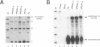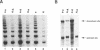Abstract
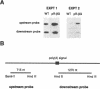
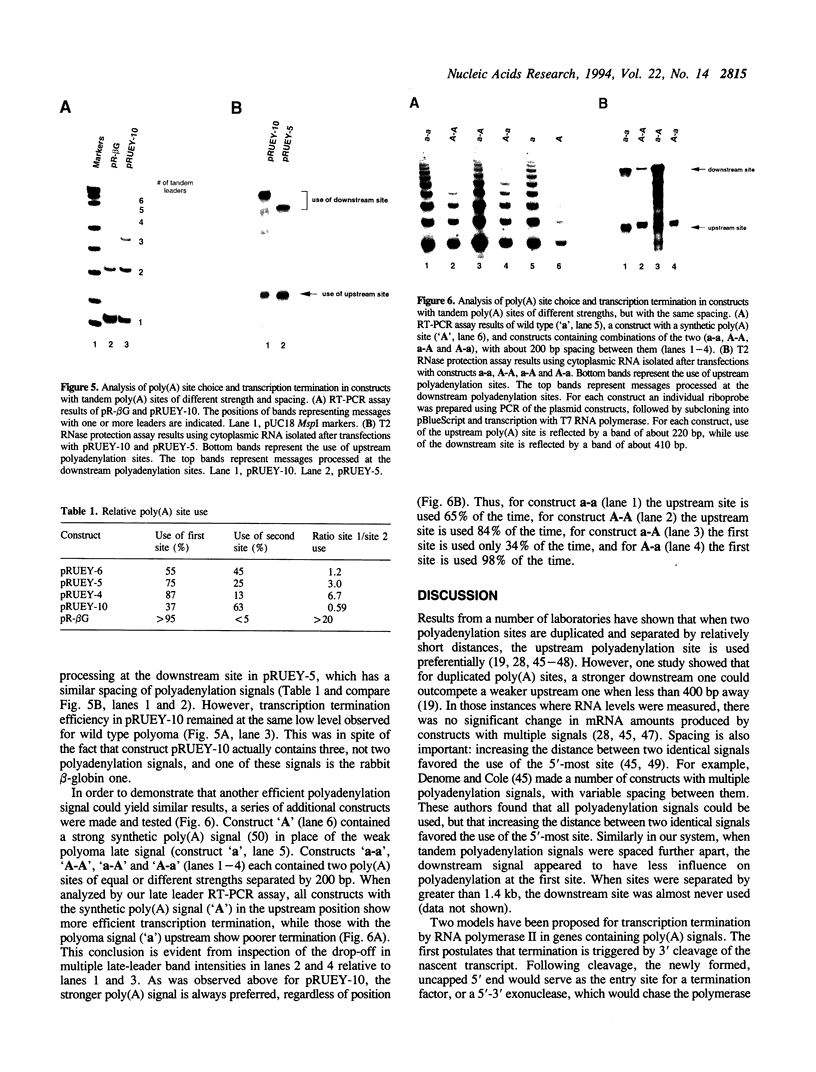
The processes of pre-mRNA 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation have been closely linked to transcription termination by RNA polymerase II. We have studied the relationship between polyadenylation and transcription termination in gene constructs containing tandem poly(A) signals, at least one of which is the inefficient polyomavirus late poly(A) site. When identical tandem viral signals were separated by fewer than 400 bp, they competed for polyadenylation. The upstream site was always chosen preferentially, but relative site choice was influenced by the distance between the signals. All of these constructs showed the same low level of transcription termination as wild type polyomavirus, which contains a single late poly(A) site. When tandem poly(A) signals were not identical, a stronger downstream signal could outcompete a weaker upstream signal for polyadenylation without altering the efficiency of transcription termination characteristic for use of the upstream signal. Thus, if a weak polyoma virus late poly(A) signal (associated with inefficient transcription termination) preceded a strong rabbit beta-globin signal (associated with efficient transcription termination), termination remained inefficient, but the distal signal was most often chosen for polyadenylation. These results are consistent with independent regulation of polyadenylation and transcription termination in this system and are discussed in light of current models for the dependence of transcription termination on a functional poly(A) site.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Kinetics and efficiency of polyadenylation of late polyomavirus nuclear RNA: generation of oligomeric polyadenylated RNAs and their processing into mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):722–729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Marlor C. W., Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G. Leader-to-leader splicing is required for efficient production and accumulation of polyomavirus late mRNAs. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):85–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.85-93.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baek K. H., Sato K., Ito R., Agarwal K. RNA polymerase II transcription terminates at a specific DNA sequence in a HeLa cell-free reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7623–7627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Carmichael G. G. Deletion analysis of the polyomavirus late promoter: evidence for both positive and negative elements in the absence of early proteins. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3634–3642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3634-3642.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. B., Roome A. J., Carmichael G. G. Replication-dependent transactivation of the polyomavirus late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):992–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.992-1001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B., Falck-Pedersen E., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination occurs within a 1000 base pair region downstream from the poly(A) site of the mouse beta-globin (major) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8723–8731. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. A CCAAT box sequence in the adenovirus major late promoter functions as part of an RNA polymerase II termination signal. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. A functional mRNA polyadenylation signal is required for transcription termination by RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):440–452. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. RNA polymerase II transcription termination is mediated specifically by protein binding to a CCAAT box sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5254–5259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denome R. M., Cole C. N. Patterns of polyadenylation site selection in gene constructs containing multiple polyadenylation signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4829–4839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwalds-Gilbert G., Prescott J., Falck-Pedersen E. 3' RNA processing efficiency plays a primary role in generating termination-competent RNA polymerase II elongation complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3472–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez-Harris P., Levitt N., Briggs D., Proudfoot N. J. A pause site for RNA polymerase II is associated with termination of transcription. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1833–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Mandel G., Carmichael G. G., Barncastle J. P., Dawe C. J., Benjamin T. L. Polyomavirus tumor induction in mice: influences of viral coding and noncoding sequences on tumor profiles. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2232–2239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2232-2239.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Cribbs D. L., Schibler U. Termination of transcription in the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-2a occurs at multiple sites downstream of the polyadenylation site. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. V., Denome R. M., Cole C. N. Spatial constraints on polyadenylation signal function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9098–9104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R. P., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late pre-mRNA processing: DNA replication-associated changes in leader exon multiplicity suggest a role for leader-to-leader splicing in the early-late switch. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5823–5832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5823-5832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde-DeRuyscher R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus early-late switch is not regulated at the level of transcription initiation and is associated with changes in RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8993–8997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Acheson N. H. A rabbit beta-globin polyadenylation signal directs efficient termination of transcription of polyomavirus DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2515–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Tseng R. W., Acheson N. H. Duplication of functional polyadenylation signals in polyomavirus DNA does not alter efficiency of polyadenylation or transcription termination. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):733–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.733-742.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law R., Kuwabara M. D., Briskin M., Fasel N., Hermanson G., Sigman D. S., Wall R. Protein-binding site at the immunoglobulin mu membrane polyadenylylation signal: possible role in transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9160–9164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M. A., Galliot B., Gerlinger P. Termination of the ovalbumin gene transcription. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2779–2786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A., Barrett N. L., Carmichael G. G. Simple, inexpensive preparation of T1/T2 ribonuclease suitable for use in RNase protection experiments. Biotechniques. 1992 Feb;12(2):231–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Falck-Pedersen E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Shenk T. A poly(A) addition site and a downstream termination region are required for efficient cessation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in the mouse beta maj-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8306–8310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Carmichael G. G. Splice site choice in a complex transcription unit containing multiple inefficient polyadenylation signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5291–5300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Carmichael G. G. Splice site skipping in polyomavirus late pre-mRNA processing. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6637–6644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6637-6644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Proudfoot N. J., Platt T. RNA 3'-end formation. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2218–2222. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Vuocolo G. A. Synthesis of two mRNAs by utilization of alternate polyadenylation sites: expression of SV40-mouse immunoglobulin mu chain gene recombinants in Cos monkey cells. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):689–699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. Regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA requires linkage of the poly(A) addition sites and is dependent on the length of the mu s-mu m intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8883–8887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl T. M., Martinson H. G. Transcription termination at the chicken beta H-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5369–5377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Connelly S., Manley J. L., Alwine J. C. Identification of a sequence element on the 3' side of AAUAAA which is necessary for simian virus 40 late mRNA 3'-end processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ito R., Baek K. H., Agarwal K. A specific DNA sequence controls termination of transcription in the gastrin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1032–1043. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi J., Alvira M., Falck-Pedersen E. Characterization of the mouse beta maj globin transcription termination region: a spacing sequence is required between the poly(A) signal sequence and multiple downstream termination elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):578–587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng R. W., Acheson N. H. Use of a novel S1 nuclease RNA-mapping technique to measure efficiency of transcription termination on polyomavirus DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1624–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Keller W. The biochemistry of 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:419–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Proudfoot N. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a poly(A) site mutation reveals that transcriptional termination is linked to 3' end processing in the human alpha 2 globin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2915–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]