Abstract
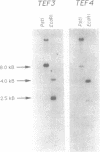
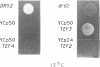
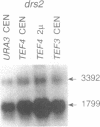
A gene encoding a yeast homologue of translation elongation factor 1 gamma (EF-1 gamma), TEF3, was isolated as a gene dosage extragenic suppressor of the cold-sensitive phenotype of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae drs2 mutant. The drs2 mutant is deficient in the assembly of 40S ribosomal subunits. We have identified a second gene, TEF4, that encodes a protein highly related to both the Tef3p protein (Tef3p), and EF-1 gamma isolated from other organisms. In contrast to TEF3, the TEF4 gene contains an intron. Gene disruptions showed that neither gene is required for mitotic growth. Haploid spores containing disruptions of both genes are viable and have no defects in ribosomal subunit composition or polyribosomes. Unlike TEF3, extra copies of TEF4 do not suppress the cold-sensitive 40S ribosomal subunit deficiency of a drs2 strain. Low-stringency genomic Southern hybridization analysis indicates there may be additional yeast genes related to TEF3 and TEF4.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Pringle J. R. Use of a screen for synthetic lethal and multicopy suppressee mutants to identify two new genes involved in morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1295–1305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M. D., Carvalho J. F., Merrick W. C. Biological characterization of various forms of elongation factor 1 from rabbit reticulocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraburtty K., Kamath A. Protein synthesis in yeast. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(6):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin K. V., Cade C., Brostrom C. O., Galuska E. M., Brostrom M. A. Calcium-dependent regulation of protein synthesis at translational initiation in eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16509–16514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Sikorski R. S., Dante M., Shero J. H., Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormier P., Osborne H. B., Morales J., Bassez T., Poulhe R., Mazabraud A., Mulner-Lorillon O., Bellé R. Molecular cloning of Xenopus elongation factor 1 gamma, major M-phase promoting factor substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6644–6644. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Skogerson L., Chakraburtty K. Protein synthesis in yeast. II. Purification and properties of the elongation factor 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10005–10011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Walter P. The signal recognition particle in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90577-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga K., Suzuki K., Tsuchiya E., Miyakawa T. Cloning and characterization of the elongation factor EF-1 beta homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EF-1 beta is essential for growth. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 25;316(2):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81208-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker T. C., Hoyt M. A., Botstein D. Genetic analysis of the yeast cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:259–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. M., Möller W. Elongation factor 1 beta gamma from Artemia. Purification and properties of its subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):119–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambouris N. G., Burke D. J., Creutz C. E. Cloning and genetic characterization of a calcium- and phospholipid-binding protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that is homologous to translation elongation factor-1 gamma. Yeast. 1993 Feb;9(2):151–163. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang H. A., Schwelberger H. G., Hershey J. W. The two genes encoding protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-5A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are members of a duplicated gene cluster. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):487–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00265449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumabe T., Sohma Y., Yamamoto T. Human cDNAs encoding elongation factor 1 gamma and the ribosomal protein L19. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2598–2598. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnirov V. V., Ter-Avanesyan M. D., Telckov M. V., Surguchov A. P., Smirnov V. N., Inge-Vechtomov S. G. Nucleotide sequence of the SUP2 (SUP35) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maessen G. D., Amons R., Zeelen J. P., Möller W. Primary structure of elongation factor 1 gamma from Artemia. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80532-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C., Dever T. E., Kinzy T. G., Conroy S. C., Cavallius J., Owens C. L. Characterization of protein synthesis factors from rabbit reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90173-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic mapping in Saccharomyces. Genetics. 1966 Jan;53(1):165–173. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima K., Kasai M., Nagata S., Kaziro Y. Structure of the two genes coding for polypeptide chain elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1986;45(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Palfrey H. C. Identification of the major Mr 100,000 substrate for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III in mammalian cells as elongation factor-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17299–17303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. J., Ziegelhoffer T., Nicolet C., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A. The translation machinery and 70 kd heat shock protein cooperate in protein synthesis. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90269-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perentesis J. P., Phan L. D., Gleason W. B., LaPorte D. C., Livingston D. M., Bodley J. W. Saccharomyces cerevisiae elongation factor 2. Genetic cloning, characterization of expression, and G-domain modeling. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1190–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripmaster T. L., Vaughn G. P., Woolford J. L., Jr DRS1 to DRS7, novel genes required for ribosome assembly and function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7901–7912. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Shestakova E. A., Natapov P. G. Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):170–173. doi: 10.1038/334170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S. K., Chakraburtty K. Protein synthesis in yeast. Isolation of variant forms of elongation factor 1 from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12599–12603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobin L. I., Möller W. Purification and properties of an elongation factor functionally analogous to bacterial elongation factor Ts from embryos of Artemia salina. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):69–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. G., Culbertson M. R. SUF12 suppressor protein of yeast. A fusion protein related to the EF-1 family of elongation factors. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):559–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]