Abstract
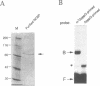
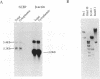
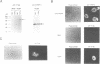
It has been shown that the monomethylated cap structure plays important roles in nuclear events. The cap structure has been implicated in the enhancement of pre-mRNA splicing. More recently, this structure has also been suggested to facilitate RNA transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. We have previously identified and purified an 80kD Nuclear Cap Binding Protein (NCBP) from a HeLa cell nuclear extract, which could possibly mediate these nuclear activities. In this report, we describe cloning of complementary DNA (cDNA) encoding NCBP. The partial protein sequences of NCBP were determined, and the full-length cDNA of NCBP was isolated from HeLa cDNA libraries. This cDNA encoded an open reading frame of 790 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 91,734 daltons, which contained most of the determined protein sequences. However, the protein sequence had no significant homology to any known proteins. Transfection experiments demonstrated that the epitope-tagged NCBP, transiently expressed in HeLa cells, was localized exclusively in the nucleoplasm. Similar experiments using a truncated NCBP cDNA indicated that this nuclear localization activity is conferred by the N-terminal 70 amino-acid region.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Monoclonal antibody characterization of the C proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes in vertebrate cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1997–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargemont C., Kühn L. C. Export of mRNA from microinjected nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):1–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Sonenberg N. Cap-dependent RNA splicing in a HeLa nuclear extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7590–7594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Monomethylated cap structures facilitate RNA export from the nucleus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90292-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Ohno M., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Effect of the cap structure on pre-mRNA splicing in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1472–1479. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Stepinski J., Darzynkiewicz E., Mattaj I. W. A cap binding protein that may mediate nuclear export of RNA polymerase II-transcribed RNAs. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1287–1295. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarmolowski A., Boelens W. C., Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. Nuclear export of different classes of RNA is mediated by specific factors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(5):627–635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.5.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. Small-scale preparation of extracts from radiolabeled cells efficient in pre-mRNA splicing. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:20–30. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Kataoka N., Shimura Y. A nuclear cap binding protein from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6989–6995. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Preferential excision of the 5' proximal intron from mRNA precursors with two introns as mediated by the cap structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5187–5191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Shimura Y. Nuclear cap binding protein from HeLa cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:209–215. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81123-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt E., Blaas D., Kuechler E. CAP binding proteins associated with the nucleus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5821–5835. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt E., Thalmann E., Hartmuth K., Blaas D., Kuechler E. Assembly of pre-mRNA splicing complex is cap dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1387–1399. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Sonenberg N. Identification of nuclear cap specific proteins in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6489–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. mRNA cap binding proteins: essential factors for initiating translation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]