Abstract
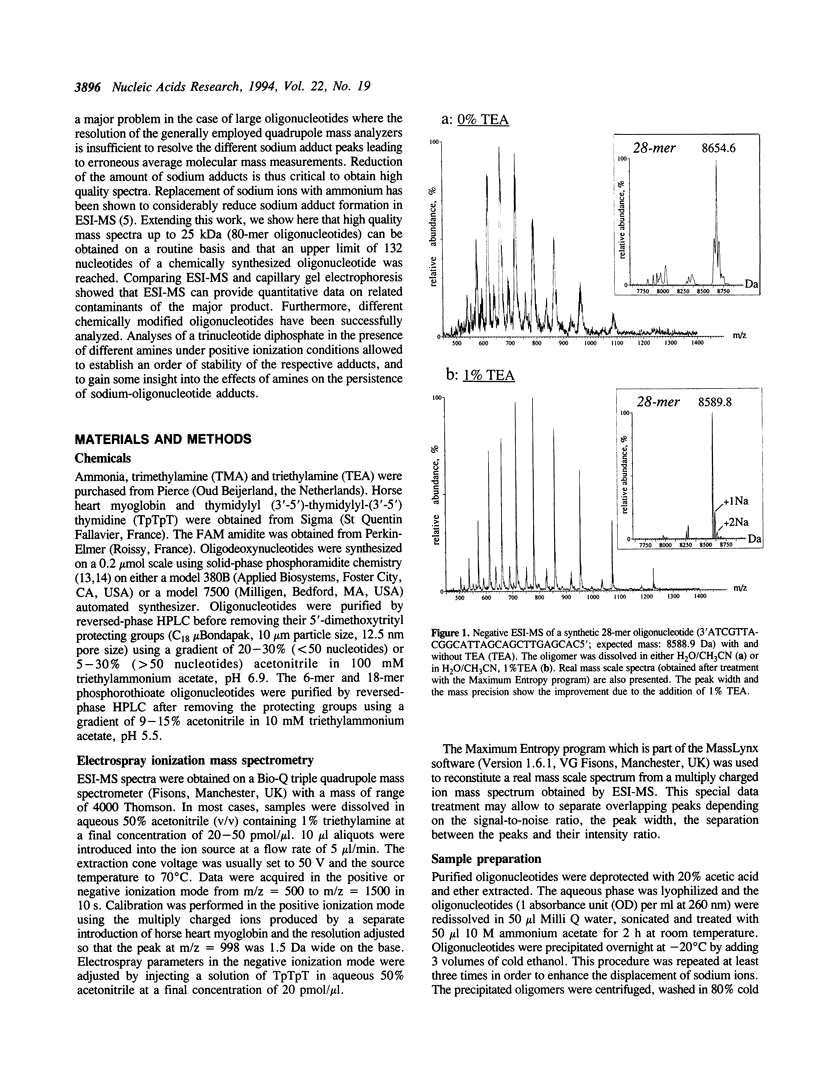
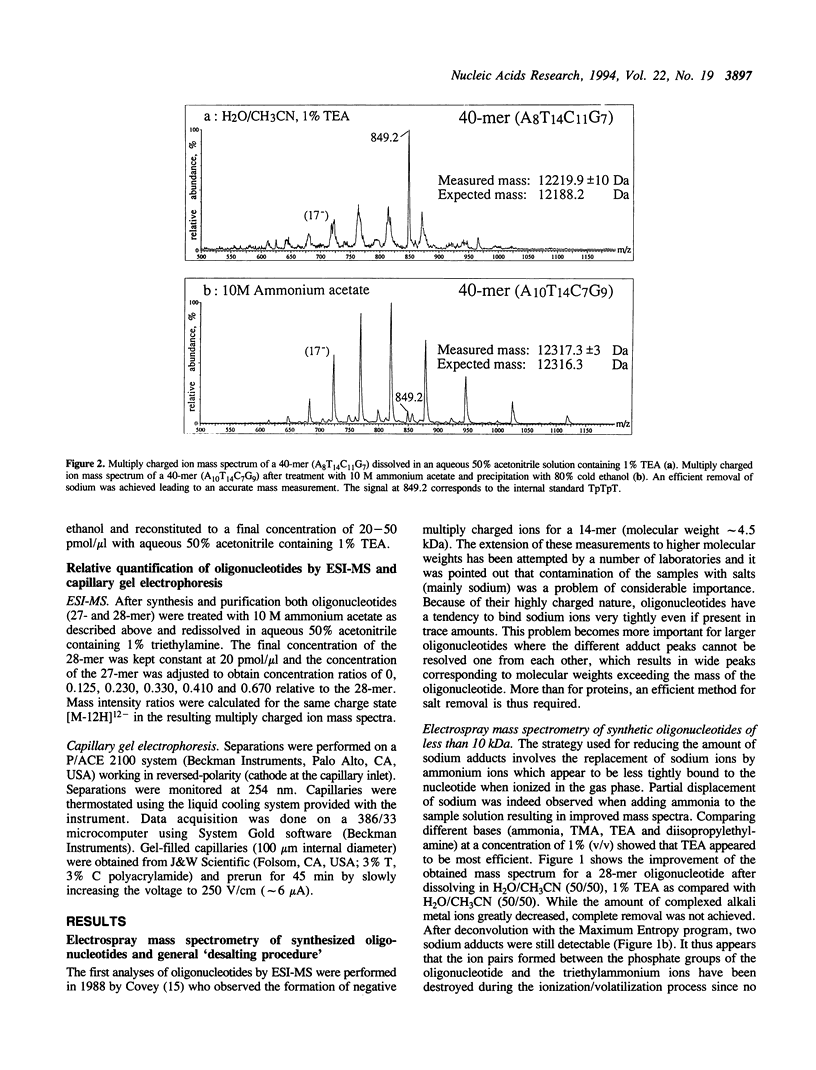
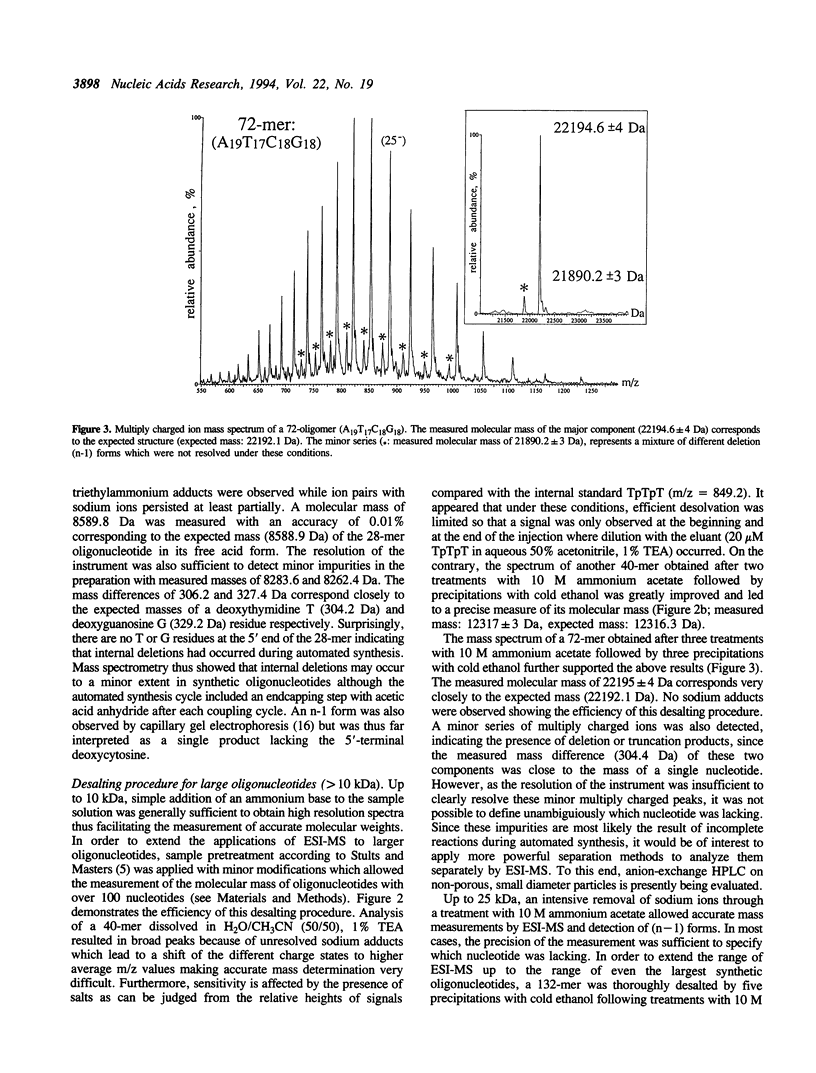
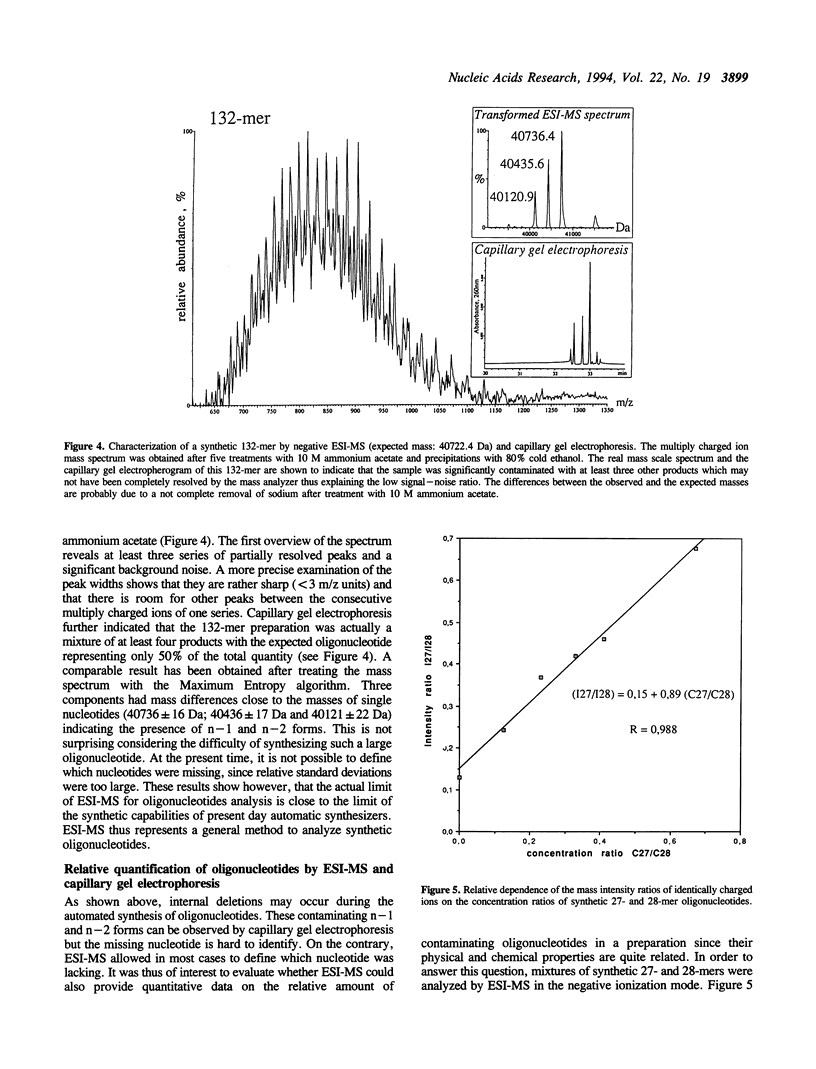
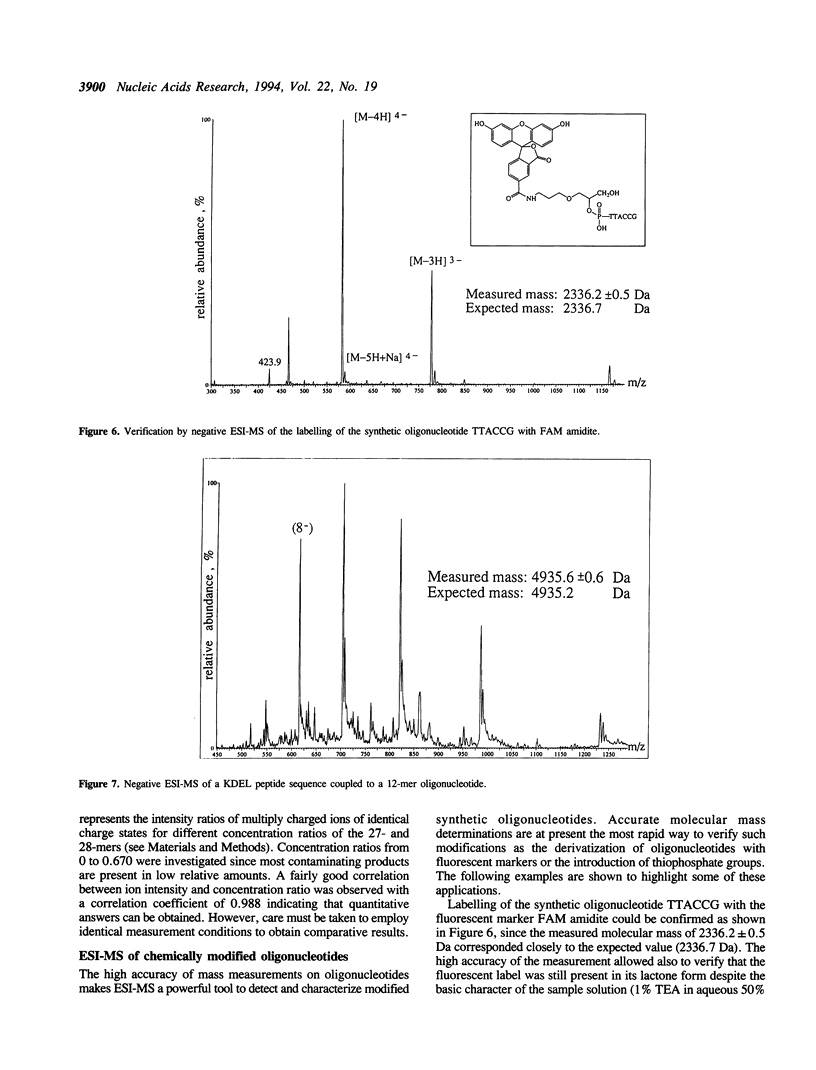
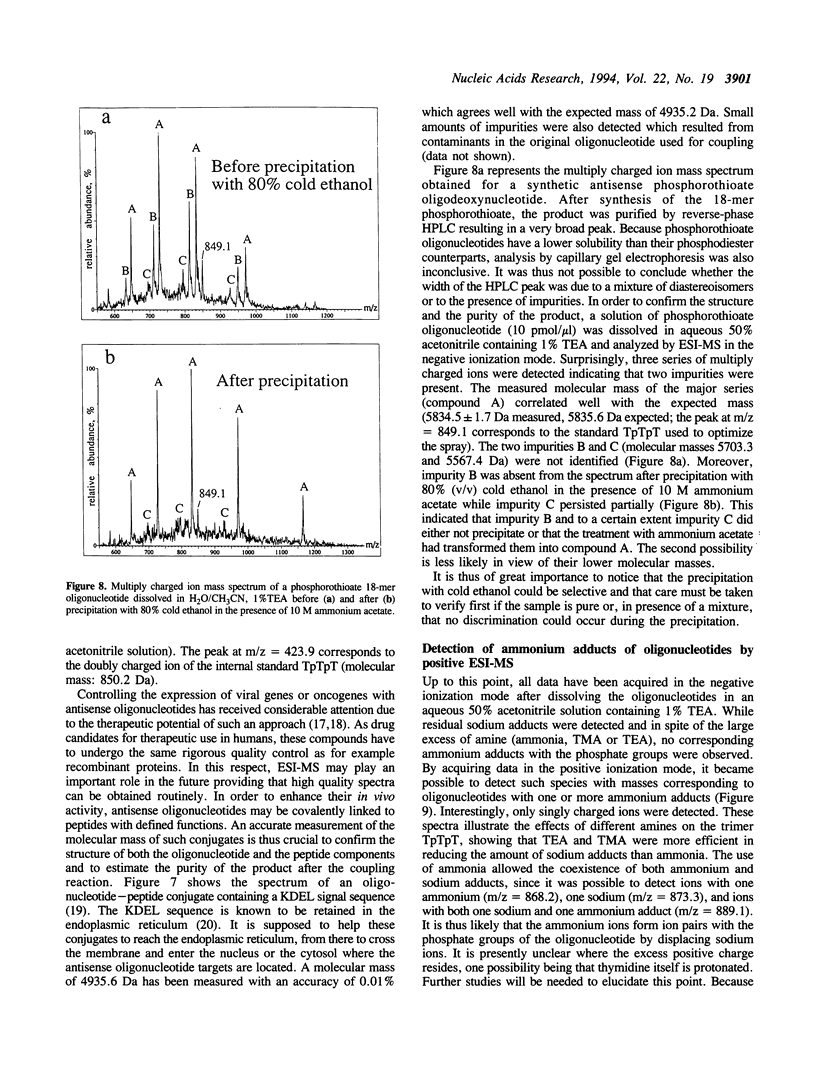
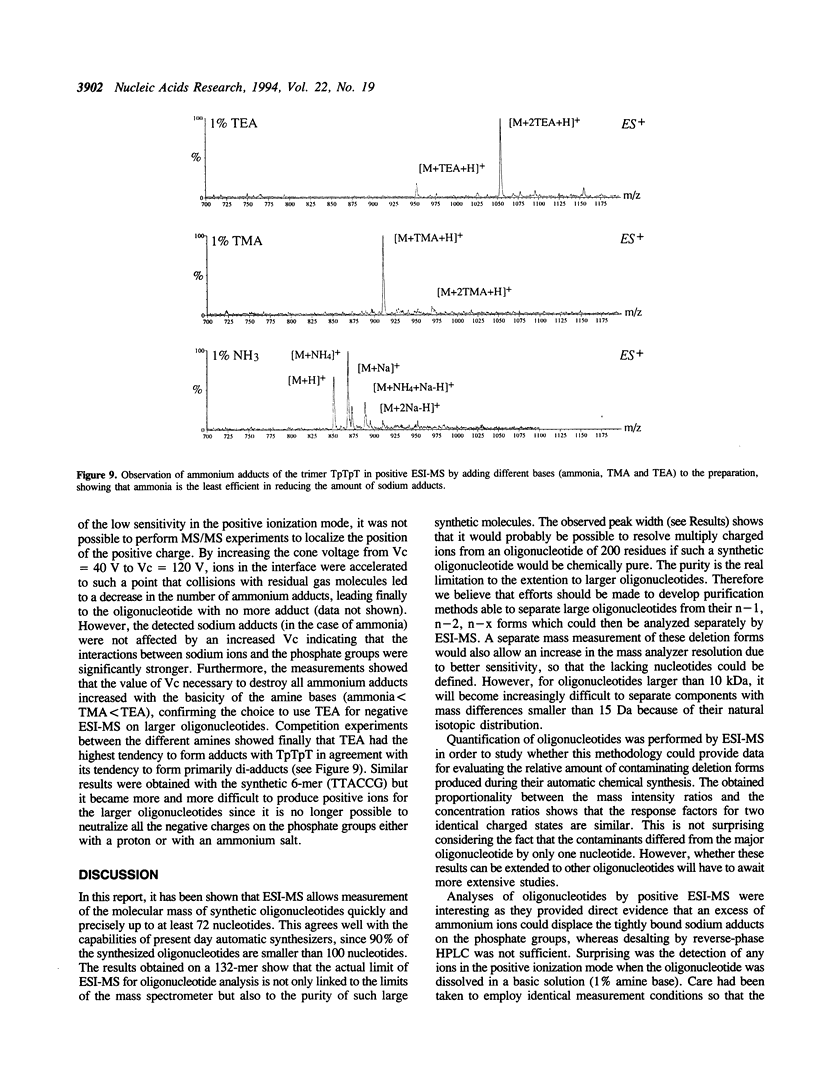
We report here on the analysis of synthetic oligonucleotides by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). After intensive removal of salt ions (especially sodium cations), negative ion mass spectra, allowing mass measurement with an accuracy of 0.01%, were obtained on several oligonucleotides up to 80 nucleotides. In most cases, the resolution was sufficient to observe n-1 and n-2 forms due to internal deletions during automated synthesis, and to identify the missing nucleotides. A 132-mer, whose size is close to the limit of automated chemical synthesis, was also successfully mass measured. A quantitative study showed that ESI-MS can provide quantitative data on oligonucleotides of similar size and structure. The described methodology is used to characterize oligonucleotide analogues such as phosphorothioate oligonucleotides designed for antisense applications. Finally, analyses in the positive ion mode on a trimer TpTpT in the presence of different amine bases were performed and allowed a better understanding of the influence of these bases on the ions formation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleicher K., Bayer E. Various factors influencing the signal intensity of oligonucleotides in electrospray mass spectrometry. Biol Mass Spectrom. 1994 Jun;23(6):320–322. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200230604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey T. R., Bonner R. F., Shushan B. I., Henion J. The determination of protein, oligonucleotide and peptide molecular weights by ion-spray mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1988 Nov;2(11):249–256. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290021111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Degols G., Clarenc J. P., Mechti N., Lebleu B. Cell delivery and mechanisms of action of antisense oligonucleotides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:143–166. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure T. D., Schram K. H. Mass spectrometry of nucleotides and oligonucleotides. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;26:319–345. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59259-513-6_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Matteucci M. D., Martin J. C. Current concepts in antisense drug design. J Med Chem. 1993 Jul 9;36(14):1923–1937. doi: 10.1021/jm00066a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordhoff E., Cramer R., Karas M., Hillenkamp F., Kirpekar F., Kristiansen K., Roepstorff P. Ion stability of nucleic acids in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3347–3357. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieles U., Zürcher W., Schär M., Moser H. E. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: a powerful tool for the mass and sequence analysis of natural and modified oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3191–3196. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J., Sarver N. RNA enzymes (ribozymes) as antiviral therapeutic agents. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Jul;8(7):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Loo J. A., Edmonds C. G., Barinaga C. J., Udseth H. R. New developments in biochemical mass spectrometry: electrospray ionization. Anal Chem. 1990 May 1;62(9):882–899. doi: 10.1021/ac00208a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cheng Y. C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1004–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.8351515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. J., Shaler T. A., Becker C. H. Time-of-flight mass spectrometry of underivatized single-stranded DNA oligomers by matrix-assisted laser desorption. Anal Chem. 1994 May 15;66(10):1637–1645. doi: 10.1021/ac00082a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



