In response to growth factor stimulation, integrins transit through recycling endosomes to reach newly forming focal adhesions at the cell’s leading edge.
Abstract
During cell migration, integrins are redistributed from focal adhesions undergoing disassembly at the cell’s trailing edges to new focal adhesions assembling at leading edges. The initial step of integrin redistribution is thought to require clathrin-mediated endocytosis. However, whether clathrin-mediated endocytosis functions in different contexts, such as basal versus stimulated migration, has not been determined. In this paper, we examine the spatial and temporal redistribution of integrins from focal adhesions upon stimulation by growth factors. Four-dimensional confocal live-cell imaging along with functional analysis reveals that surface integrins do not undergo significant endocytosis at ventral focal adhesions upon cell stimulation with the platelet-derived growth factor. Rather, they abruptly redistribute to dorsal circular ruffles, where they are internalized through macropinocytosis. The internalized integrins then transit through recycling endosomal compartments to repopulate newly formed focal adhesions on the ventral surface. These findings explain why integrins have long been observed to redistribute through both surface-based and internal routes and identify a new function for macropinocytosis during growth factor–induced cell migration.
Introduction
Cell migration is a dynamic process that involves the coordination of multiple cellular events, which include the disassembly of focal adhesions at the trailing edges and the assembly of new focal adhesions at the migrating fronts (Lauffenburger and Horwitz, 1996; Caswell et al., 2009). Constitutive integrin turnover, internalization, and recycling have been demonstrated under basal cell migration conditions (Pellinen and Ivaska, 2006; Mosesson et al., 2008). In recent years, clathrin-mediated endocytosis has been shown to play a pivotal role in the internalization of surface integrins at focal adhesions that are undergoing basal turnover (Chao and Kunz, 2009; Ezratty et al., 2009). However, few studies have examined dynamic integrin disassembly, redistribution, and reassembly in highly motile cells (Webb et al., 2002). In fact, in vivo cell migration is often significantly increased by growth factor up-regulation under physiological and pathological conditions, such as inflammation, wound healing (Ross et al., 1986), and cancer (Price et al., 1999). It is unknown whether the mechanisms of integrin redistribution from the trailing edge to the migrating front are the same as in basal cell migration.
Unexpectedly, we found that growth factor–stimulated cell migration is achieved by using a special circular dorsal ruffle (CDR) macropinocytosis mechanism that recruits, internalizes, and recycles integrins. CDRs are massive actin cytoskeletal remodeling structures that form within minutes at the dorsal cell surface after stimulation by growth factors, such as PDGF, EGF, and VEGF, in various cell types (Chinkers et al., 1979; Mellström et al., 1988; Wu et al., 2003; Orth and McNiven, 2006). Although the function of these structures is largely unknown, they have been suggested to be part of an initial step leading to massive macropinocytosis (Orth et al., 2006). Here, we delineate the pathway by which focal adhesions rapidly disassemble as integrins translocate to CDRs, are internalized by macropinocytosis, and then distribute to newly forming focal adhesions at the leading edge of cells during stimulated cell migration. This pathway was found to be entirely distinct from the clathrin-dependent or caveolin-dependent constitutive pathway of integrin turnover at focal adhesions in basal cell migration.
Results and discussion
Growth factor stimulation induces integrin focal adhesion disassembly at the ventral cell surface and massive CDR formation with the accumulation of integrins at the dorsal cell surface
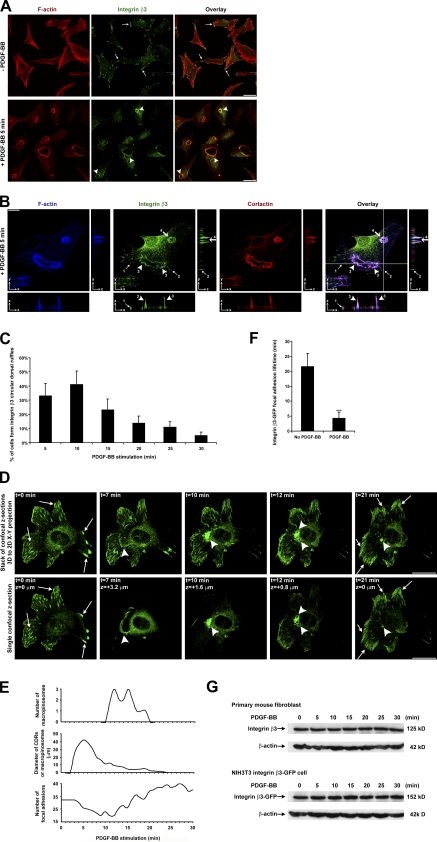
Stimulation of fibroblasts by PDGF is a model system to study stimulated cell migration (Ballestrem et al., 2001; Roberts et al., 2001). Examining integrin β3 in these cells, we detected that integrins concentrate at focal adhesions (Fig. 1 A). Remarkably, after the addition of PDGF for 5 min, the integrins accumulated at actin-rich circular structures (Fig. 1 A). According to our previous findings in PDGF-stimulated actin cytoskeleton remodeling (Gu et al., 2007), such actin-enriched circular structures are CDRs. Comparing the distribution of integrin β3 with two markers of CDRs, F-actin and cortactin (Buccione et al., 2004), we found that all three molecules showed colocalization. 3D analysis showed integrin β3, F-actin, and cortactin concentrating at cup-shaped structures that were raised upward from the dorsal cell surface (Fig. 1 B, Fig. S1 A, and Video 1). As a control, actin-independent membrane protein major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I did not translocate to CDRs under the same conditions (Fig. S1 B). Kinetic quantification showed that 33, 41, 25, 15, 11, and 5% of cells had integrin β3 at CDRs at 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min after PDGF stimulation, respectively (Fig. 1 C). This temporal profile was concordant with previous lifetime studies on CDRs (Buccione et al., 2004; Orth et al., 2006). Besides integrin β3, we also observed that integrin β1 redistributes to CDRs (Fig. S1 C). After surface integrin β1 antibody labeling in live cells, we confirmed surface integrin β1 translocation to CDRs within as short as 3 min after PDGF stimulation (Fig. S1 D). Such fast and massive surface integrin redistribution suggests that surface integrins follow a direct cell surface route rather than the slow surface–cytosol–surface endocytosis and recycling route.
Figure 1.
Integrin β3 localizes at CDRs after PDGF-BB stimulation and integrin β3–GFP translocation 4D tracing in a live cell. (A) Primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with or without PDGF-BB, fixed, and IF stained. Arrows denote integrin β3 at focal adhesions, and arrowheads denote integrin β3 at CDRs. (B) Primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with PDGF-BB, fixed, and IF stained. Confocal image stacks were scanned along the z axis. Arrows 1 and 2 denote remnant integrin β3 at focal adhesions. Arrowheads 3 and 4 denote integrin β3 at a large (early) CDR and a condensed (late) CDR, respectively. Crossed lines denote the orthogonal position. The z distance in the orthogonal views was exaggerated five times. (C) Primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with PDGF-BB for various times, fixed, and IF stained. The number of cells forming integrin β3 CDRs per 100 cells was counted (n = 5). (D) NIH3T3 cells stably expressing integrin β3–GFP were stimulated with PDGF-BB. The temporal and spatial translocation of integrin β3–GFP was traced by 4D time-lapse confocal live-cell imaging. Sections of confocal images were scanned along the cell z axis every 1 min. The ventral cell surface position was defined as z = 0 µm. A positive z distance defined the position distance above the ventral cell surface. t defined the time after PDGF-BB addition. Arrows denote integrin β3–GFP at focal adhesions. Large arrowheads denote integrin β3–GFP at early CDRs, late condensed CDRs, macropinosomes, and the perinuclear region. (E) The number of focal adhesions, diameter of CDRs or macropinosomes, and number of macropinosomes at various times after PDGF-BB stimulation were counted to determine the temporal and spatial translocation of integrin β3–GFP in D and Video 2. (F) The lifetimes of ventral surface integrin β3–GFP focal adhesions were quantified in PDGF-BB–stimulated cells and unstimulated control cells as in Video 2 and Video 3, respectively. A focal adhesion lifetime <30 min was recorded as actual time, and a lifetime >30 min was recorded as 30 min. The lifetimes of 30 focal adhesions per cell were recorded (n = 3). (G) Primary mouse fibroblasts or NIH3T3 cells stably expressing integrin β3–GFP were stimulated with PDGF-BB for various times. Integrin β3 protein levels from whole-cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Error bars represent means ± SD. ***, P < 0.05. Bars: (A) 50 µm; (B and D) 20 µm.
CDRs have also been observed in EGF-stimulated epithelial cells (Chinkers et al., 1979; Connolly et al., 1984) and VEGF-stimulated endothelial cells (Wu et al., 2003). Thus, we examined EGF-stimulated MDA-MB-231 cells and VEGF-stimulated HUV-EC-C cells. We found that integrin β1 also redistributed to CDRs in these cells (Fig. S1, E and F).
We used 4D analysis that involved time-lapse confocal live-cell imaging experiments on NIH3T3 cells stably expressing integrin β3–GFP. Before PDGF stimulation, this integrin was observed at ventral focal adhesions (Fig. 1 D, t = 0 min, z = 0 µm, arrows; and Video 2). Upon PDGF stimulation, integrin β3–GFP redistributed to CDRs on the dorsal surface (Fig. 1 D, t = 7 min, z = 3.2 µm, arrowhead; and Video 2). After CDR formation, the progenitor cup condensed and sank below the cell surface to become macropinosomes (Fig. 1 D, t = 10 min, z = 1.6 µm and t = 12 min, z = 0.8 µm; and Video 2). The strongest GFP fluorescence signals moved from z = 3.2 µm down to z = 1.6 µm and then down to z = 0.8 µm, where the cytoplasm mostly resided. We quantified the number of focal adhesions, the diameter of CDRs/macropinosomes, as well as the number of macropinosomes in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 1 E). As a control, in unstimulated cells, we detected neither such rapid integrin β3–GFP focal adhesion disassembly nor CDR formation (Video 3). Focal adhesion lifetime quantification showed that PDGF stimulation significantly accelerated focal adhesion disassembly (Fig. 1 F). We also observed no obvious protein degradation of integrin β3 upon PDGF stimulation (Fig. 1 G). These data suggest that stimulation by PDGF resulted in the redistribution of cell surface integrin β3 to CDRs followed by their internalization into macropinosomes.
Integrin macropinocytosis occurs at CDRs followed by integrin recycling back to the ventral cell surface to form new focal adhesions
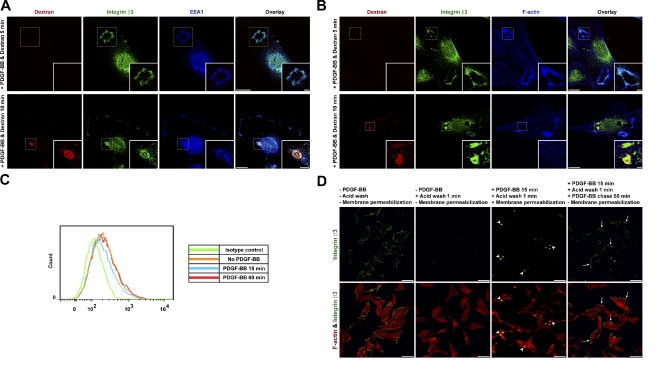
Macropinosomes form as internal spherical structures that can be characterized by their ingestion of extracellular fluid, recruitment of EEA1, and loss of F-actin during maturation (Swanson, 2008; Kerr and Teasdale, 2009). To confirm that surface integrin β3 was internalized through macropinosomes, we incubated cells in medium containing fluorescent dextran. After a 5-min PDGF stimulation, we observed integrin β3 in structures that appeared circular and contained EEA1 and F-actin but not dextran (Fig. 2, A and B, top). Such characteristics were consistent with CDRs, which are open cell surface structures that do not retain fluid. However, after 10 min, we detected integrin β3 in structures that contained both dextran and EEA1 (Fig. 2 A, bottom) but had lost F-actin (Fig. 2 B, bottom). Such characteristics were consistent with macropinosomes, which are closed internal structures that do retain fluid.
Figure 2.
PDGF-BB stimulates integrin β3 macropinocytosis at CDRs and recycling back to the ventral cell surface to form new focal adhesions. (A and B) Primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with PDGF-BB in TMR-dextran (red)–containing medium for 5 (top) or 10 min (bottom). Cells were then washed, fixed, and IF stained. Insets of structures in the dashed boxes are shown enlarged in the bottom right corners. (C) Primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with or without PDGF-BB. Cells were then detached and live stained by the anti–integrin β3 antibody (1–55-4) or isotype control antibody for 1 h at RT. Cells were fixed and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. A total cell surface integrin β3 fluorescence intensity histogram is plotted. (D) Primary mouse fibroblasts were live stained by a nonblocking anti–integrin β3 antibody and subjected to the endocytosis and recycling assay. Arrowheads denote internalized integrin β3 at macropinosomes. Arrows denote recycled integrin β3 at focal adhesions. Bars: (A and B) 20 µm; (A and B, insets) 5 µm; (D) 100 µm.
Live imaging further revealed that, after macropinocytosis, cells started to migrate, and focal adhesions that contained integrin β3–GFP reappeared at the migrating front (Fig. 1 D, t = 21 min, z = 0 µm; and Video 2). These observations suggested that integrin β3 internalized by macropinocytosis at the dorsal surface was recycled through endosomal compartments for reappearance in new focal adhesions on the ventral surface. To confirm this, we quantified the change in total cell surface integrin β3 protein amount by flow cytometry. 15-min PDGF stimulation shifted the fluorescence intensity curve of surface integrin β3 to the left (Fig. 2 C, blue curve, compared with the orange curve of no stimulation), whereas after 60-min PDGF stimulation, the curve shifted back almost to the same position as no stimulation (Fig. 2 C, red curve). Quantification showed that the total surface integrin β3 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in the whole cell population dropped 13% after PDGF stimulation. Considering that different cells start CDR formation and subsequent macropinocytosis internalization at various times after PDGF stimulation (Fig. 1 C), the flow cytometric detection of a 13% drop in total cell surface integrin β3 MFI at one time point for the whole cell population represents a large amount of cell surface integrin β3 internalization in those cells undergoing macropinocytosis.
Next, we tracked surface integrin by an antibody-binding, acid-stripping endocytosis and recycling assay. Live cells were incubated with a nonblocking anti–integrin β3 antibody to label surface integrin β3. After washing to remove unbound antibodies, we stimulated cells with PDGF for 15 min to allow the antibody-bound integrins to undergo macropinocytosis. The pool that remained at the cell surface after this time period was removed by acid washing. Cells were chased for another 60 min in the presence of PDGF to allow the recycling of the antibody-bound integrin. This protocol revealed that internalized integrin β3 reappeared in focal adhesions on the ventral surface and, thus, confirmed that endocytic recycling was involved in its redistribution (Fig. 2 D).
Growth factor–induced integrin recycling follows a route of macropinosomes→early endosomes→recycling endosomes→cell surface
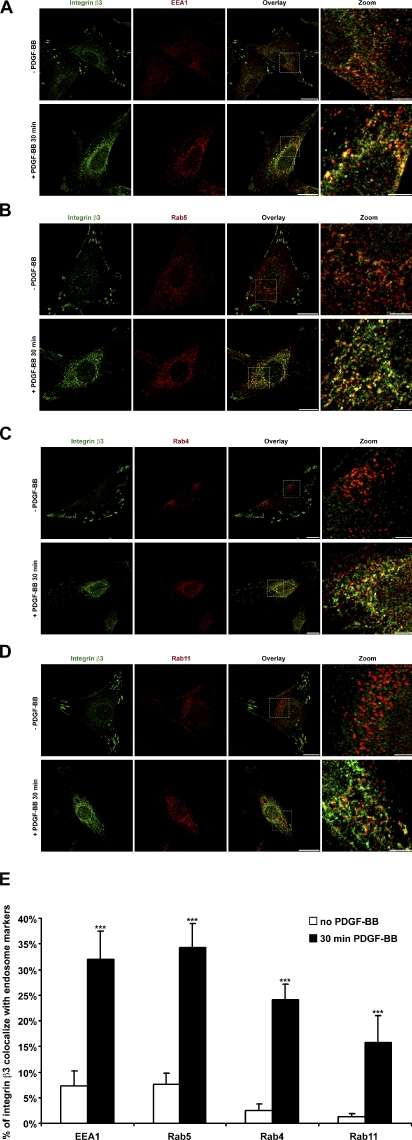
Next, we found that, after PDGF-stimulated macropinocytosis, integrin β3 accumulated at perinuclear regions, where it exhibited increased colocalization with early endosome markers EEA1 (Fig. 3 A), Rab5 (Fig. 3 B), and Rab4 (Fig. 3 C) and the recycling endosome marker Rab11 (Fig. 3 D). Image quantification revealed that the extent of such colocalization induced by PDGF was more than fivefold compared with no stimulation (Fig. 3 E). Thus, the data suggests that internalized integrin β3 after stimulation by growth factors resulted in its recycling through early and recycling endosomes.
Figure 3.
After macropinosome disassembly, internalized integrin β3 colocalizes with early endosomes (EEA1, Rab5, and Rab4) and recycling endosomes (Rab11). (A−D) Primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with or without PDGF-BB, fixed, and IF stained. (E) Series of overlay images in A−D were analyzed by a colocalization assay module in MetaMorph software. Percentages of integrin β3 that colocalized with EEA1, Rab5, Rab4, and Rab11 are plotted (n = 10). Error bars represent means ± SD. ***, P < 0.05. Bars: (overlay) 20 µm; (zoom) 5 µm.
Growth factor–induced integrin macropinocytosis is brefeldin A–ADP-ribosylated substrate (BARS) dependent but clathrin and caveolin-1 (CAV1) independent
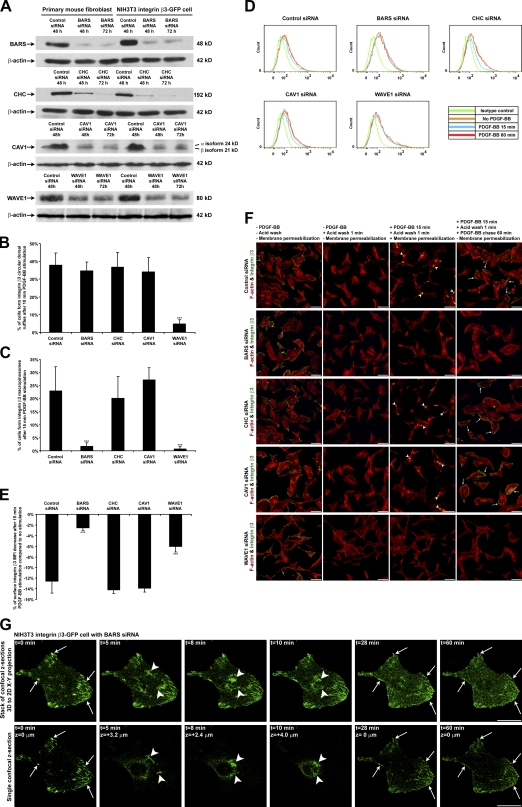
Next, we sought to compare the relative importance of clathrin- and CAV1-mediated endocytosis versus macropinocytosis in the PDGF-stimulated integrin internalization. Because BARS is critical for the fission stage of macropinocytosis (Liberali et al., 2008; Haga et al., 2009), but not for clathrin-mediated endocytosis (Bonazzi et al., 2005; Kaksonen et al., 2006), we examined the effect of targeting BARS.
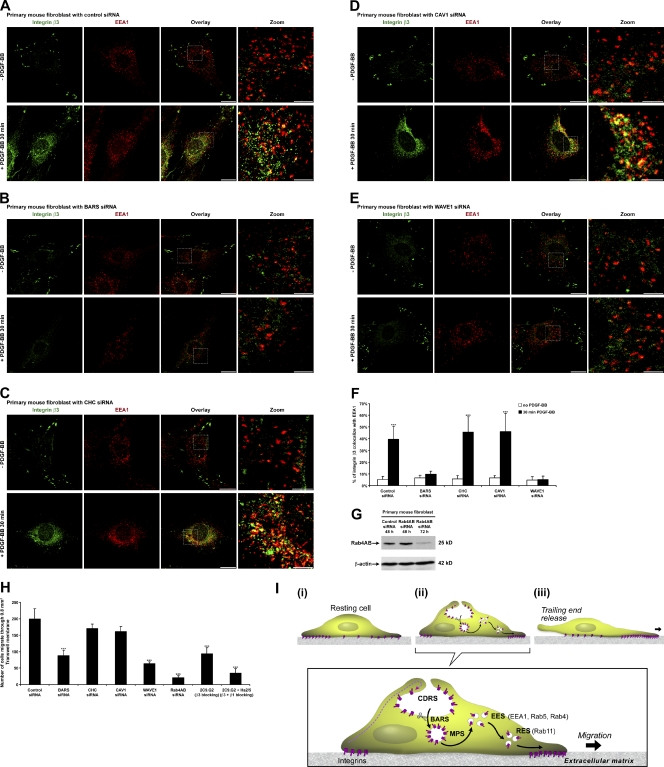
We confirmed that after targeting BARS with siRNA, BARS protein levels dropped to <5% of control (Fig. 4 A). BARS down-regulation did not block CDR formation (Fig. 4 B). However, BARS down-regulation significantly reduced the number of cells forming integrin β3 macropinosomes (Fig. 4 C). Consistent with this, flow cytometry analysis showed that BARS down-regulation failed to reduce the amount of integrin β3 on the cell surface after PDGF stimulation (Fig. 4, D and E). BARS down-regulation also blocked integrin β3 macropinosome formation and subsequent integrin recycling in the endocytosis and recycling assay (Fig. 4 F and Fig. S2 F). Next, we cotransfected BARS siRNA and fluorescence-tagged control siRNA as a way to select cells that had down-regulated BARS in live-cell imaging experiments (Fig. S2 A). 4D live imaging showed that these cells were still able to form CDRs after PDGF stimulation (Fig. 4 G, t = 5 min, z = 3.2 µm, arrowheads; and Video 4). However, these CDRs did not fully condense and failed to form macropinosomes (Fig. 4 G, t = 8 min, z = 2.4 µm and t = 10 min, z = 4.0 µm, arrowheads; and Video 4). Note that the strongest GFP fluorescence signal moved from z = 3.2 µm down to z = 2.4 µm and then back up to z = 4.0 µm without macropinosome formation, suggesting that the CDR cup was still able to invaginate but could not close to form macropinosomes when BARS was silenced. Previously, we had observed the reappearance of integrin β3 in focal adhesions on the ventral surface after PDGF stimulation (Fig. 1 D, t = 21 min; and Video 2). However, such targeted redistribution was inhibited in cells with BARS siRNA, as these cells exhibited integrin β3 to be more diffusely distributed over the cell surface (Fig. 4 G, t = 28 min and t = 60 min; and Video 4). Further, we found that PDGF stimulation could no longer induce enhanced colocalization of integrin β3 with EEA1 at perinuclear regions after macropinocytosis (Fig. 5, B and F). Consistent with these findings, live-imaging videos revealed that cells treated with siRNA against BARS showed a reduced ability to migrate upon PDGF stimulation (Video 4). Quantifying the number of integrin β3 focal adhesions per cell showed BARS down-regulation did not block the rapid focal adhesion disassembly upon PDGF stimulation. However, it did block subsequent integrin β3 recycling to form new focal adhesions (Fig. S2 C). Thus, we conclude that the inhibition of macropinocytosis by BARS down-regulation blocked the internalization of integrin β3 and its subsequent recycling as well as cell migration.
Figure 4.
PDGF-BB–stimulated integrin β3 macropinocytosis is BARS dependent but clathrin and CAV1 independent. (A) BARS, CHC, CAV1, and WAVE1 protein expression levels from whole-cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. (B and C) siRNA-transfected primary mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with PDGF-BB for 10 or 15 min, fixed, and IF stained. The number of cells forming integrin β3 CDRs or macropinosomes per 100 cells was counted (n = 5). (D) siRNA-transfected primary mouse fibroblasts were prepared as in Fig. 2 C. (E) Quantified from the flow cytometry data in D, the percentages of cell surface integrin β3 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) decrease after 15-min PDGF-BB stimulation compared with no stimulation are plotted (n = 3). (F) siRNA-transfected primary mouse fibroblasts were prepared as in Fig. 2 D. Arrowheads denote internalized integrin β3 at macropinosomes. Arrows denote recycled integrin β3 at focal adhesions. (G) The BARS siRNA-transfected cell in Fig. S2 A was stimulated with PDGF-BB. The temporal and spatial translocation of integrin β3–GFP was traced by 4D time-lapse confocal live-cell imaging as in Fig. 1 D. Arrows in the t = 0 min image denote the integrin β3–GFP at original focal adhesions; arrows in t = 28 min and 60 min images point at the same positions to denote the disappearance of integrin β3–GFP at focal adhesions without integrin β3–GFP recycling to form new focal adhesions. Arrowheads in t = 5 min, 8 min, and 10 min images denote the integrin β3–GFP at a CDR that did not fully close up or sink into the cytosol to form macropinosomes because of the lack of the BARS protein. Error bars represent means ± SD. ***, P < 0.05. Bars: (F) 100 µm; (G) 20 µm.
Figure 5.
PDGF-BB–stimulated fast cell migration is BARS dependent. (A−E) siRNA-transfected primary mouse fibroblasts were prepared as in Fig. 3 A. (F) Overlay images in A−E were analyzed by a colocalization assay module in MetaMorph software. The percentages of integrin β3 that colocalized with EEA1 are plotted (n = 10). (G) Rab4A and Rab4B protein expression levels from whole-cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. (H) siRNA-transfected cells were seeded with or without antiintegrin-blocking antibodies into Transwell inserts and subjected to the PDGF-BB cell migration assay. The number of cells that had migrated through a 0.8-mm2 Transwell membrane was counted (n = 3). (I) Schematics of growth factor–stimulated fast cell migration. CDRS, circular dorsal ruffles; MPS, macropinosomes; EES, early endosomes; RES, recycling endosomes. Error bars represent means ± SD. ***, P < 0.05. Bars: (overlay) 20 µm; (zoom) 5 µm.
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis has been reported to regulate basal integrin turnover at focal adhesions (Nishimura and Kaibuchi, 2007; Teckchandani et al., 2009), and CAV1 has been reported to associate with integrins at focal adhesions (Wary et al., 1998; Wei et al., 1999). In addition, the actin remodeling–regulating protein WAVE1 blocks PDGF-stimulated CDR formation (Suetsugu et al., 2003). Thus, we examined the effects of perturbing clathrin and CAV1 as well as WAVE1 after PDGF stimulation.
First, we confirmed that siRNA against clathrin heavy chain (CHC), CAV1, and WAVE1 resulted in significant protein down-regulation (Fig. 4 A). A transferrin endocytosis assay showed that CHC down-regulation functionally blocked clathrin-mediated endocytosis (Fig. S2 B). Neither CHC nor CAV1 down-regulation blocked integrin β3 CDR formation and subsequent macropinosome formation. In contrast, WAVE1 down-regulation blocked this process, suggesting that actin remodeling is required for integrin translocation to CDRs (Fig. 4, B and C). Consistent with this, flow cytometry indicated that, after CHC or CAV1 down-regulation, the MFI of surface integrin β3 in the whole cell population still dropped by >13% after PDGF stimulation. In contrast, WAVE1 down-regulation blocked this process (Fig. 4, D and E). Furthermore, CHC or CAV1 down-regulation did not block integrin β3 macropinosome formation or its subsequent recycling in the endocytosis and recycling assay, whereas WAVE1 down-regulation did (Fig. 4 F and Fig. S2, G−I). Finally, we found that PDGF stimulation still enhanced colocalization of integrin β3 with EEA1 at perinuclear regions after macropinocytosis in CHC and CAV1 down-regulated cells but not in WAVE1 down-regulated cells (Fig. 5, C–F). Quantification of the number of integrin β3 focal adhesions per cell showed CHC or CAV1 down-regulation did not block focal adhesion disassembly or subsequent integrin β3 recycling to form new focal adhesions, whereas WAVE1 down-regulation did block focal adhesion disassembly, and thus, the number of integrin β3 focal adhesions per cell remained almost unchanged over time (Fig. S2 C).
Next, we examined fast cell migration using cells seeded in the upper chamber of Transwells with vitronectin-coated membranes. After 2 h of cell adhesion to the membrane, PDGF was added to the lower chamber, and cell migration across the membrane for 2 h was assessed to quantitate stimulated fast cell migration. As a control, we targeted integrin β3 or both integrin β3 and integrin β1 with blocking antibodies. These results confirmed that stimulated cell migration on vitronectin is integrin dependent. As previous experiments showed that PDGF-stimulated recycling of integrin β3 required Rab4 (Roberts et al., 2001), we also found that siRNA against Rab4 decreased this cell migration. We found that PDGF-stimulated fast cell migration was significantly delayed by siRNA against BARS or WAVE1, whereas such a fast cell migration was only slightly delayed by siRNA against CHC or CAV1 (Fig. 5, G and H; and Fig. S2 D). These results suggest that clathrin- or CAV1-dependent constitutive integrin turnover plays only a minor role in growth factor–stimulated fast cell migration. In contrast, WAVE1-dependent CDR formation, BARS-dependent integrin macropinocytosis, and subsequent Rab4-dependent integrin recycling contributed significantly to growth factor–stimulated fast cell migration.
In conclusion, we found that cell surface integrins in focal adhesions undergo internalization by macropinocytosis after stimulation by growth factors (summarized in Fig. 5 I). This result is in contrast to those previously observed for surface integrins at disassembling focal adhesions, which have been observed to undergo clathrin- or CAV1-mediated endocytosis. As the previous observations were made under conditions that did not involve the addition of growth factors, a likely explanation is that integrins use clathrin- or CAV1-mediated endocytosis under basal conditions and BARS-dependent macropinocytosis under the growth factor–stimulated conditions studied here. Subsequently, the internalized integrins undergo a recycling itinerary similar to that previously documented for how integrins recycle in stimulated cells (Powelka et al., 2004). Notably, this itinerary also explains why integrins were observed to move both along the cell surface and also through internal vesicular routes during cell migration (Regen and Horwitz, 1992). Integrins were previously noted at cell edge membrane ruffles (Bretscher, 2008; Sung et al., 2008). CDRs are distinct from cell edge membrane ruffles in terms of their location, formation, signaling, and especially their link to macropinocytosis. Here, we report that CDRs also rapidly recruit a majority of the cell surface integrins and internalize them through macropinocytosis for subsequent fast recycling. These results provide direct evidence to support the hypothesis that CDRs function as indicators of cellular transition from static to motile states (Buccione et al., 2004). Macropinocytosis is known to mediate the bulk uptake of membranes, fluid, and signaling receptors. Our findings suggest that macropinocytosis also can participate in the very rapid turnover of cell surface integrins, a pathway that is critical for stimulated cell migration.
Materials and methods
Mice and cell culture
Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were maintained as homozygous inbred lines in the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute animal facility. All mice were male and 8–12 wk old at the time of the study. Mouse experiments followed Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines. Primary wild-type mouse synovial fibroblasts were recovered from normal mouse joints and were cultured in DME supplemented with 10% FBS (Hyclone), l-glutamine, penicillin/streptomycin, 2-mercaptoethanol, and essential and nonessential amino acids at 37°C under 10% CO2. Cells had fibroblast-like morphology and were VCAM-1 positive but lacked F4/80 and were CD45 negative by flow cytometry (Lee et al., 2007; Agarwal et al., 2008). Cell culture reagents were purchased from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Retrieved mouse synovial fibroblasts were used between passages 5 and 10. NIH3T3 cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection and cultured in DME supplemented with 10% bovine calf serum (Hyclone), l-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C under 10% CO2. MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection and cultured in American Type Culture Collection–formulated Leibovitz’s L-15 medium supplemented with 10% FBS, l-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C without CO2. HUV-EC-C human umbilical vein endothelial cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection and cultured in American Type Culture Collection–formulated F-12K medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Hyclone), 0.1 mg/ml heparin (Sigma-Aldrich), 0.03–0.05 mg/ml endothelial cell growth supplement (Sigma-Aldrich), l-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C under 5% CO2.
Plasmids, siRNA, and transfection
cDNA encoding the full-length mouse integrin β3–EGFP fusion protein in a pcDNA3 expression vector was a gift from B. Wehrle-Haller (University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland; Ballestrem et al., 2001). siRNA against BARS (Yang et al., 2005), CHC (Li et al., 2007), and WAVE1 (Suetsugu et al., 2003) were previously described. siRNAs against CAV1, Rab4A, and Rab4B were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. Nonsilencing negative control siRNA was purchased from QIAGEN. Plasmids were transfected with Lipofectamine LTX reagent (Invitrogen), and siRNAs were transfected with Lipofectamine RNAiMAX reagent (Invitrogen).
Antibodies
Armenian hamster anti–integrin β3 (clone 2C9.G2), mouse anti-EEA1, mouse anti-Rab5, mouse anti-Rab4, mouse anti-Rab11, mouse anti-WAVE1, mouse anti-CAV1, and rat anti–integrin β1 (clone Ha2/5) antibodies were purchased from BD. Nonblocking rat anti–integrin β3 antibody (clone 1–55-4) was obtained from MBL International. The rat anti–integrin β1 antibody (clone MB1.2) was obtained from Millipore. The mouse anti–integrin β1 antibody (clone 12G10) was obtained from Abcam. The rabbit anticortactin antibody was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The rabbit anti-BARS antibody (clone p50-2) was raised against GST-BARS and purified as described previously (Spanò et al., 1999). The mouse anti-CHC antibody was obtained from American Type Culture Collection. The mouse anti–β-actin antibody was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. The mouse anti-MHC class I antibody was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. Alexa Fluor–conjugated anti–mouse, anti–rat, and anti–rabbit secondary antibodies and Alexa Fluor–conjugated phalloidin were purchased from Invitrogen. FITC-conjugated anti–Armenian hamster IgG secondary antibody and peroxidase-conjugated anti–mouse, anti–rat, and anti–rabbit secondary antibodies were obtained from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc.
Immunofluorescence (IF), dextran endocytosis assay, cell surface antibody-binding, acid-stripping endocytosis and recycling assay, and transferrin endocytosis assay
For IF microscopy experiments, cells were cultured on 10-mm glass coverslips coated with 0.1 µg/cm2 vitronectin (Sigma-Aldrich) for integrin β3 experiments or 1 µg/cm2 fibronectin (Sigma-Aldrich) for integrin β1 experiments. PDGF-BB and VEGF were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. EGF was obtained from Invitrogen. For IF staining, cells were serum starved for 16 h and stimulated with 20 ng/ml PDGF-BB, 30 ng/ml EGF, or 30 ng/ml VEGF in serum-free medium for various times as indicated in the following paragraphs. Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (Electron Microscopy Sciences) for 15 min. For intracellular protein staining, cells were permeabilized with 0.3% Triton X-100 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 10 min. Permeabilized cells were labeled with primary antibodies for 1 h at RT or 16 h at 4°C followed by secondary antibody labeling for 1 h and mounted on slides with FluorSave reagent (EMD). Tetramethylrhodamine (TMR)-conjugated, 10,000-MW fixable dextran was obtained from Invitrogen.
For the PDGF-BB– and TMR-dextran–chasing endocytosis assay, cells were serum starved for 16 h and then stimulated with 20 ng/ml PDGF-BB together with 200 µg/ml TMR-dextran in serum-free medium for various times. The cells were then washed three times to remove all cell surface–remaining TMR-dextran and fixed, and IF staining was performed.
For the cell surface antibody-binding, acid-stripping endocytosis and recycling assay, surface integrin β3 on live cells was stained by a nonblocking rat anti–integrin β3 monoclonal antibody (clone 1–55-4) in serum-free medium containing 1% BSA as blocking reagent for 1 h at RT. Cells were washed in antibody-free medium three times. Then, cells were treated with 20 ng/ml PDGF-BB for 15 min to allow cells time to internalize the antibody-bound integrin β3 by CDR macropinocytosis. Then, cells were equilibrated to 4°C followed by a 1-min ice-cold acid (0.5% acetic acid and 0.5 M NaCl, pH 3.0)-washing step to remove leftover cell surface integrin β3–bound antibodies. After acid washing, cells were washed in ice-cold medium to bring the pH back to 7.4 as indicated by phenol red. Cells were then incubated at 37°C in 20 ng/ml PDGF-BB–containing medium for another 60 min to allow cells time to recycle the antibody-bound integrin β3 back to the cell surface. Cells were then fixed, and without cell membrane permeabilization, the recycled cell surface antibody-bound integrin β3 was detected by IF staining with an Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti–rat secondary antibody. After PBS wash, cell membranes were permeabilized with 0.3% Triton X-100 for 5 min. F-actin was stained by Alexa Fluor 568 phalloidin and visualized by confocal microscopy.
For transferrin endocytosis assays, nonsilencing negative control siRNA or CHC siRNA-transfected primary mouse fibroblasts were incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 transferrin (Invitrogen) for 1 h at 4°C. Unbound transferrin was washed, and cells were then incubated at 37°C for various times. After incubation, cells were equilibrated to 4°C followed by a 1-min ice-cold acid (0.5% acetic acid and 0.5 M NaCl, pH 3.0)-washing step to remove leftover cell surface transferrin. After acid washing, cells were washed in ice-cold medium to bring the pH back to 7.4 as indicated by phenol red. Cells were then fixed and subjected to confocal microscopy to detect internalized Alexa Fluor 488 transferrin.
3D confocal microscopy and 4D time-lapse confocal live-cell imaging
IF images were captured on an inverted microscope (TE2000-U; Nikon) equipped with a confocal system (C1; Nikon) controlled by EZ-C1 software (Nikon) using a Plan Apochromat 60×/1.40 NA oil objective or a Plan Apochromat 20×/0.75 NA objective (Nikon). 3D confocal microscopy was performed by scanning multiple confocal layers along the z axis. For 4D time-lapse confocal live-cell imaging experiments, cells were grown in 35-mm glass-bottomed Petri dishes (World Precision Instruments). These dishes were mounted onto the confocal microscope with a heating chamber at 37°C and were superfused with 10% CO2. 4D confocal microscopy was performed by 3D confocal microscopy scanning over time. Fluorescent 3D or 4D image reconstructions and protein colocalization analysis were performed in MetaMorph Imaging software (version 7.6.1.0; Universal Imaging).
Flow cytometry
Cells were detached by a brief incubation with 0.05% trypsin-EDTA (Invitrogen) at RT to minimize endocytosis. Trypsin was quenched by a trypsin inhibitor from Glycine max (soybean; Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were then washed by 2% FBS in PBS and stained with anti–integrin β3 monoclonal antibody (1–55-4) or isotype control antibody for 1 h at RT followed by Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody staining. After staining, cells were fixed in 1% paraformaldehyde in PBS and subjected to flow cytometry analysis by a flow cytometer (FACS Canto; BD). FlowJo software (Tree Star) was used to analyze the flow cytometry data.
Cell migration assay
56 h after siRNA transfection, cells were serum starved for another 16 h and detached by a brief incubation with 0.05% trypsin-EDTA at RT. Trypsin was quenched by a trypsin inhibitor from Glycine max (soybean). Cells were washed and seeded with or without antiintegrin-blocking antibodies into the upper wells of vitronectin-coated Transwell inserts (8.0-µm pore size; Corning) in serum-free media. After a 2-h incubation at 37°C, 50 ng/ml PDGF-BB–containing serum-free media were then added into the lower well to drive cell migration. After a 2-h migration, the upper filter membrane surface was wiped to remove cells that had not migrated through the filter, and then the filter was fixed and stained to detect cells on the lower filter membrane surface using a stain set (Diff-Quik; Dade Behring). The number of cells that had migrated through a 0.8-mm2 Transwell membrane was counted.
SDS-PAGE and Western blotting
For SDS-PAGE experiments, cells were lysed and scraped at 4°C in a cell lysis buffer of the following composition: 1% Triton X-100, 50 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 5 mM EGTA, 20 mM NaF, 20 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM PMSF, and 1 mM Na3VO4, pH 7.4. DC protein assays (Bio-Rad Laboratories) were performed on cell lysate samples. Equal amounts of protein from each sample were run on each lane of 7.5% SDS-PAGE gels. After gel electrophoresis, proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for Western blotting analysis. Proteins on the membranes were labeled with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C and then labeled by peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies and visualized by ECL detection reagents (Thermo Fisher Scientific). β-Actin was blotted as a protein loading control.
Statistics
Numerical data are presented as means ± SD. Student’s t test was used for the comparison of two means (P < 0.05 was considered significant as marked by asterisks in the figures).
Online supplemental material
Fig. S1 shows that integrin β3 and integrin β1 localize at CDRs in various cell types after growth factor stimulation. Fig. S2 shows that PDGF-BB–stimulated integrin β3 macropinocytosis is BARS dependent but clathrin and CAV1 independent. Video 1 shows a 3D view of CDRs with integrin β3, F-actin, and cortactin colocalization. Video 2 shows integrin β3–GFP translocation 4D tracing in a live NIH3T3 cell after PDGF-BB stimulation. Video 3 shows integrin β3–GFP translocation 4D tracing in a live NIH3T3 cell without PDGF-BB stimulation. Video 4 shows integrin β3–GFP translocation 4D tracing in a BARS siRNA-transfected live NIH3T3 cell after PDGF-BB stimulation. Online supplemental material is available at http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007003/DC1.
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Wehrle-Haller for providing the integrin β3–GFP plasmid; J. Yang and J. Li (Harvard University, Boston, MA) for providing the siRNAs and antibodies against BARS and CHC; and J. Norman (Beatson Institute for Cancer Research, Glasgow, Scotland, UK), S. Linder (Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, München, Germany), M. Gimona (University of Salzburg, Salzburg, Austria), and C. Hai (Brown University, Providence, RI) for helping to locate reagents.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants AI065858 and AR048114 to M.B. Brenner and National Institutes of Health grant GM073016 to V.W. Hsu.
Author contributions: Z. Gu raised the hypothesis, designed and performed the experiments, and wrote the paper. E.H. Noss retrieved primary synovial fibroblasts from mice and helped with the Transwell migration assay. V.W. Hsu suggested the BARS experiments and contributed to writing the paper. M.B. Brenner supervised all aspects of the project and contributed to writing the paper.
Footnotes
Abbreviations used in this paper:
- BARS
- brefeldin A–ADP-ribosylated substrate
- CAV1
- caveolin-1
- CDR
- circular dorsal ruffle
- CHC
- clathrin heavy chain
- IF
- immunofluorescence
- MFI
- mean fluorescence intensity
- MHC
- major histocompatibility complex
- TMR
- tetramethylrhodamine
References
- Agarwal S.K., Lee D.M., Kiener H.P., Brenner M.B. 2008. Coexpression of two mesenchymal cadherins, cadherin 11 and N-cadherin, on murine fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 58:1044–1054 10.1002/art.23369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballestrem C., Hinz B., Imhof B.A., Wehrle-Haller B. 2001. Marching at the front and dragging behind: differential αVβ3-integrin turnover regulates focal adhesion behavior. J. Cell Biol. 155:1319–1332 10.1083/jcb.200107107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonazzi M., Spanò S., Turacchio G., Cericola C., Valente C., Colanzi A., Kweon H.S., Hsu V.W., Polishchuck E.V., Polishchuck R.S., et al. 2005. CtBP3/BARS drives membrane fission in dynamin-independent transport pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:570–580 10.1038/ncb1260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M.S. 2008. On the shape of migrating cells—a ‘front-to-back’ model. J. Cell Sci. 121:2625–2628 10.1242/jcs.031120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buccione R., Orth J.D., McNiven M.A. 2004. Foot and mouth: podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal ruffles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5:647–657 10.1038/nrm1436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell P.T., Vadrevu S., Norman J.C. 2009. Integrins: masters and slaves of endocytic transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:843–853 10.1038/nrm2799 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W.T., Kunz J. 2009. Focal adhesion disassembly requires clathrin-dependent endocytosis of integrins. FEBS Lett. 583:1337–1343 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.03.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J.A., Cohen S. 1979. Rapid induction of morphological changes in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factors. J. Cell Biol. 83:260–265 10.1083/jcb.83.1.260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J.L., Green S.A., Greene L.A. 1984. Comparison of rapid changes in surface morphology and coated pit formation of PC12 cells in response to nerve growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J. Cell Biol. 98:457–465 10.1083/jcb.98.2.457 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezratty E.J., Bertaux C., Marcantonio E.E., Gundersen G.G. 2009. Clathrin mediates integrin endocytosis for focal adhesion disassembly in migrating cells. J. Cell Biol. 187:733–747 10.1083/jcb.200904054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Kordowska J., Williams G.L., Wang C.L., Hai C.M. 2007. Erk1/2 MAPK and caldesmon differentially regulate podosome dynamics in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp. Cell Res. 313:849–866 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.12.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga Y., Miwa N., Jahangeer S., Okada T., Nakamura S. 2009. CtBP1/BARS is an activator of phospholipase D1 necessary for agonist-induced macropinocytosis. EMBO J. 28:1197–1207 10.1038/emboj.2009.78 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaksonen M., Toret C.P., Drubin D.G. 2006. Harnessing actin dynamics for clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:404–414 10.1038/nrm1940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M.C., Teasdale R.D. 2009. Defining macropinocytosis. Traffic. 10:364–371 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00878.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffenburger D.A., Horwitz A.F. 1996. Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process. Cell. 84:359–369 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81280-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D.M., Kiener H.P., Agarwal S.K., Noss E.H., Watts G.F., Chisaka O., Takeichi M., Brenner M.B. 2007. Cadherin-11 in synovial lining formation and pathology in arthritis. Science. 315:1006–1010 10.1126/science.1137306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Peters P.J., Bai M., Dai J., Bos E., Kirchhausen T., Kandror K.V., Hsu V.W. 2007. An ACAP1-containing clathrin coat complex for endocytic recycling. J. Cell Biol. 178:453–464 10.1083/jcb.200608033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberali P., Kakkonen E., Turacchio G., Valente C., Spaar A., Perinetti G., Böckmann R.A., Corda D., Colanzi A., Marjomaki V., Luini A. 2008. The closure of Pak1-dependent macropinosomes requires the phosphorylation of CtBP1/BARS. EMBO J. 27:970–981 10.1038/emboj.2008.59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellström K., Heldin C.H., Westermark B. 1988. Induction of circular membrane ruffling on human fibroblasts by platelet-derived growth factor. Exp. Cell Res. 177:347–359 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90468-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson Y., Mills G.B., Yarden Y. 2008. Derailed endocytosis: an emerging feature of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 8:835–850 10.1038/nrc2521 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Kaibuchi K. 2007. Numb controls integrin endocytosis for directional cell migration with aPKC and PAR-3. Dev. Cell. 13:15–28 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth J.D., McNiven M.A. 2006. Get off my back! Rapid receptor internalization through circular dorsal ruffles. Cancer Res. 66:11094–11096 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth J.D., Krueger E.W., Weller S.G., McNiven M.A. 2006. A novel endocytic mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor sequestration and internalization. Cancer Res. 66:3603–3610 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2916 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellinen T., Ivaska J. 2006. Integrin traffic. J. Cell Sci. 119:3723–3731 10.1242/jcs.03216 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powelka A.M., Sun J., Li J., Gao M., Shaw L.M., Sonnenberg A., Hsu V.W. 2004. Stimulation-dependent recycling of integrin beta1 regulated by ARF6 and Rab11. Traffic. 5:20–36 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00150.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J.T., Tiganis T., Agarwal A., Djakiew D., Thompson E.W. 1999. Epidermal growth factor promotes MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration through a phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and phospholipase C-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 59:5475–5478 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regen C.M., Horwitz A.F. 1992. Dynamics of β 1 integrin-mediated adhesive contacts in motile fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 119:1347–1359 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Barry S., Woods A., van der Sluijs P., Norman J. 2001. PDGF-regulated rab4-dependent recycling of alphavbeta3 integrin from early endosomes is necessary for cell adhesion and spreading. Curr. Biol. 11:1392–1402 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00442-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E.W., Bowen-Pope D.F. 1986. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 46:155–169 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanò S., Silletta M.G., Colanzi A., Alberti S., Fiucci G., Valente C., Fusella A., Salmona M., Mironov A., Luini A., Corda D. 1999. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of brefeldin A-ADP-ribosylated substrate. A novel protein involved in the maintenance of the Golgi structure. J. Biol. Chem. 274:17705–17710 10.1074/jbc.274.25.17705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suetsugu S., Yamazaki D., Kurisu S., Takenawa T. 2003. Differential roles of WAVE1 and WAVE2 in dorsal and peripheral ruffle formation for fibroblast cell migration. Dev. Cell. 5:595–609 10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00297-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung B.H., Yeo M.G., Oh H.J., Song W.K. 2008. v-Crk induces Rac-dependent membrane ruffling and cell migration in CAS-deficient embryonic fibroblasts. Mol. Cells. 25:131–137 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J.A. 2008. Shaping cups into phagosomes and macropinosomes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9:639–649 10.1038/nrm2447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teckchandani A., Toida N., Goodchild J., Henderson C., Watts J., Wollscheid B., Cooper J.A. 2009. Quantitative proteomics identifies a Dab2/integrin module regulating cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 186:99–111 10.1083/jcb.200812160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wary K.K., Mariotti A., Zurzolo C., Giancotti F.G. 1998. A requirement for caveolin-1 and associated kinase Fyn in integrin signaling and anchorage-dependent cell growth. Cell. 94:625–634 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81604-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D.J., Parsons J.T., Horwitz A.F. 2002. Adhesion assembly, disassembly and turnover in migrating cells — over and over and over again. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:E97–E100 10.1038/ncb0402-e97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y., Yang X., Liu Q., Wilkins J.A., Chapman H.A. 1999. A role for caveolin and the urokinase receptor in integrin-mediated adhesion and signaling. J. Cell Biol. 144:1285–1294 10.1083/jcb.144.6.1285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R.F., Gu Y., Xu Y.C., Nwariaku F.E., Terada L.S. 2003. Vascular endothelial growth factor causes translocation of p47phox to membrane ruffles through WAVE1. J. Biol. Chem. 278:36830–36840 10.1074/jbc.M302251200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J.S., Lee S.Y., Spanò S., Gad H., Zhang L., Nie Z., Bonazzi M., Corda D., Luini A., Hsu V.W. 2005. A role for BARS at the fission step of COPI vesicle formation from Golgi membrane. EMBO J. 24:4133–4143 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]