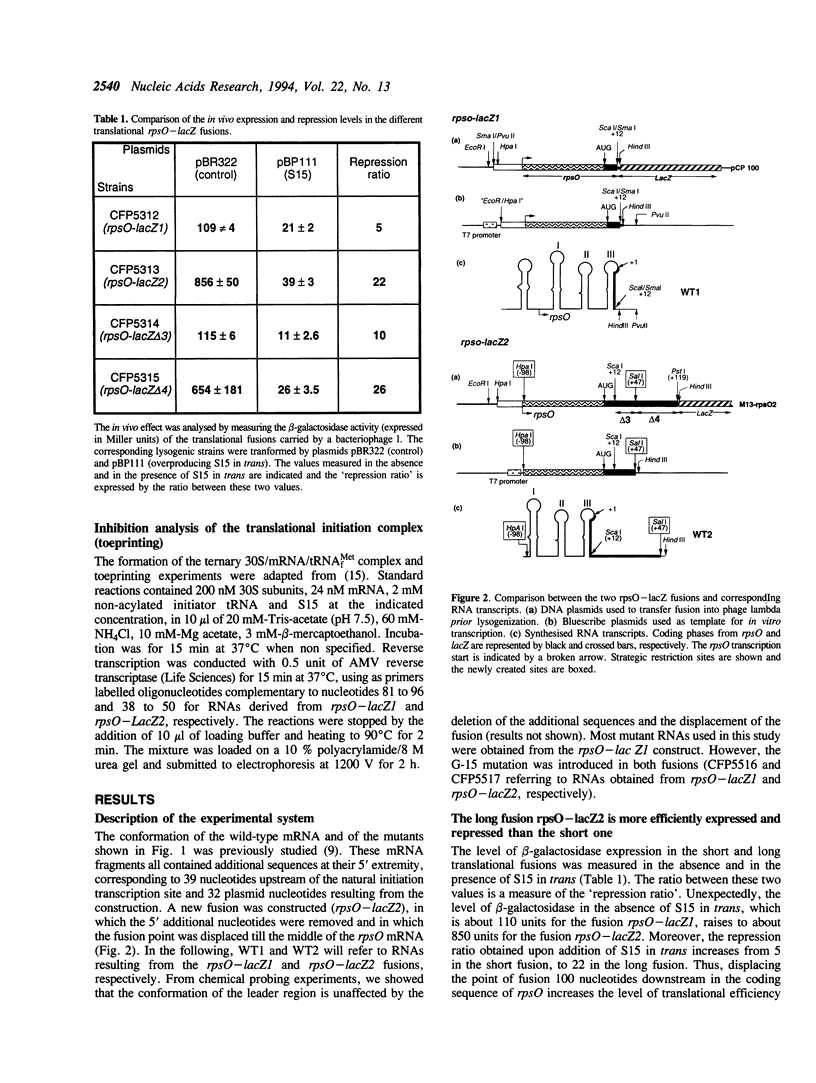
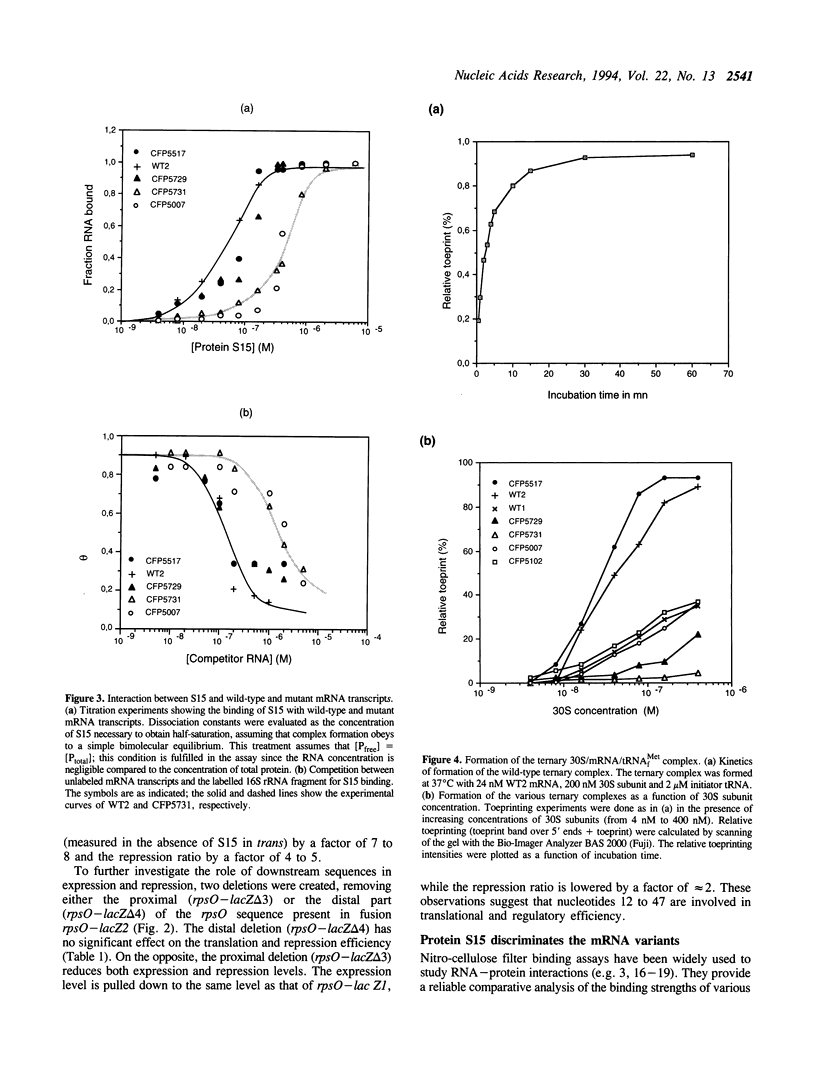
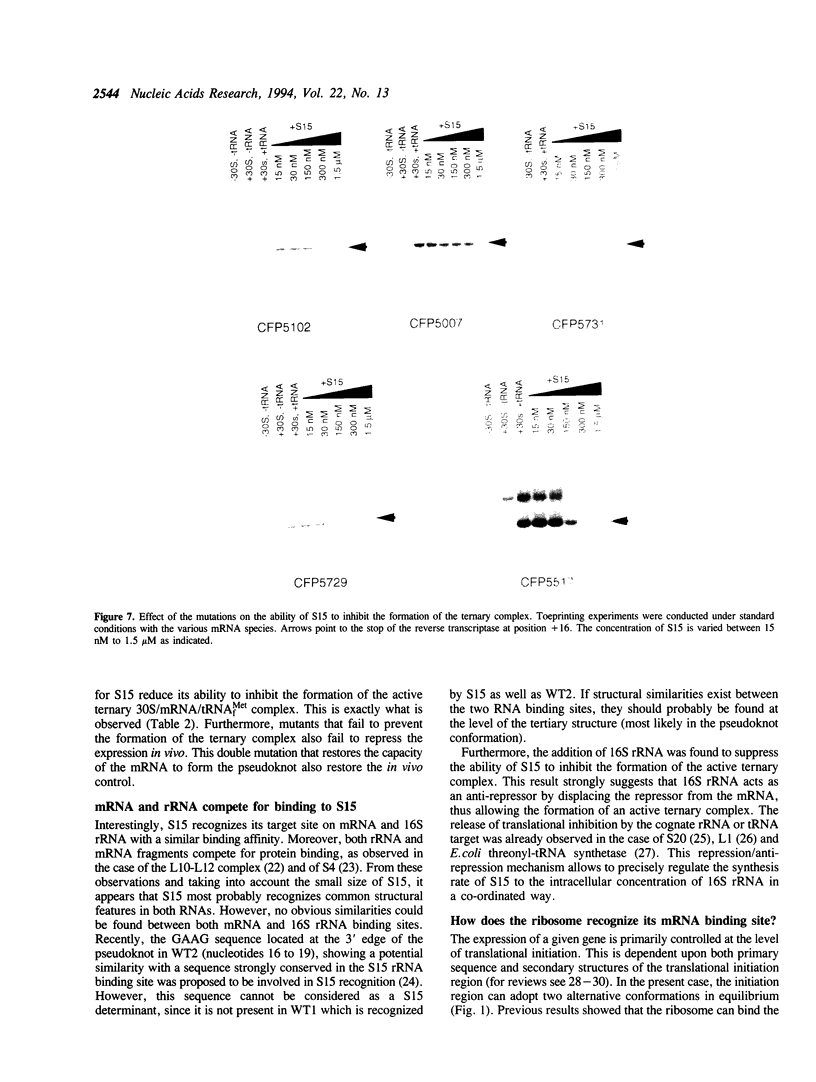
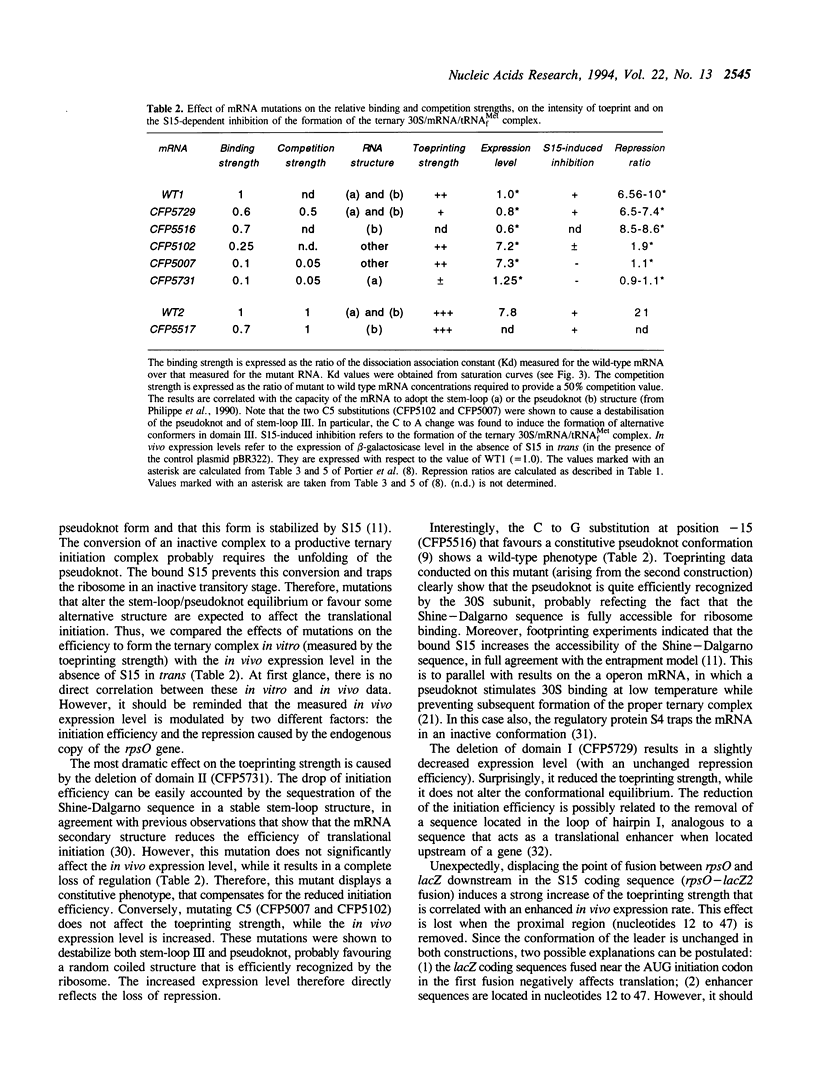
Previous experiments showed that S15 inhibits its own translation by binding to its mRNA in a region overlapping the ribosome loading site. This binding was postulated to stabilize a pseudoknot structure that exists in equilibrium with two stem-loops and to trap the ribosome on its mRNA loading site in a transitory state. In this study, we investigated the effect of mutations in the translational operator on: the binding of protein S15, the formation of the 30S/mRNA/tRNA(fMet) ternary initiation complex, the ability of S15 to inhibit the formation of this ternary complex. The results were compared to in vivo expression and repression rates. The results show that (1) the pseudoknot is required for S15 recognition and translational control; (2) mRNA and 16S rRNA efficiently compete for S15 binding and 16S rRNA suppresses the ability of S15 to inhibit the formation of the active ternary complex; (3) the ribosome binds more efficiently to the pseudoknot than to the stem-loop; (4) sequences located between nucleotides 12 to 47 of the S15 coding phase enhances the efficiency of ribosome binding in vitro; this is correlated with enhanced in vivo expression and regulation rates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudin F., Romaniuk P. J., Romby P., Brunel C., Westhof E., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Involvement of "hinge" nucleotides of Xenopus laevis 5 S rRNA in the RNA structural organization and in the binding of transcription factor TFIIIA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90874-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachia C., Flamion P. J., Schreiber J. P. Fast preparative separation of 'native' core E coli 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochimie. 1991 May;73(5):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90029-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerretti D. P., Mattheakis L. C., Kearney K. R., Vu L., Nomura M. Translational regulation of the spc operon in Escherichia coli. Identification and structural analysis of the target site for S8 repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):309–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90578-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen T., Johnsen M., Fiil N. P., Friesen J. D. RNA secondary structure and translation inhibition: analysis of mutants in the rplJ leader. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1609–1612. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckman I. C., Draper D. E. S4-alpha mRNA translation regulation complex. II. Secondary structures of the RNA regulatory site in the presence and absence of S4. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90693-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckman I. C., Draper D. E. Specific interaction between ribosomal protein S4 and the alpha operon messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):7860–7865. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E., Deckman I. C., Vartikar J. V. Physical studies of ribosomal protein-RNA interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:203–220. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. J., Cahill P. B., Thurlow D. L., Zimmermann R. A. Interaction of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S8 with its binding sites in ribosomal RNA and messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90577-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C., Risuleo G., Pon C. Mechanism of the spontaneous and initiation factor 3-induced dissociation of 30 S.aminoacyl-tRNA.polynucleotide ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):44–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Traut R., Gold L. Extension inhibition analysis of translation initiation complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Kawakami K., Nakamura Y. Multiple control of Escherichia coli lysyl-tRNA synthetase expression involves a transcriptional repressor and a translational enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen M., Christensen T., Dennis P. P., Fiil N. P. Autogenous control: ribosomal protein L10-L12 complex binds to the leader sequence of its mRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):999–1004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney K. R., Nomura M. Secondary structure of the autoregulatory mRNA binding site of ribosomal protein L1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):60–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00337759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhno V. I., Peshin N. N., Semenkov Iu P., Kirillov S. V. Modifitsirovannyi sposob polucheniia "tight" 70S ribosom iz Escherichia coli, vysokoaktivnykh v otdel'nykh stadiiakh tsikla élongatsii. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1988 May-Jun;22(3):670–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. E., Gualerzi C. Translational control of prokaryotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moine H., Romby P., Springer M., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNA(Thr) modulate the binding of the ribosome to the translational initiation site of the thrS mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougel M., Allmang C., Eyermann F., Cachia C., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Minimal 16S rRNA binding site and role of conserved nucleotides in Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S8 recognition. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):787–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougel M., Philippe C., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. The E. coli 16S rRNA binding site of ribosomal protein S15: higher-order structure in the absence and in the presence of the protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2825–2839. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Rangwala S. H. A novel sequence element derived from bacteriophage T7 mRNA acts as an enhancer of translation of the lacZ gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16973–16976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Eyermann F., Bénard L., Portier C., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Ribosomal protein S15 from Escherichia coli modulates its own translation by trapping the ribosome on the mRNA initiation loading site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Portier C., Mougel M., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Target site of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S15 on its messenger RNA. Conformation and interaction with the protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90362-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., Dondon L., Grunberg-Manago M. Translational autocontrol of the Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S15. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90361-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., Philippe C., Dondon L., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Translational control of ribosomal protein S15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90190-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shean C. S., Gottesman M. E. Translation of the prophage lambda cl transcript. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90175-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding G., Draper D. E. Allosteric mechanism for translational repression in the Escherichia coli alpha operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4399–4403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding G., Gluick T. C., Draper D. E. Ribosome initiation complex formation with the pseudoknotted alpha operon messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 5;229(3):609–622. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengart M. L., Fatscher H. P., Fuchs E. The initiation of translation in E. coli: apparent base pairing between the 16srRNA and downstream sequences of the mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1719–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth R., Kohles V., Böck A. Factors modulating transcription and translation in vitro of ribosomal protein S20 and isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):429–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in E. coli: localization of the mRNA target sites for repressor action of ribosomal protein L1. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90520-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C. Conformity of RNAs that interact with tetranucleotide loop binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4397–4400. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smit M. H., van Duin J. Control of prokaryotic translational initiation by mRNA secondary structure. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;38:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60707-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]