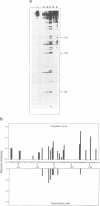
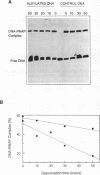
Abstract
DNA was alkylated with nitrogen mustard (HN2) and the rate of release of the alkylpurines was quantitated by HPLC. The half life of depurination of the major product (7-alkylguanine) was 9.1 h at 37 degrees C. End-labelled DNA was used to show that depurination occurred dominantly at 5'-GA, 5'-GG and 5'-GT sequences. Although extensive alkylation was observed at all 5'-GNC and 5'GNT sequences, no depurination was observed at these sites during a depurination time of 20 h at 37 degrees C. Since these sites are potential interstrand crosslinking sequences (G-adduct-G and G-adduct-A, both spanning an intervening base pair), this suggests that these regions have a greatly enhanced stability or that simultaneous depurination of both ends of the crosslink is necessary before these lesions are removed (with a predicted half-life of approximately 80 h at 37 degrees C). Depurination at the lac UV5 promoter impaired the association of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with that promoter, while in the elongation phase two distinctly different sequence-specific processes were apparent. At 5'-GNC and 5'-GNT sequences transcriptional blockages were maintained with increasing elongation time, whereas at monoadduct sites, the blockage decreased with elongation time (predominantly at 5'-GG and 5'-GC sequences), with an average half-life of approximately 10.7 h. Collectively, these results suggest that the observed read-through past monoadduct sites is due to depurination of the DNA at those sites. E. coli RNA polymerase is therefore able to transcribe efficiently past apurinic sites and presumably does so by incorporating an incorrect base into the nascent RNA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N. Mutagenesis and carcinogenesis: endogenous and exogenous factors. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;14 (Suppl 16):66–77. doi: 10.1002/em.2850140614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKES P., LAWLEY P. D. EFFECTS OF ALKYLATING AGENTS ON T2 AND T4 BACTERIOPHAGES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:138–144. doi: 10.1042/bj0890138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A. Gene specific DNA repair. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Nov;12(11):1983–1992. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.11.1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes P., Lawley P. D. The reaction of mono- and di-functional alkylating agents with nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1042/bj0800496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr F. J., Fox B. W. The effects of bifunctional alkylating agents on DNA synthesis in sensitive and resistant Yoshida cells. Mutat Res. 1982 Aug;95(2-3):441–456. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun E. H., Gonzales L., Lewis F. S., Jones J., Rutman R. J. Differences in the in vivo alkylation and cross-linking of nitrogen mustard-sensitive and -resistant lines of Lettré-Ehrlich asites tumors. Cancer Res. 1969 Jun;29(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullinane C., Phillips D. R. Induction of stable transcriptional blockage sites by adriamycin: GpC specificity of apparent adriamycin-DNA adducts and dependence on iron(III) ions. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5638–5646. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A., Philips F. S. The Biological Actions and Therapeutic Applications of the B-Chloroethyl Amines and Sulfides. Science. 1946 Apr 5;103(2675):409–436. doi: 10.1126/science.103.2675.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. J., Cullinane C., Phillips D. R. In vitro transcription analysis of DNA alkylation by nitrogen mustard. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):8036–8040. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. J., Phillips D. R. Effect of alkylating agents on initiation and elongation of the lac UV5 promoter. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12471–12477. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Kallama S. Reactions of nitrogen mustards with DNA. IARC Sci Publ. 1986;(78):55–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Ludlum D. B. Covalent modification of DNA by antineoplastic agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Nov;73(5):1021–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Peltonen K., Vodicka P. Depurination from DNA of 7-methylguanine, 7-(2-aminoethyl)-guanine and ring-opened 7-methylguanines. Chem Biol Interact. 1989;70(3-4):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(89)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevroni D., Livneh Z. Bypass and termination at apurinic sites during replication of single-stranded DNA in vitro: a model for apurinic site mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallama S., Hemminki K. Stabilities of 7-alkylguanosines and 7-deoxyguanosines formed by phosphoramide mustard and nitrogen mustard. Chem Biol Interact. 1986 Jan;57(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(86)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Spears C. L., Doty P. Inter-strand crosslinking of DNA by nitrogen mustard. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W., Borden A., Banerjee S. K., LeClerc J. E. Mutation frequency and spectrum resulting from a single abasic site in a single-stranded vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2153–2157. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3610–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Sedgwick B., Sekiguchi M., Nakabeppu Y. Regulation and expression of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Apurinic sites as mutagenic intermediates. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Preston B. D. Mutagenesis by apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:201–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlum D. B., Austin-Ritchie P., Hagopian M., Niu T. Q., Yu D. Detection of sulfur mustard-induced DNA modifications. Chem Biol Interact. 1994 Apr;91(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes W. B., Hartley J. A., Kohn K. W. DNA sequence selectivity of guanine-N7 alkylation by nitrogen mustards. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2971–2987. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P., Byfield J. E., Ward J. F., Calabro-Jones P. Effects of methylated xanthines on mammalian cells treated with bifunctional alkylating agents. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):326–329. doi: 10.1038/285326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Crothers D. M. Kinetics and sequence specificity of drug-DNA interactions: an in vitro transcription assay. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7355–7362. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper R. O., Erickson L. C. DNA adenine adducts induced by nitrogen mustards and their role in transcription termination in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Oct;11(10):1739–1746. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.10.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper R. O., Futscher B. W., Erickson L. C. Transcription-terminating lesions induced by bifunctional alkylating agents in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Jul;10(7):1307–1314. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.7.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash A. S., Gibson N. W. Sequence-selective depurination, DNA interstrand cross-linking and DNA strand break formation associated with alkylated DNA. Carcinogenesis. 1992 Mar;13(3):425–431. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. J., Kotsaki-Kovatsi V. P. Potentiation of sulphur mustard or cisplatin-induced toxicity by caffeine in Chinese hamster cells correlates with formation of DNA double-strand breaks during replication on a damaged template. Mutat Res. 1986 May;165(3):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagher D., Strauss B. Abasic sites from cytosine as termination signals for DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4285–4298. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Loeb L. A. Depurination causes mutations in SOS-induced cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Molecular mechanism of transcription-repair coupling. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8465200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Chang C. N., Johnson F., Will S., Grollman A. P. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing synthetic abasic sites. Model substrates for DNA polymerases and apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10171–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., Mattern M. R., Boyce R. A., Schein P. S. Elevated DNA topoisomerase II activity in nitrogen mustard-resistant human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7668–7671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verly W. G. Prereplicative error-free DNA repair. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 1;29(7):977–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Inducible DNA repair systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:425–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warpehoski M. A., Harper D. E., Mitchell M. A., Monroe T. J. Reversibility of the covalent reaction of CC-1065 and analogues with DNA. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2502–2508. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Phillips D. R. Transcriptional analysis of multisite drug-DNA dissociation kinetics: delayed termination of transcription by actinomycin D. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9122–9132. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou W., Doetsch P. W. Effects of abasic sites and DNA single-strand breaks on prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6601–6605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]