Abstract
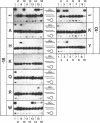
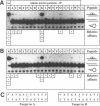
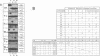
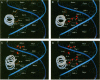
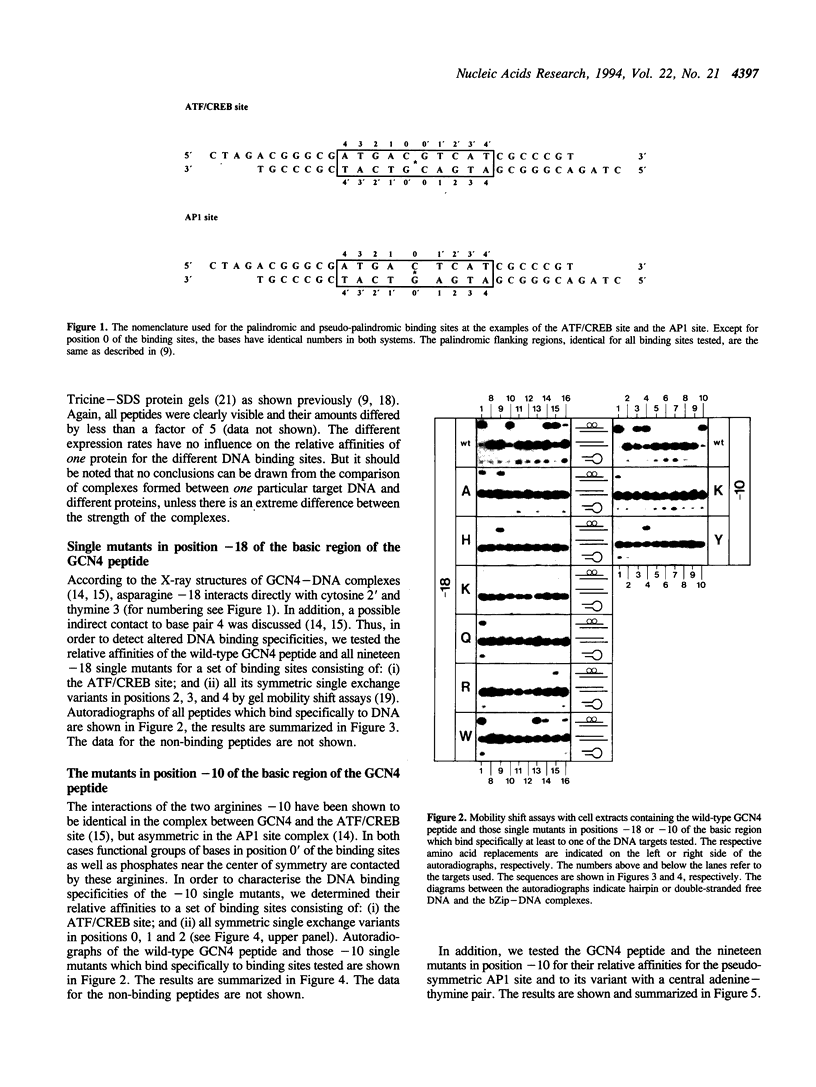
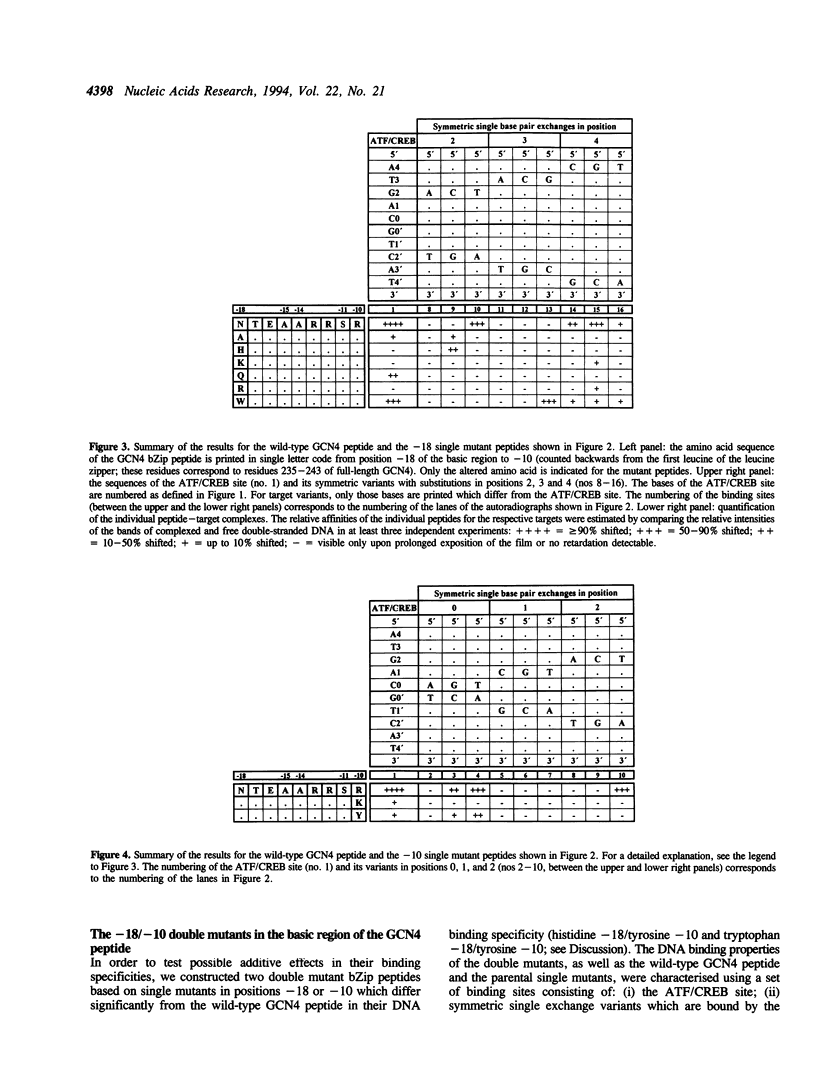
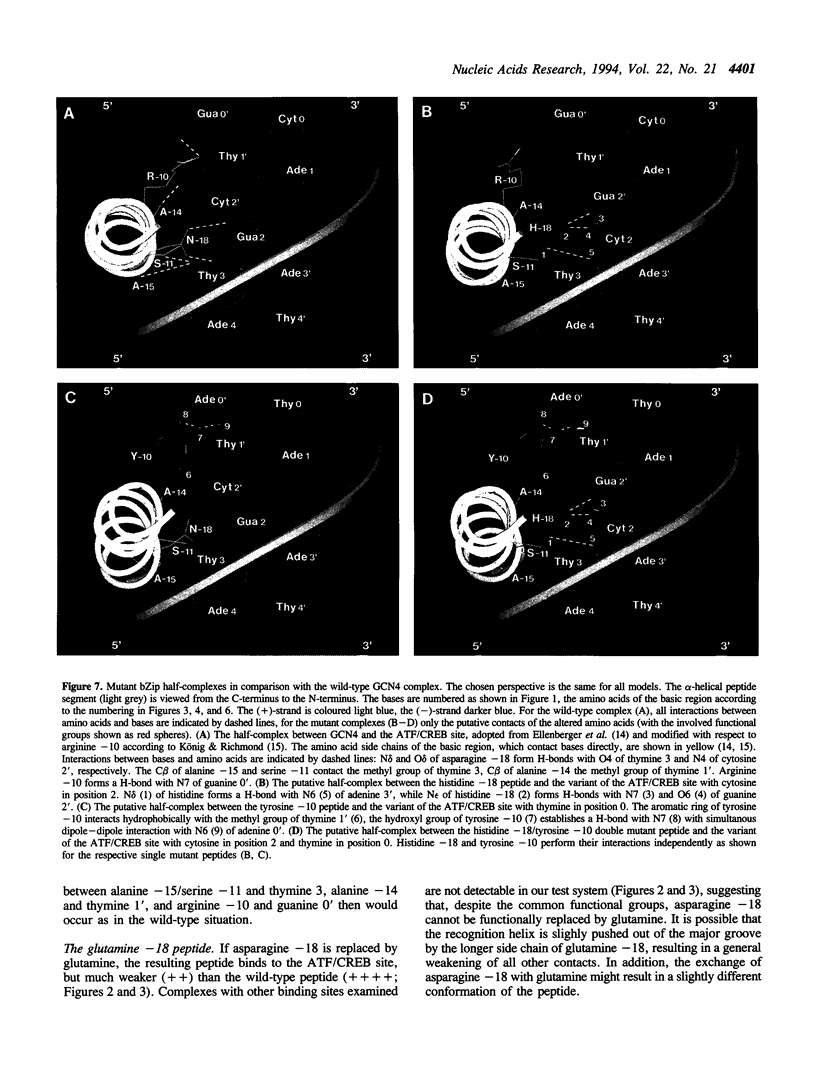
Two residues are invariant in all bZip basic regions: asparagine -18 and arginine -10 (we define the first leucine of the leucine zipper of GCN4 as +1). X-ray structures of two specific GCN4-DNA complexes (Ellenberger et al., Cell, 71, 1223-1237, 1992; König & Richmond, J. Mol. Biol., 233, 139-154, 1993) demonstrate the involvement of both residues in specific base pair recognition. We replaced either asparagine -18 or arginine -10 with all other amino acids and tested the DNA binding properties of the resulting mutant peptides by gel mobility shift assays. Peptides with histidine -18 or tyrosine -10 bind with changed specificities to variants of the ATF/CREB site 5'A4T3G2A1C0*G0'T1'C2'A3'T4'3' with symmetric exchanges in positions 2/2' or 0/0', respectively. The double mutant with histidine -18 and tyrosine -10 combines the features of the parental single mutants and binds specifically to the respective double exchange target. Furthermore, the tyrosine -10 mutant clearly prefers the palindrome 5'ATGATATCAT3' over the corresponding pseudo-palindrome 5'ATGATTCA-T3', whereas the lysine -10 mutant binds better to the pseudo-palindromic AP1 site 5'ATGACTCAT3' than to the palindromic ATF/CREB site. Thus, although invariant within natural bZip proteins, asparagine -18 or arginine -10 can be functionally replaced by other amino acids, and their replacement can lead to new DNA binding specificities.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eismann E., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Specific destruction of the second lac operator decreases repression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli fivefold. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):949–952. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90499-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann T., Alex R., Suckow J., Dildrop R., Kisters-Woike B., Müller-Hill B. Single exchanges of amino acids in the basic region change the specificity of N-Myc. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5050–5058. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B., Burley S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):38–45. doi: 10.1038/363038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Macke J. P., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):451–457. doi: 10.1126/science.3532321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Involvement of an initiation factor and protein phosphorylation in translational control of GCN4 mRNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90215-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Tzamarias D., Ellenberger T., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Adaptability at the protein-DNA interface is an important aspect of sequence recognition by bZIP proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4513–4517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König P., Richmond T. J. The X-ray structure of the GCN4-bZIP bound to ATF/CREB site DNA shows the complex depends on DNA flexibility. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):139–154. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., Hoess R. H., DeGrado W. F. Design of DNA-binding peptides based on the leucine zipper motif. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):774–778. doi: 10.1126/science.2389143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Brandl C. J., Struhl K. Defining the sequence specificity of DNA-binding proteins by selecting binding sites from random-sequence oligonucleotides: analysis of yeast GCN4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2944–2949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella D. N., Palmer C. R., Schepartz A. DNA targets for certain bZIP proteins distinguished by an intrinsic bend. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1130–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.8178171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu W. T., Struhl K. Highly conserved residues in the bZIP domain of yeast GCN4 are not essential for DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4918–4926. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. W., Vincent A. C., Struhl K. Mutations that define the optimal half-site for binding yeast GCN4 activator protein and identify an ATF/CREB-like repressor that recognizes similar DNA sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5077–5086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow M., Madan A., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Creating new DNA binding specificities in the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 by combining selected amino acid substitutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jun 25;22(12):2198–2208. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.12.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Identification of three residues in the basic regions of the bZIP proteins GCN4, C/EBP and TAF-1 that are involved in specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. The DNA binding specificity of the basic region of the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 can be changed by substitution of a single amino acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2081–2086. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. A framework for the DNA-protein recognition code of the probe helix in transcription factors: the chemical and stereochemical rules. Structure. 1994 Apr 15;2(4):317–326. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzamarias D., Pu W. T., Struhl K. Mutations in the bZIP domain of yeast GCN4 that alter DNA-binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2007–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]