Abstract
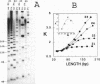
Physico-chemical and immunological studies have been done in order to further characterize the distorsions induced in DNA by the interstrand cross-links formed between the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) (cis-DDP) and two guanines on the opposite strands of DNA at the d(GC/GC) sites. Bending (45 degrees) and unwinding (79 +/- 4 degrees) were determined from the electrophoretic mobility of multimers of 21- 24-base pairs double-stranded oligonucleotides containing an interstrand cross-link in the central sequence d(TGCT/AGCA). The distorsions induced by the interstrand cross-link in the three 22-base pairs oligonucleotides d(TGCT/AGCA), d(AGCT/AGCT) and d(CGCT/AGCG) were compared by means of gel electrophoresis, circular dichroism, phenanthroline-copper footprinting and antibodies specifically directed against cis-DDP interstrand cross-links. The four different technical approaches indicate that the distorsions are independent of the chemical nature of the base pairs adjacent to the interstrand cross-link. The general conclusion is that the interstrand cross-link induces a bending and in particular an unwinding larger than other platinum adducts and the distorsions are independent of the nature of the bases (purine or pyrimidine) adjacent to the d(GC/GC) site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anin M. F., Leng M. Distortions induced in double-stranded oligonucleotides by the binding of cis- or trans-diammine-dichloroplatinum(II) to the d(GTG) sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4395–4400. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon S. F., Coleman J. H., Lippard S. J. DNA unwinding produced by site-specific intrastrand cross-links of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):8026–8035. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon S. F., Lippard S. J. Bending studies of DNA site-specifically modified by cisplatin, trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and cis-[Pt(NH3)2(N3-cytosine)Cl]+. Biophys Chem. 1990 Apr;35(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)80007-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabec V., Leng M. DNA interstrand cross-links of trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) are preferentially formed between guanine and complementary cytosine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabec V., Reedijk J., Leng M. Sequence-dependent distortions induced in DNA by monofunctional platinum(II) binding. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12397–12402. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabec V., Síp M., Leng M. DNA conformational change produced by the site-specific interstrand cross-link of trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 2;32(43):11676–11681. doi: 10.1021/bi00094a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Huang S. L., Lee L. Y., Lin-Chao S. Identification of inducible damage-recognition proteins that are overexpressed in HeLa cells resistant to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II). Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):875–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2770875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Chang E. Xeroderma pigmentosum group E cells lack a nuclear factor that binds to damaged DNA. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):564–567. doi: 10.1126/science.3175673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda Y., Job C., Anin M. F., Leng M., Job D. Spectrum of DNA--platinum adduct recognition by prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8582–8588. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Haran T. E., Nadeau J. G. Intrinsically bent DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7093–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. Reevaluation of interaction of cis-dichloro(ethylenediamine)platinum(II) with DNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3912–3915. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. The formation, isolation and characterization of DNA adducts produced by anticancer platinum complexes. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;34(2):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtinger-Schepman A. M., van der Veer J. L., den Hartog J. H., Lohman P. H., Reedijk J. Adducts of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) with DNA: formation, identification, and quantitation. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):707–713. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang B., Yeung A. T., Lambert M. W. A damage-recognition protein which binds to DNA containing interstrand cross-links is absent or defective in Fanconi anemia, complementation group A, cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4187–4192. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., Engelsberg B. N., Billings P. C. Purification of nuclear proteins that bind to cisplatin-damaged DNA. Identity with high mobility group proteins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13520–13527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Griffith J., Sancar A. Thymine dimers bend DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2558–2562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire M. A., Schwartz A., Rahmouni A. R., Leng M. Interstrand cross-links are preferentially formed at the d(GC) sites in the reaction between cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) and DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1982–1985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M. DNA bending induced by covalently bound drugs. Gel electrophoresis and chemical probe studies. Biophys Chem. 1990 Apr;35(2-3):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)80005-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfoy B., Hartmann B., Macquet J. P., Leng M. Immunochemical studies of DNA modified by cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 1981 Oct;41(10):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfoy B., Rousseau N., Leng M. Interaction between antibodies to Z-form deoxyribonucleic acid and double-stranded polynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5463–5467. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payet D., Gaucheron F., Sip M., Leng M. Instability of the monofunctional adducts in cis-[Pt(NH3)2(N7-N-methyl-2-diazapyrenium)Cl](2+)-modified DNA: rates of cross-linking reactions in cis-platinum-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5846–5851. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmouni A., Leng M. Reaction of nucleic acids with cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II): interstrand cross-links. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7229–7234. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J. A., Crothers D. M., Pinto A. L., Lippard S. J. The major adduct of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) with DNA bends the duplex by approximately equal to 40 degrees toward the major groove. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4158–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Leng M. DNase I footprinting of cis- or trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-modified DNA. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 4;236(4):969–974. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Marrot L., Leng M. Conformation of DNA modified at a d(GG) or a d(AG) site by the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):7975–7979. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S. Chemical nucleases. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9097–9105. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sip M., Schwartz A., Vovelle F., Ptak M., Leng M. Distortions induced in DNA by cis-platinum interstrand adducts. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2508–2513. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Lippard S. J., Stollar B. D. Monoclonal antibodies to DNA modified with cis- or trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8225–8229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon C., Kuwabara M. D., Law R., Wall R., Sigman D. S. Sequence-dependent variability of DNA structure. Influence of flanking sequences and fragment length on digestion by conformationally sensitive nucleases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8458–8463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhen W., Link C. J., Jr, O'Connor P. M., Reed E., Parker R., Howell S. B., Bohr V. A. Increased gene-specific repair of cisplatin interstrand cross-links in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3689–3698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]