Abstract
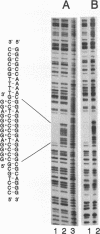
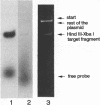
A homopurine-homopyrimidine region of murine c-pim-1 proto-oncogene was chosen as a target for triple-helix-forming oligonucleotide. Oligonucleotide 5'-GGG-GAGGGGGAGG-3' was shown to bind to its target sequence in the presence of 50 mM Na+ or K+, 10 mM MgCl2 and 20 mM Tris-acetate, pH 7.5. This oligonucleotide is bound in an antiparallel orientation with respect to the homopurine sequence. As was shown by co-migration assay the triplex is stable up to 65 degrees C. At 37 degrees C it was practically irreversible: after 24 hours of co-migration assay there was no traces of triplex dissociation. The rate of triplex formation was highly accelerated with increase of temperature and Mg2+ concentration. This rate was higher for superhelical DNA when compared to the linear and circular ones and the preference was dependent from temperature and Mg2+ concentration. The precision of this interaction is extremely high: sequences in c-pim-1 promoter region with only one substitution when compared to the target gave negligible triplex formation under investigated conditions. These data suppose that natural triplex structures could play an important role in eukaryotic gene regulation and/or chromatin structure formation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacolla A., Wu F. Y. Mung bean nuclease cleavage pattern at a polypurine.polypyrimidine sequence upstream from the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1639–1647. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasty A. M., Behe M. J. An oligopurine sequence bias occurs in eukaryotic viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1517–1528. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng A. J., Van Dyke M. W. Monovalent cation effects on intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple-helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 11;21(24):5630–5635. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus F., Sola B., Fichelson S., Varlet P., Charon M., Tambourin P., Wendling F., Gisselbrecht S. Rearrangements of the Pim-1, c-myc, and p53 genes in Friend helper virus-induced mouse erythroleukemias. Leukemia. 1990 Aug;4(8):590–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Guieysse A. L., Robin P., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. Inhibition of gene expression by triple helix-directed DNA cross-linking at specific sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3501–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryaznov S. M., Lloyd D. H. Modulation of oligonucleotide duplex and triplex stability via hydrophobic interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5909–5915. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., van der Lugt N. M., Clarke A., Domen J., Linders K., McWhir J., Berns A., Hooper M. In vivo analysis of Pim-1 deficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 11;21(20):4750–4755. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.20.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker T. C., Loeb J., Ayres M., Sellers W. The human Pim-1 gene is selectively transcribed in different hemato-lymphoid cell lines in spite of a G + C-rich housekeeping promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1680–1688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill D., Bornschlegel K., Flamm M., Castle M., Bank A. A DNA-binding factor in adult hematopoietic cells interacts with a pyrimidine-rich domain upstream from the human delta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8953–8957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Stability and properties of double and triple helices: dramatic effects of RNA or DNA backbone composition. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1463–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.1279808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougée M., Faucon B., Mergny J. L., Barcelo F., Giovannangeli C., Garestier T., Hélène C. Kinetics and thermodynamics of triple-helix formation: effects of ionic strength and mismatches. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9269–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Boelens W., Robanus-Maandag E., Verbeek J., Domen J., van Beveren C., Berns A. The primary structure of the putative oncogene pim-1 shows extensive homology with protein kinases. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90886-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton S. F., Dervan P. B. Influence of pH on the equilibrium association constants for oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple helix formation at single DNA sites. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):10995–11003. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. H., Breslauer K. J., Stein S. Polyamine-linked oligonucleotides for DNA triple helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5489–5494. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voloshin O. N., Mirkin S. M., Lyamichev V. I., Belotserkovskii B. P., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Chemical probing of homopurine-homopyrimidine mirror repeats in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):475–476. doi: 10.1038/333475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Verbeek S., Krimpenfort P., Domen J., Saris C., Radaszkiewicz T., Berns A. Predisposition to lymphomagenesis in pim-1 transgenic mice: cooperation with c-myc and N-myc in murine leukemia virus-induced tumors. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]