Abstract
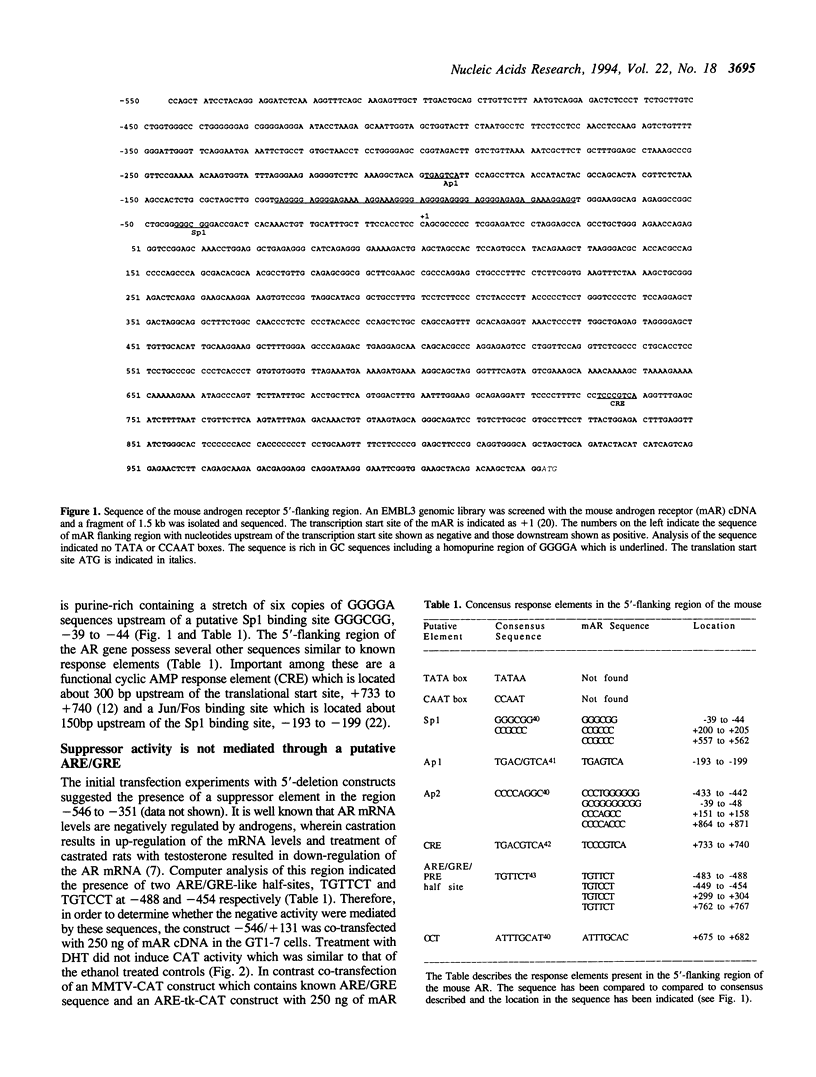
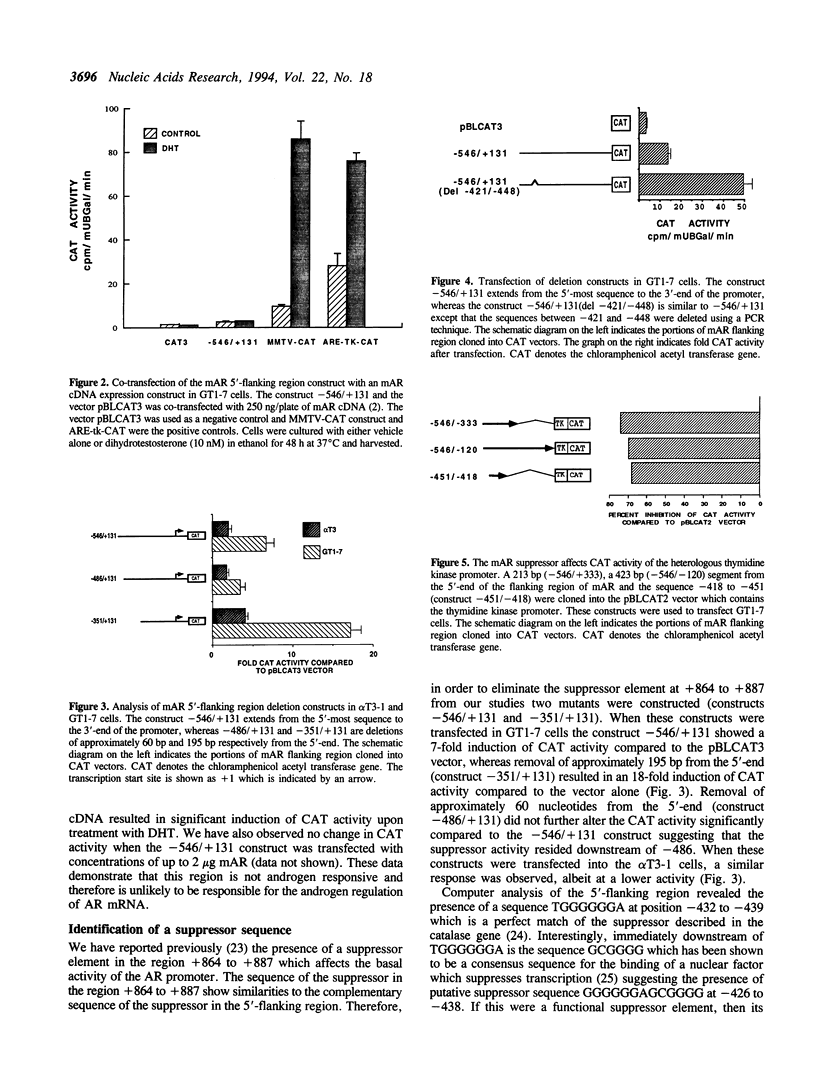
Androgens play an important role in the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs through the androgen receptor (AR). In order to study the mechanism of regulation of AR at the molecular level, a 1571 bp fragment in the 5'-flanking region of the mouse androgen receptor (mAR) gene was isolated and sequenced. Transfection of 5'-deletion constructs cloned into vectors containing the chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) gene indicated the presence of a promoter in the sequence -146 to +131. These experiments also suggested the presence of a suppressor element. Further characterization indicated that the suppressor is present between -486 to -351. It is functional in the context of the natural AR promoter and the heterologous thymidine kinase promoter. Transfection of a -546/ + 131 construct in which the putative suppressor element (-421 to -448) had been deleted caused increased basal CAT activity suggesting that the suppressor is limited to this 28 bp element in the 5'-flanking region of the mouse AR gene.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerblom I. E., Slater E. P., Beato M., Baxter J. D., Mellon P. L. Negative regulation by glucocorticoids through interference with a cAMP responsive enhancer. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.2838908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baarends W. M., Themmen A. P., Blok L. J., Mackenbach P., Brinkmann A. O., Meijer D., Faber P. W., Trapman J., Grootegoed J. A. The rat androgen receptor gene promoter. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Nov 12;74(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90207-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. A purified Drosophila homeodomain protein represses transcription in vitro. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok L. J., Mackenbach P., Trapman J., Themmen A. P., Brinkmann A. O., Grootegoed J. A. Follicle-stimulating hormone regulates androgen receptor mRNA in Sertoli cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 May;63(1-2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok L. J., Themmen A. P., Peters A. H., Trapman J., Baarends W. M., Hoogerbrugge J. W., Grootegoed J. A. Transcriptional regulation of androgen receptor gene expression in Sertoli cells and other cell types. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;88(1-3):153–164. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson-Jurica M. A., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990 May;11(2):201–220. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Structural analysis of complementary DNA and amino acid sequences of human and rat androgen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7211–7215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber P. W., King A., van Rooij H. C., Brinkmann A. O., de Both N. J., Trapman J. The mouse androgen receptor. Functional analysis of the protein and characterization of the gene. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2780269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann M. E., Lindzey J., Kumar M. V., Tindall D. J. The mouse androgen receptor is suppressed by the 5'-untranslated region of the gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Apr;8(4):448–455. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.4.8052266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He W. W., Fischer L. M., Sun S., Bilhartz D. L., Zhu X. P., Young C. Y., Kelley D. B., Tindall D. J. Molecular cloning of androgen receptors from divergent species with a polymerase chain reaction technique: complete cDNA sequence of the mouse androgen receptor and isolation of androgen receptor cDNA probes from dog, guinea pig and clawed frog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Active repression of transcription by the engrailed homeodomain protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1427–1433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley C., Winoto A. Cloning of GT box-binding proteins: a novel Sp1 multigene family regulating T-cell receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4251–4261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutoh E., Strömstedt P. E., Poellinger L. Functional interference between the ubiquitous and constitutive octamer transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) and the glucocorticoid receptor by direct protein-protein interaction involving the homeo subdomain of OTF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4960–4969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindzey J., Grossmann M., Kumar M. V., Tindall D. J. Regulation of the 5'-flanking region of the mouse androgen receptor gene by cAMP and androgen. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Dec;7(12):1530–1540. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.12.7511785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Joseph D. R., Sullivan P. M., Willard H. F., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Cloning of human androgen receptor complementary DNA and localization to the X chromosome. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.3353727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Windle J. J., Goldsmith P. C., Padula C. A., Roberts J. L., Weiner R. I. Immortalization of hypothalamic GnRH neurons by genetically targeted tumorigenesis. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90028-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizokami A., Saiga H., Matsui T., Mita T., Sugita A. Regulation of androgen receptor by androgen and epidermal growth factor in a human prostatic cancer cell line, LNCaP. Endocrinol Jpn. 1992 Jun;39(3):235–243. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.39.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K. Regulation of cAMP-inducible genes by CREB. Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90045-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarmby V. E., Yarbrough W. G., Lubahn D. B., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Autologous down-regulation of androgen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;4(1):22–28. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter E., Bonnet P., Sente B., Dombrowicz D., de Leval J., Closset J., Hennen G. Growth hormone and prolactin stimulate androgen receptor, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-I receptor levels in the prostate of immature rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;88(1-3):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90011-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. The "megaprimer" method of site-directed mutagenesis. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):404–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ito K., Kohara H., Yamaguchi Y., Adachi K., Endo H. Negative regulation of catalase gene expression in hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2525–2533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan L. X., Rodriguez M. C., Jänne O. A. Regulation of androgen receptor protein and mRNA concentrations by androgens in rat ventral prostate and seminal vesicles and in human hepatoma cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1636–1646. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. A., Joseph D. R., Quarmby V. E., Lubahn D. B., Sar M., French F. S., Wilson E. M. The rat androgen receptor: primary structure, autoregulation of its messenger ribonucleic acid, and immunocytochemical localization of the receptor protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1276–1285. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. A., Lee E., Lawe D., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor-induced derepression of peripherin gene expression is associated with alterations in proteins binding to a negative regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2501–2513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley W. D., Marcelli M., McPhaul M. J. Expression of the human androgen receptor gene utilizes a common promoter in diverse human tissues and cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13776–13781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran P., Zhang X. K., Salbert G., Hermann T., Lehmann J. M., Pfahl M. COUP orphan receptors are negative regulators of retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4666–4676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Weiner R. I., Mellon P. L. Cell lines of the pituitary gonadotrope lineage derived by targeted oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):597–603. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D. A., Herzinger T., Hermeking H., Blaschke D., Hörz W. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of human androgen receptor expression by androgen. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jul;7(7):924–936. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.7.8413317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X. Y., Hung M. C. Negative autoregulation of the neu gene is mediated by a novel enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2739–2748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



