Abstract
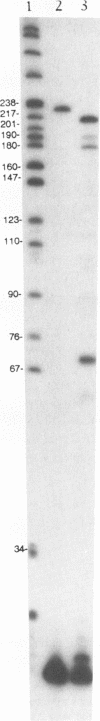
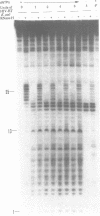
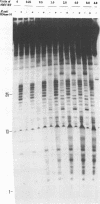
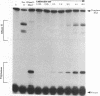
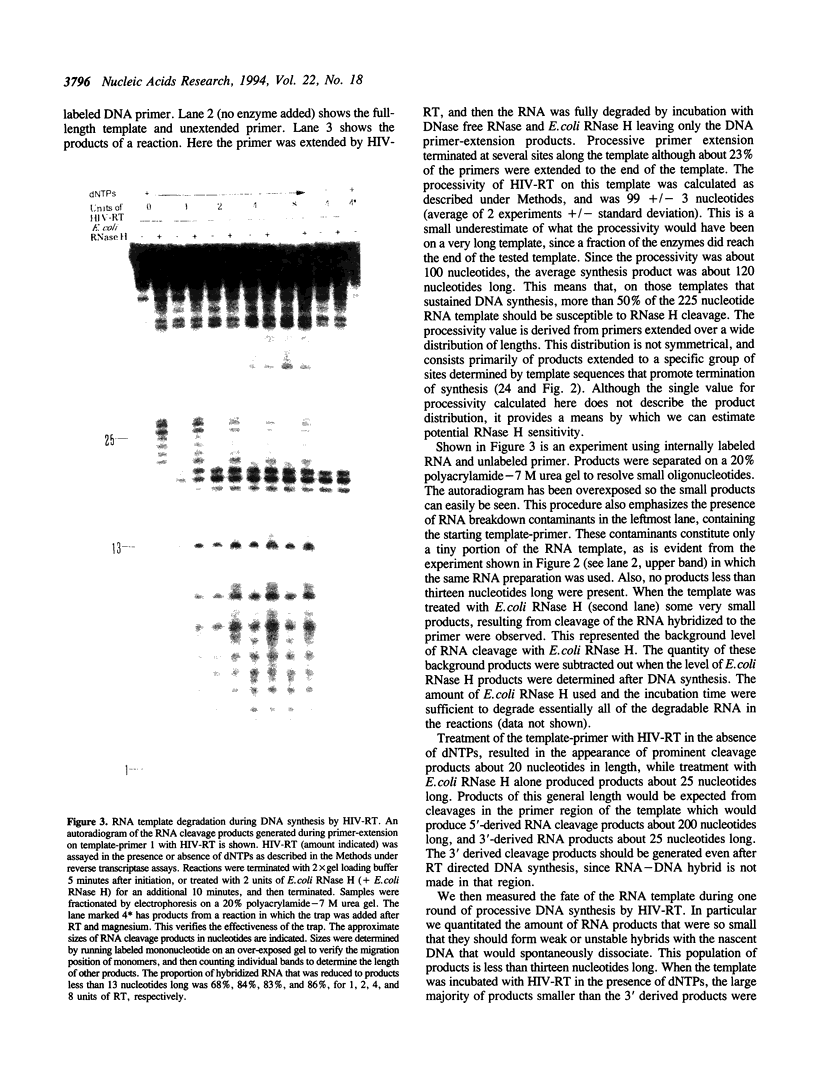
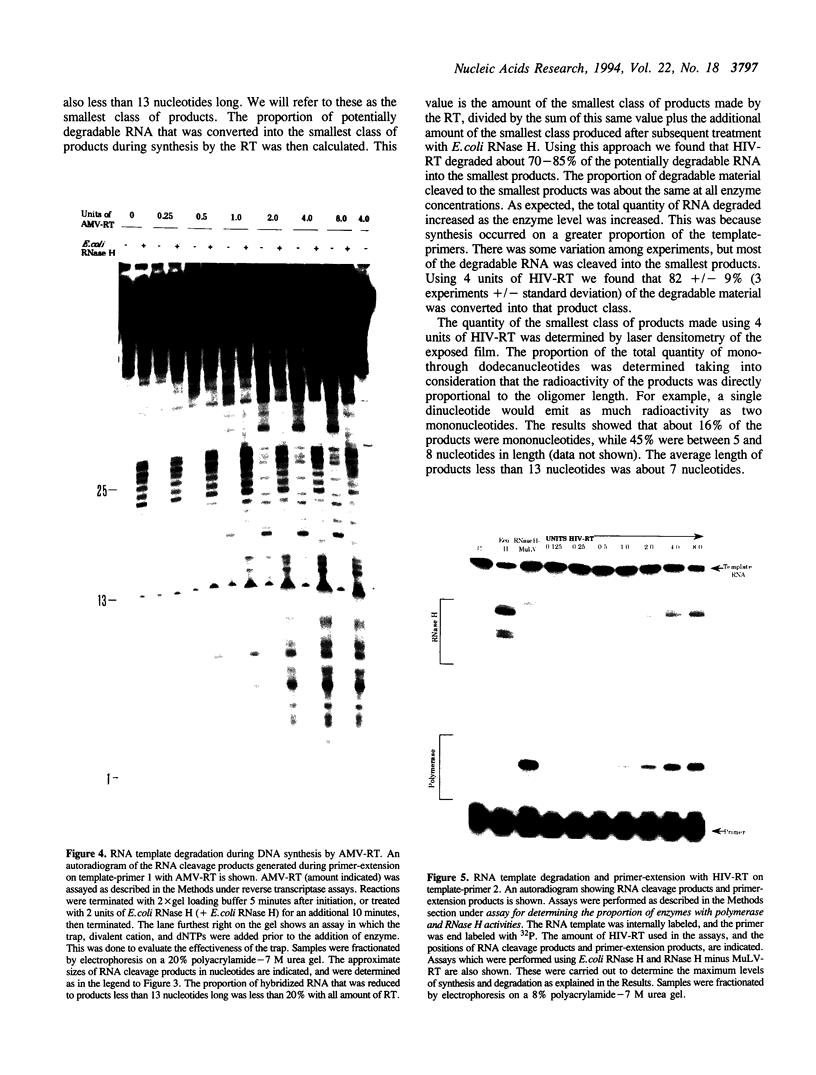
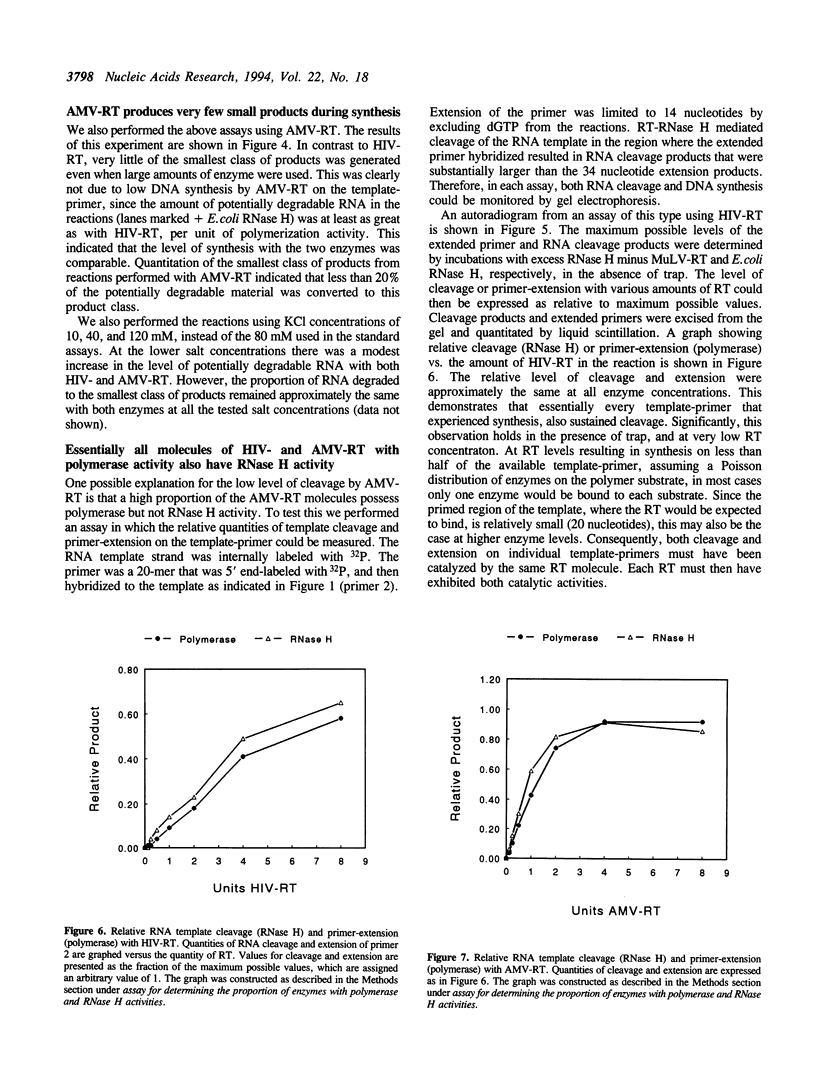
We have determined the extent of RNA cleavage carried out during DNA synthesis by either human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV) reverse transcriptases (RTs). Conditions were chosen that allowed the analysis of the cleavage and synthesis performed by the RT during one binding event on a given template-primer. The maximum quantity of ribonuclease H (RNase H) sensitive template RNA left after synthesis by the RTs was determined by treatment with Escherichia coli RNase H. RNA cleavage products that were expected to be too short to remain hybridized, less than 13 nucleotides in length, were quantitated. Results showed that HIV- and AMV-RT degraded about 80% and less than 20%, respectively, of the potentially degradable RNA to these short products. Survival of longer, hybridized RNA was not a result of synthesis by a population of RTs that had selectively lost RNase H activity. Using an assay that evaluated the proportion of primers extended versus RNA templates cleaved during primer-extension by the RTs, we determined that essentially each molecule of HIV- and AMV-RT with polymerase also has RNase H activity. The results indicate that although both HIV- and AMV-RTs cleave the RNA template during synthesis, the number of cleavages per nucleotide addition with HIV-RT is much greater. They also suggest that some hybridized RNA segments remain right after the passage of the RT making the first DNA strand. In vivo, these segments would have to be cleaved or displaced in later reactions before second strand DNA synthesis could be completed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewer L. C., Wells R. D. Mechanistic independence of avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1494–1502. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1494-1502.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Gilboa E., Baltimore D. Mechanism of RNA primer removal by the RNase H activity of avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.686-691.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Leis J. P., Smith M. S., Faras A. J. Unwinding-like activity associated with avian retrovirus RNA-directed DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):498–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.498-509.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano J. J., Buiser R. G., Mallaber L. M., Bambara R. A., Fay P. J. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase displays a partially processive 3' to 5' endonuclease activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24295–24301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano J. J., Buiser R. G., Mallaber L. M., Fay P. J., Bambara R. A. Parameters that influence processive synthesis and site-specific termination by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase on RNA and DNA templates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 15;1131(3):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90025-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano J. J., Buiser R. G., Mallaber L. M., Myers T. W., Bambara R. A., Fay P. J. Polymerization and RNase H activities of the reverse transcriptases from avian myeloblastosis, human immunodeficiency, and Moloney murine leukemia viruses are functionally uncoupled. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7423–7431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano J. J., Mallaber L. M., Rodriguez-Rodriguez L., Fay P. J., Bambara R. A. Requirements for strand transfer between internal regions of heteropolymer templates by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6370–6378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6370-6378.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudding L. R., Nkabinde N. C., Mizrahi V. Analysis of the RNA- and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities of point mutants of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase lacking ribonuclease H activity. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10498–10506. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finston W. I., Champoux J. J. RNA-primed initiation of Moloney murine leukemia virus plus strands by reverse transcriptase in vitro. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):26–33. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.26-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. B., Taylor J. When retroviral reverse transcriptases reach the end of their RNA templates. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4271-4278.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furfine E. S., Reardon J. E. Reverse transcriptase.RNase H from the human immunodeficiency virus. Relationship of the DNA polymerase and RNA hydrolysis activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P. Retroviral reverse transcriptase: synthesis, structure, and function. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):817–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan V., Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase: spatial and temporal relationship between the polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10763–10767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Moelling K. RNase H activity associated with bacterially expressed reverse transcriptase of human T-cell lymphotropic virus III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., McCoy J. M., Seehra J. S., Richardson C. C. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase. Template binding, processivity, strand displacement synthesis, and template switching. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Richardson C. C. Processing of the primer for plus strand DNA synthesis by human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10565–10573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kati W. M., Johnson K. A., Jerva L. F., Anderson K. S. Mechanism and fidelity of HIV reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25988–25997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S. W., Chow M., Champoux J., Baltimore D. Synthesis of murine leukemia virus plus strong stop DNA initiates at a unique site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):5983–5986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R., Omer C. A., Faras A. J. Involvement of retrovirus reverse transcriptase-associated RNase H in the initiation of strong-stop (+) DNA synthesis and the generation of the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.813-821.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. K., Cywinski A., Taylor J. M. Initiation of plus-strand DNA synthesis during reverse transcription of an avian retrovirus genome. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):200–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.200-204.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. K., Cywinski A., Taylor J. M. Specificity of initiation of plus-strand DNA by Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.314-319.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes M. C., Cheng Y. C. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase-associated RNase H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7073–7077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Zhang J., Li Z. Y., Tarpley W. G., Downey K. M., So A. G. Functional characterization of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and RNase H activities of a recombinant HIV reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 12;30(10):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00224a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann S., Wöhrl B. M., Tisdale M., Moelling K. Enzymatic analysis of two HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mutants with mutations in carboxyl-terminal amino acid residues conserved among retroviral ribonucleases H. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2674–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. F., Schendel P. L., Rosok M. J., Ramsey L. R. Model RNA-directed DNA synthesis by avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and its associated RNase H. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3210–3219. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrl B. M., Moelling K. Interaction of HIV-1 ribonuclease H with polypurine tract containing RNA-DNA hybrids. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10141–10147. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]