Abstract
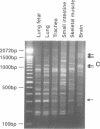
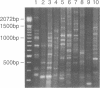
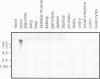
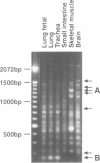
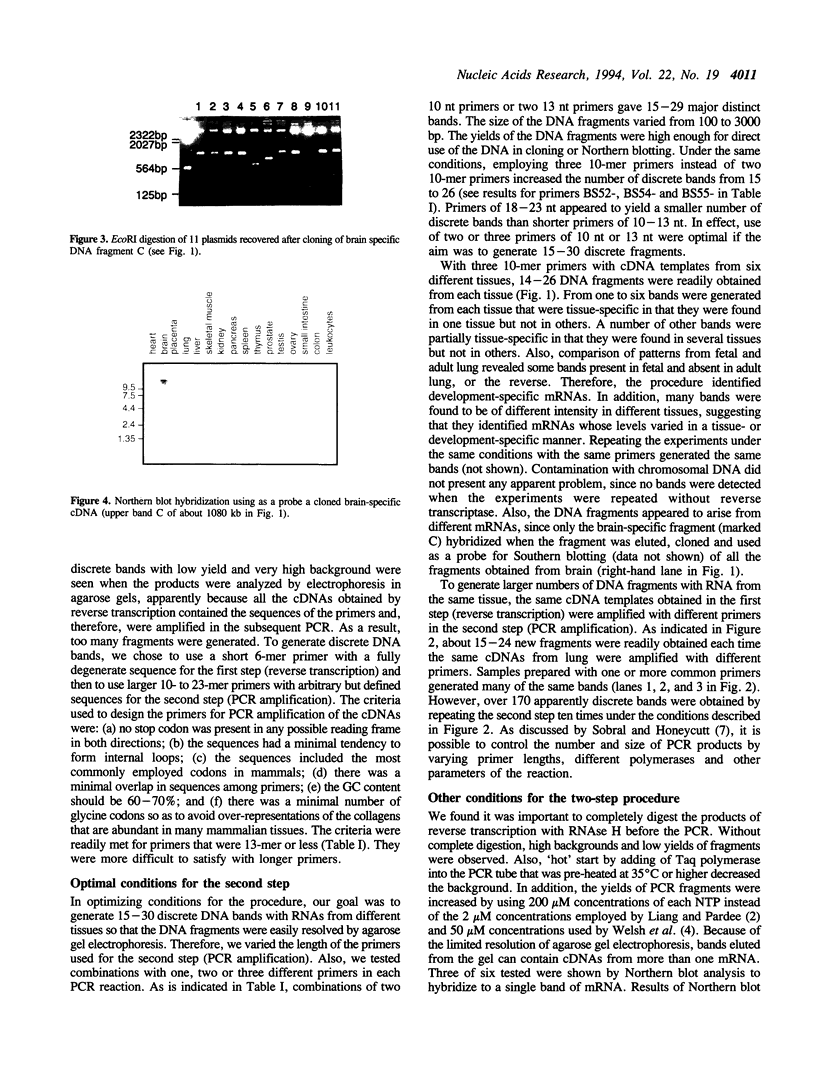
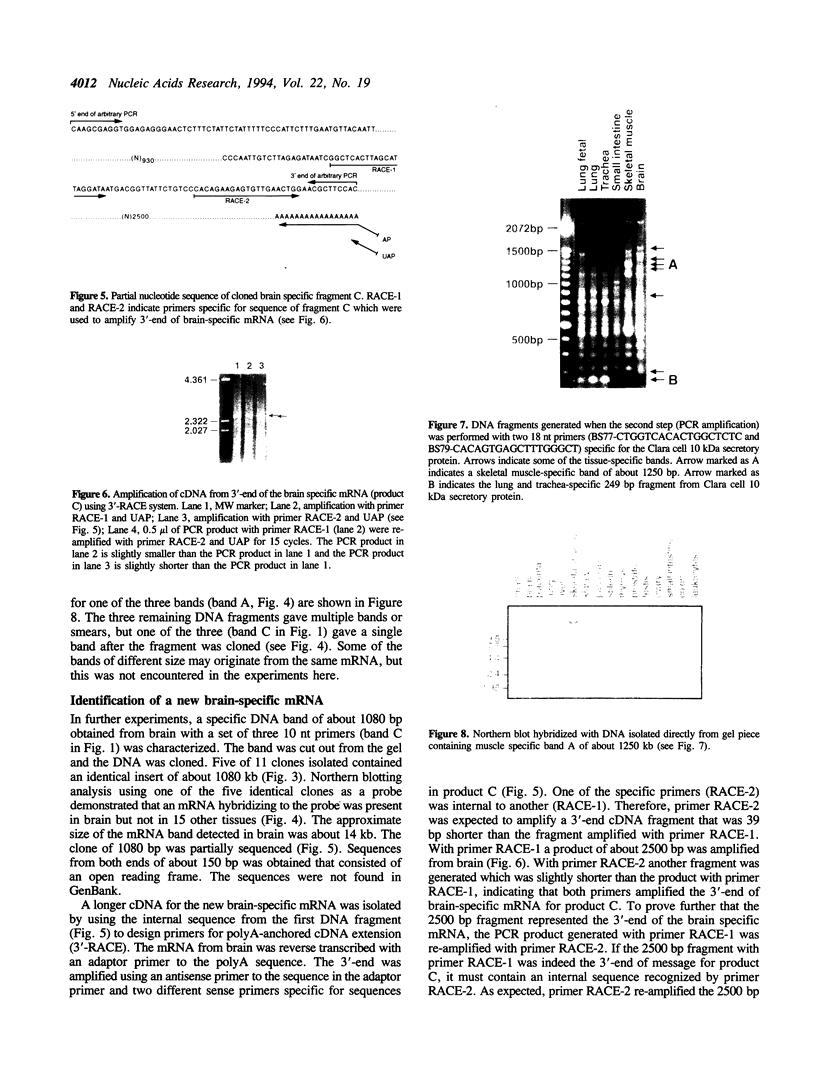
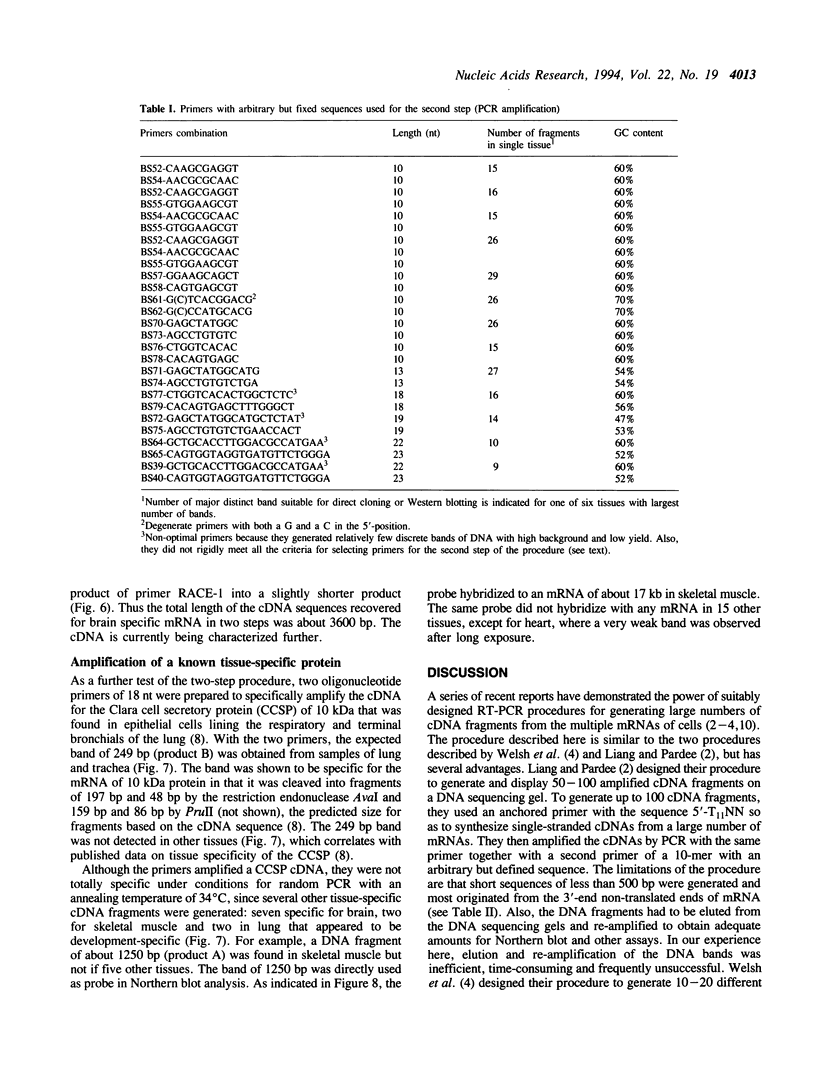
Recently two techniques have been reported which use arbitrarily primed RT-PCR amplification of cDNA fragments from subsets of mRNAs to detect cDNA fragments from differentially expressed mRNAs. Here we report a simple and rapid PCR-based protocol to both detect and isolate cDNA fragments of up to 3000 base pairs from differentially expressed genes in two easy steps. To generate cDNAs from most mRNAs, the first step consisted of reverse transcription using a fully degenerated 6-mer oligonucleotide as primer. The second step consisted of PCR amplification of internal regions of the cDNAs with two or three longer primers with arbitrary but defined sequences. DNA fragments were easily displayed by agarose gel electrophoresis and then excised for direct use in cloning, sequencing, and Northern blot analysis. By repeating the PCR amplification (second step) on the same cDNA templates (first step) ten times with different sets of primers, over 170 discrete cDNA fragments were obtained from a single tissue. By combining the two-step procedure with 3'-RNA-anchored cDNA extension, additional DNA fragments can be generated from the same mRNA. The new procedure was used here to define 3600 bp of a new brain-specific mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Wolf M., Katyal S. L., Singh G., Beato M., Suske G. Tissue-specific expression, hormonal regulation and 5'-flanking gene region of the rat Clara cell 10 kDa protein: comparison to rabbit uteroglobin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2939–2946. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D. K., Donohue P. J., Alberts G. F., Winkles J. A. Fibroblast growth factor-1 induces phosphofructokinase, fatty acid synthase and Ca(2+)-ATPase mRNA expression in NIH 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 30;197(3):1483–1491. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Tomasetto C., Sager R. Positive selection of candidate tumor-suppressor genes by subtractive hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2825–2829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Pardee A. B. Distribution and cloning of eukaryotic mRNAs by means of differential display: refinements and optimization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3269–3275. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Katyal S. L., Brown W. E., Phillips S., Kennedy A. L., Anthony J., Squeglia N. Amino-acid and cDNA nucleotide sequences of human Clara cell 10 kDa protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Chada K., Dalal S. S., Cheng R., Ralph D., McClelland M. Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):4965–4970. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.4965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]