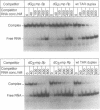
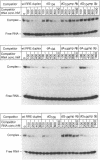
Abstract
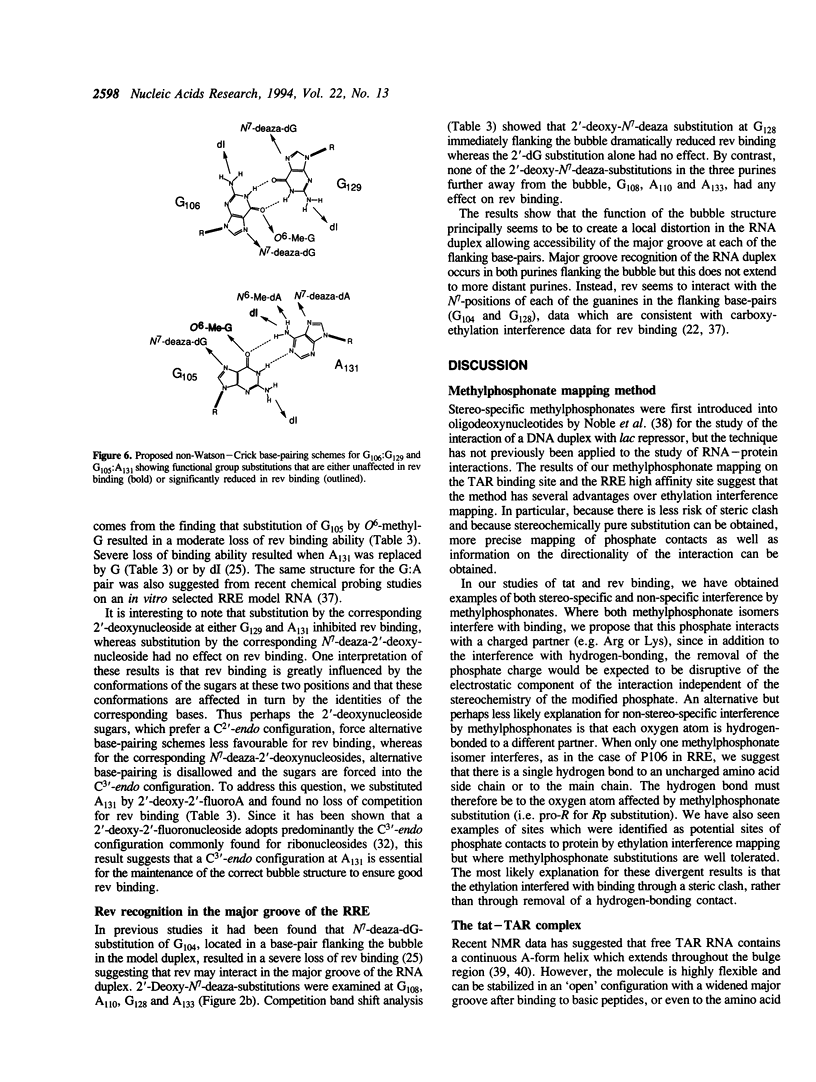
The HIV-1 regulatory proteins tat and rev are both RNA binding proteins which recognize sequences in duplex RNA which are close to structural distortions. Here we identify phosphate contacts which are critical for each binding reaction by use of a new method. Model RNA binding sites are constructed carrying substitutions of individual phosphodiesters by uncharged methylphosphonate derivatives isolated separately as Rp and Sp diastereoisomers and tested for protein binding by competition assays. In the binding of tat to the trans-activation response region (TAR), three phosphates, P21 and P22 which are adjacent to the U-rich bulge and P40 on the opposite strand, are essential and in each case both isomers inhibit binding. Similarly, in the interaction between the HIV-1 rev protein and the rev-responsive element (RRE) both methylphosphonate isomers at P103, P104, P124 and P125 interfere with rev binding. At P106, only the Rp methylphosphonate isomer is impaired in rev binding ability and it is proposed that the Rp oxygen is hydrogen-bonded to an uncharged amino acid or to a main chain hydrogen atom. Synthetic chemistry techniques also provide evidence for the conformations of non-Watson-Crick G106:G129 and G105:A131 base-pairs in the RRE 'bubble' structure upon rev binding. Almost all functional groups on the 5 bulged residues in the bubble have been ruled out as sites of contact with rev but, by contrast, the N7-positions of each G residue in the flanking base-pairs are identified as sites of likely hydrogen-bonding to rev. The results show that both tat and rev recognize the major groove of distorted RNA helixes and that both proteins make specific contacts with phosphates which are displaced from the sites of base-pair contact.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel D. P., Zapp M. L., Green M. R., Szostak J. W. HIV-1 Rev regulation involves recognition of non-Watson-Crick base pairs in viral RNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battiste J. L., Tan R., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Binding of an HIV Rev peptide to Rev responsive element RNA induces formation of purine-purine base pairs. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 15;33(10):2741–2747. doi: 10.1021/bi00176a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Tidor B., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Arginine-mediated RNA recognition: the arginine fork. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1167–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher M. J., Lamont C., Hamy F., Dingwall C., Green S. M., Lowe A. D., Butler J. G., Gait M. J., Karn J. High affinity binding of TAR RNA by the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat protein requires base-pairs in the RNA stem and amino acid residues flanking the basic region. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):90–110. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delling U., Reid L. S., Barnett R. W., Ma M. Y., Climie S., Sumner-Smith M., Sonenberg N. Conserved nucleotides in the TAR RNA stem of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are critical for Tat binding and trans activation: model for TAR RNA tertiary structure. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3018–3025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3018-3025.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 tat protein stimulates transcription by binding to a U-rich bulge in the stem of the TAR RNA structure. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4145–4153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J. A., Johnson R. C., Dickerson R. E. Hin recombinase bound to DNA: the origin of specificity in major and minor groove interactions. Science. 1994 Jan 21;263(5145):348–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8278807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gait M. J., Karn J. RNA recognition by the human immunodeficiency virus Tat and Rev proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jul;18(7):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90176-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giver L., Bartel D., Zapp M., Pawul A., Green M., Ellington A. D. Selective optimization of the Rev-binding element of HIV-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5509–5516. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasby J. A., Jonathan P., Butler G., Gait M. J. The synthesis of oligoribonucleotides containing O6-methylguanosine: the role of conserved guanosine residues in hammerhead ribozyme cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4444–4450. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamy F., Asseline U., Grasby J., Iwai S., Pritchard C., Slim G., Butler P. J., Karn J., Gait M. J. Hydrogen-bonding contacts in the major groove are required for human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat protein recognition of TAR RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):111–123. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Finch J. T., Gait M. J., Karn J., Singh M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 regulator of virion expression, rev, forms nucleoprotein filaments after binding to a purine-rich "bubble" located within the rev-responsive region of viral mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7366–7370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai S., Pritchard C., Mann D. A., Karn J., Gait M. J. Recognition of the high affinity binding site in rev-response element RNA by the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 rev protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6465–6472. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. B., Green L., MacDougal-Waugh S., Tuerk C. Characterization of an in vitro-selected RNA ligand to the HIV-1 Rev protein. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 7;235(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J. Control of human immunodeficiency virus replication by the tat, rev, nef and protease genes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(4):526–536. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90016-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Brown M., Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Structural analysis of the interaction between the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein and the Rev response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):683–687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Sharp P. A. Specific binding of a basic peptide from HIV-1 Rev. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1119–1129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc F., Cedergren R., Ellington A. D. A three-dimensional model of the Rev-binding element of HIV-1 derived from analyses of aptamers. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 May;1(5):293–300. doi: 10.1038/nsb0594-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires the binding of multiple Rev monomers to the viral RRE: implications for HIV-1 latency. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90158-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble S. A., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H. Methylphosphonates as probes of protein-nucleic acid interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3387–3404. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieken W. A., Olsen D. B., Benseler F., Aurup H., Eckstein F. Kinetic characterization of ribonuclease-resistant 2'-modified hammerhead ribozymes. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):314–317. doi: 10.1126/science.1857967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Chen L., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Role of RNA structure in arginine recognition of TAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tan R., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Conformation of the TAR RNA-arginine complex by NMR spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1621097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Roy S., Barnett R., Reid L. S., Kuperman R., Delling U., Sonenberg N. Critical chemical features in trans-acting-responsive RNA are required for interaction with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5196–5202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5196-5202.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan R., Chen L., Buettner J. A., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. RNA recognition by an isolated alpha helix. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao J., Frankel A. D. Electrostatic interactions modulate the RNA-binding and transactivation specificities of the human immunodeficiency virus and simian immunodeficiency virus Tat proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1571–1575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao J., Frankel A. D. Specific binding of arginine to TAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2723–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiley L. S., Malim M. H., Tewary H. K., Stockley P. G., Cullen B. R. Identification of a high-affinity RNA-binding site for the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):758–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Crothers D. M. RNA recognition by Tat-derived peptides: interaction in the major groove? Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):577–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]